Tufts DPT - Physiology Week 2
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
ischemia
Insufficient Blood flow
decreased delivery of nutrients
decreased removal of waste products
Hypoxia
Low oxygen saturation of the body, not enough oxygen in the blood
Anoxia
Complete loss of Oxygen
Bacterial infectious Agents
Toxins
Viral infectious Agents
either directly or indirectly cytopathic
Cell injury or death: Immune reaction
- antibody attachment
- complement activation
-activation of inflammatory cells: macrophages, T&B lymphocytes, basophils, neutrophils
Cell Injury or death: Genetic Factors
- Chromosomal alterations
- Single or multiple mutation(s) of genes
Cell injury or death: Mechanical Factors
- Physical stress theory: chronic or single high magnitude event
- Failure of tissue when load exceeds failure tolerance
Cell injury or death: Physical Factors
Extreme:
- Temp
-Radiation
- Electricity
Cell Injury or death: Chemical Factors
- Direct injury (think mercury)
- Indirect (reactive oxygen species)
reactive oxygen species
highly reactive forms of oxygen due to loss of one electron creating a "free radical" which causes chain reaction of electron stealing
Nitric Oxide
important modulator in physiologic responses
increased bioavailability with exercise
Cell injury or death: Psychological Factors
Fear, tension, anxiety
Irreversible Cell damage characteristics
- Plasma membrane blebs
-Pyknotic Nucleus
-Swelling of cell
- Accumulation of fluid in Endoplasmic reticulum
- Release of ribosomes
Reversible Cell damage characteristics
- Plasma Membrane blebs
- Swelling
- Accumulation of fluid in Endoplasmic reticulum
- Release of ribosomes
Necrosis
Apoptosis
Organized and programmed cell death
Atrophy
Decrease in cell or orgran size
Hypertrophy
Increase in cell or organ size (striated and heart muscle)
Hyperplasia
Increase number of cells and organ size
Metaplasia
Change in cell morphology/function
Dysplasia
Increase in number of cells and change in cell morphology
Inflammation involves responses from these various levels:
- Vascular
- Humoral
- Neurologic
- Cellular
Inflammatory reaction functions: (3)
- inactivate injurious agent
- breakdown and remove dead cells
- initiate healing
Four Cardinal Signs of Inflammation
-Erythema
-Heat
-Edema
-Pain
Three outcomes of acute inflammation
- Resolution
- healing by Fibrosis
- Healing via chronic inflammation
Acute inflammation: resolution
- clearance of injurious stimuli
- replacement of injured cells
- normal function restores
Acute Inflammation: healing by fibrosis
- collagen deposition
- Loss of function
Acute Inflammation: healing by Chronic inflammation
- Angiogenesis
- mononuclear cell infiltrate
- fibrosis
Acute Inflammation: mechanism of injury
- Infarction
- Bacterial Infection
- Toxins
- Trauma
Chronic Inflammation: mechanism of injury
- Viral infections
- Chronic infections
- Persistent Injury
-Autoimmune diseases
Acute Inflammation cellular infiltrates
- Platelets
- Neutrophils
- Monocyte/macrophage
- Fibrocytes/Fibroblasts
-Endothelial cells
Chronic Inflammation cellular infiltrates
- Monocyte/macrophage
-Lymphocytes
-Plasma cells
- Fibrocytes/fibroblasts
-Endothelial cells
Histamine, Bradykinins, and Leuokotrienes/prostaglandins affect:
Blood flow
Lymphokines and Monokines
attract and stimulate cells
Extrinsic Pathway
- Tissue Injury
1. Thromboplastin (Factor IIa)
2. Thrombin (factor IIa)
3. Fibrinogen (factor I)
4. Fibrin (factor Ia)
Intrinsic Pathway
- Endothelial Injury
- Factor 12
2. Hageman Factor XII
3. Prothrombin (factor II)
4. Thrombin (factor IIa)
5. Fibrinogen (factor I)
6. Fibrin (factor Ia)
Fibrin (factor Ia)
mesh-like structure that forms blood clot
Internal bleeding activates both intrinsic and extrinsic pathway (T or F)
True
Tissue healing occurs by:
1. Regeneration
2. Repair
Components of Tissue Healing
- Fibronectin
- Collagen
- Proteoglycans and Elastin
Type 1 Collagen Characteristics
- Thick
-Predominant in strong tissues
- Mature Scar
(think tendons and bones)
Type 2 Collagen Characteristics
- Thin Supporting Filaments
- Predominant in cartilaginous tissue
Type 3 Collagen Characteristics
- Thin Filaments
- Makes tissue strong but supple and elastic
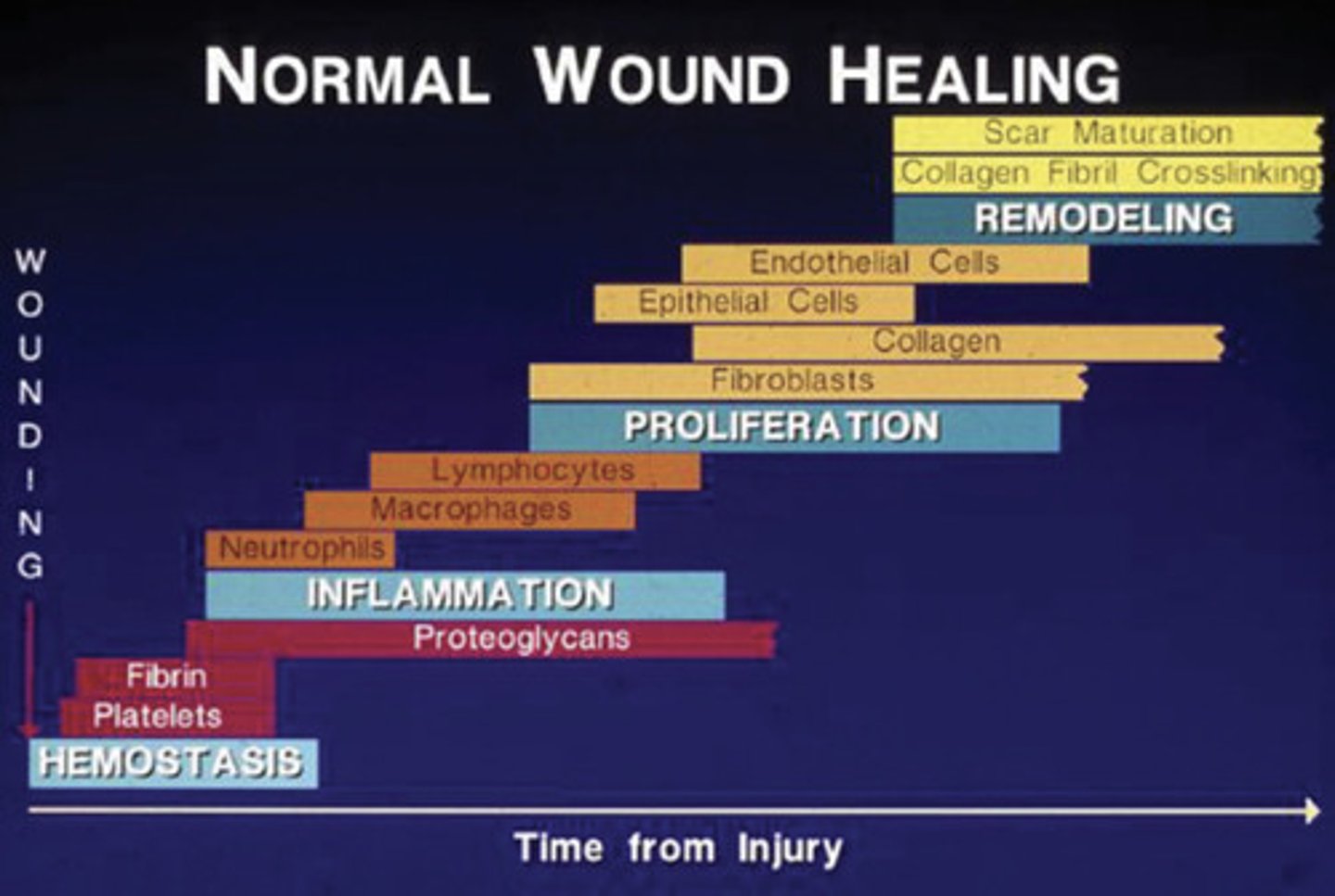
Phases of Tissue Healing
1. Hemostasis and Degeneration
2. Inflammation
3. Proliferation and migration
4. Remodeling and Maturation
Hemostasis and Degeneration Phase
- Seconds to hours
- Vasoconstriction
- Platelet aggregation
- Leucocyte migration
Inflammatory Phase
- Hours to days
- Phagocytosis and removal of foreign bodies/bacteria
-macrophages
Proliferation and Migration Phase
- Days to week
- ECM reorganization
- Angiogenesis
- Granulation Tissue Formation
- Epithelialization
Remodeling and Maturation Phase
- ECM Remodeling
- Increase in tensile strength of wound
- Collagen Fibril Cross linking
Tissue Healing overlap
Healing by Primary intention
- Clean cut and easily healed
-minimal scaring
Healing by Secondary Intention
- Edges cannot be approximated
- Cannot be closed surgically
- slower healing
- Large scar
Healing by Tertiary Intention
- Contaminated
- Delayed closure as wound needs to be closed
Wallerian Degeneration
Degeneration of the part of the axon distal to site of injury
Phases of skeletal muscle healing
- Hemostasis
- Phagocytosis
- Regeneration
Phase 1 Fracture Healing
- Hematoma formed
- Bleeding delivers fibroblasts, platelets and Osteoprogenitor cells
- stimulate initial hematoma into more organized granular tissue
Phase 2 Fracture Healing
- Inflammatory cells arrive
- Formation of granulation tissue
- Initial Fibrocartilage formation
Phase 3 Fracture Healing
- Soft callus formed
-endochondral ossification
Phase 4 Fracture Healing
- disorganized bone turns into mature lamellar bone
-excessive bony callus is resorbed and remodels according to stresses placed on it
Tendons and Ligaments are made up of __% water, __% collagen, and __% glycosaminoglycans
78, 20, 2
Which type of ligament has a poorer healing response ?
A.) extra-articular ligaments
B.) Intra-articular ligaments
Intro-articular Ligaments
Tendons and Ligaments regain normal strength in _____ to ______ weeks
40-50 weeks
Articular surface of cartilage resists which type of force
Sheer force
Radial zone of cartilage resists which type of force
Compressive force
Outer Annulus Collagen type
Type 1
Inner Annulus Collagen type
Type 2
Nucleus Pulpous Collagen type
Type 2
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) branches
- autonomic nervous system (sympathetic and parasympathetic)
- somatic nervous system
Somatic nervous system controls
motor systems (concious)
Autonomic Nervous system controls
Visceral Function (involuntary)
Preganglionic neurons in sympathetic nervous system originate in
Thoracolumbar spinal cord
Preganglionic neurons in parasympathetic nervous system originate in
Brain stem and sacral spinal cord
Preganglionic neurons always release:
acetylcholine (ACH)
Cholinergic Neurons
release acetylcholine (all preganglionic neurons since they release ACH)
Andrenergic neurons
release norepinephrine
Postganglionic neurons of the sympathetic nervous system
can either be Adrenergic (release NE) or Cholinergic (release ACH)
Postganglionic Neurons of the Parasympathetic nervous system
Almost always Cholinergic (release ACH)
Cholinoreceptors
muscarinic and nicotinic receptors for ACH on effector organs (M)
Adrenoreceptors
Receptors for NE on effector organs (a1, a2, b1, b2)