Labour markets
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
What does the labour demand curve show?
The inverse relationship between employment and the wage rate - where the wage rate is higher, the demand for labour by firms is lower
Why is the demand for labour considered derived demand?
Labour demand is derived from the demand for goods and services - workers are needed in order to supply those goods and services
How does consumer demand affect demand for labour?
Higher consumer demand causes an outward shift of the labour demand curve
How does a change in price affect labour demand?
Higher prices reduce consumer demand so labour demand reduces - however, this is dependant on elasticity
How does productivity affect labour demand?
Higher productivity of labour may mean that they are more cost-effective than capital, therefore, labour demand shifts outward
How does a subsidy affect labour demand?
Subsidies reduce the cost of production causing labour demand to shift outward
Marginal revenue product of labour
The additional revenue generated when an additional worker is empoyed
How is marginal revenue product of labour calculated?
MRPL = marginal product of labour x marginal revenue
What are the limitations of the MRPL theory?
Measuring labour efficiency in some areas are difficult - i.e. education and consultancy
Self-employed and director set their own pay
When is labour demand wage elastic?
When labour expenses are high
Easy and cheap to substitute
Elasticity for the final product
Long-run means factor inputs are easier to change
What does the labour supply curve show?
The direct relationship between wage and supply - a higher wage = expansion in labour supply
What factors affect the labour supply?
Extra pay
Wages in substitute occupations
Barriers to entry
Improvements in occupational mobility of labour
Non-monetary factors
Net inward migration
Non-monetary factors that affect labour supply
Job risk
Anti-social hours
Pension schemes
When is labour supply elastic?
In lower-skilled jobs where there is a larger labour pool available
When mobility of labour is higher
In the long-run
When is labour supply inelastic?
Where jobs require higher skills and training
Short run
When labour is immobile
What are the causes of occupational immobility?
Skill gaps
Training gaps
Experience gaps
What are the causes of geographical immobility?
Cost of living
Family and social ties
Visa restrictions
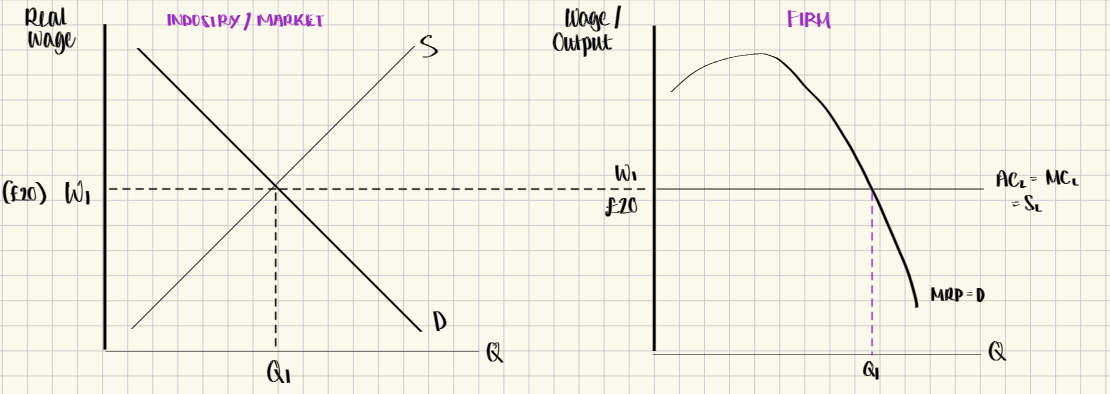
How are wages determined in a competitive labour market?
Firms will hire where MRP= Wage (MCL) in order to maximise their revenue
What is a monopsony?
The sole employer in a labour market
How are wages determined in a monopsony?
Monopsonies have wage-setting power so will often exploit their workers
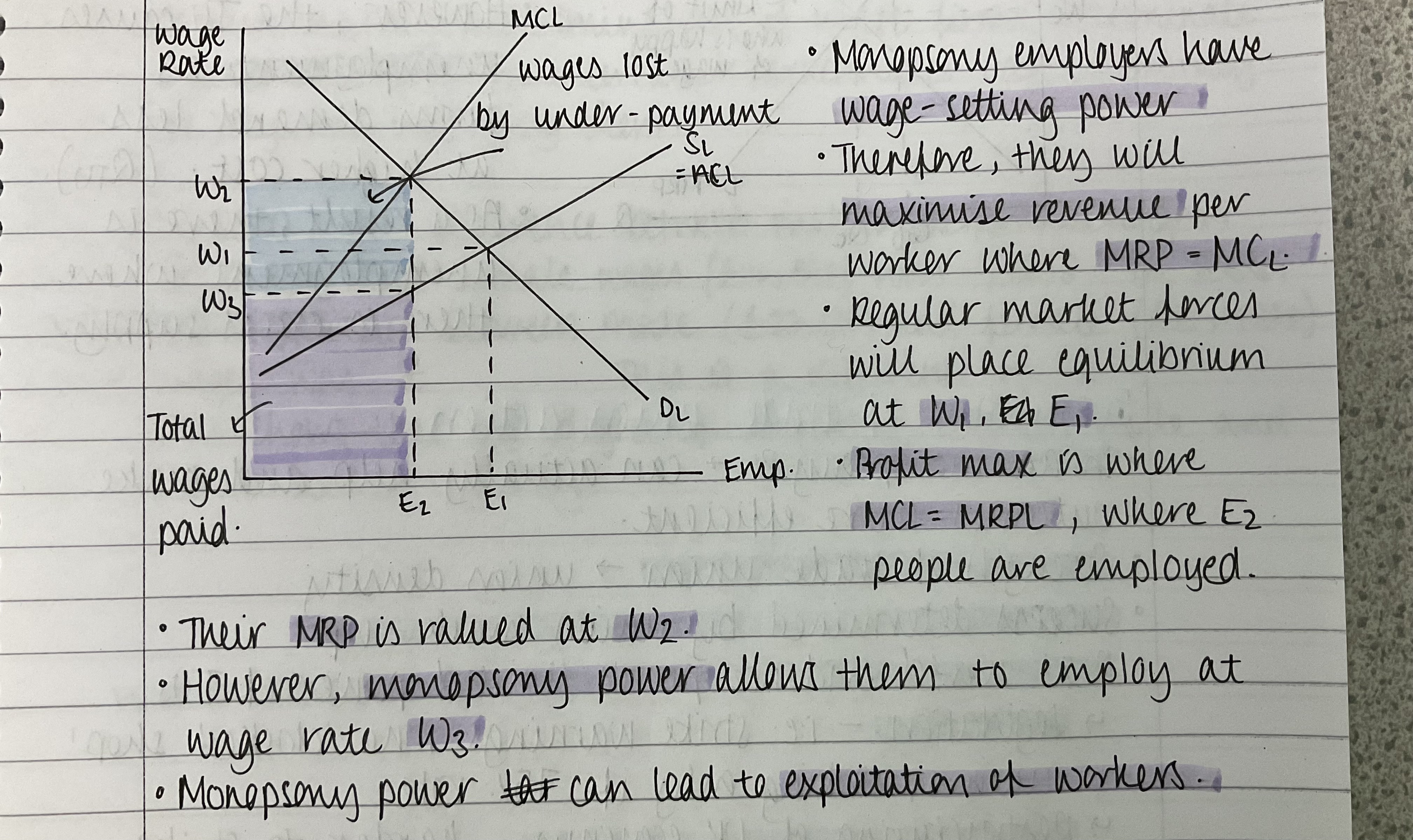
How does a monopsony contribute to labour market failure?
Lower wages = reduced disposable income
Reduced employment
Diminished job quality
Economic inequality
How can trade unions affect the wage rate?
Can increase the wage rate due to collective bargaining
Leads to excess supply
Results in unemployment
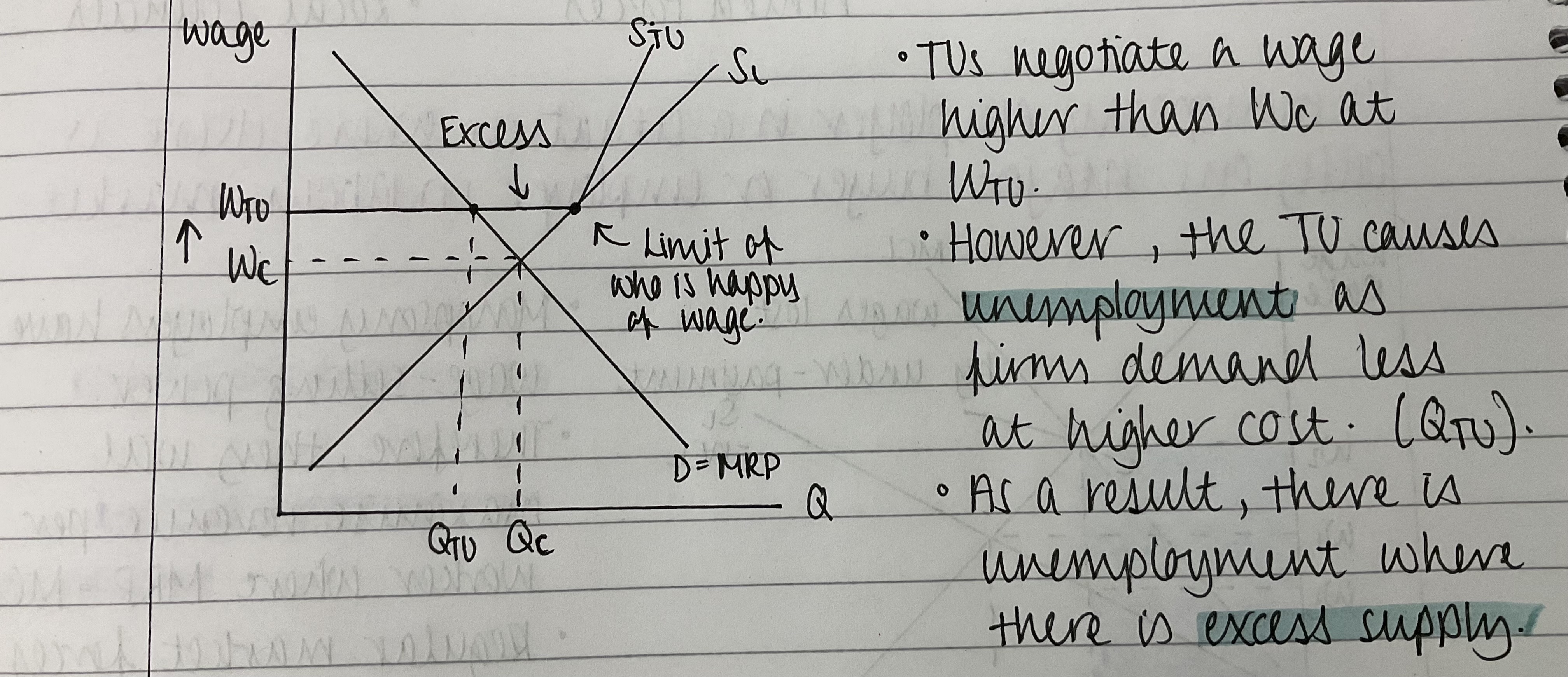
Evaluation of trade union power
Effective in a monopsony
Strength dependant on union density
Real world evidence shows limited power
legislation
competitive pressures on firms
What is National Minimum Wage?
The minimum wage that firms can legally give to workers
Advantages of National Minimum Wage
Poverty reduction
Boosting consumer spending
Reducing reliance on state welfare
Encouraging workforce participation
Efficiency wages
What are the disadvantages of National Minimum Wage?
Job losses
Higher prices
Small business struggles
Fall in investment
Analysis of National Minimum Wage
Wage put above equilibrium
Results in an excess supply of labour
Results in real wage unemployment
Analysis of Minimum Wage in a Monopsony
Monopsony wage is below competitive wage rate
Price floor increases from monopsony wage rate to the competitive wage rate
This also results in an expansion of employment
Employment where D and S are inelastic where there is minimum wage
Employment is less compared to the standard model
Employment where D and S are elastic where there is minimum wage
Unemployment is higher compared to the standard model
Labour market discrimination
When employers make decisions on wages and employment based on prejudices
What may employers discriminate against?
Race
Gender
Religion
Age
Social Class
Disability