Central Dogma, Transcription, Translation, and Mutations in Molecular Biology
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What does the Central Dogma of Molecular Biology state?
Genes specify the sequences of mRNAs, which in turn specify the sequences of amino acids in proteins.
What are the two processes involved in the Central Dogma?
Transcription and translation.
What is the structure of DNA?
DNA is a double helix that stores genetic information in the form of nucleotides.
What are the three stages of transcription?
Initiation, elongation, and termination.
What occurs during the initiation stage of transcription?
The DNA double helix partially unwinds, and RNA polymerase binds at the promoter.
What is a promoter in the context of transcription?
A short sequence of DNA nucleotides that bind to start the transcription process.
What happens during the elongation stage of transcription?
RNA polymerase adds RNA nucleotides by base pairing with the DNA template.
What is the DNA template used for during transcription?
Only one DNA strand is used during transcription.
What signals the termination of transcription?
The polymerase is instructed to dissociate from the DNA template.
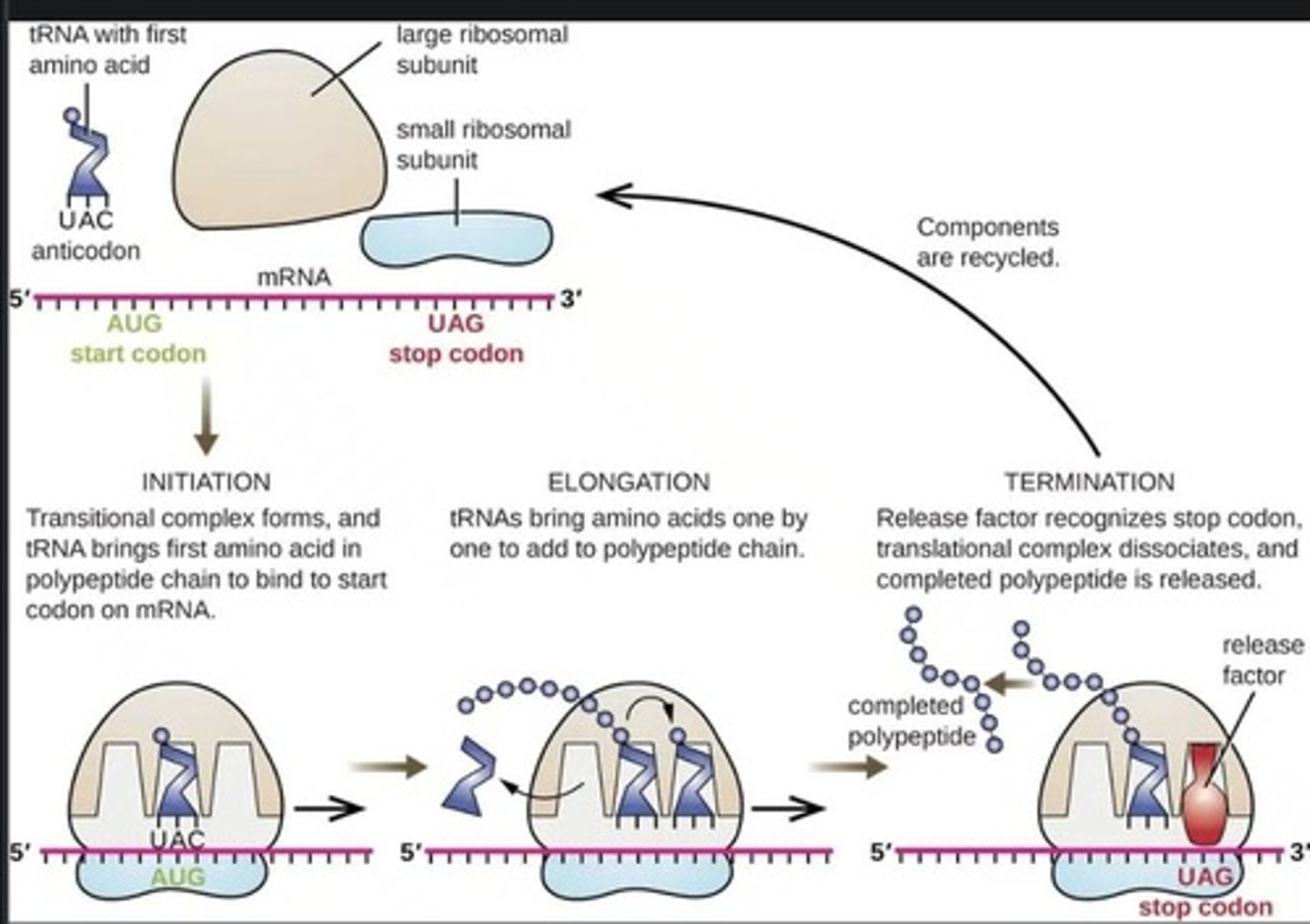
What is the start codon in translation?
AUG is the start codon.
What are the three compartments of the large ribosomal subunit during translation?
The A, P, and E sites.
What is an anti-codon?
An anti-codon is a sequence on tRNA that matches with a codon on mRNA.
What occurs during the termination stage of translation?
Translation is complete when a stop codon (UAA, UAG, or UGA) is encountered, releasing the polypeptide.
What does the universal genetic code imply?
Virtually all species use the same genetic code for protein synthesis.
What is a mutation?
A change in the DNA sequence of a gene.
How can mutations affect proteins?
Mutations can change the sequence of amino acids in a protein, potentially modifying or destroying its function.
What is the difference between genotype and phenotype?
Genotype is an organism's genetic makeup, while phenotype is the observable trait.
What is a gene?
A specific region on DNA that codes for a polypeptide.
What is a locus?
The physical location of a gene on a chromosome.
What is an allele?
Alternative forms of the same gene.
What distinguishes homozygous individuals from heterozygous individuals?
Homozygous individuals have two copies of the same allele, while heterozygous individuals have two different alleles.
How can a mutation in DNA lead to a phenotypic change?
By altering the protein's function or structure, leading to a different trait.
What specific mutation causes sickle cell disease?
A mutation that changes one amino acid (glutamic acid to valine) in the hemoglobin protein, causing it to clump together under low oxygen conditions.