M1 Vascular Access & Vascular Closure Devices_acc
1/98
Earn XP
Description and Tags
w assignment for w1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
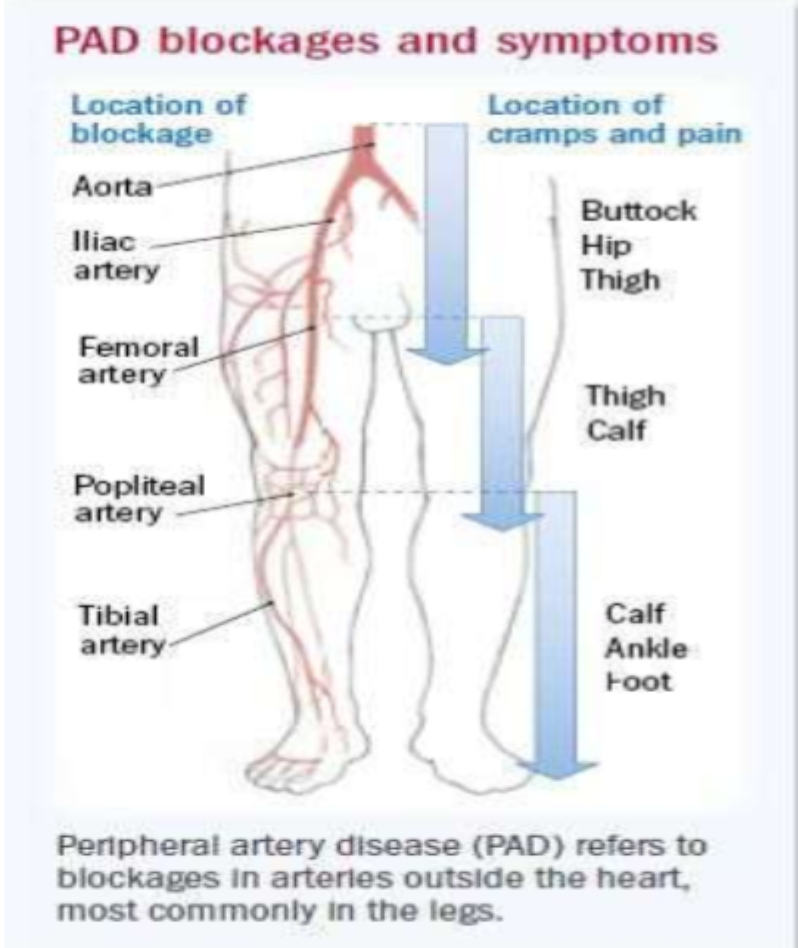
What zone is the target site for vascular access
Zone A
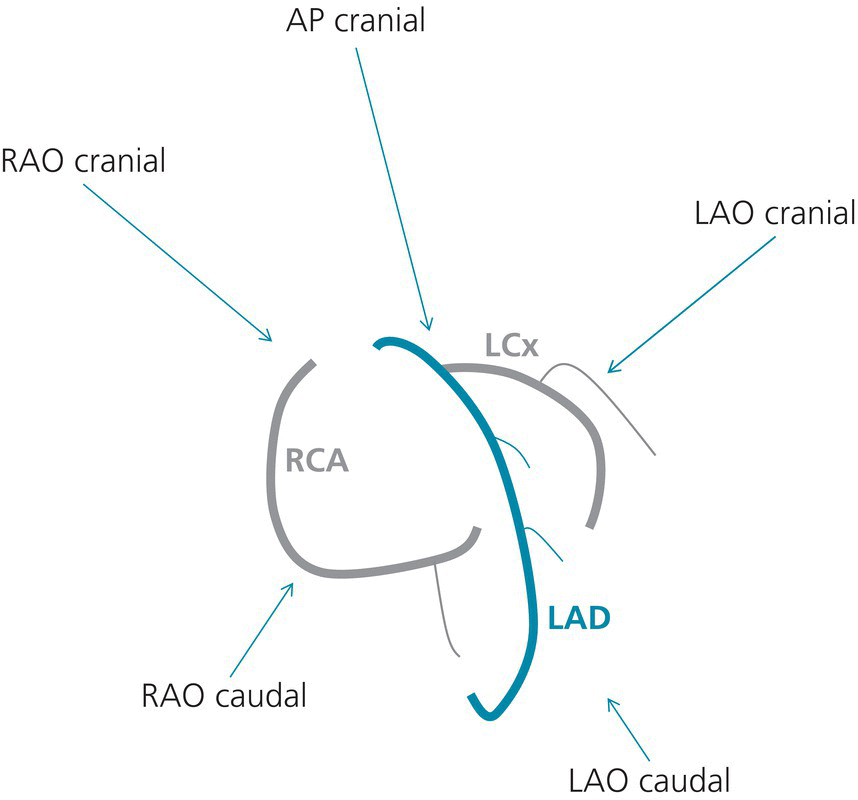
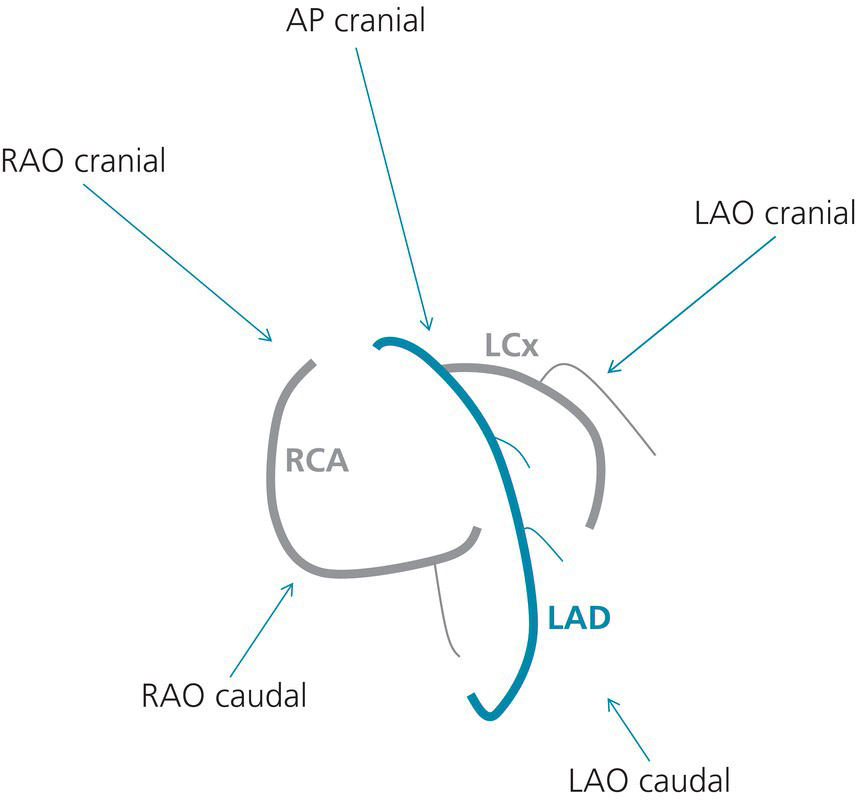
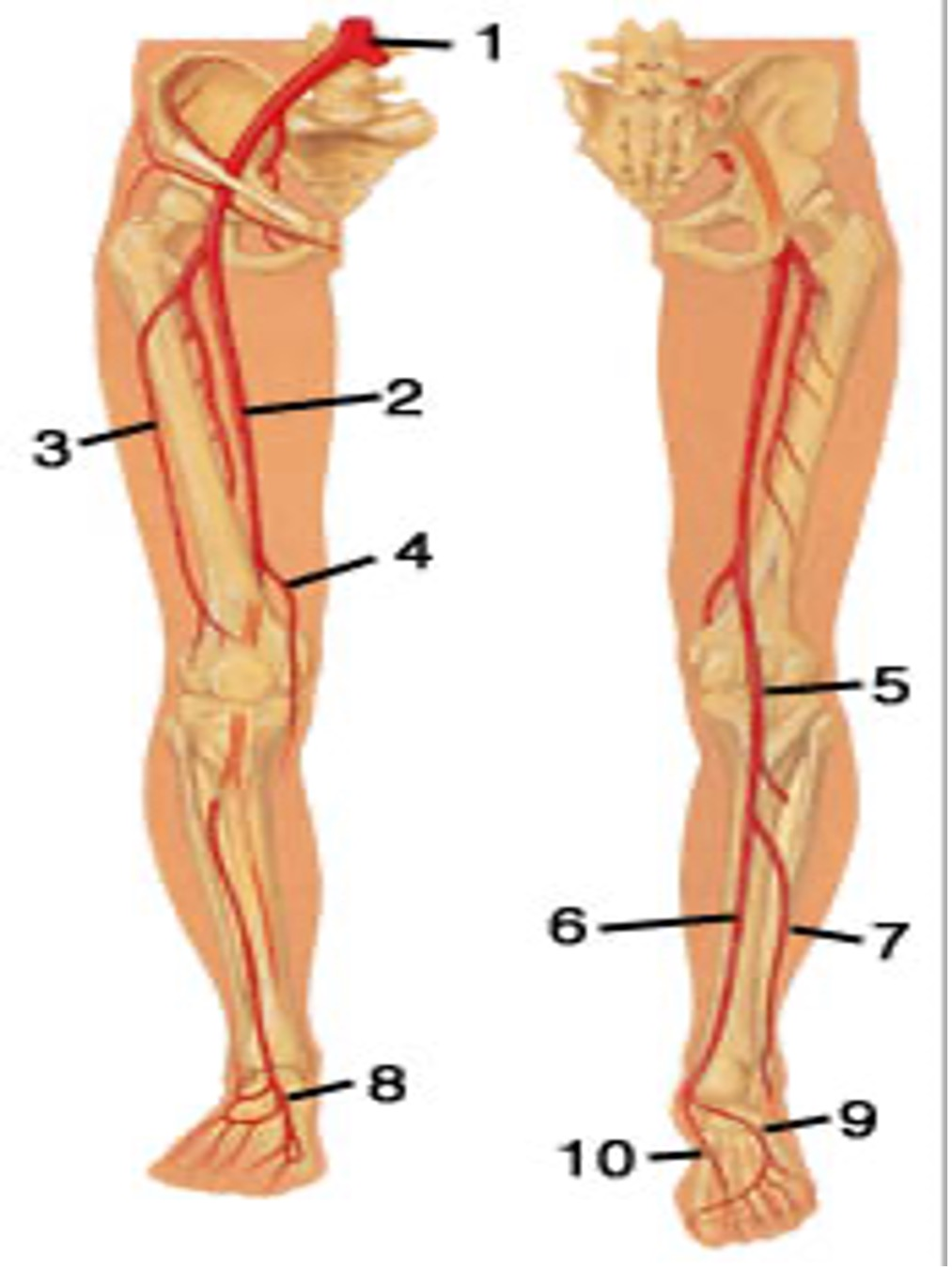
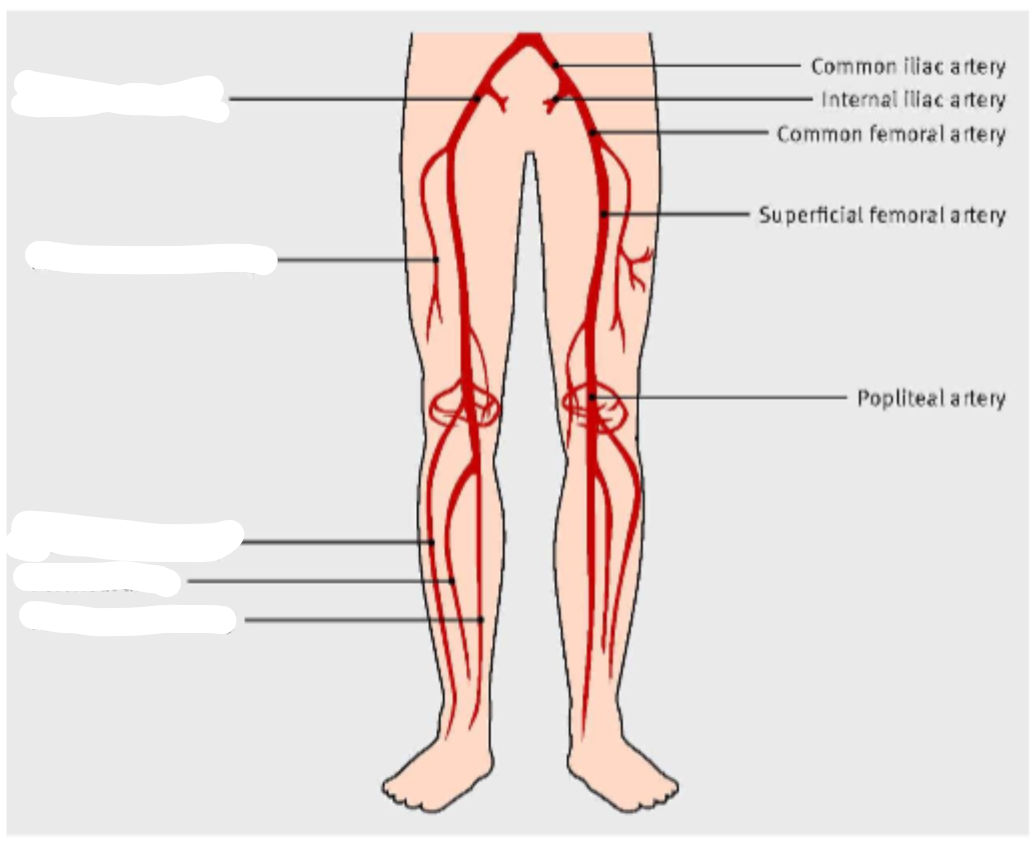
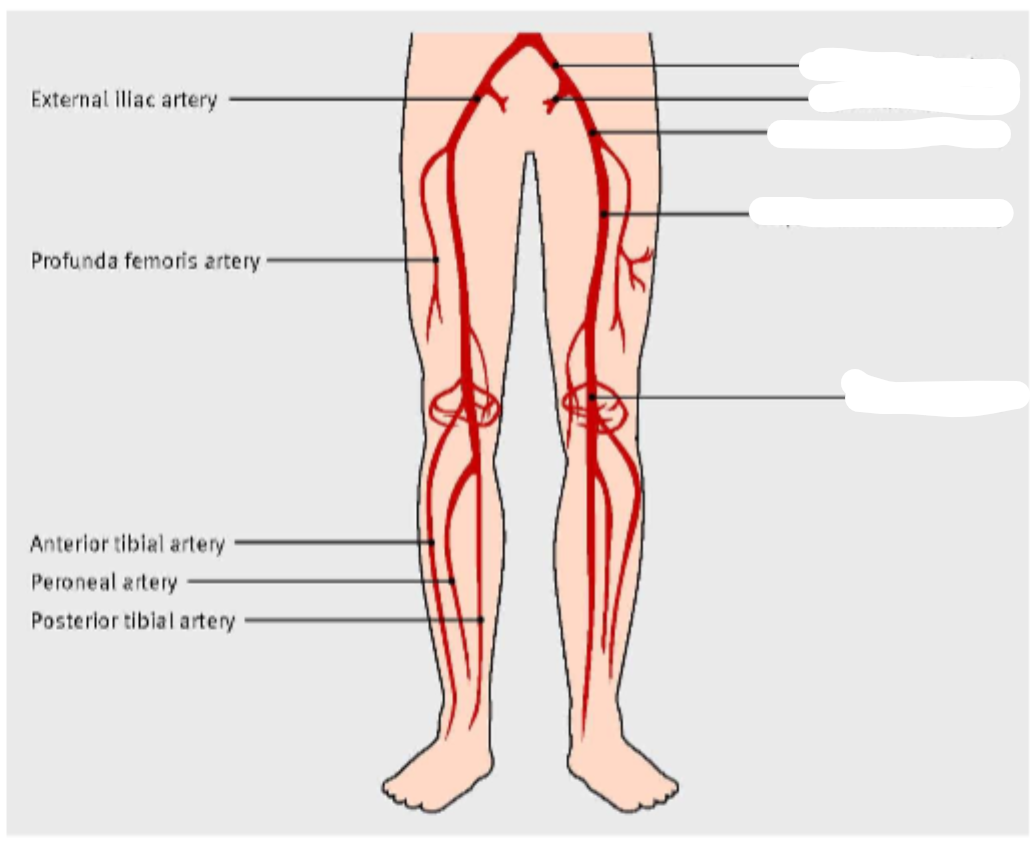
what is
1..
2..
3..
common iliac artery
femoral artery
Profunda fem artery ( its actually not, the profunda is medial alongside the femoral bone)
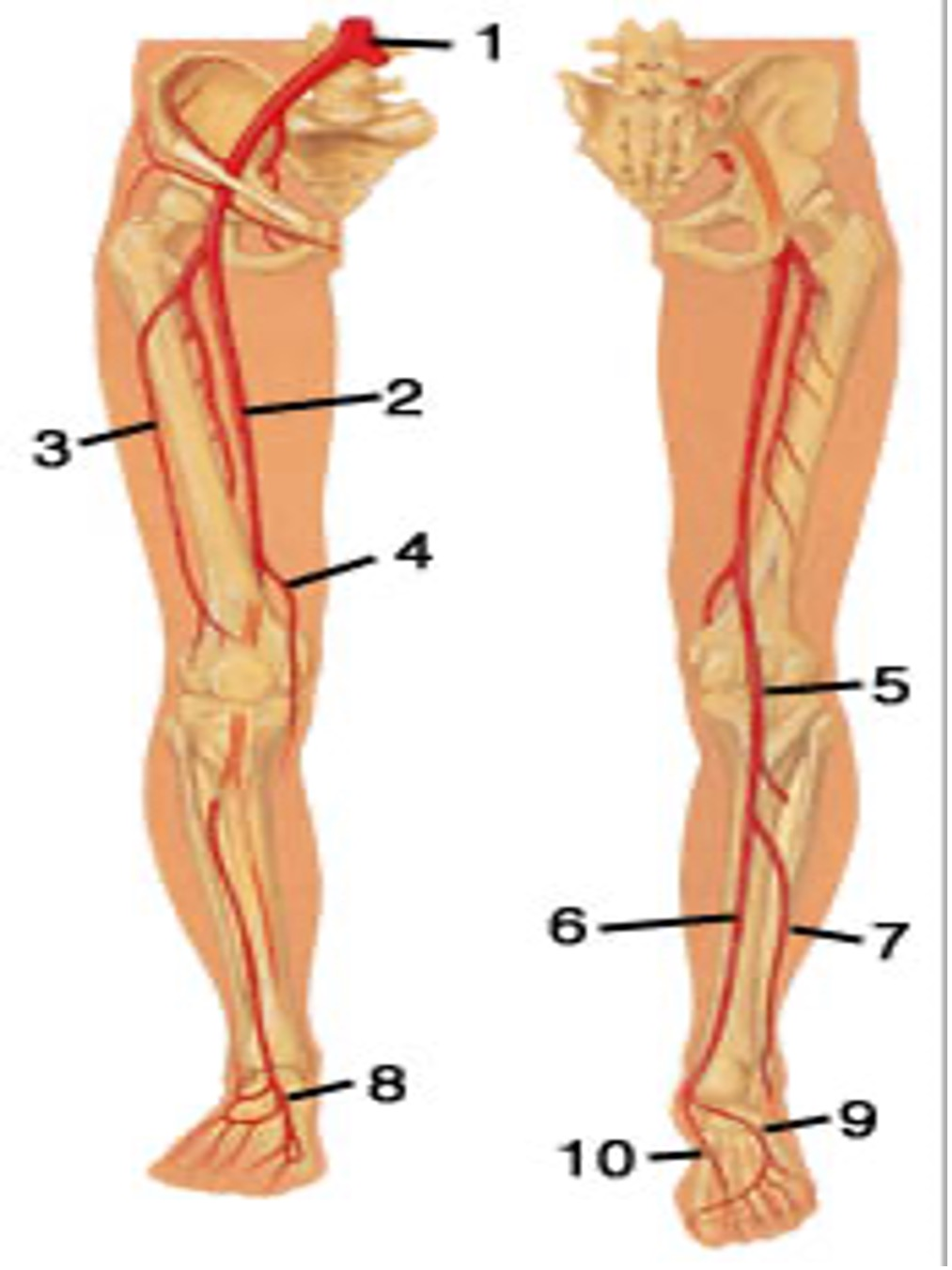
5..
6..
popliteal artery POPA
PTA posterior tibial artery
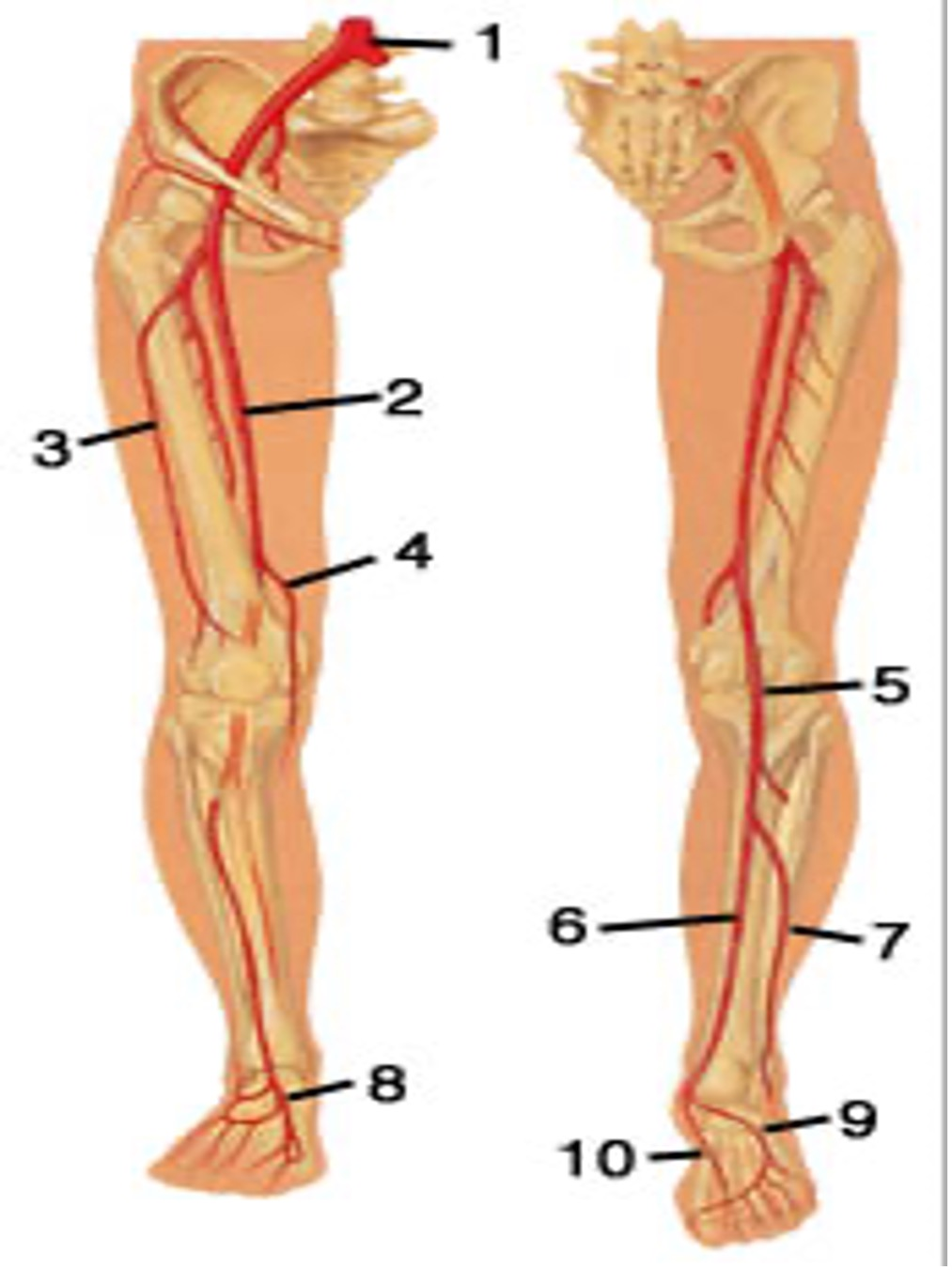
7..
8..
peroneal artery PeroA
dorsalis pedis DP
For 5F to 6F femoral sheaths recovery usually requires ******* hours or more of bed rest
requires 4 hours or more of bed rest
For procedures using sheath of 5F or less or procedures in which hemostasis is obtained w a VCD ****** hours of bed rest with 4 hours of observation before discharge
2 hours of bed rest with 4 hours of observation
Midazolam (Versed@, Dormicum@) ; benzodiazepine dosage
0.5 0 1.0 mg
Main difference between modified Allens test and original allens test
a pulse ox may be used and the test relies on visual cueses
patient reporting allergic reactions to contrast media should be premedicated w ******** and *******************
Prednisone (corticosteroid) and diphenhydramine (Benadryl)
Normal value for hemoglobin is
12.0-16.0 g.dl
The barbeaus test has 4 types
type A no change in waveform
Type B reduced waveform but recovers
Type C *************
Typed D No waveform recovery after release
What artery are we testing for patency ? bonus
Type C
Loss of waveform but recovers after release
Radial artery
The barbeaus test is used to measure the ______ of the _________ artery by objectively measuring restoration of circulation after having the vessel compressed. objectively by using a pulse ox
the patency of the radial artery
Type A in Barbeaus test deems the _______ ___ ____ ____ used
type A - ****************
Radial artery can be used
NO CHANGE
Should the radial artery be used after scoring a type d in the Barbeaus test
NO
NO WAVEFORM RECOVERY AFTER COMPRESSING
DO NOT USE
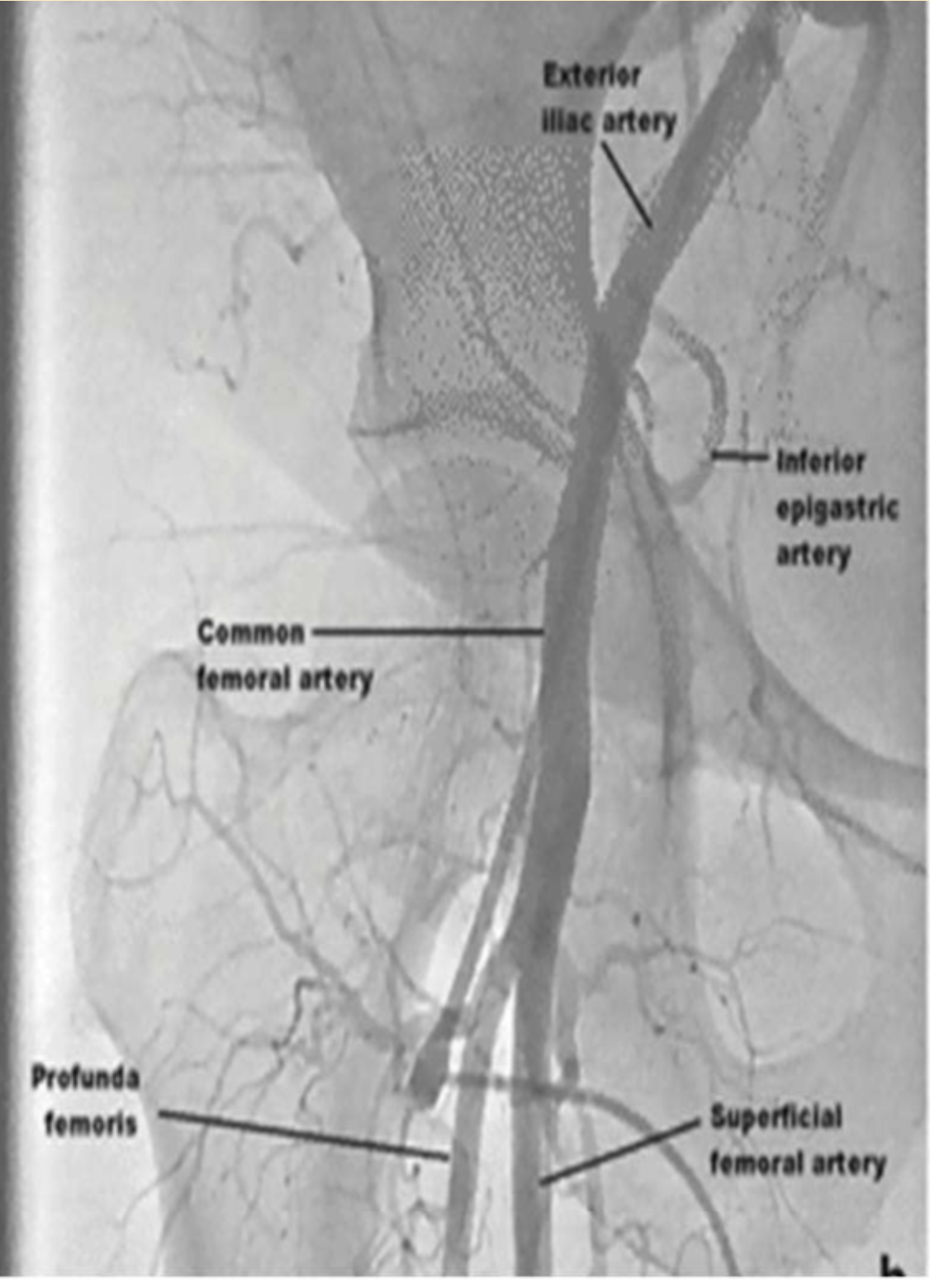
In femoral access the superior landmark is
Superficial epigastric artery
This vascular complication can occur when the CFA arterial stick is too low
Most common
Pseudoaneurysm formation
or fistula
Postprocedural management checks for bleeding should occur every __________ minutes for the first hour.
15 minutes
How long should manual pressure be held after pulling a 6 fr sheath
18 min.
_________ develop due to a subcutaneous bleeding
Hematomas
What is the potential consequence of a hematoma at the access site?
Compression of surrounding structures and potential loss of access. AKA compartment syndrome
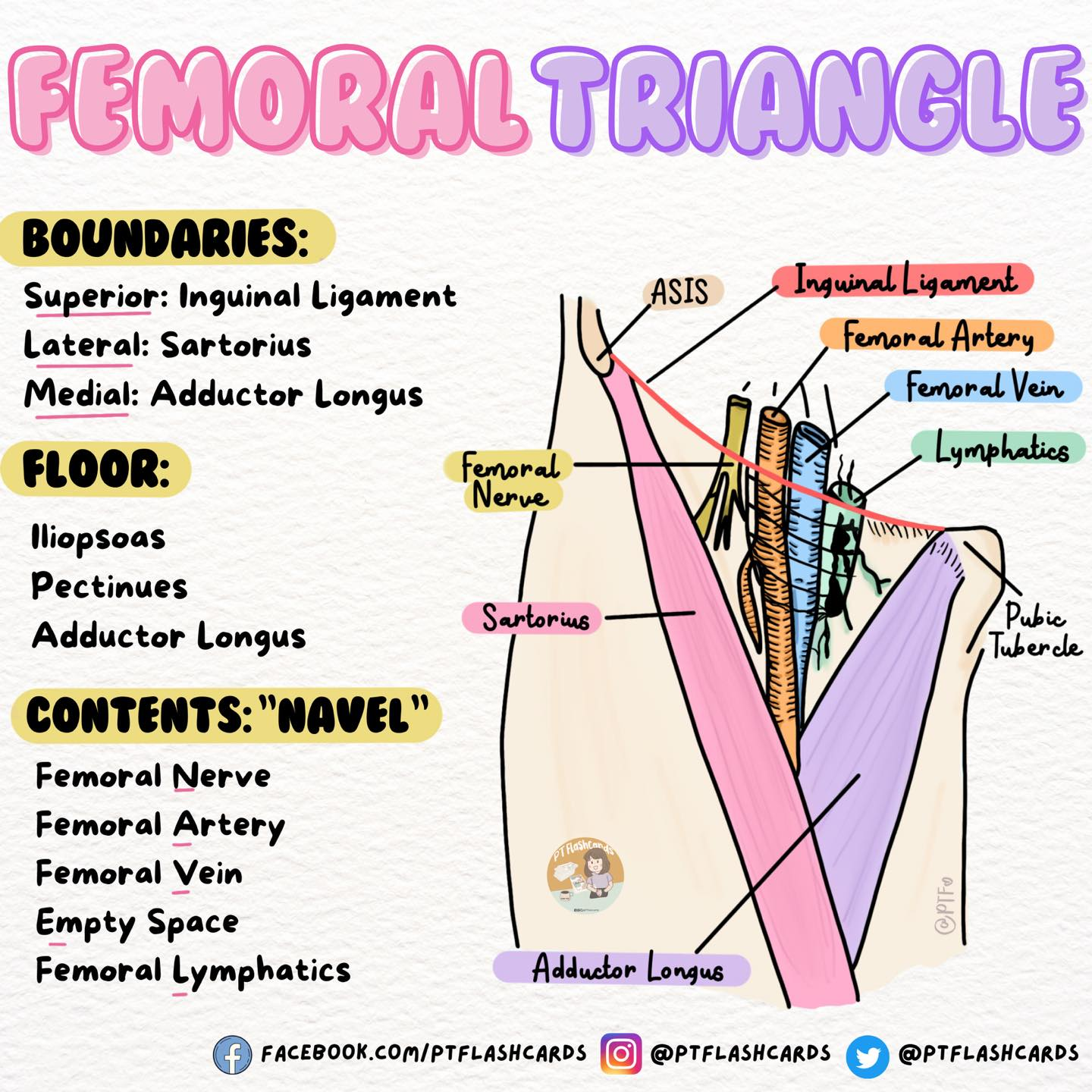
Femoral triangle ACRONYMN is what
5
NAVL
NERVE
ARTERY
VEIN
E Empty space (femoral vanal)
LYMPH
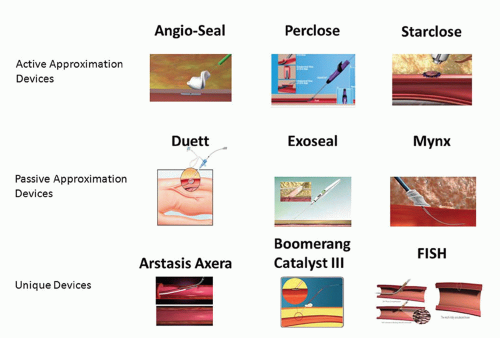
Name one passive closure device
MYNX is a passive closure device that uses a bioabsorbable polymer to seal the access site.
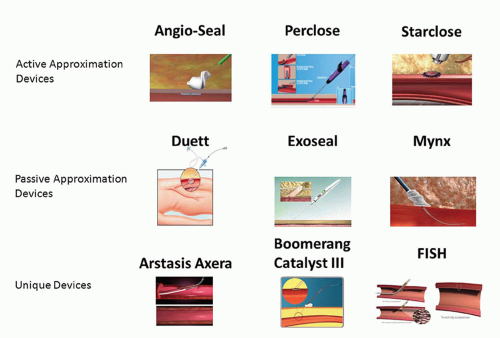
Passive closure device is a device that ********************
promotes natural clot formation rather than actively sealing with mechanical suture based or collagen based closure.
Stat seal is a _____ patch
what kind of closure device is it
Hemostatic patch
hemostatic patches device
Ultrasound guided compression can be used to treat which vascular complication
paseudoaneurysm
What are symptoms of a retroperitoneal bleed
hypotension
tachy
back flank pain
A palpable thrill is present in which vascular complication
AV fistula
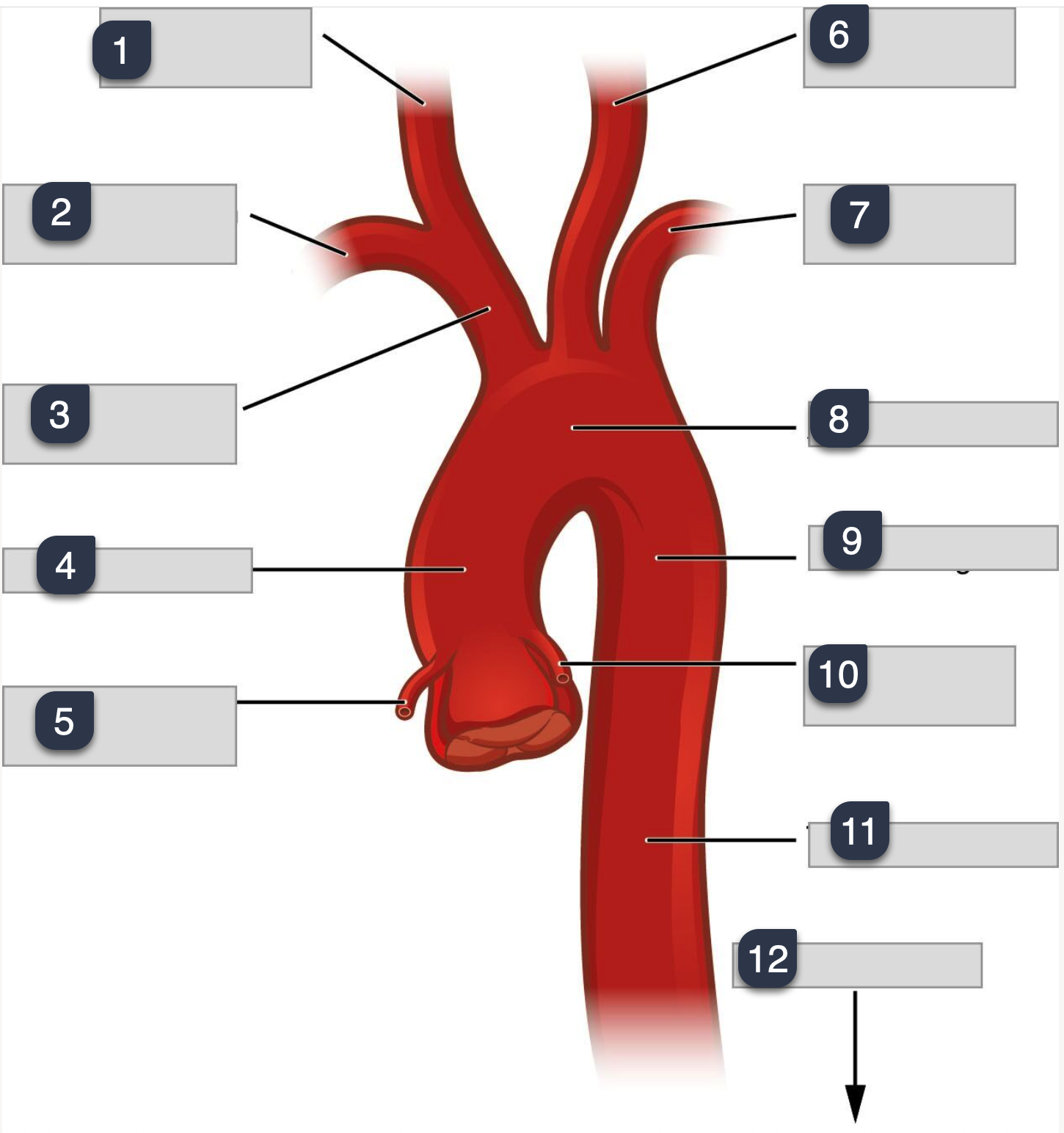
What is 1-4
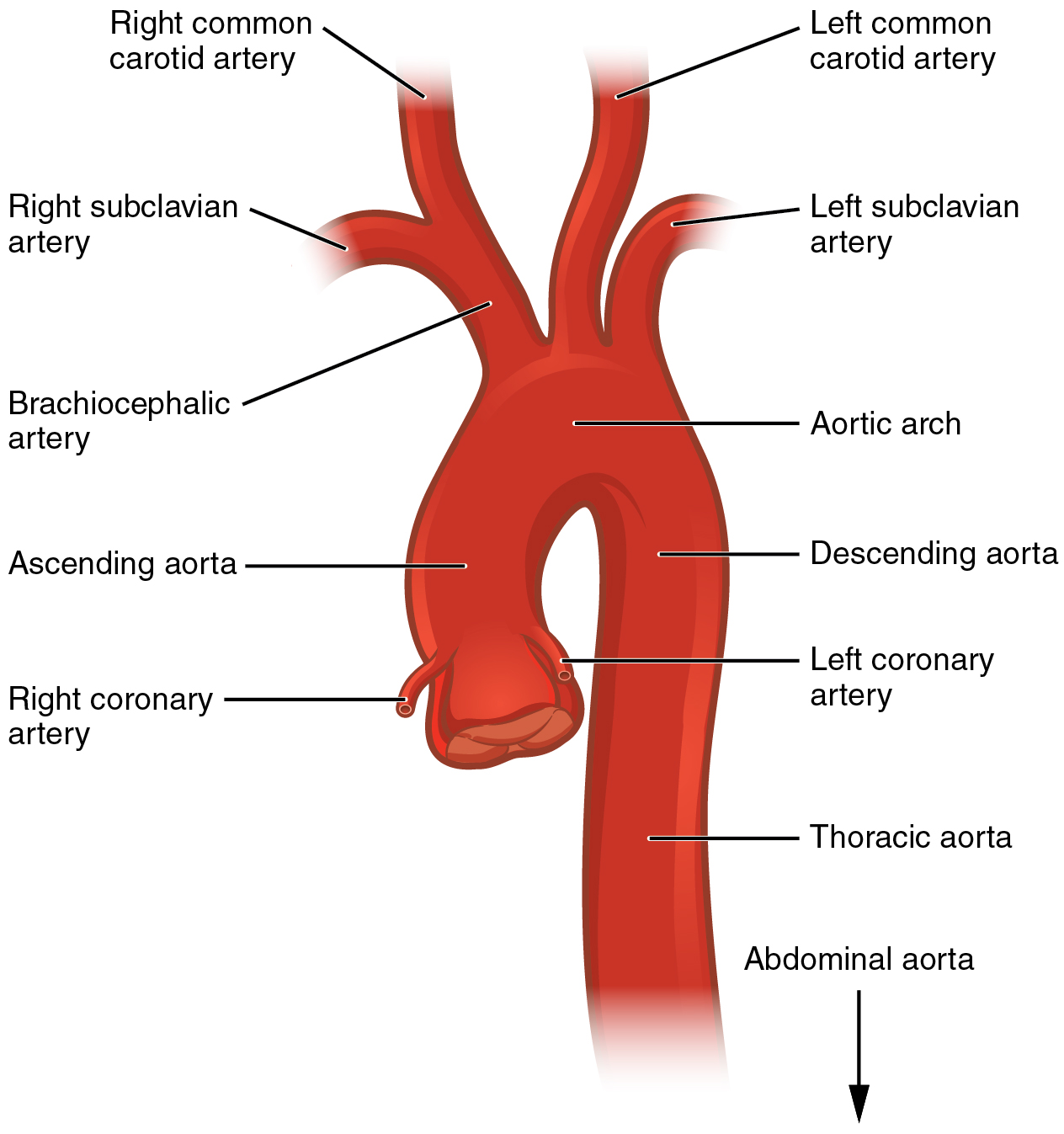
What is 4-8
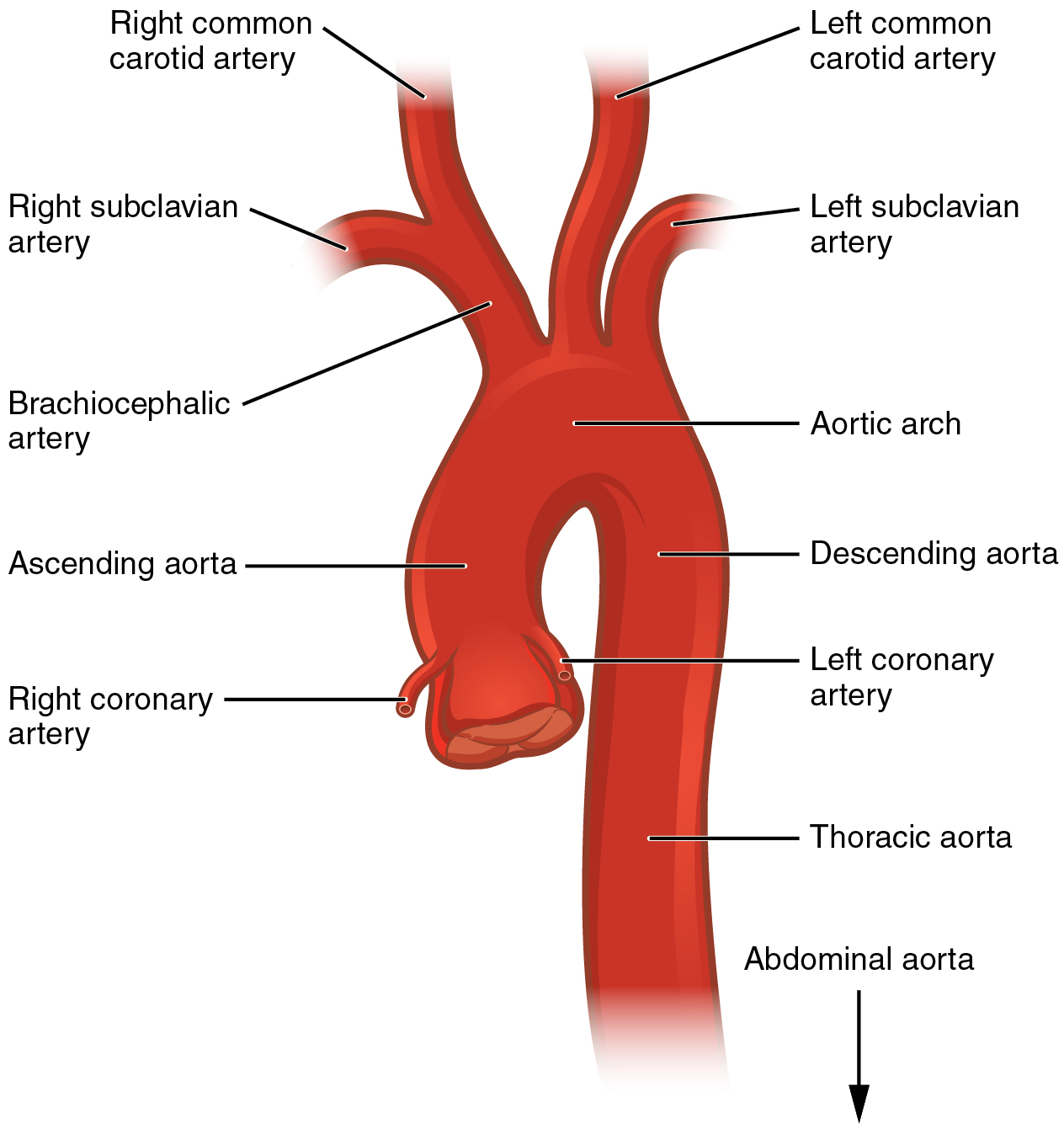
What is 8-12
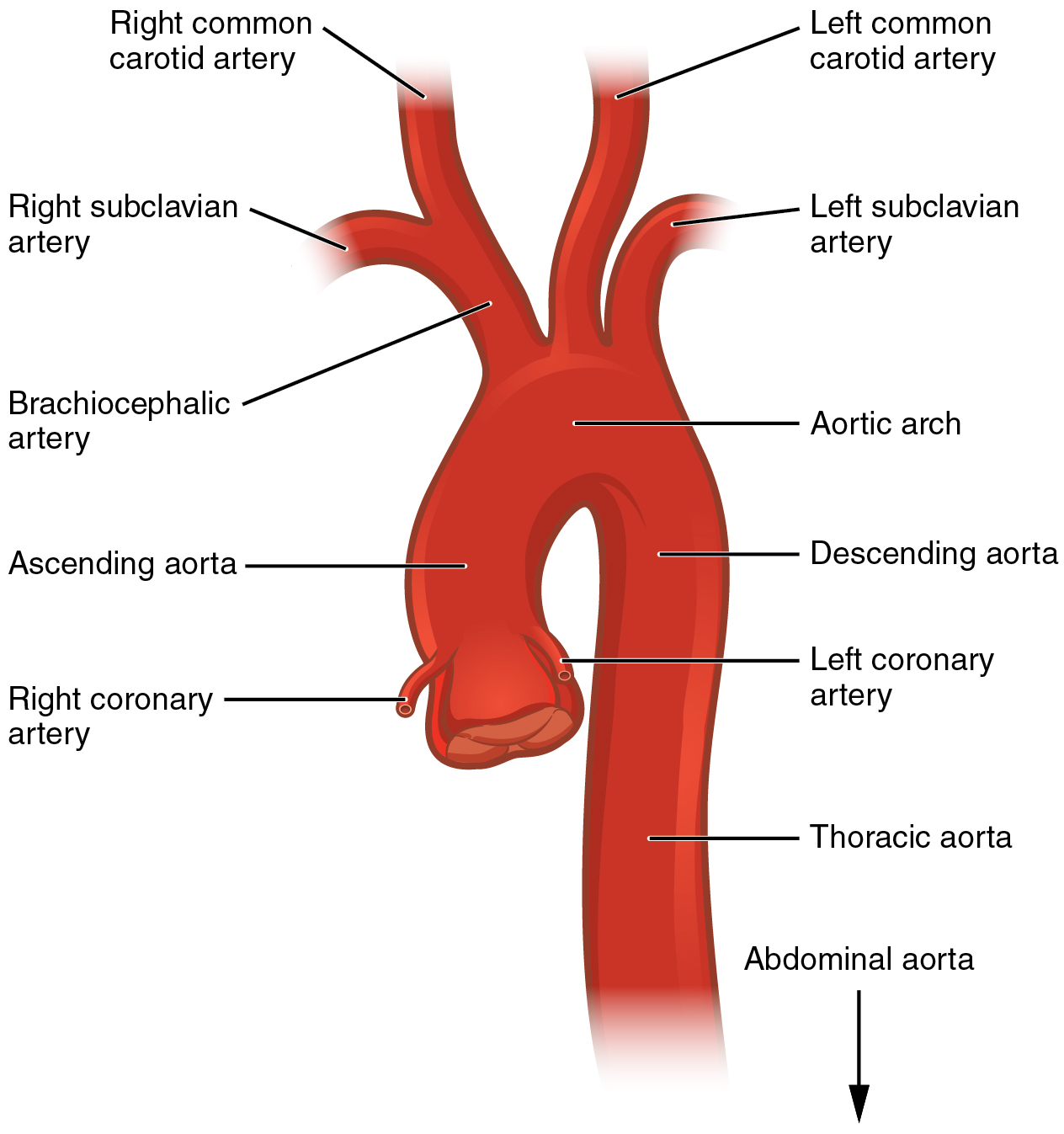
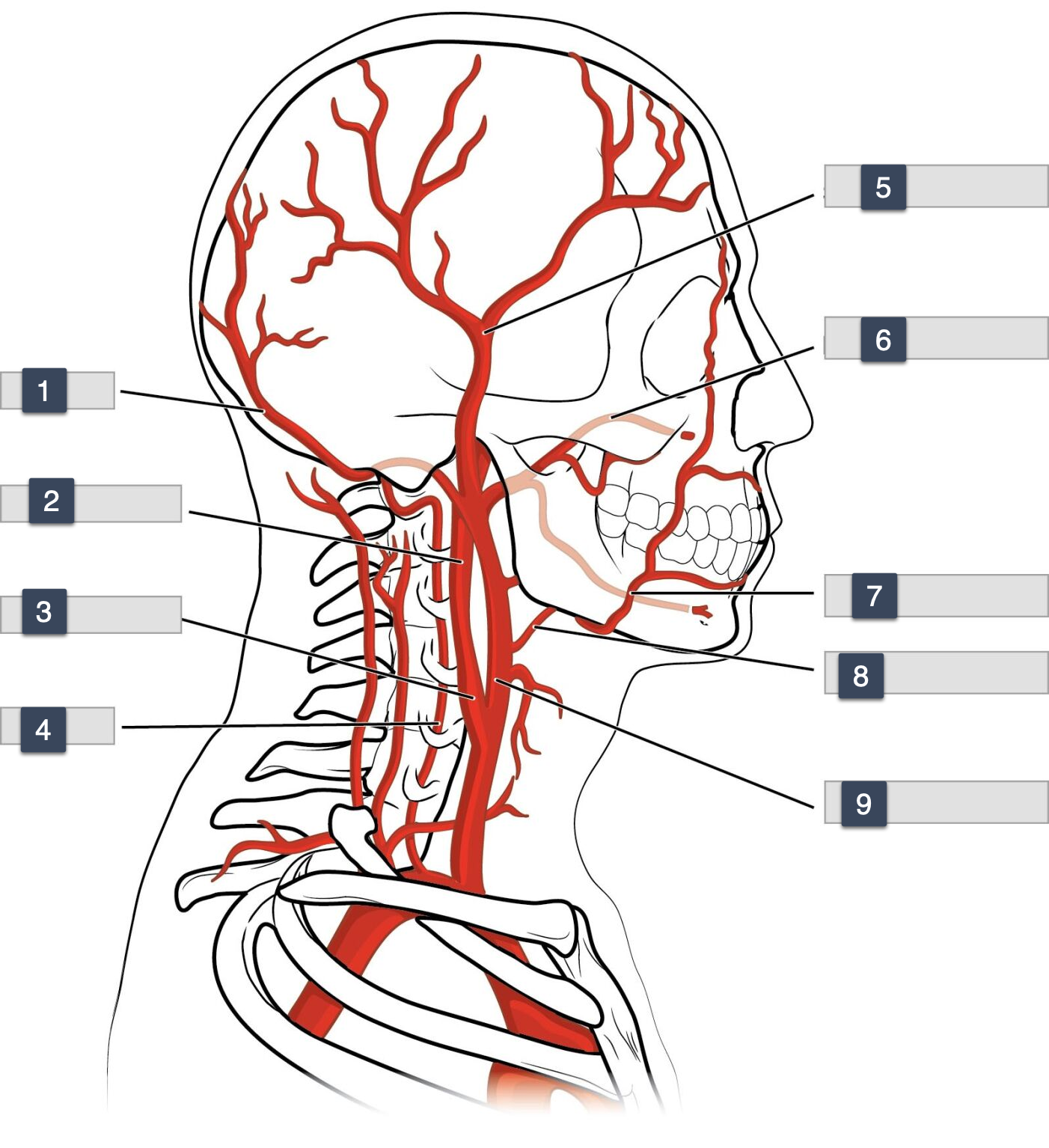
1-3
Occiptal
internal carotid
carotid sinus
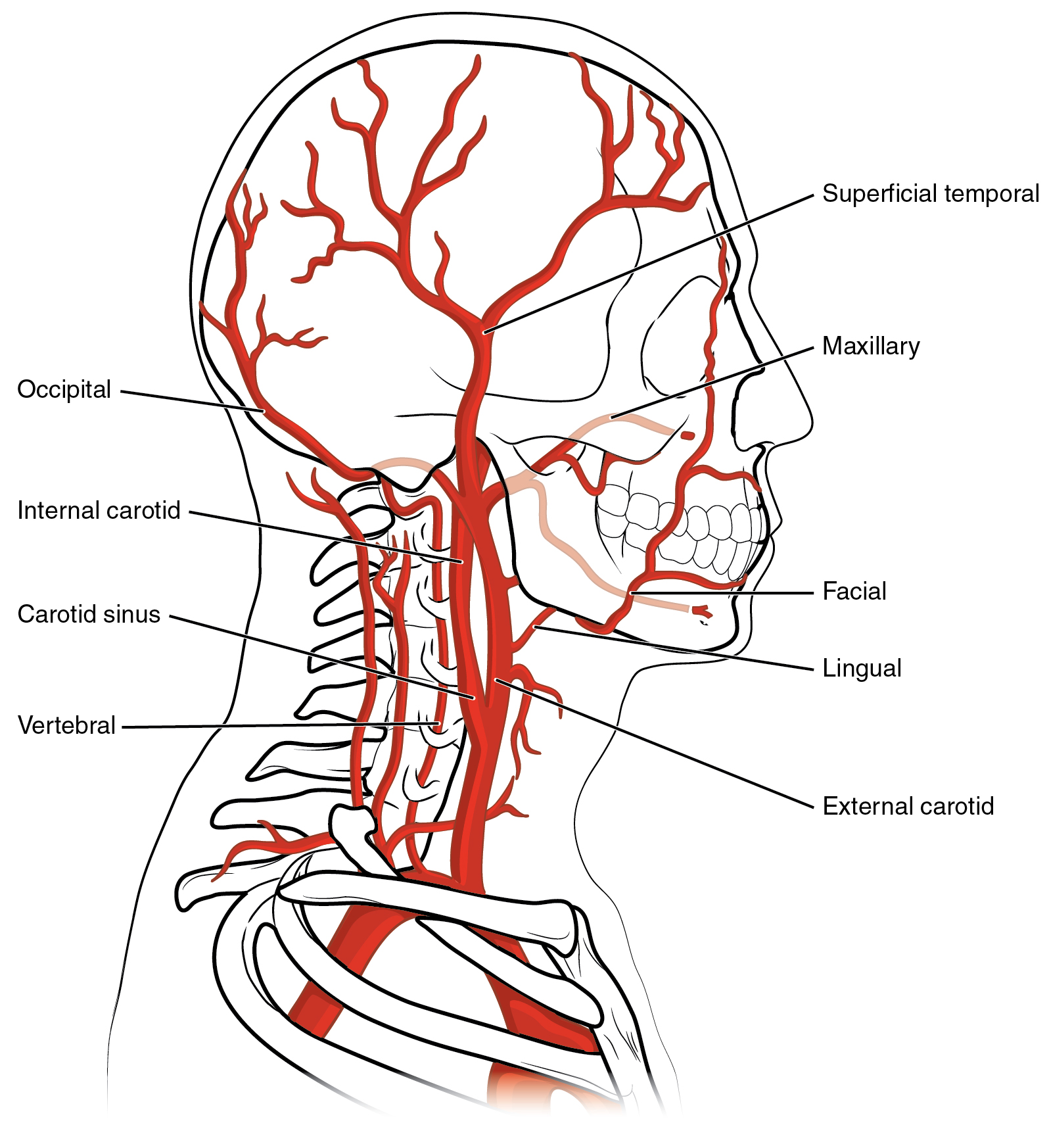
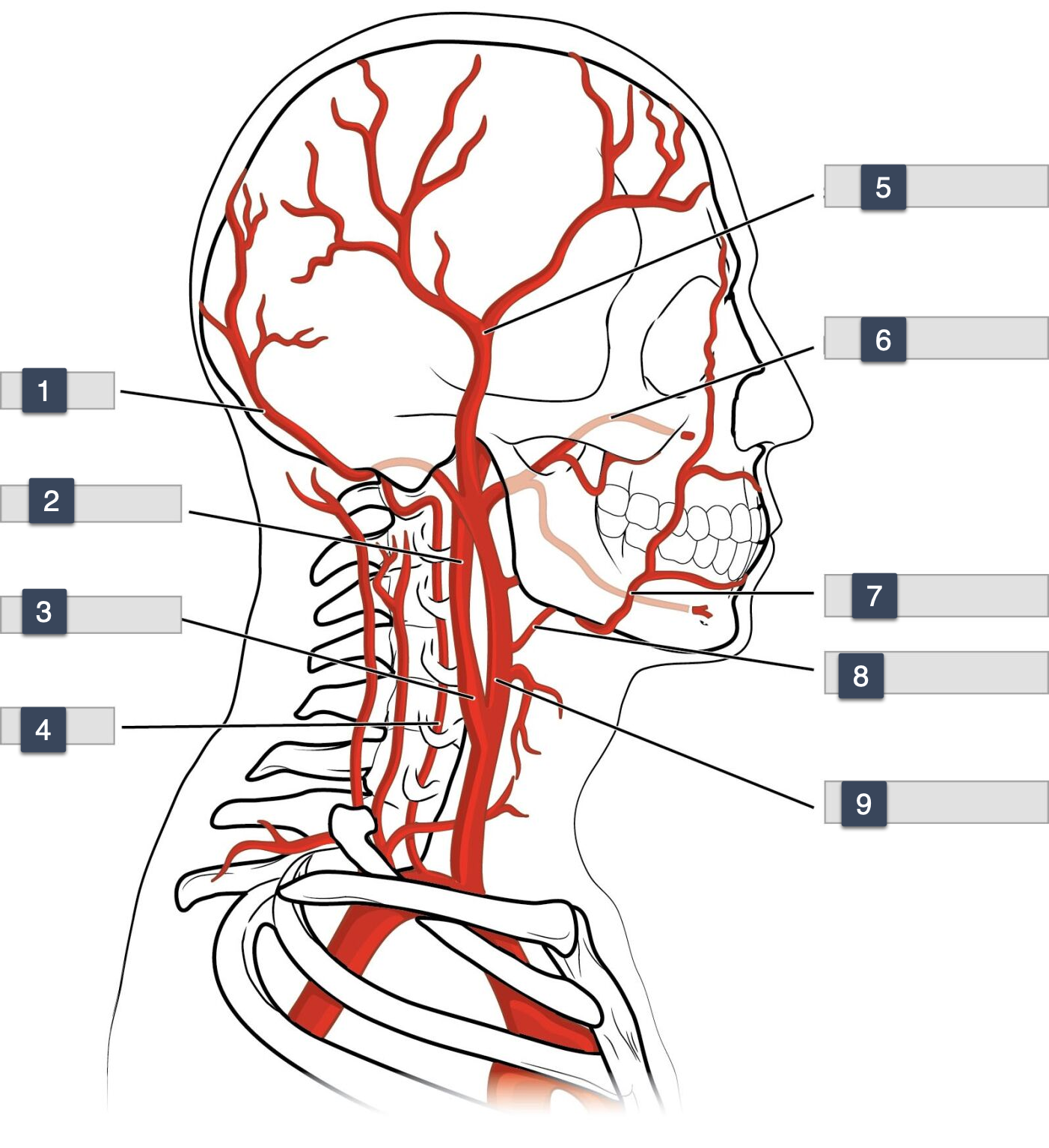
3-6
carotid sinus
vertebral
superficial temporal
maxillary
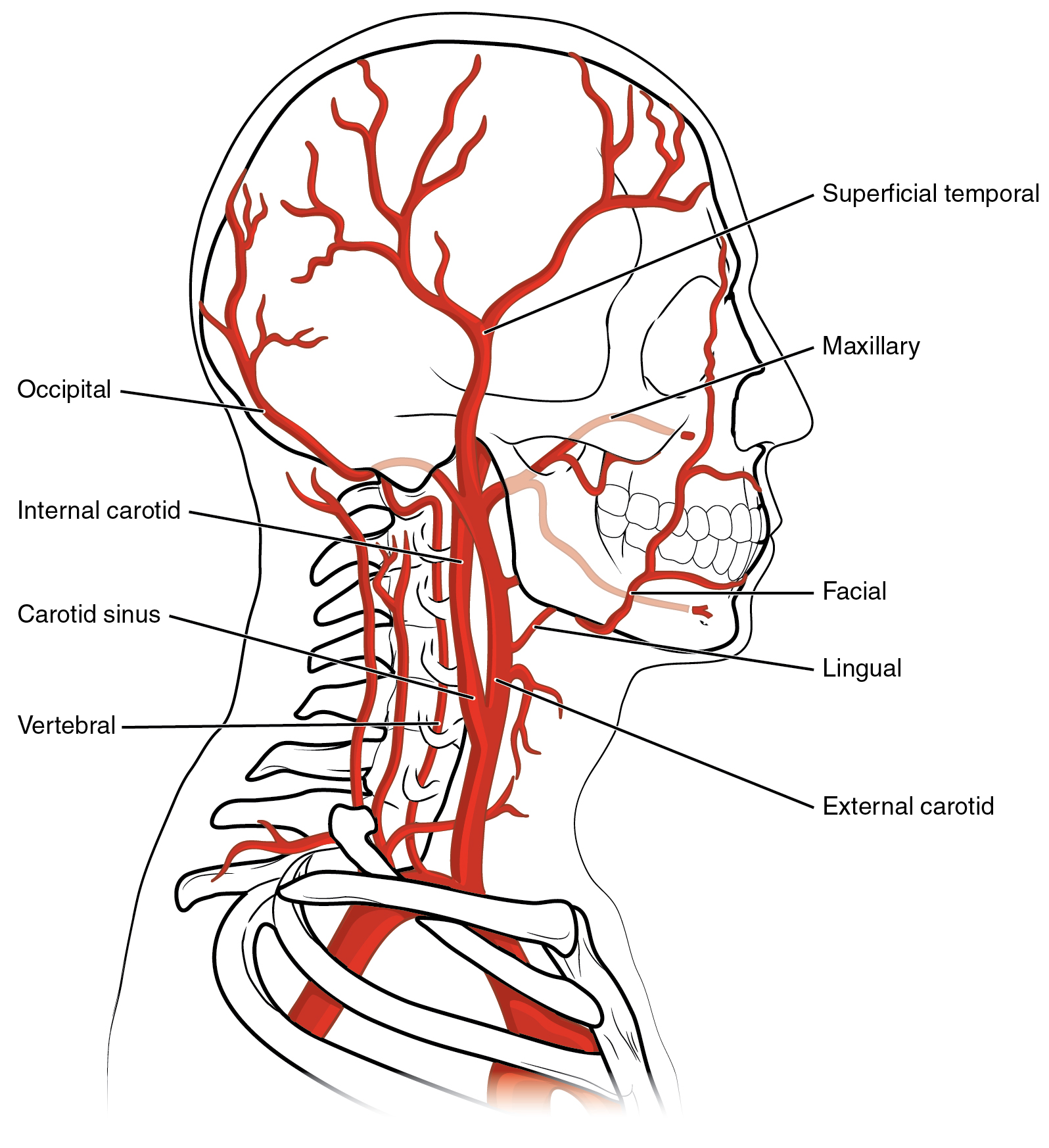
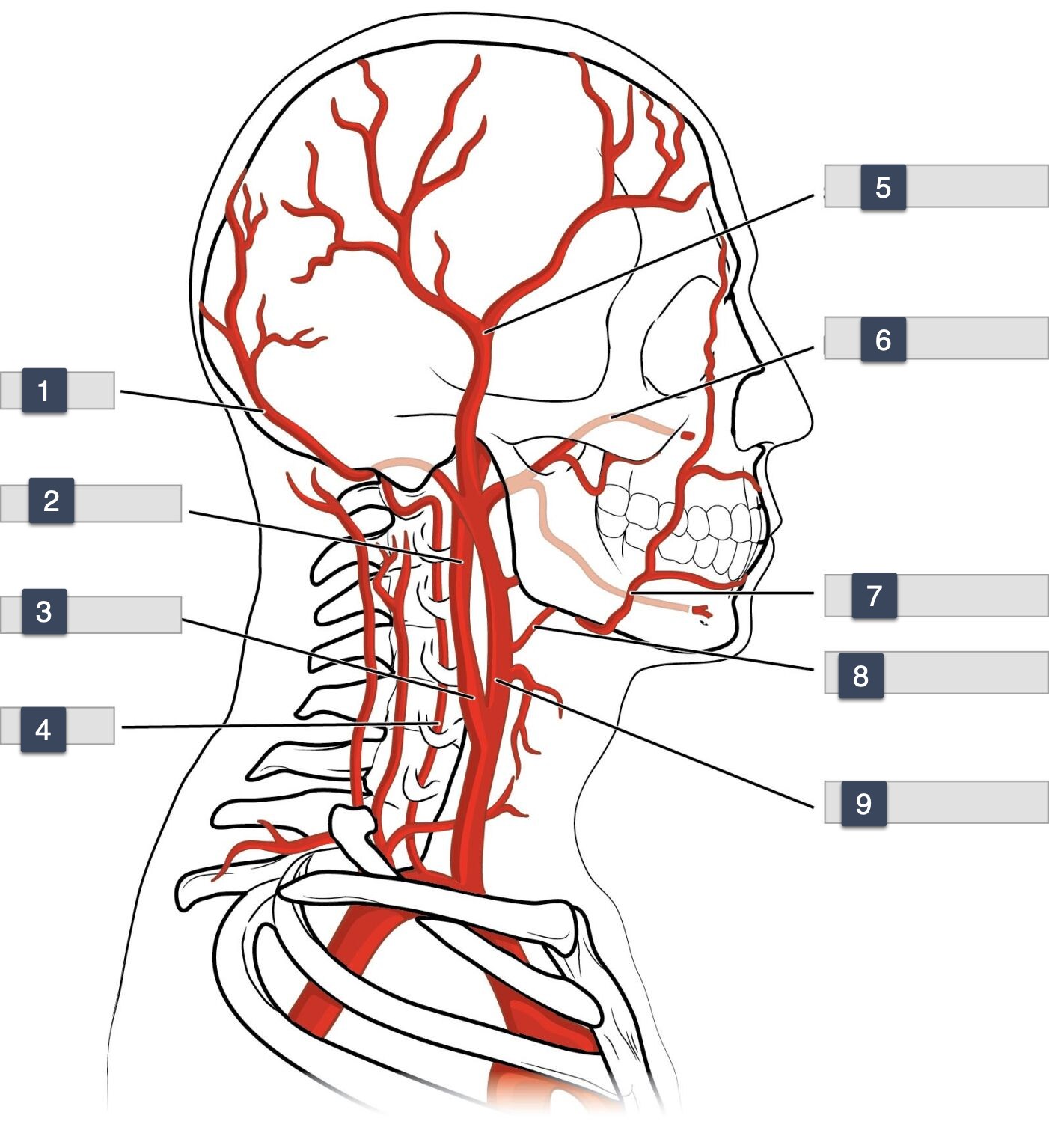
6-9
maxillary
facial
lingual
A pathological process characterized by the proliferation of smooth muscle cells and extracellular matrix in the intimal layer of a blood vessel, often leading to stenosis after vascular interventions. is known as
neointimal hyperplasia
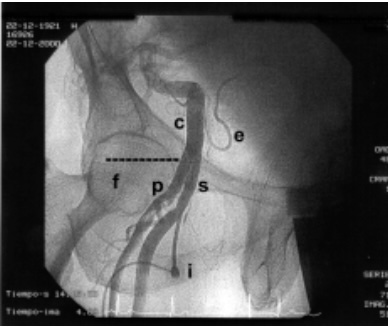
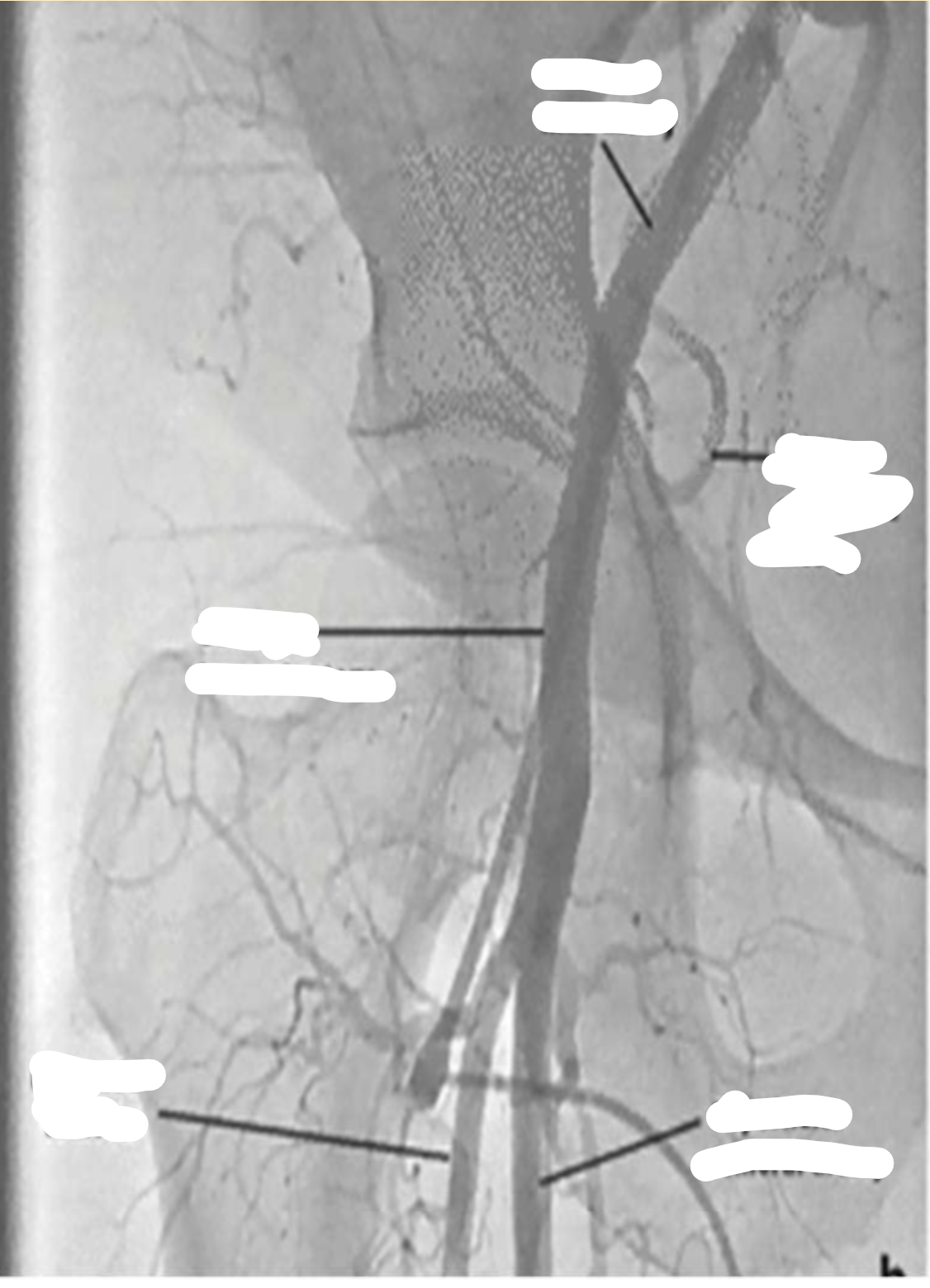
label
C
E
F
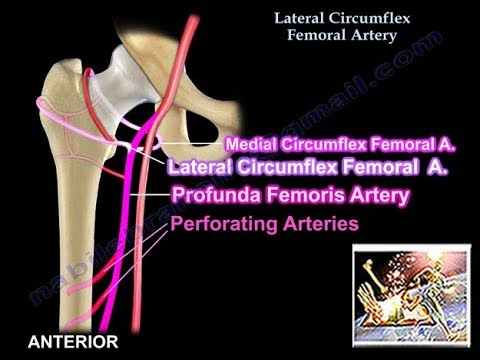
C. Common iliac artery
E. Epigastric artery
F. Femoral head
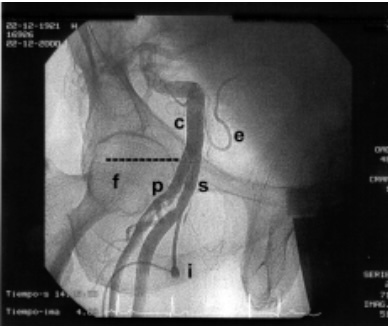
P.
S
I.
P. Profunda artery
S. Common Femoral artery
I. Vascular sheath
What direction does the guidewire travel in antegrade LCFA access
antegrade would mean wire traveling at the direction of blood, towards the feet away from heart.
TOWARDS FEET AWAY FROM HEART
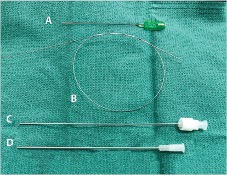
C.
D.
C. dilator (stylet)
D. micro puncture sheath
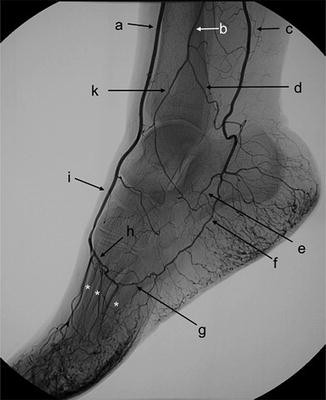
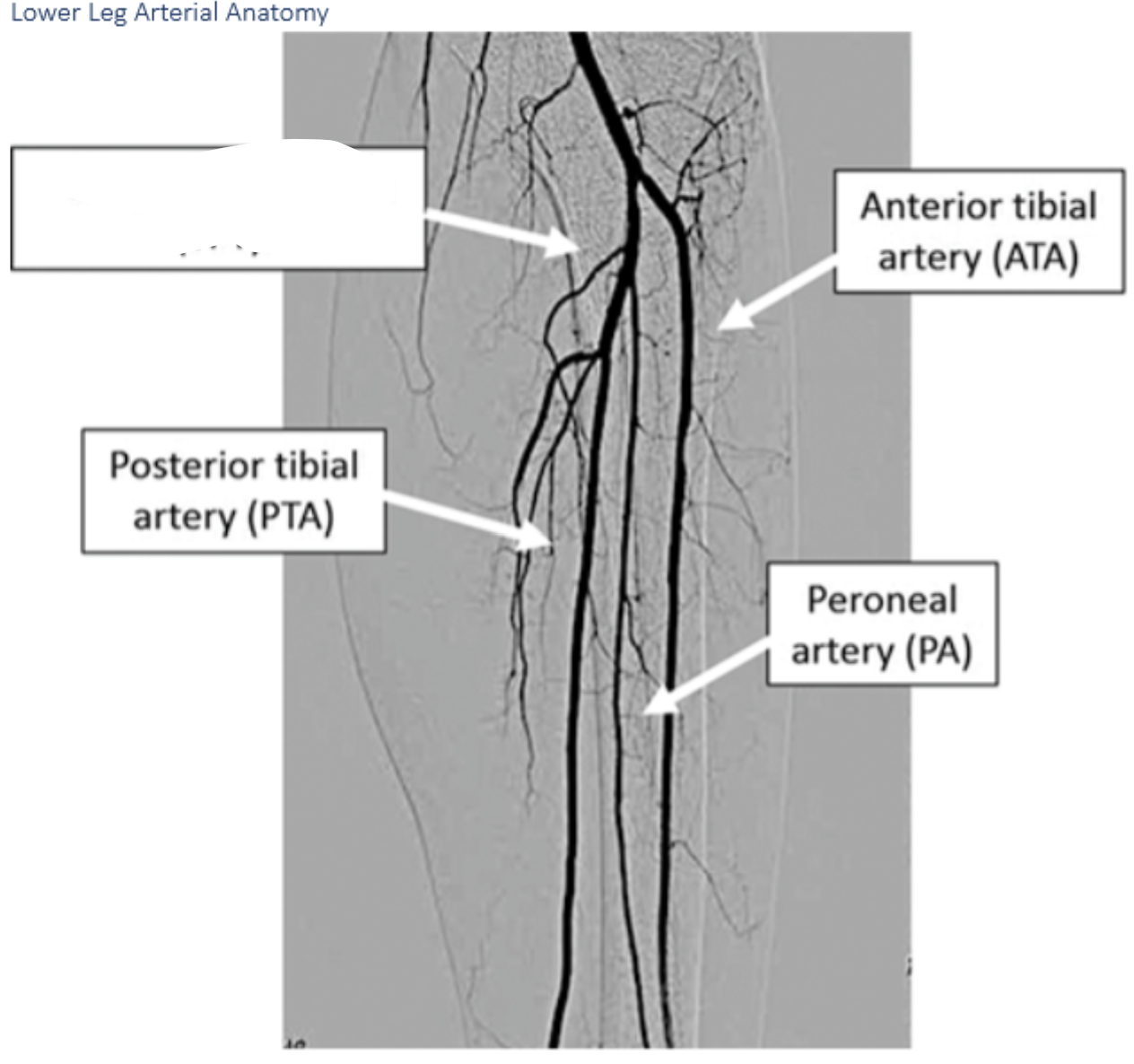
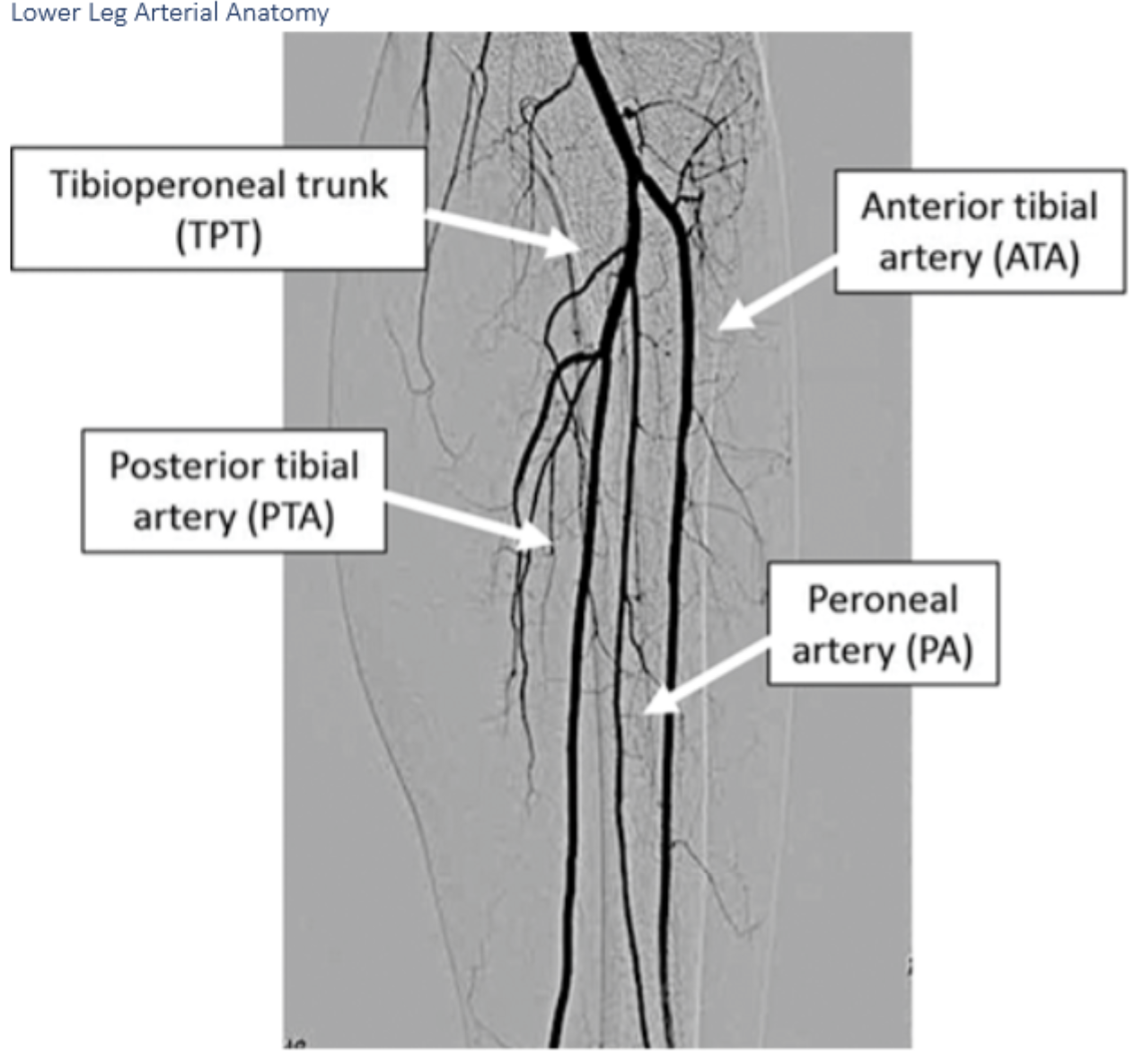
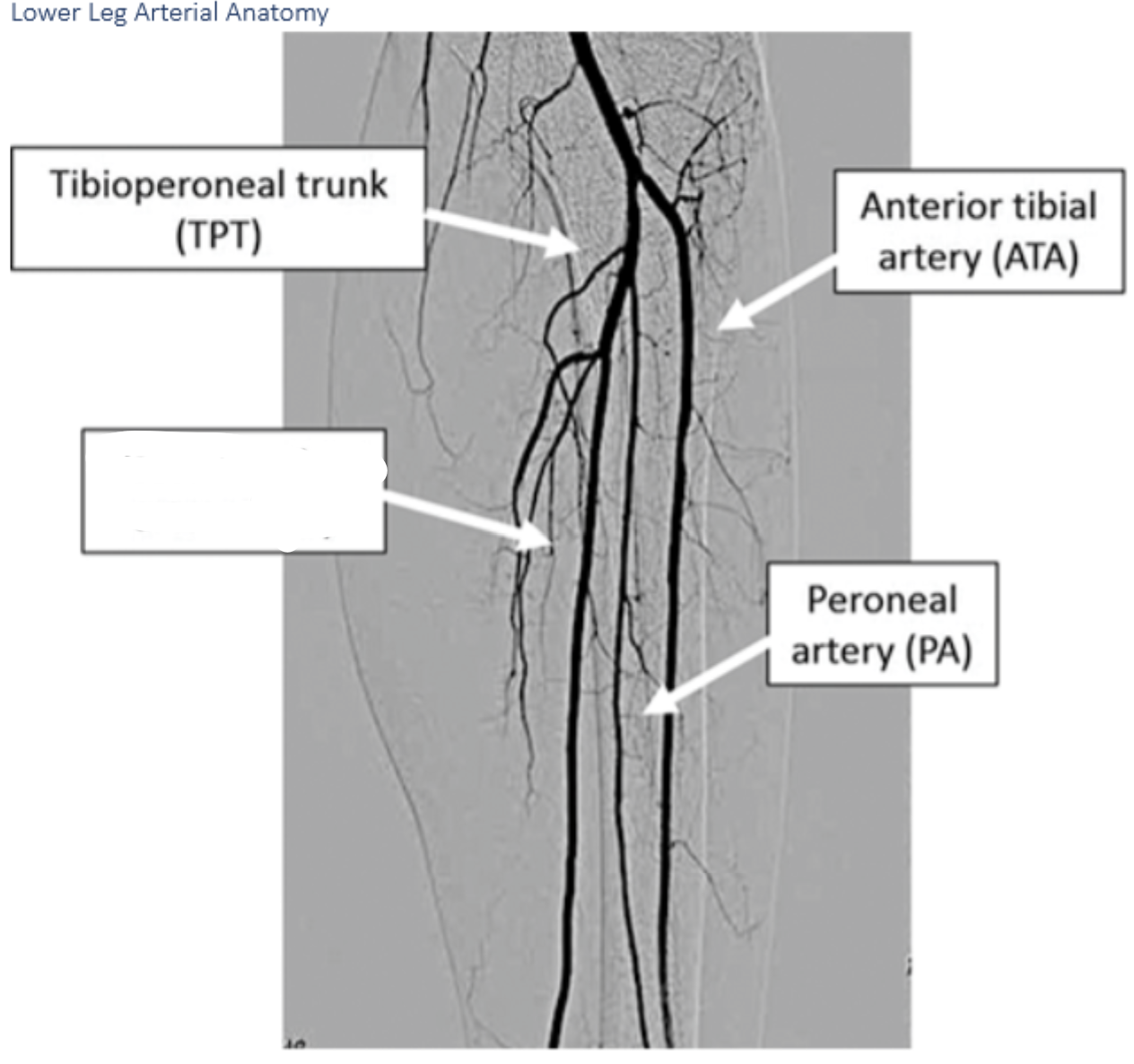
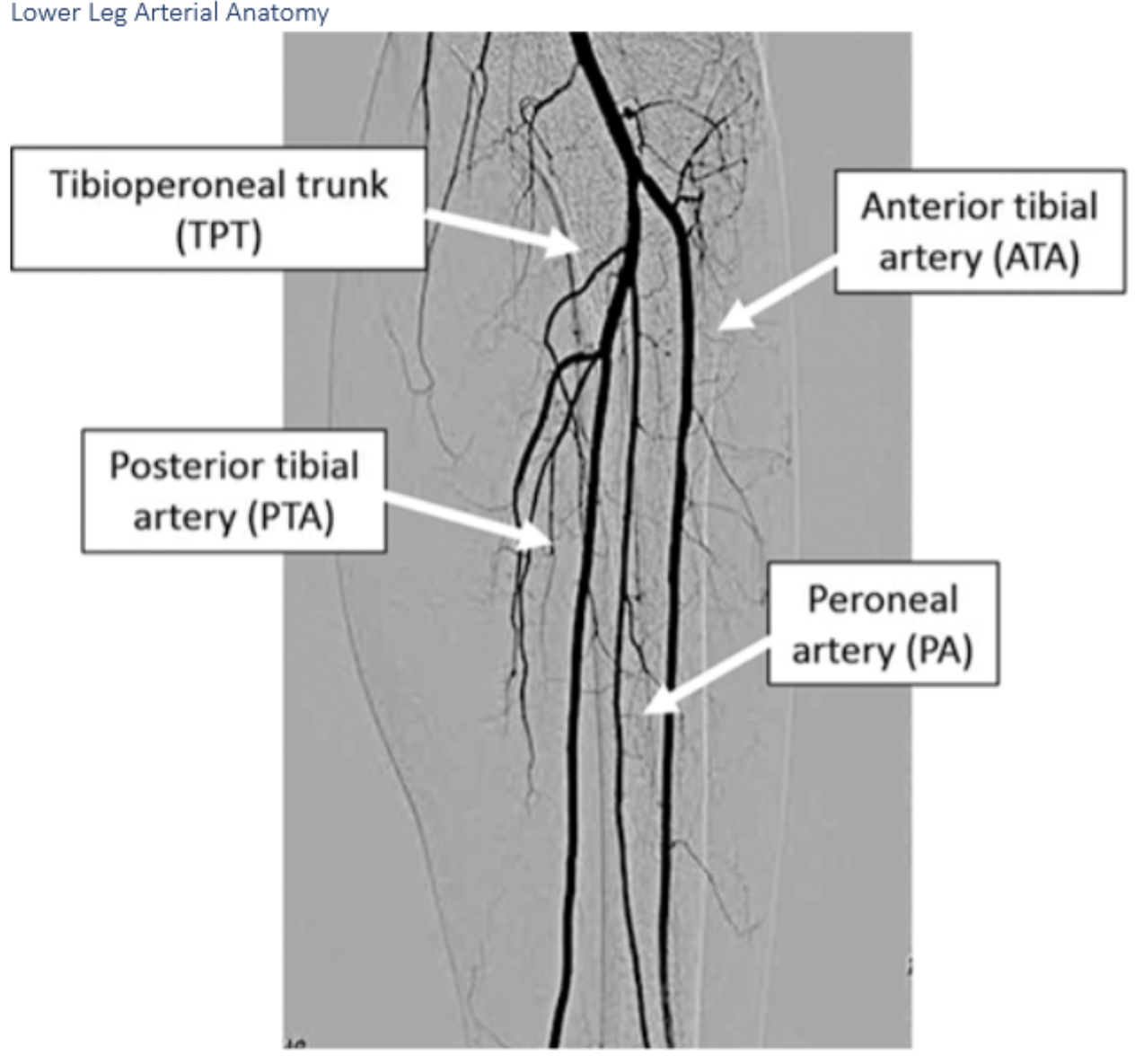
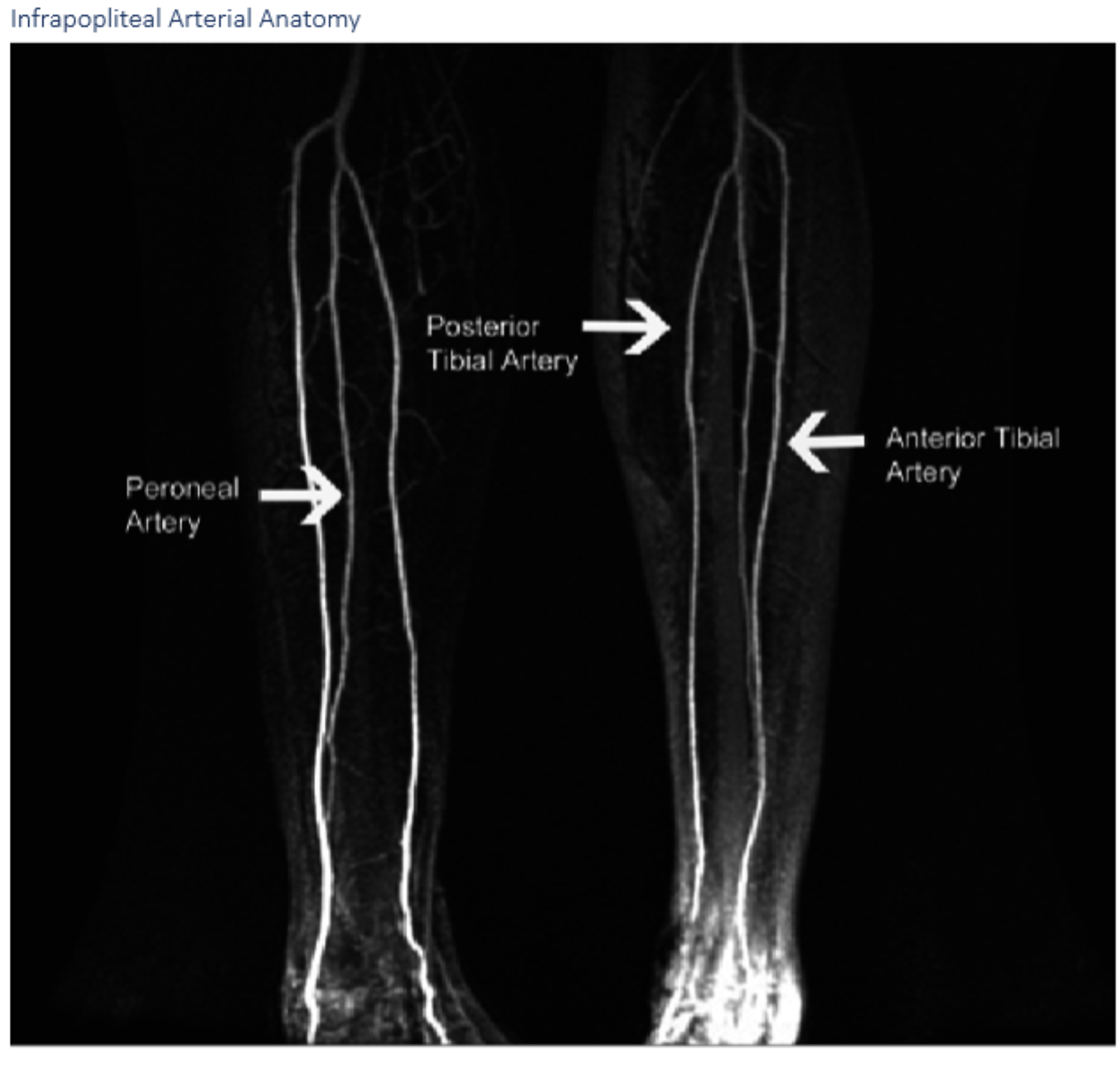
Label A.
Anterior tibial arteryLabel A. Dorsalis pedis artery
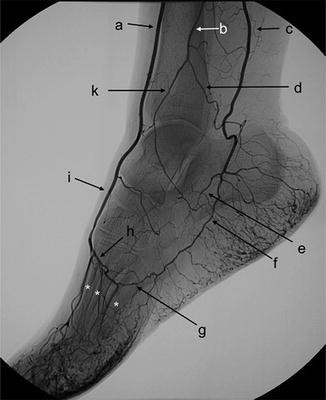
B.
B. peroneal artery
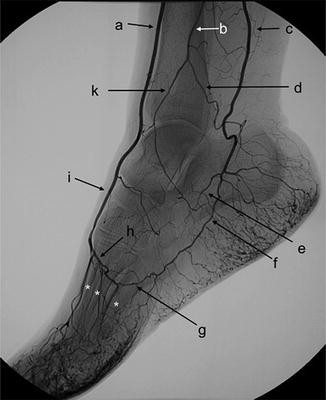
C.
C. posterior tibial artery
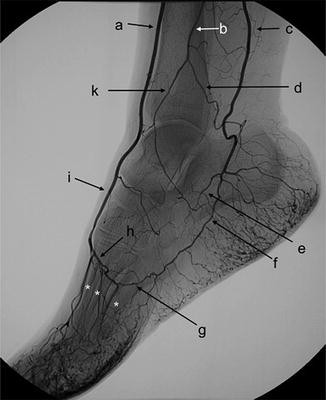
I.
I. Dorsalis Pedis
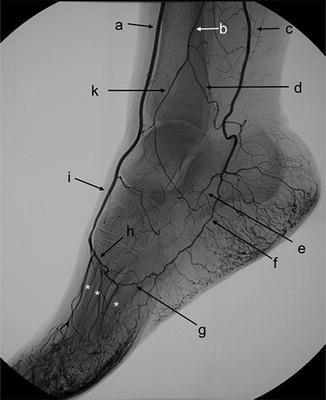
H.
H. Deep plantar arch
The common femoral **** is directly lateral to the common femoral ***** and will be pulsatile and not easily compressible
The common femoral artery is directly lateral to the common femoral vein and will be pulsatile and not easily compressible. (Kandarpa, pg. 3) |
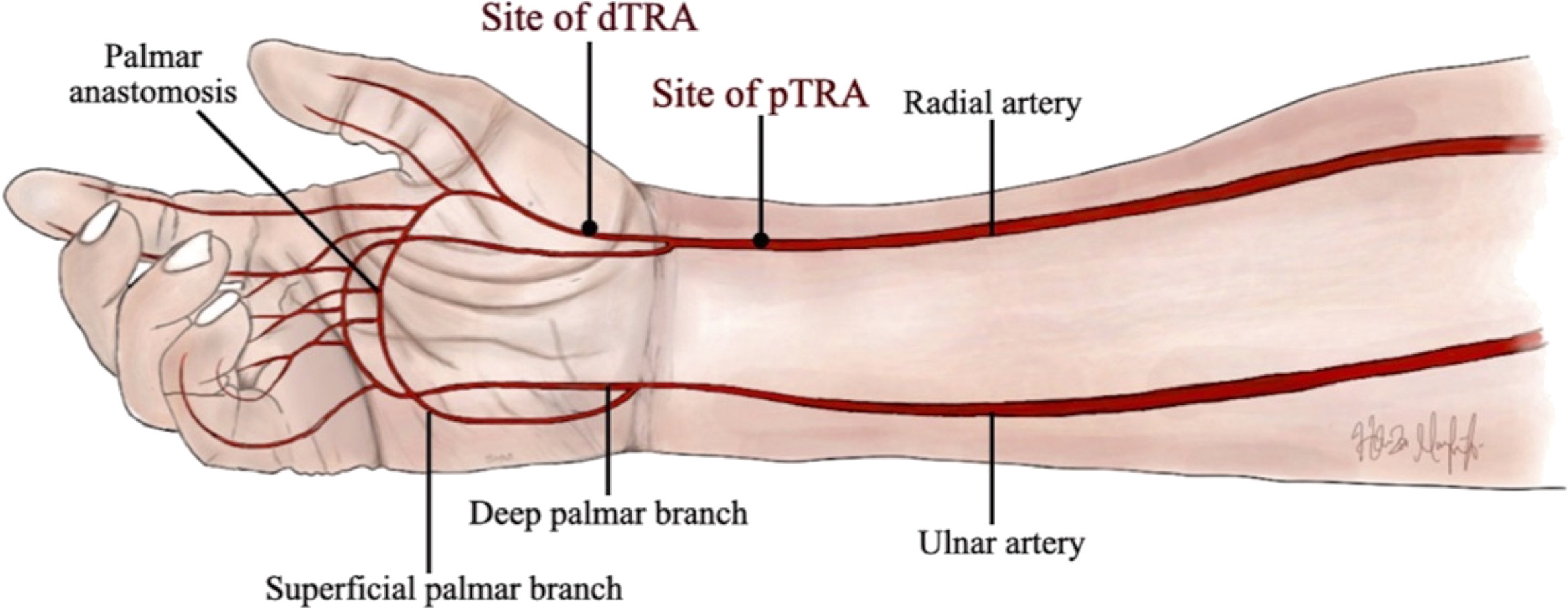
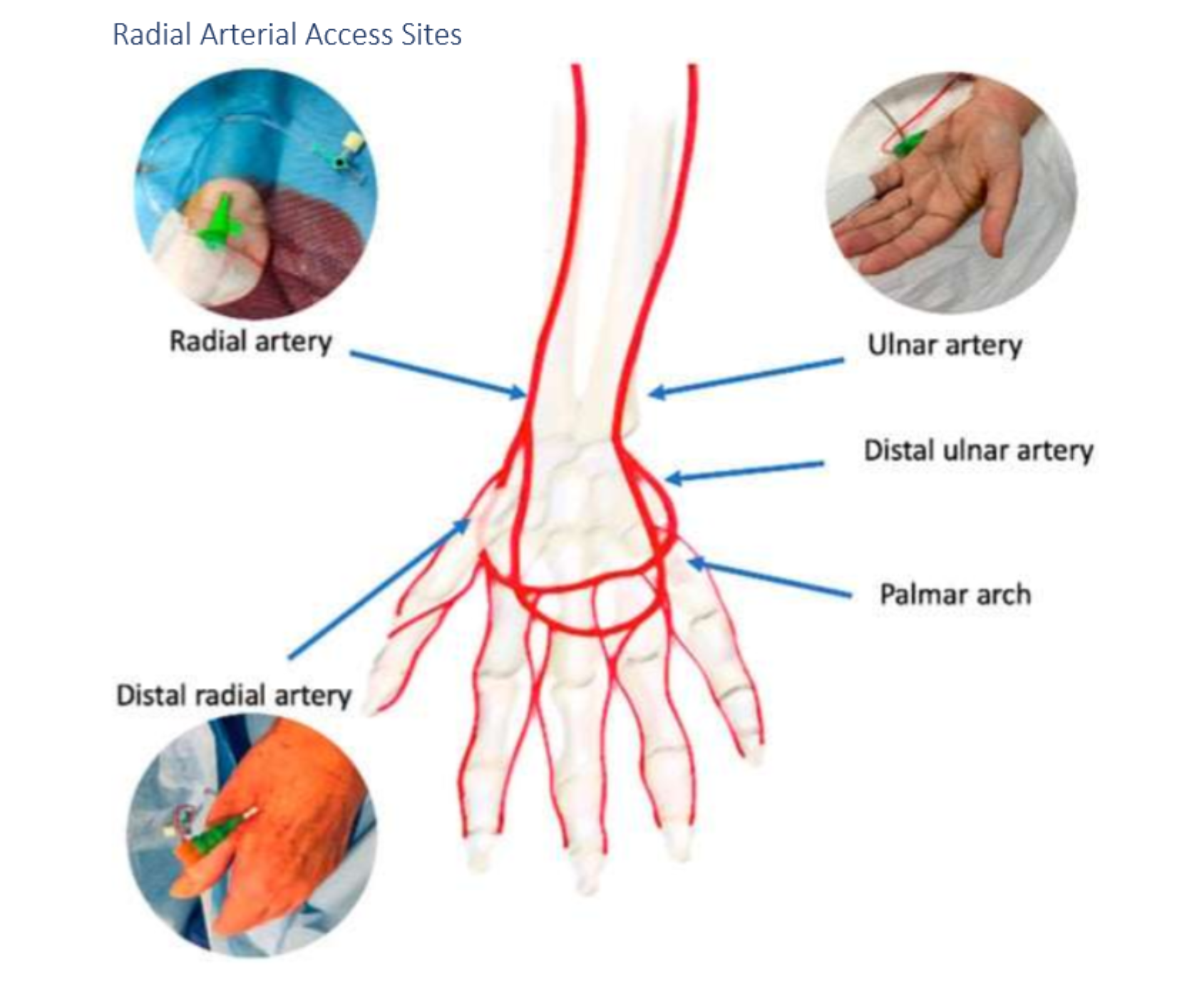
"Distal radial artery access involves access to the radial artery in the region of the anatomic *******
"Distal radial artery access involves access to the radial artery in the region of the anatomic snuffbox.
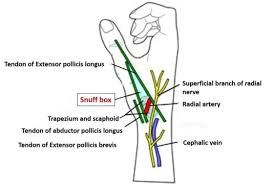
what is dTRA in regards to access
dTRA stands for distal transradial access, a technique used for catheterization that minimizes complications and improves patient comfort.
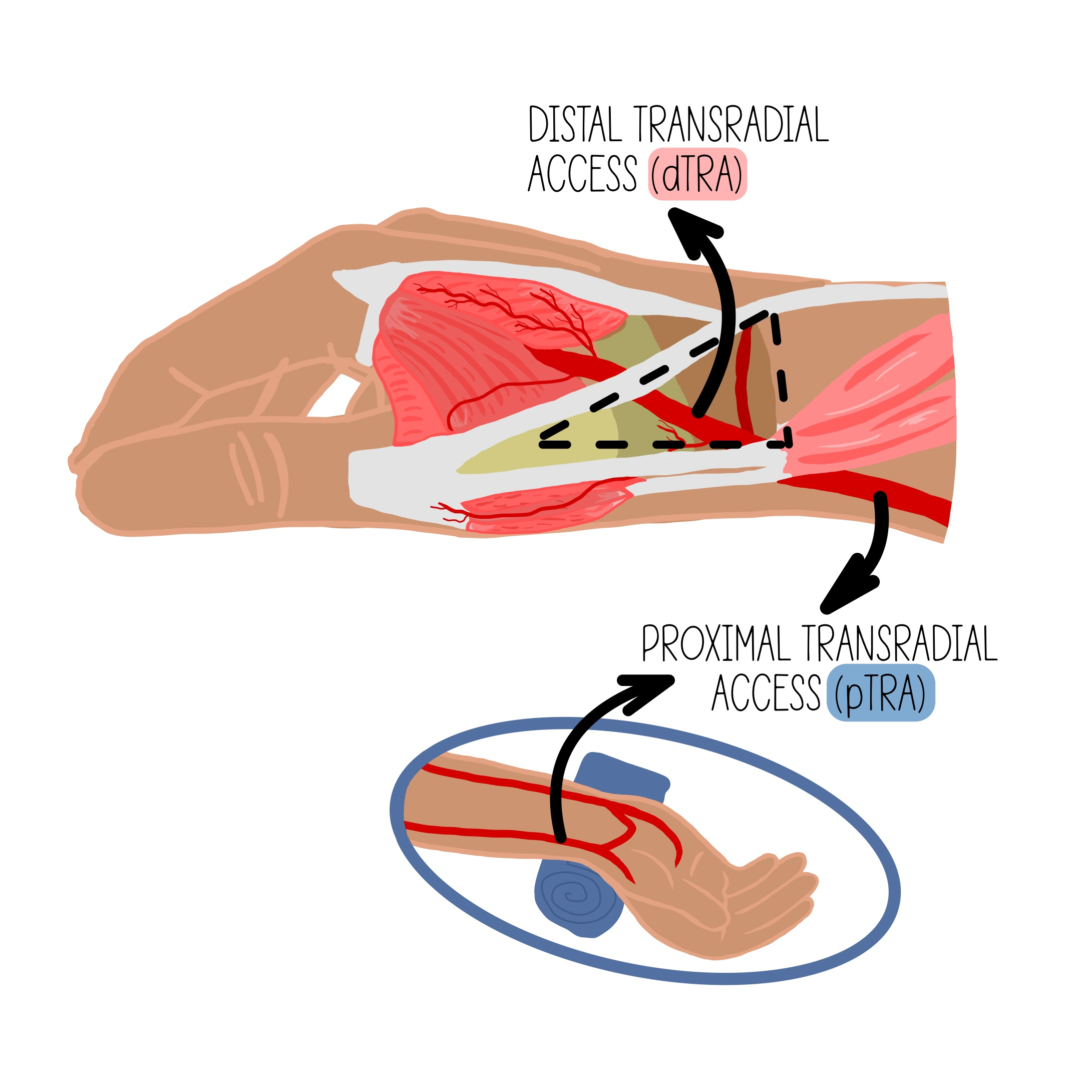
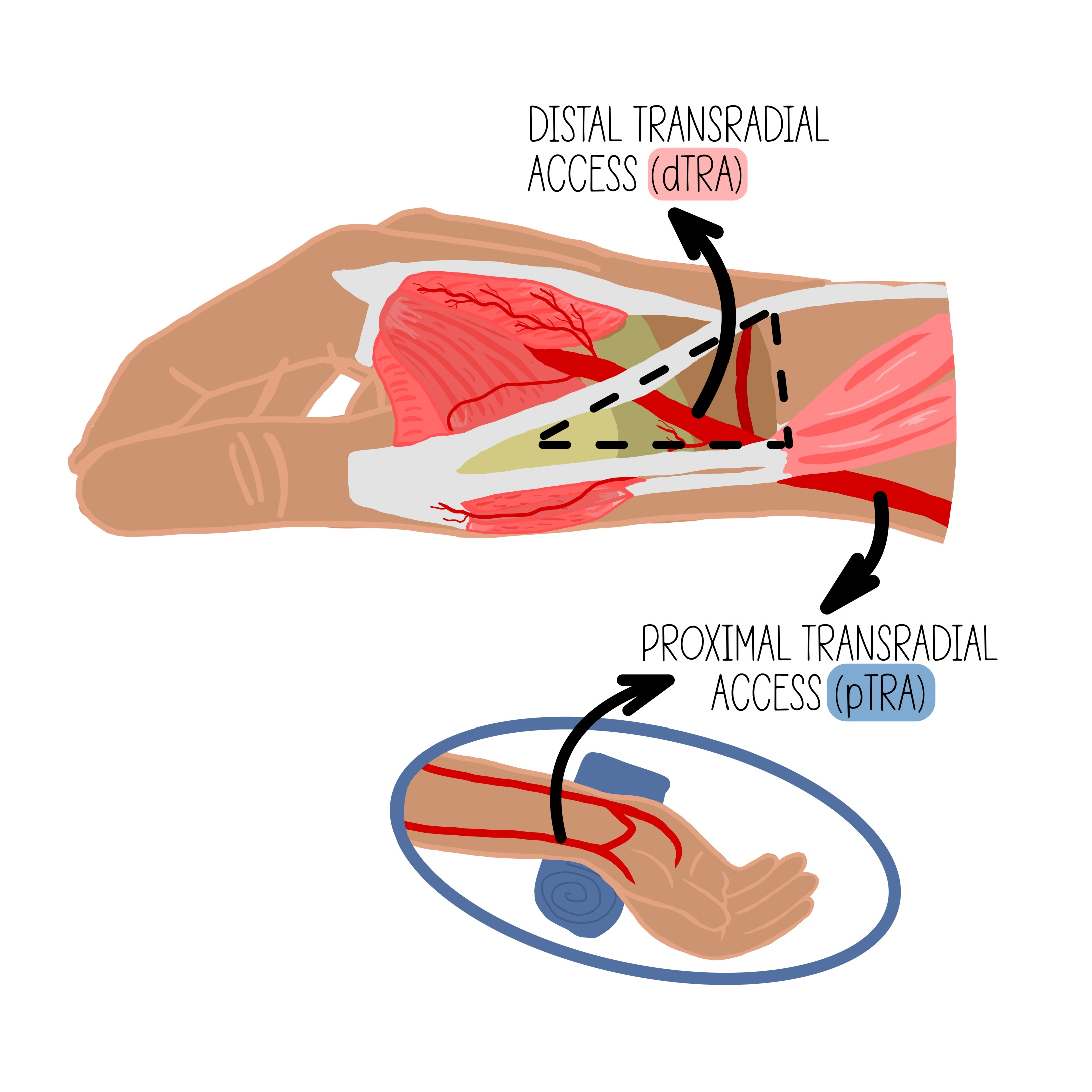
What are some advantages of dTRA over TRA?
Patient and operator comfort since the hand can be neutral or pronated and operator and equipment positioning may be similar to femoral access; access is distal to the superficial palmar branch of the radial artery supplying the superficial palmar arch, theoretically reducing risk of hand ischemia with distal radial artery occlusion.
****** artery access remains a viable option if TRA/dTRA is contraindicated due to vessel size, spasm, or lack of suitable device catheter lengths
Brachial artery access
What is the proper protocol for achieving popliteal vein hemostasis?
post procedure
manual compression 5-10 minutes
What is the appropriate ACT level for safe arterial sheath removal on a heparinized patient?
Approximately 150 seconds
If the patient has been heparinized during the procedure, make sure the coagulation parameters have normalized (partial thromboplastin time PTT close to control value or activated time of approximately 150 seconds) before the catheter is removed and the puncture site is compressed.
When evaluating the CFA angiogram for VCD placement
The puncture site should be between the takeoff of the ****** ****** ******* and the **** ****, in a vessel ** mm in caliber.
The puncture site should be between the takeoff of the inferior epigastric artery and the femoral bifurcation, in a vessel >5 mm in caliber.
What are 5 types of vascular closure devices listed in your textbook
active approximators (mechanical suture mediated or clip devices)
passive approximators (mechanical plug devices)
compression assist devices
hemostatic patches
mechanical compression aids
name 2 examples of active approximators VCD’s (mechincal suture mediated or clip devices)
Proglide - perclose
starclose
prostar XL
name <2 passive approximators (mechanical plug devices)
Mynx
Angio Seal
EXOSEAL
FISH
Vascade
Name 1 example of compression assist devices
CATALYST
Name 2 examples of hemostatic patches
D-stat-DRY
SYVEK EXCEL
CLO-SUR PAD
chitoclot pad
stat seal disc
quickclot
name one mechincal compression aids
femostop
label these 5
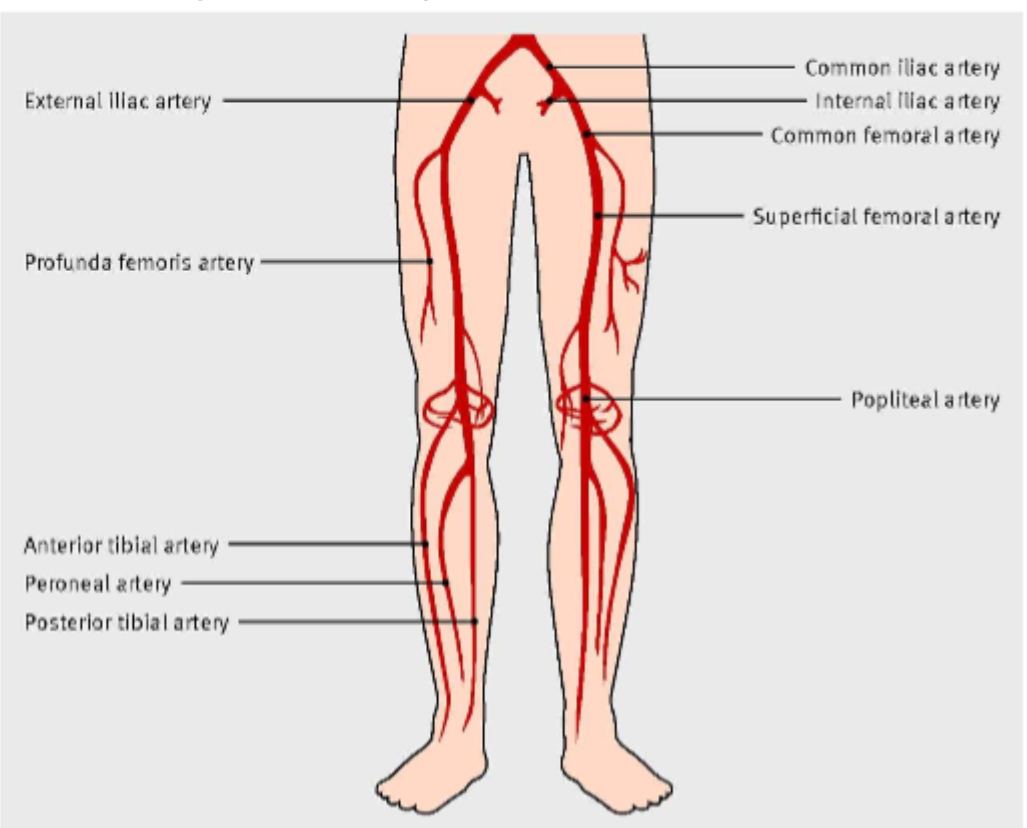
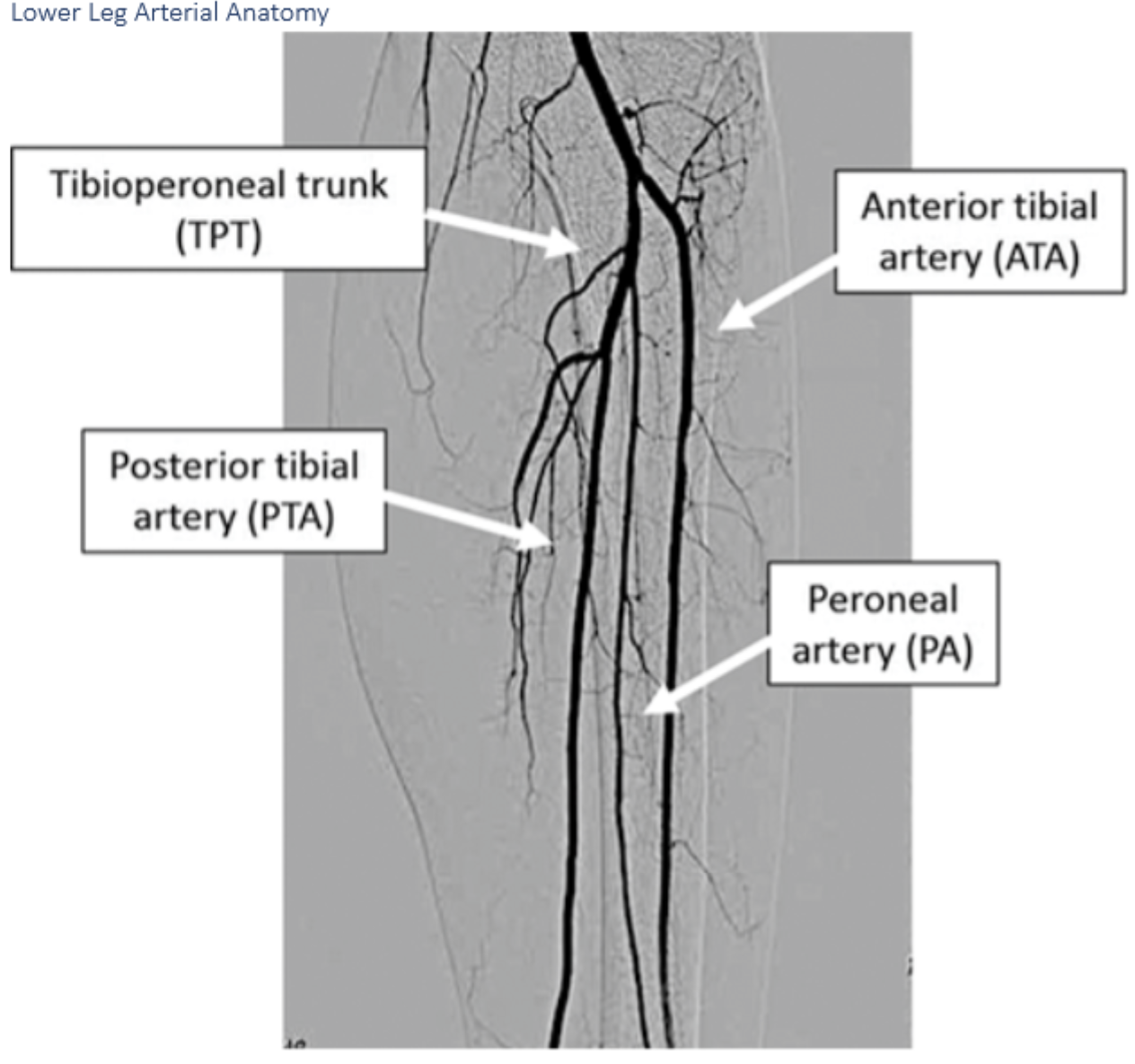
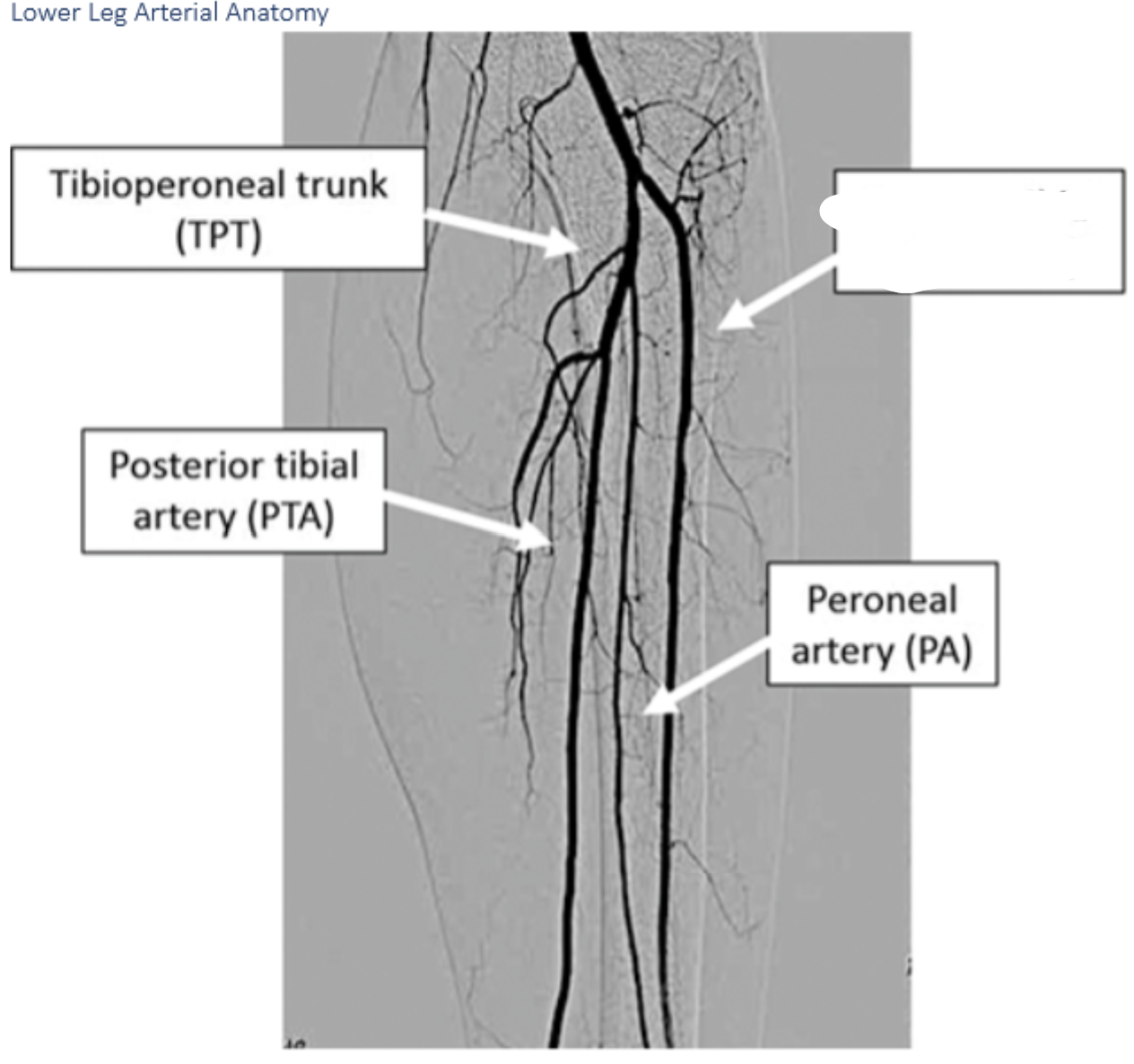
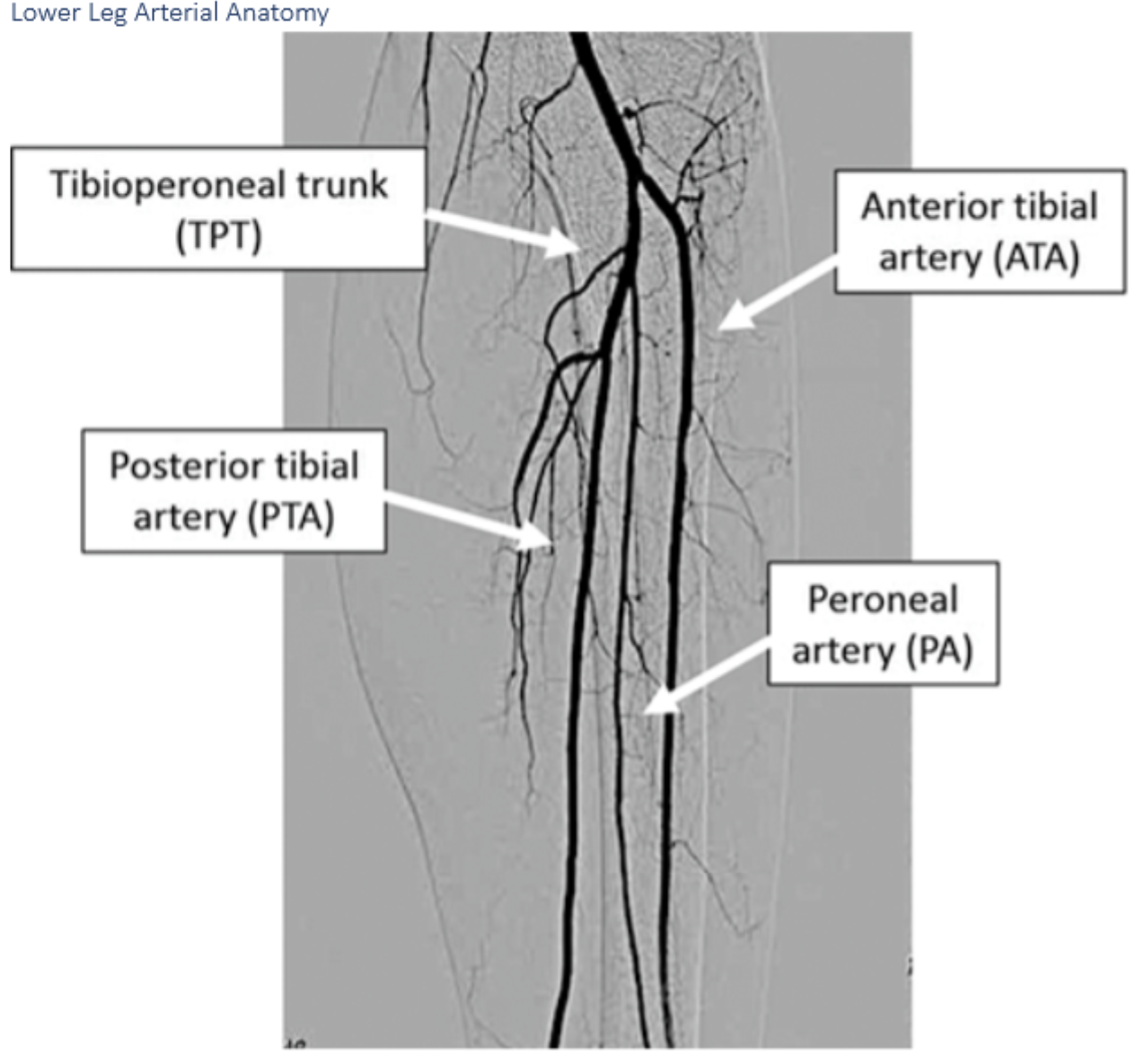
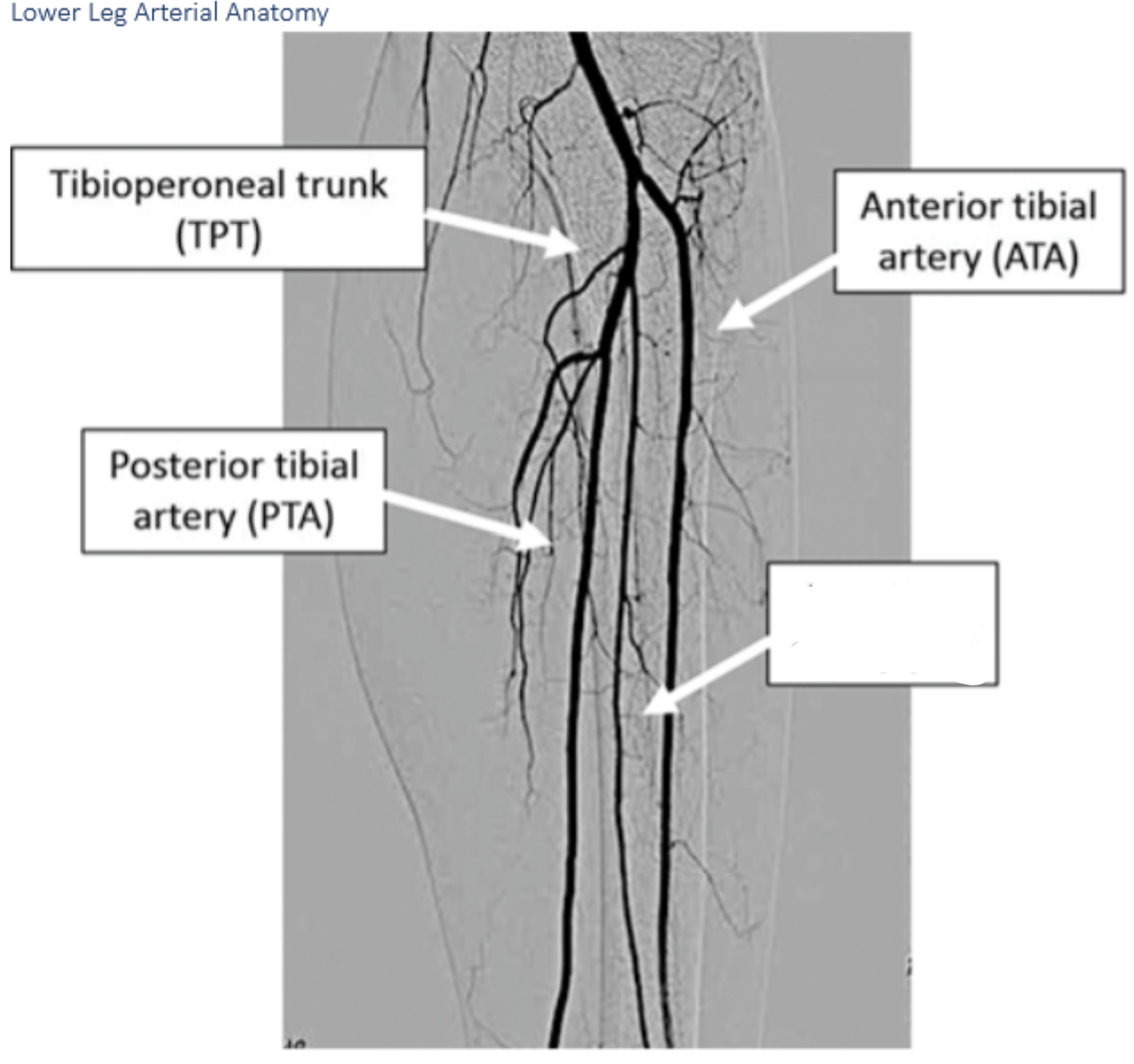
6 p’s of ALI
The 6 P's of Acute Limb Ischemia (ALI) are
pain,
pallor,
pulselessness,
paresthesia,
paralysis, and
poikilothermia. These signs help in diagnosing and assessing the severity of limb ischemia.
term that describes an abnormal sensation of tingling, prickling, burning, or numbness in the skin.
paresthesia,
inability to regulate core body temperature (as by sweating to cool off or by putting on clothes to warm up), found especially in some spinal cord injury patients and in patients under general anesthesia.
poikilothermia
NAVEL acronym
Ultrasound guidance is ideal for patients with poorly **** ****** and patients who are **** or who have bleeding risks
Ultrasound guidance is ideal for patients with poorly palpable pulses and patients who are obese or who have higher bleeding risks
emitting high-frequency sound waves that bounce off moving red blood cells. The changes in frequency of the reflected waves allow the ultrasound machine to determine the speed and direction of blood flow.
Doppler ultrasound
manual compression of both radial and ulnar arteries while the patient clenches their fist until the hand becomes blanched (Fig. 1.9). The hand is opened and compression of the ulnar artery released, observing for the presence of capillary refill in the hand. To see if ulnar arterial flow is sufficient to reperfuse the hand.
Allen test
Tests radial artery perfusion (release radial artery). w no pulse ox
Reverse Allen’s Test
compress both radial and ulnar artery until pulse ox waveform flattens then release ulnar artery
barbeaus test
in barbeaus test if the wave form doesnt return after 2 min it is classified as a
D
These devices physically close the arteriotomy with suture- or nitinol clip-based material that is fixed to the vessel wall to achieve a limited form of surgical closure. With these devices, the arteriotomy is cinched closed. ****** ******* are considered the most secure form of VCD for large arteriotomies. Adjunctive MC is theoretically unnecessary.
These devices physically close the arteriotomy with suture- or nitinol clip-based material that is fixed to the vessel wall to achieve a limited form of surgical closure. With these devices, the arteriotomy is cinched closed. Active approximators are considered the most secure form of VCD for large arteriotomies. Adjunctive MC is theoretically unnecessary.
These devices deploy a sealant, gel, or plug onto the arteriotomy site that creates a mechanical barrier to achieve hemostasis. With some of these devices, hemostasis is augmented through use of a collagen-based plug to promote clot formation. Adjunctive MC is often held for 1 to 3 minutes.
passive approximators (mechanical plug device)
This heterogeneous group of devices mechanically promote hemostasis, but do not leave any material behind at the end of the procedure. With these devices, there is theoretical lower risk of infection or embolization/arterial occlusion given lack of implanted material. Adjunctive MC must be held, but for a shorter duration than expected with MC alone.
compression devices
These patches are placed externally over the dermatotomy at the end of the procedure. With these products, substances interact with blood products to augment hemostasis. Adjunctive MC must be held, but for a shorter duration than expected with MC alone.
Hemostatic patches
These entirely external devices allow MC to be performed by the device rather than an operator. Routine duration of MC is required with these devices.
Mechanical compression aid
what 2 thing are needed for VCD vascular assessment
5 -10 mL contrast hand injection thru sheath
oblique prokection often necessary to seperate sheath and CFA
typically RAO
contrast
RAO
vessel damage is most likely to occur with the use of what kind of VCD
active approximator devices (mechanical suture mediated or clip devices)
name the 6 major complications of VCD
limb ischemia
device embolization
artery occlusion
arterial laceration
retroperitoneal hematoma
access site infection
name 4 minor complications
hematoma
pseudoaneurysm
av fistula
nerve injury
angioseal can not be used to plug a high stick because
The Angioseal collagen plug may get entrapped in the layers of the abdominal muscles and the plug may move once the patient becomes ambulatory.
collagen plug (inside vessel) may get stuck in abs and plug (outside) might move when pt moves
Dr. Birlakis stated in video 1 that inserting the vascular sheath into the lateral circumflex iliac artery instead of the external iliac artery could potentially lead to which complication?
dissection or perforation
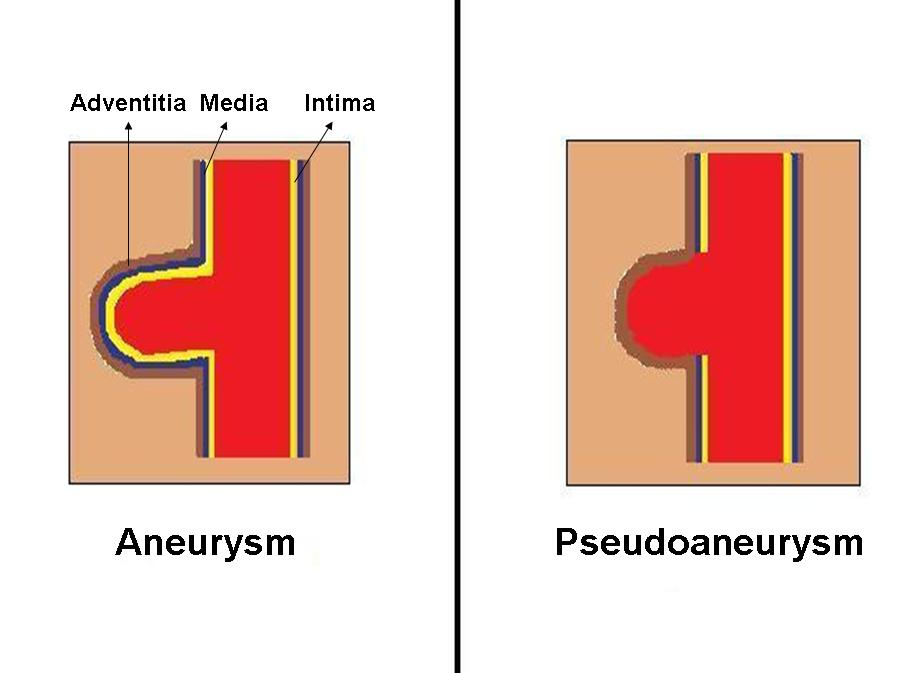
What are the measures mentioned to confirm or exclude the presence of a retroperitoneal hematoma in the cath lab?
2 things
fluro bladder to see displacement of the bladder
access site angiogram to locate site of bleeding
What is the dented bladder sign
bladder displacement to left caused by retroperitoneal hematoma
How do you prevent AV fistulas?
2x
Optimal access technique & removal of the arterial 1st then the venous sheath.
How do you treat an AV fistula?
for most cases treatment is usually not needed for severe cases where there is a lot of shun
No treatment, covered stent of surgery.
What are 6 causes of a pseudoaneurysm?
1. low sticks
2. sub optimal compression
3. challenging access
4. access of both artery and vein
5. intensive coagulation
6. vascular closure device needed
When treating a pseudoaneurysm by thrombin injection, where is the thrombin injected? (video 3)
thrombin is injected in the cavity of the pseudoaneurysm that is found in the cavity by ultrasound
Definition: A localized collection of blood outside the vessel but within the adventitia due to inadequate hemostasis.
Cause: Poor manual compression, patient movement, high anticoagulation, or improper closure device deployment.
Signs/Symptoms: Swelling, tenderness, and discoloration at the puncture site.
Management: Compression, monitoring, and, in severe cases, surgical evacuation.
Hematoma
Cause: Low puncture leading to simultaneous artery and vein injury.
Signs/Symptoms: Continuous bruit, palpable thrill, or limb edema if large.
Diagnosis: Duplex ultrasound or angiography.
Management:
Small fistulasmay resolve spontaneously; larger ones may require surgical or endovascular repair.
Arteriovenous fistula
Definition: A severe, life-threatening hemorrhage occurring when arterial puncture is too high (above the inguinal ligament), allowing blood to track into the retroperitoneal space.
Cause: High arterial puncture, improper closure device deployment, excessive anticoagulation.
Signs/Symptoms: Hypotension, back/flank pain, and possible signs of hypovolemic shock.
Diagnosis: CT scan of the abdomen/pelvis with contrast.
Management: Fluid resuscitation, blood transfusion if needed, and surgical or interventional repair.
Retroperitoneal hemorrhage
Patient with FFR .8
IFR.85
coronary angiography 70% stenosis in the mid RCA
occasional chest pain
Would we treat this patient?
FFR borderline threshold .8
iFR low iFR threshold is .89
70% borderline
occasional chest pain with moderate excretion
theyre not a diabetic so we could treat them with meds
bp meds