Risk Assessment & Biosecurity
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
what are hazards? give some examples
any agent that has the potential to cause adverse health effects in animals or humans
e.g. pathogens (viruses, bacteria, parasites), toxins or poor envi conditions
what are risks
the likelihood of the occurrence of an event
and the likely magnitude of the consequences on the system of concern following exposure to a hazard
(risk = likelihood of occurence + consequence)
For this example, identify the hazard & the risk:
A pig farm is located near a forested area with a high population of wild boars
This farm has inadequate biosecurity measures, such as: no fencing to prevent wild boar access
hazard: African Swine Fever virus (ASF) carried by infeced wild boars
risk:
likelihood: risk is very high. b/c wild boars have easy access to the farm & have the potential for contamination
consequence: potentially outbreak, high pig mortality, mandatory culling
what is risk assessment
= the systematic process of assessing or evaluating the magnitude of the risk of an unwanted outcome resulting from a hazard
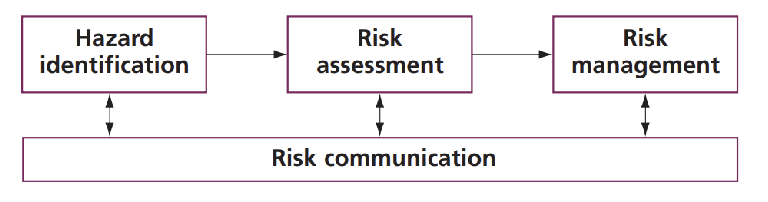
what are the 4 main components of the risk analysis process (& how are they interconnected?)
hazard identifcation
risk assessment
risk management
risk communication
(identifying what is causing the issue, assess the magnitiude of the risk, manage the risk accordingly, communcate what went well/badly)
why is risk assessment in animal health important? (4 benefits)
prevent disease outbreaks: harzard identification & evaluating risks. providing early warnings to mitigate risks
optimizing resource allocation: prioritizing risks based on severity
guide decision-making: evidence-based insights for designing prevention & control strategies
protects public health: risk of zoonotic disease spreading to human
what are the 6 steps of risk assessement
hazard identificaiton
entry assessment
exposure assessment
consequence assessment
risk management
risk communication
Using the African Swine Fever example, explain how the 6 steps of risk assessment can be applied
identifying ASF virus as a hazard in imported pigs
assessing thr risk of introducing ASF virus via imported animals, feed or equipment
determining how susceptible animals may come in to contact with the hazard (e.g feeding pigs with contaminated swill or direct contact with sick pigs)
evaluating potential impact of ASF on animal health, farm producitvity & trade.
desgining measures to control the identified risks (e.g. quarantine protocols, vaccination programs, enhanced biosecurity)
sharing risk asssement findings & recommendations with stakeholders
what are the 2 types of risk assessment methods? which type is more commonly used?
qualitative
more commonly used, b/c use less time. so good when immediate action is needed
quantitative
describing risks in numerical values
define what is biosecurity
set of measures designed to
reduce risk of pathogen
limit their spread within the farm
what are the 3 levels at which biosecurity can be applied?
farm
regional
national
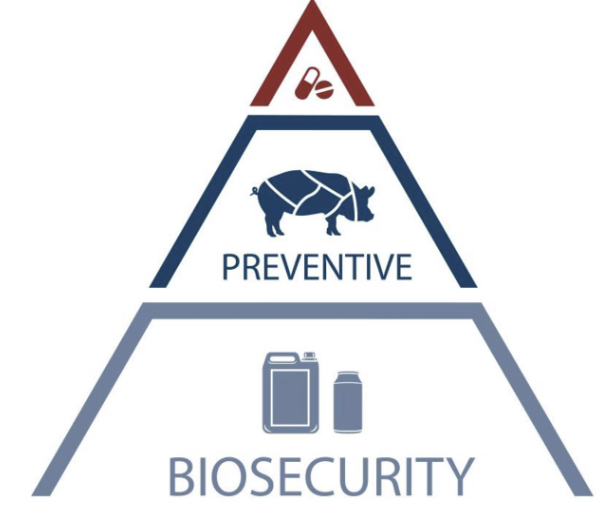
what is at the base of all disease control program
biosecurity
(biosecurity —> preventative —> medicine)
why is biosecurity important? (how does it affect…)
disease on farms
production efficiency
foreign disease
market competitiveness
public health
antimicrobial use
bases of ANY disease control problem (without biosecurity, none of the disease control measures will hold)
reduce disease or infection pressure on farm
improve production efficiency (e.g. faster growth)
prevent introduction of exotic/foreign diseases (e.g. emerging & re-emerging diseases)
ensure market access & competitiveness (consumers prefer animal products w/o use of antibiotics)
protecting public health (zoonotic disease)
supporting responsible antimicrobial use (AMR & consumer preference)
what are the 2 things that we need to understand to implement biosecurity
exposure: how susceptible animals are exposed
transimission: how disease/pathogen are transmitted from one agent to another (i.e. how the disease is spread)
disease transmission methods (5 ways)
direct contact (animal to animal)
aerosol (inhalation of droplets)
ingestion (oral route)
vectors (flies, ticks)
fomites (vehicles, equipment, people)
what are the 2 major components of biosecurity
external biosecurity (bio-exclusion)
internal biosecurity (bio-containment)
describe how external biosecurity measures work
prevent intro of pathogen from outside the farm
e.g. physical barriers or rules banning the introduction of animals, people or vehicles
gives some examples on how to implement external biosecurity measures for the following activity
purchase of breeding animals & semen
limiting the frequency of animal introduction
only purchase from disease free sources (not buying from unknown source)
implement Good Quarantine Measures
gives some examples on how to implement external biosecurity measures for the following activity
transport of animals, removal of manure & deadstock
cleaning the vehicles that were used to transport the animals (e.g. disinfection bath to clean the wheels)
storage of carcasses to ensure that dead animals are removed & stored in hygienic manner

gives some examples on how to implement external biosecurity measures for the following activity
visitors & farmworker movement control
limiting number of people with access to farm
wear only farm specific clothes & boots (protects both the human & the animal)

gives some examples on how to implement external biosecurity measures for the following activity
feed & water supply
purchasing feed from a trusted source
regularly (at least once a yr) test the water quality
regular cleaning of the water pipes
gives some examples on how to implement external biosecurity measures for the following activity
vermin & bird control
perimeter fence around the buildings (preventing potential disease vector animals from entering the farm facility)
place grids/fences over all air inlets to prevent contact btwn wild birds & pigs (for birds)
implement effective pest control program (include rodents, birds & insects)
describe how internal biosecurity measures work
what is the goal?
aims to limit the spread of pathogens within the farm once they are present (isolation/quarantine to stop the spread of the disease)
many measures are associated with herd management, cleaning & disinfection
internal measures are often associated management methods (e.g. separating the animals by age)
gives some examples on how to implement internal biosecurity measures for the following activity
disease management
proper diagnostic, vaccination
isolation of the sick animals, following procedures in one direction (prevent cross contamination)
record keeping
properly store medicines & sterile use of needles
clear separation of animals of different age groups (start from younger to older)
why start working from young animal then to old animals
the young are naive to most of the disease (have had less exposure)
also their immune system is less well developed compared to the older animals
gives some examples on how to implement internal biosecurity measures for the following activity
cleaning & disinfection
develop & implement a production facility cleaning & disinfection program
frequently clean & disinfect all stables (inc. isolation areas) & equipment used (e.g. cleaning the pig herding board)
select disinfectants based on target organisms & needs
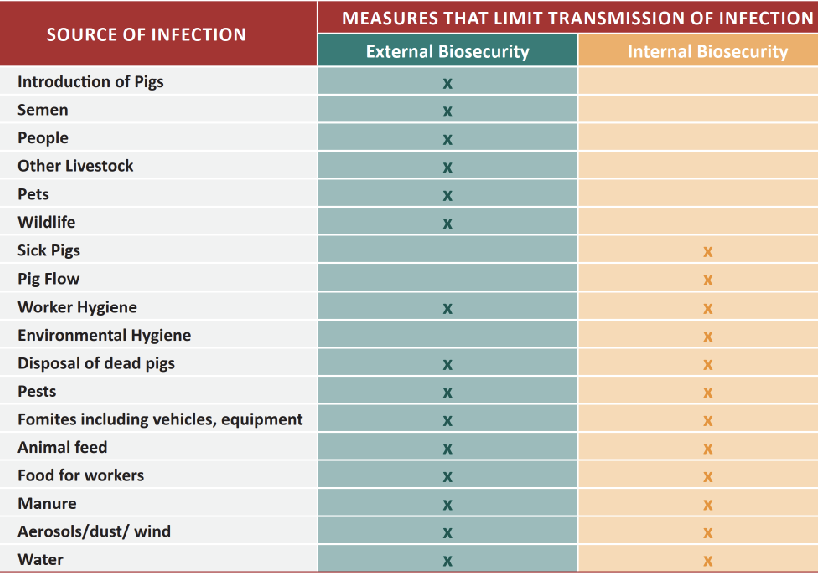
Who should be involved in the biosecurity practices?
everyone is responsible
but some important stakeholders include
agriculture sector
NGOs
academic sector
gov’t
public opinion
industry
producers of food & agricultural commodities
what does pig “free” time refer to?
pig farms often requiring a minimum 24-hour "pig freedom" period away from other pigs before you can visit a new farm