Respiratory Viruses
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
What are the main viruses involved in respiratory disease?
-Orthomyxoviridae: Influenza A-C, Isavirus
-Coronaviruses: SARS, HEV, Infectious bronchitis, CRCV
-Calicivirus: Feline calicivirus
-Herpesvirus: Feline Herpesvirus, Infectious bovine rhinotracheitis
How do new types of viruses emerge?
-Point mutation and genetic reassortment
-Mutations = antigenic (genetic) drift
-Reassortment = antigenic (genetic) shift: Two or more viruses infect the same cell and develop new sub-types
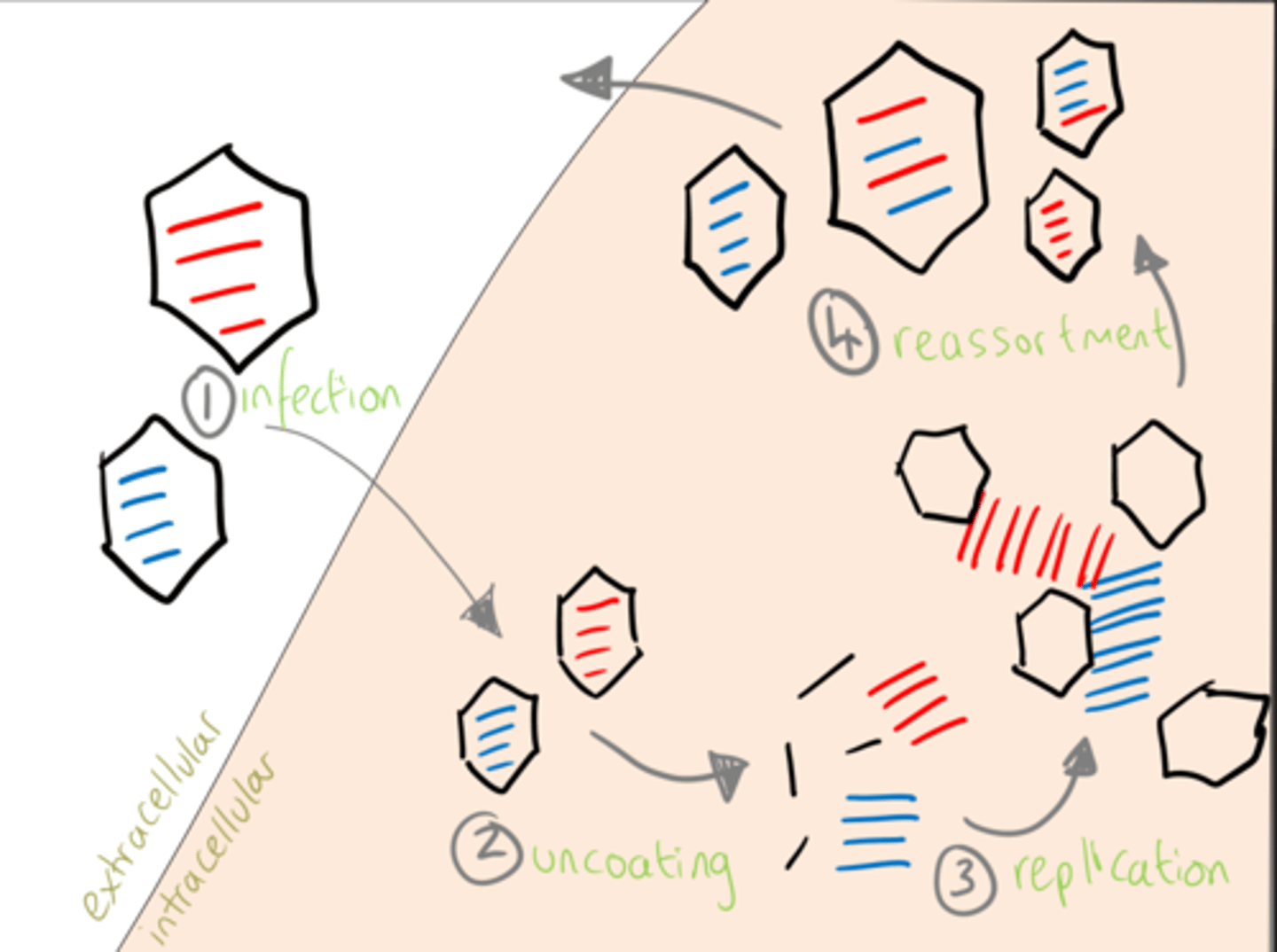
What is the significance of reassortment (antigenic shift) on viral diseases?
-Can lead to novel viruses being created an is a common cause of species hopping
-Can lead to pandemic-causing viruses developing
-Occurs very quickly and frequently
What is the relevance of the influenza virus in the world today?
-Often species jumps
-Causes respiratory disease in animals and humans
-Causes typical flu-like symptoms
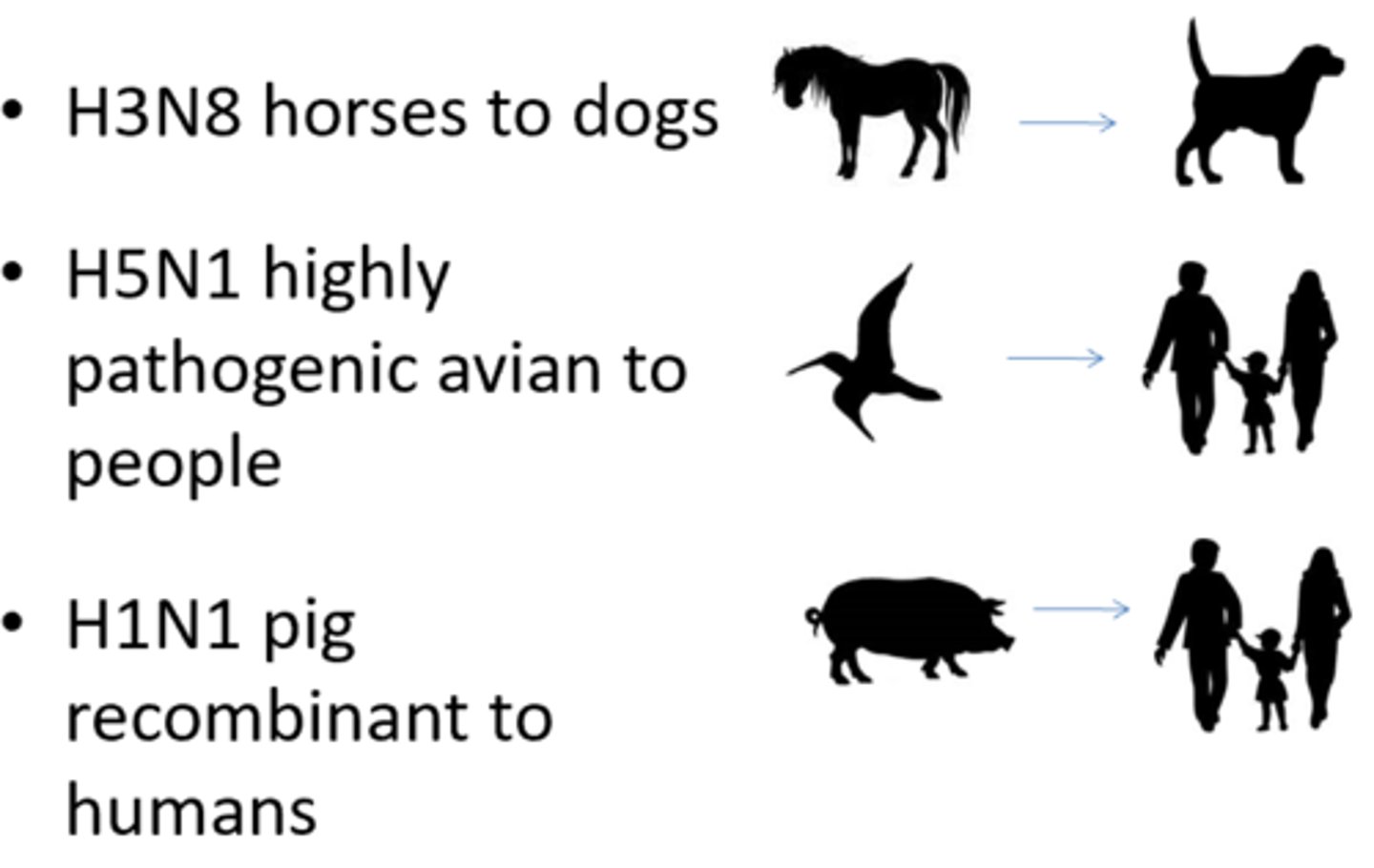
Give an example of when the influenza virus species jumped and how this might have happened
-Equine influenza (H3N8) mutated to form canine influenza (H3HA) and infected dogs causing respiratory disease
-Jumped from Horses to Dogs
-Thought to be associated with the close interaction of the environment of racing horses and dogs
--Also could have been that uncooked horse meat was fed to dogs which lead to its transmission
---Mutation of equine influenza to canine influenza then lead to dog-to-dog transmission
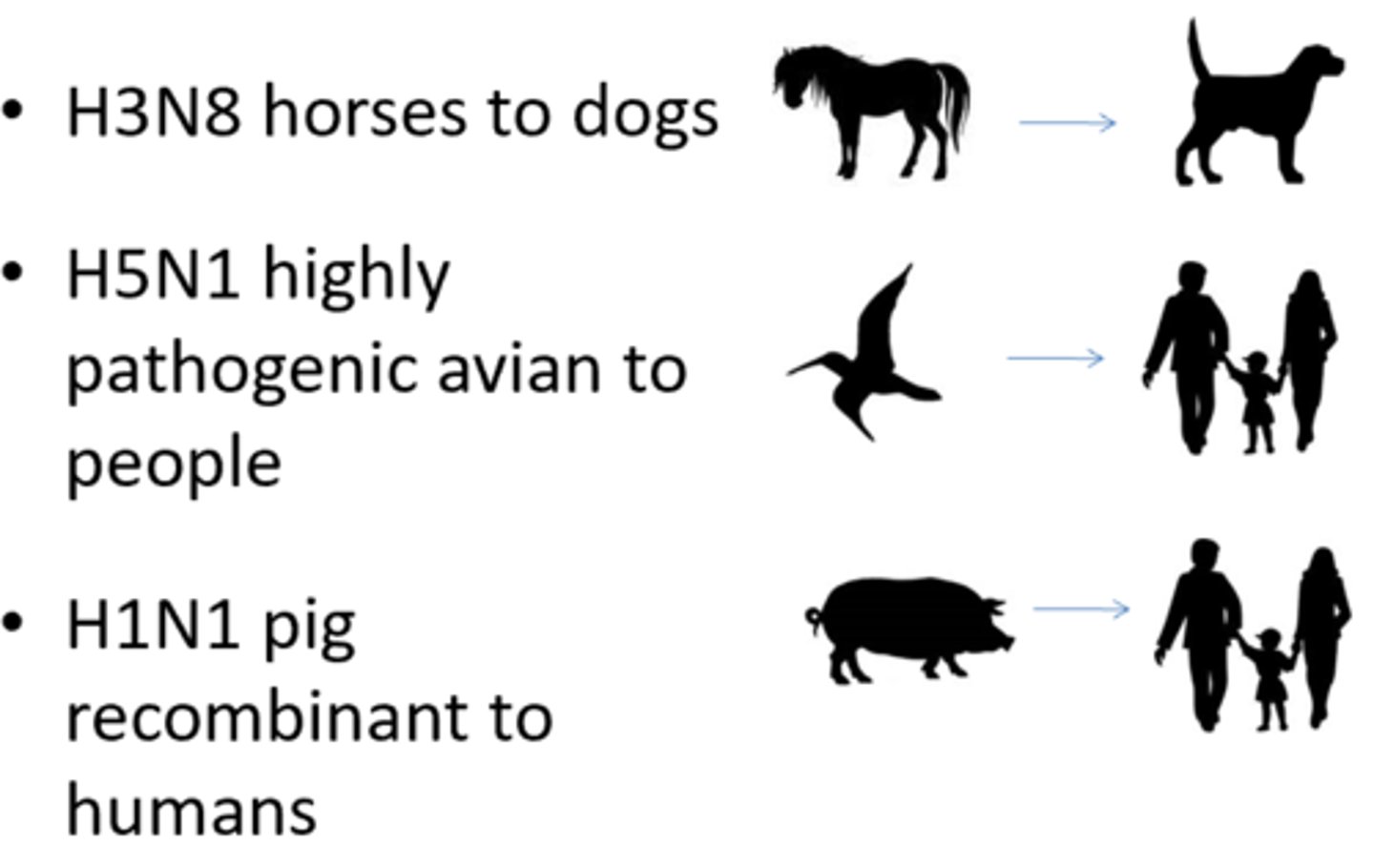
List the significant influenza viruses and what species they effect
-HPAI (H5N1): Birds, Cats, humans
-H1N1: Pigs, humans
-H3N8: Horses, dogs
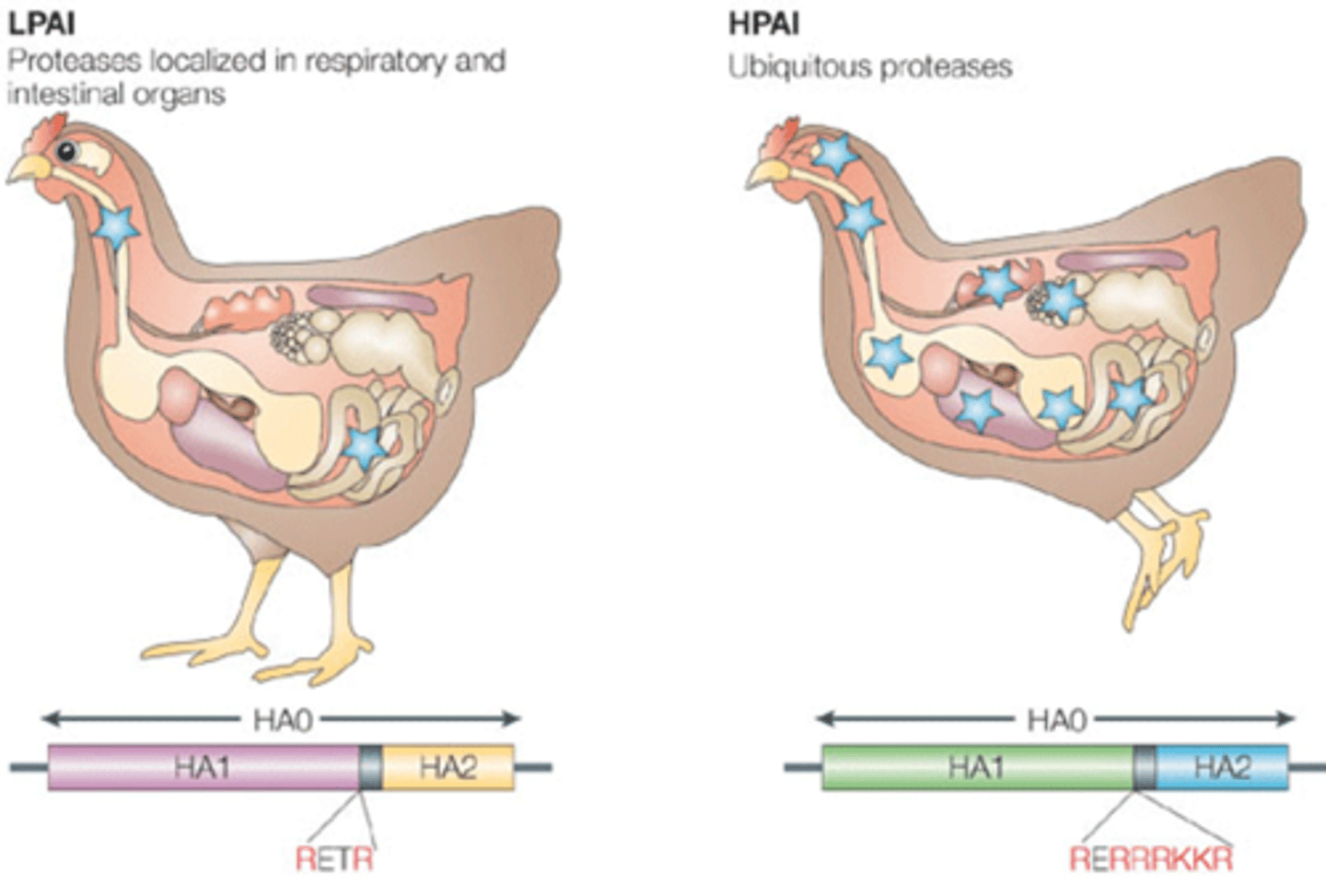
What differentiates low pathogenic avian influenza to high pathogenic avian influenza?
-HPAI has ubiquitous proteases where as LPAI has proteases that are localised in respiratory and intestinal organs
-The ubiquity of proteases determines the severity of diseases caused
-High ubiquity = severe disease
Describe the general characteristics of infectious bronchitis virus
-Acute, highly contagious disease of chickens
-High mortality rate in chicks
-Strains vary in their pathogenicity and tissue tropism
-Can show tissue tropism for urogenital tract (and hence can cause reproductive loses)
-Chicks are vaccinated with an attenuated vaccine by aerosol or in drinking water
--However outbreaks can still occur in vaccinated flocks
Why can outbreaks of infectious bronchitis still occur in vaccinated flocks?
-Emergence of new genotypes in the flock
--By substitution, insertion, deletion or recombination
What are the causes of "Cat Flu"
-Feline Calicivirus (FCV)
-Feline Herpesvirus (FHV)
What proportion of cats in the UK have cat flu?
1/10.
What is the main difference between FCV and FHV?
-FCV is an RNA virus where as FHV is a DNA virus
-Cause differing symptoms
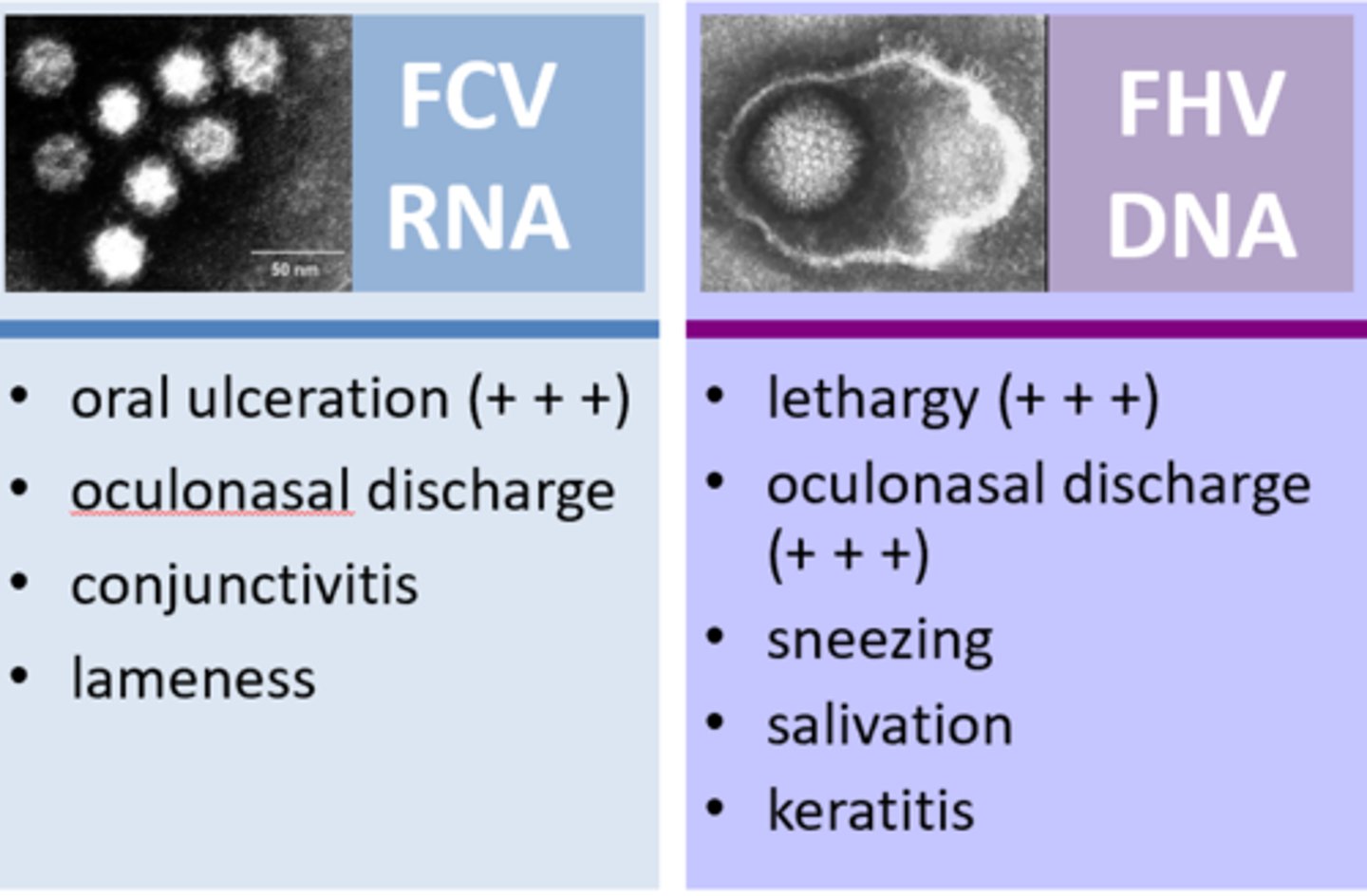
What are the carrier states for FCV and FHV?
FCV:
-30 days
-Most self-cure
-Most continually
shed virus
-75 day 1/2 life
-Dont present with clinical disease
FHV:
-Life-long
-Have intermittent reactivation (shedding but clinically normal)
-Typical latent infection
-Recrudescence (shedding but clinically unwell)
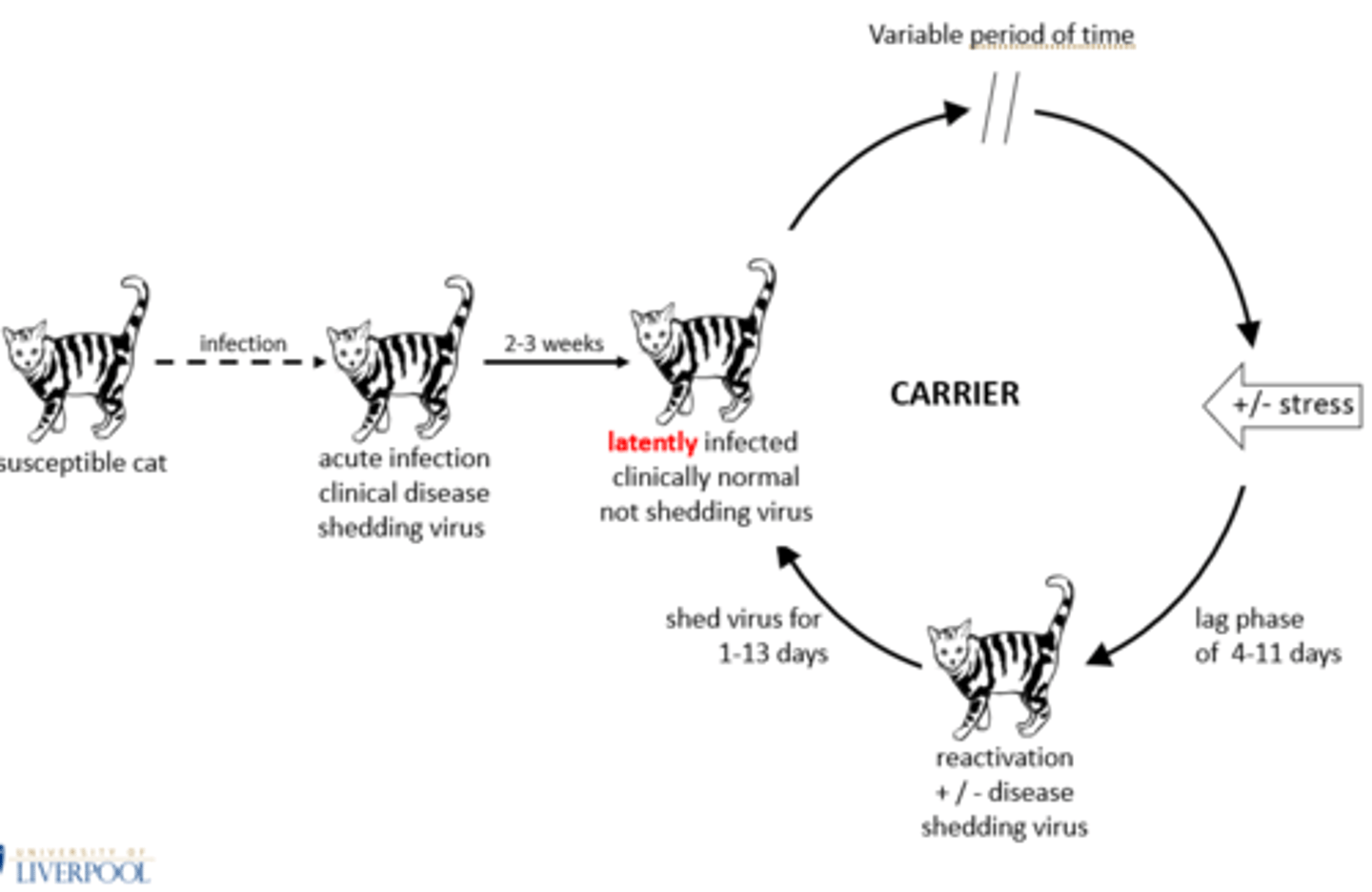
What is a latent infection?
The residence in the body of a specific infectious agent without any manifest symptoms.
What stressors may reactivate FHV in a cat?
-Having kittens
-Being given steroidal drugs
What is a big challenge for vaccinating against RNA viruses?
They mutate often so they vary a lot over time.
How can we control respiratory viruses?
-Husbandry
--Ventilation
--Stocking density
-Biosecurity
-Vaccination