Bio260 Unit 3 Resource 2. Water & Salt Physiology in Animals (new ver)
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
How do plants conserve water?
____ adaptations
_____ leaves (____ SA)
_____ leaves (____ stomata)
____ leaves (____ exposure of stomata to air)
____ waxy cuticle
controlling _____ opening and closing
stomata in pits: stomata surr by ____ trap _____ vapor and ____ transpiration
CAM and C4 physiology: open _____ at _____ to reduce water loss
____ growth
grow roots _____ to access more water
leaf
reduced, less
smaller, fewer
rolled, less
thick
stomata
hairs, water, reduce
stomata, night
root
deep
How do plants get rid of waste?
store the substance in some plant tissue that is ____ (___, _____, ______)
diffusion of ____ and _____ out of stomata & by _____ (root pressure)
_____ _____ (waste) also serves as important mech to ______
converts them to _____, _____ them in vacuoles of ____, _____ and _____ which will be shed later
shed, leaves, fruit, bark
gas, water, guttation
mineral salts, osmoregulation
crystals, stores, leaves, fruit, bark
What type of wastes do plants produce?
photosynthetic wastes: ______ and _____, prod of photosynthesis
respiratory wastes: _____ and _____, prod of respiration
water is lost thru ________ or used to maintain _____ in cell
organic acids formed as byprod of ______
abun in leaves & fruits, ____ acid in lemons & limes, _____ acid in tamarind
_____ and ____ (nonvolatile) stored in the old ____ which is excreted via ____, _____ or _____ that is shed
gum made by decomp of ____ in cell wall
oxygen, water
CO2, water
transpiration, turgor
respiration
citric, tartaric
gim, resin, xylem, bark, leaves, stems
cellulose
Additional excretory products - Essential oils
____ oils are volatile oils present in fruits and flowers
made by _______ ______
essential
glandular trichomes
Additional excretory products - Tannin
secondary _______ that serves as a ______ against herbivores
stored in ____/______ ____
metabolite, protection
vac/surface wax
Additional excretory products - Latex
white _____ ______ of proteins
stored in _____ cells
milky emulsion
specialized
Additional excretory products - alkaloids
are ______ waste products
_____, _____, ______, ______
stored in central ______ or in ____ cells
nitrogenous
nicotine, caffeine, morphine, cocaine
vacuole, special
Freshwater Animals vs Other Animals in Water Conservation
freshwater
adaptations that ____ water _____ and conserves ____
terrestrial & marine
face _______ env with the potential to quickly _______ the body water
(nothing)
reduce, uptake, solutes
(nothing)
dessicate, deplete
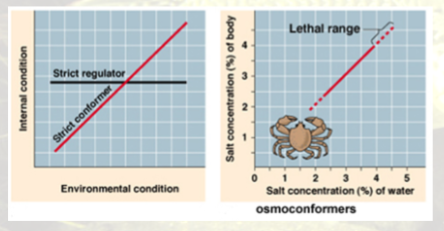
Marine mammals in water uptake
have strongly ______ urine
blood is ______ to sea water
_____ _____ drink sea water
breath air so _____ expose resp surface to salt water
hypertonic
hypertonic
do NOT
doesn’t
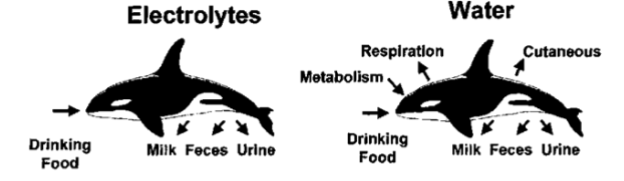
How do marine animals gain and lose water and salt?
gain water thru _____ and _____ food, lose thru ______, ____, _____, and ____
gain salts thru _____ of food and lose salts thru _____ urine, ___, and ____
metabolism, ingesting, respiration, milk, feces, urine
ingestion, hypertonic, milk, feces
Osmoreg of mammals in freshwater
blood is _______ to freshwater
problems: passively gain water by _____ & lose ion/electrolytes by _____
solutions: _____ drink water, make lots of _____, & add _____ by diet and ____ transport
hypertonic
osmosis, diffusion
don’t, urine, electrolytes, active
Osmoreg of mammals on land
problems: lose water by ___ & ____, lose ion/elelctrolytes by ____
solutions: drink water, reg _____ production, add ______ by diet
land animals manage water budgets by drinking and eating ____ foods by using ______ water and managing water ____
evap, urine, urine
urine, electrolytes
moist, metabolic, loss
Some Characteristics of Desert Animals
____ body size → better for ____ _____/_______
all species of large herbivores req considerable amounts of _____ water
camels ______ water well
_____ ______ keep their brains _____ even when the rest of the body rises in temp
____, _____ coat
can produce ___ feces and very ________ _____
______ heat loss/gain behaviorally
____ tolerance for dehydration
large, water loss/retention
external
conserve
counter current, cool
thick, glossy
dry, concentrated urine
minimize
high
Seed eating mammals in desert
live in deserts without needing to _____
depend on _____ selection of ______
supplement diets w/ _____ rich diet (insects)
counter current exchange in _____ passages
long loops of ____ that allow a very ______ ____ to ____ concentration
even dried seeds contain some _____
drink
behavior, microhabitats
water
nasal
Henle, hypertonic urine, blood
water
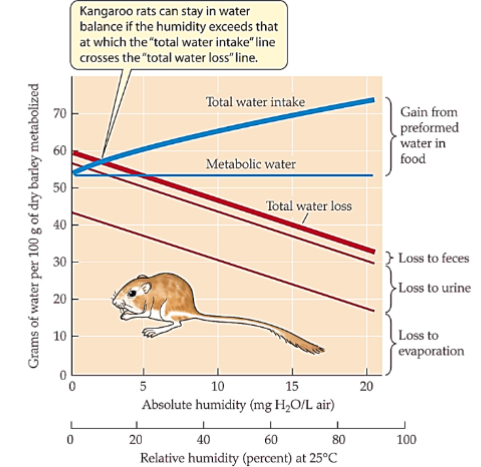
Sources of water in terrestrial animals - metabolic water
made by processing of ____ & ______
generally _____ + ____ + ___ + chem energy + heat
(do we need to know averages on slide 44)
lipid, carbohydrates
nutrients, o2, co2, h2o
Metabolic water production
______ produces water
______ uses water and creates an obligatory _____ ____
more important in animals that _____ _____ effectively
____ food → ____ amount of metabolic water
catabolism
anabolism, water loss
conserve water
any, same
Different things that cause water loss
catabolism
urine
respiration
feces
evaporation
other
breat feeding
diet
nitrogenous waste
Obligatory water loss in urine
mandated by _____/_____ of food
_____ _____usually has highest
Waste excretion → water excretion
can be reduced by making _______ ______/by making poorly ____ ______ end prod
only 3 groups can make urine _______ to their blood
_____
_____
_____
ingestion/catabolism
protein catabolism
(nothing)
concentrated urine, soluble nitrogenous
hyperosmotic
insects
birds
mammals
Obligatory respiratory water loss
amount of water that is ___ in order to obtain __ _______
______ across the respiratory surface
lost, O2 catabolism
evaporation
Land and water problems
terrestrial animals have resp surfaces directly exposed to ___
most have evolved invaginated resp surfaces w/ integument _____ to ____ and ______
air
impermeable, O2, CO2
How is water conserved in the respiratory system?
by having an _____ respiratory surface
______ of exhaled air using ______ passages
by ______ ______ exchange mechanisms
external
cooling, nasal
counter current
What does respiratory evaporative water loss depend on?
its _____ rate (__ consumption)
amount of water ____ per unit of _____ consumed
may be _____ by ________ ______ in the nasal exhalant air
rate of water loss thru ______ = to the rate of _____ consumption times the water ___ per unit of oxygen _____
metabolic, O2
lost, oxygen
reduced, counter current
respiration, oxygen, loss, consumed
Obligatory fecal water loss
water loss in feces due to catabolism of ingested food
Water loss across the integument (skin)
terrestrial animals show varying degrees of skin ______ to water ___
w/i a group, the ____ amount of water loss is an _____ function to body size
low rates of evap water → have advantages of law integumentary ______ to water, tightly controlled access of air to ________ _____, ____ metabolic rates
_____ integumentary permeability to water is a key to _____ evap water loss on land
permeability, loss
total, allometric
permeability, breathing organs, low
low, reducing
Integument water loss in mammals, birds, and nonavian reptiles
layers of complexes of ____ and _____ in the ______ layer of the _____
often assoc w/ ___ ______ to further reduce ____ loss
some species have _____ _____ for ______
lipids, keratin, outermost, epidermis
oil glands, water
sweat glands, thermoreg
Other avenues of water loss
_____
_____ rich foods can be ______ for terrestrial animals
even air-dried foods can contain ____
______ waste: processing req water for ____
_____ prod in lactating females
diet
protein, dehydrating
water
nitrogenous, lysis
milk
Body fluids in animals
2 principle types of body fluids and 4 body fluid compartments
intracell: inside
extracell: outside
______ fluid: ___ cells
______ _____
_____
(nothing)
interstitial, b/w
blood plasma
lymph
Blood plasma in animals
usually higher [______] than ______ fluid
in humans, the BP is abt 3.3 kPa or 1.5mOsm, ___ than the _____ that of the interstitial fluid
protein, interstitial
higher, osmotic
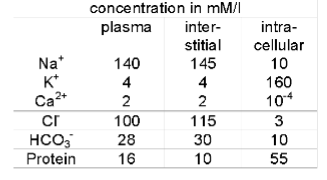
Interstitial fluid
can be affected by 2 types of capillaries in the tissues
______ capillaries
______ capillaries
______ capillaries
(nothing)
continuous
fenestrated
sinusoidal
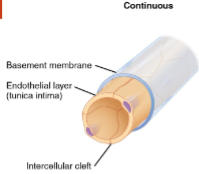
Continuous capillaries
________ lining
only allow _____ molec, such as ____ and ions to diffuse thru ____ ___
uninterrupted
smaller, water, tight junctions
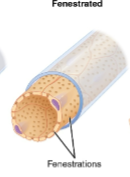
Fenestrated capillaries
have pores in the _____ cells
some are _____ by a diaphragm that allow _____ molec and _____ amount of _____ to diffuse
in the _____ ______, there are cells w/ no diaphragms (_____) food processes that have slit pores
both types of blood vessels have cont _____ ______ and are primarily located in the ______ glands, ______, ______, and _____ of kidney
endothelial
spanned, small, limited, proteins
renal glomerulus, podocytes
basal lamina, endocrine, intestines, pancreas, glomeruli, kidney
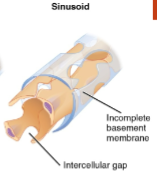
Sinusoidal capillaries
special type of _______ capillaries that have ______ openings in ______
allow ___ and _____ BC and various ______ _____ to pass aided by discon basal lamina
located in ____ _____, _____ ______, and ______ _____, ____and _____
fenestrated, larger, endothelium
red, white, serum proteins
bone marrow, lymph nodes, adrenal gland, liver, spleen
What are the 3 types of regulation of the composition of the blood plasma are possible?
osmotic regulation
ionic regulation
volume regulation
What is osmoregulation?
active regulation of osomtic pressure
What is ionic regulation?
maintenance of a relatively constant [inorganic ion] in the blood plasma
each ion has specific physiological controls
![<ul><li><p>maintenance of a relatively constant [inorganic ion] in the blood plasma</p></li><li><p>each ion has specific physiological controls</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/16512804-e099-4e8f-b18c-243f4ff4ace2.png)
What is volume regulation?
regulation of the _____ amount of _____ in body fluids
influx of water into an animals body has 3 simultaneous effects
it will _____ the _____ pressure of the _____ _____
it will ____ ions in the ______ ______
it will _____ the volume of the _____ ____
many cells alter their content of _____ molecules to achieve cell-volume regulation
total, water
lower, osmotic, blood plasma
dilute, blood plasma
increase, blood plasma
organic
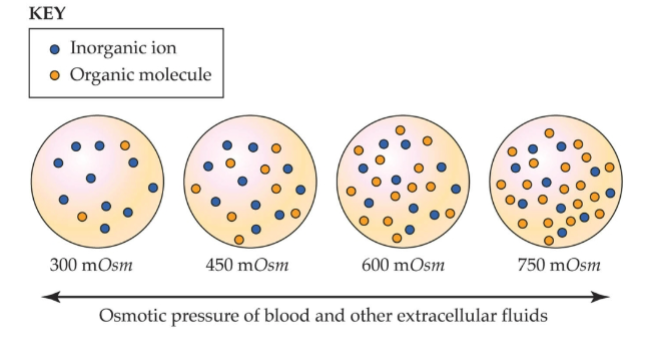
What does volume regulation apply to?
_______ & ______ fluids
volume conformity
completely _____ changes in ____-____ volume
driven by _____
interstitial, intracellular
passive, body-fluid
osmosis
What are the fundamental principles of cell-volume regulation?
cell is moved into a more _____ solution → _____ w/ water → cell _____ its contents to restore origin volume
cell is moved into a more _____ solution → _____ water and ______→ cell must _____ its content to restore the origin volume
dilute, swells, reduces
concentrated, loses, shrinks, increase
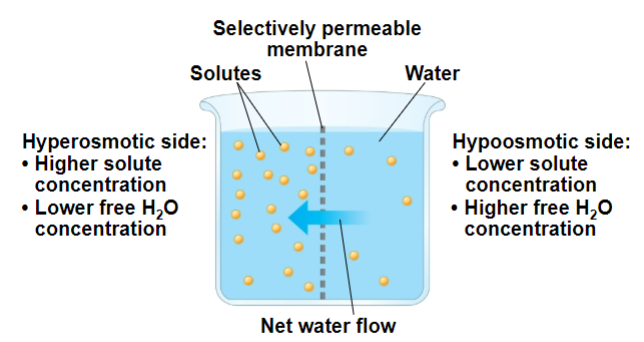
What is osmolarity?
______ _____ of a solution
determines mvmt of water across a _____ _____ mem
if 2 solutions are ___-_____ → mvmt of water is _____ in _____ directions
if 2 solutions differ in osmolarity → net flow of water is from _____ to ________ solution
solute concentration
selectively permeable
iso-osmotic, equal, both
hypo-osmotic, hyper-osmotic
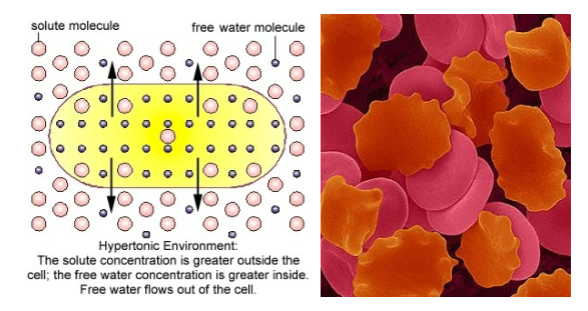
What is hypertonic solution?
____ concentration of solution is _____than cell
_____ dissolved particles _____ than _____ of cell
water ______ ____ of ___ into the ______
cell ______
solute, higher
more, outside, inside
moves out, cell, solution
shrinks
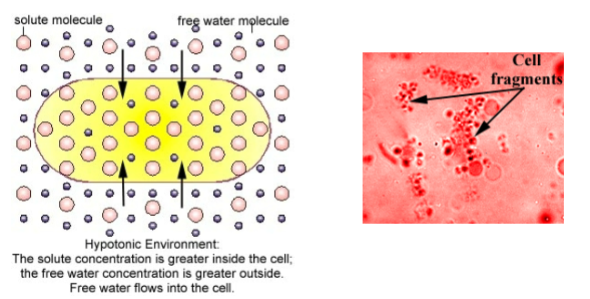
What is hypotonic solution?
_____ concentration of solution _____ than cell
hypo = _____ dissolved particles
water _____ _____ ____ from _____
cell _____ and may _____
solute, lower
less
moves into cell, solution
expands, burst