Oncology 2 final all
1/846
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
847 Terms
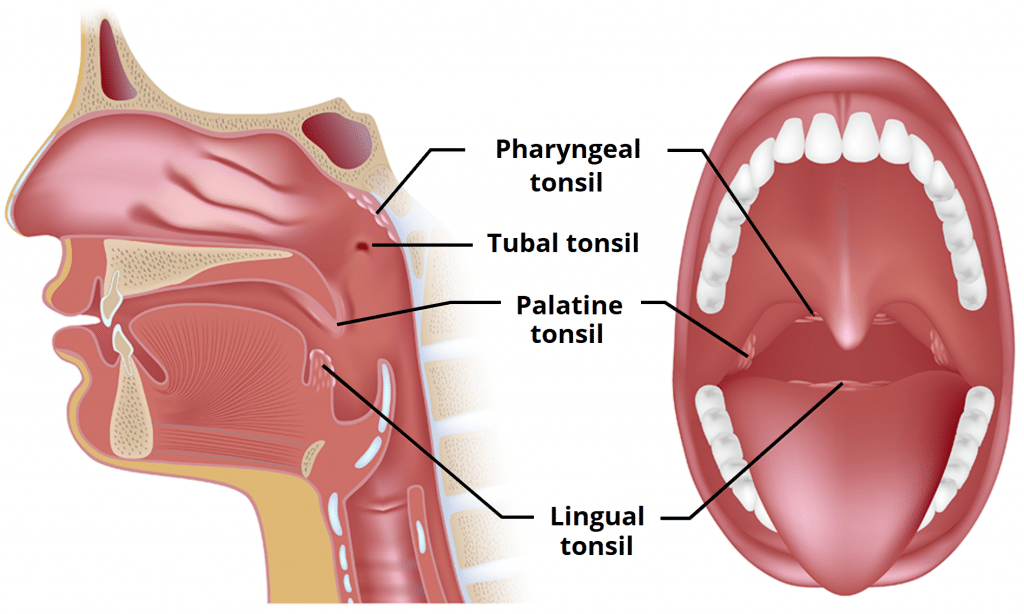
These lymphatic organs are also known as the adenoids:
pharyngeal tonsils
The cisterna chyli is located around what spinal level
L1
(fyi on notes L2)`
This person is primarily responsible for the first controlled clinical trials using radiation therapy to treat Hodgkin's disease in 1962
Kaplan
The median age for Hodgkin’s disease incidence is approximately age:
26
The lecture describes this virus as being associated with Hodgkin's disease:
EBV
List all Hodgkin’s disease cell types
Lymphocyte predominant aka Lymphocyte Rich HD- best prognosis
Nodular Sclerosing (NSHD)- most common
Lymphocyte Depleted- least common + worst prognosis
Mixed cellularity - 2nd most common
(new mexico PD)
This Hodgkin's disease cell type has the least favorable prognosis and is the least common
Lymphocyte depleted
The two primary differences between them from a (non-Hodgkin's lymphoma) and Hodgkin's disease are:
HD has:
Presence of Reed-Sternberg cell
Contiguous Spread
FYI: What type of Staging System is used for Hodgkin’s Disease
Ann Arbor Staging System- 1971
FYI: Ann Arbor Staging System
mesenteric nodes/ splenic nodes down = below the diaphragm
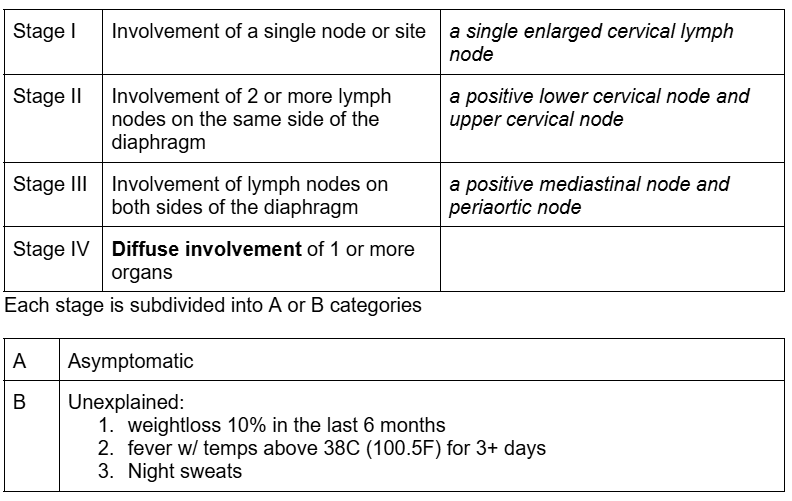
FYI: In the Ann Arbor staging system, a stage 4 lymphoma involves diffuse involvement of 1 or more organs. List those organs
H+ Hepat/o (liver)
L+ Lung
M + marrow
P+ Pleura
O+ Osseous tissue
D+ Dermis
A patient presents with Hodgkin’s Disease in a supraclavicular node and 4 cervical lymph nodes, the patient has also experienced night sweats and a 10% weight loss. What Stage is this patient?
IIB
more than one node and nodes on same side of diaphragm → stage 2
symptomatic → B
This is the name of the typical patient position utilized for treating mantle field/Hodgkin's disease
Akimbo position
In terms of Gy, what would be the best typical dose range for Hodgkins disease?
35-45 Gy
Overall five year survival for Hodgkins disease is approximately:
80%
True/ False: Non-Hodgkin's lymphomas are more common than Hodgkin's disease
True
FYI: Cell types for NHL
40% Follicular (Nodular)- less aggressive
60% Diffuse- more aggressive
T/F: Follicular pathologies for lymphomas are more aggressive than the diffuse types of lymphomas
False, they are less aggressive
Which of the following is not a combination chemotherapy regimen described in use for non-Hodgkin's lymphoma? (list instead)
CHOP
MACOP-B
Monoclonal antibodies like Rituximab
The cancer site that most commonly metastasizes to the bones
Prostate
This radiopharmaceutical agent, slow IV push liquid pure beta emitter, has been shown to be effective for treating widespread bony metastases
Strontium 89
A typical adult has this many bones
206
This is the life support sheath providing nutrient blood for bone cells and a source of bone developing cells during growth and after fracture. It is the hard dance covering of the bone
Periosteum
Which of the following is not an etiologic factor described in lecture for primary bone tumors?( list instead)
RGV Dawg
Radiation exposure
Genetic disorders
Viruses
Developmental abnormalities
What are the two types of primary bone lesions
Osteolytic (destroy bone)- black on film
Osteoblastic (create bone)- white on film
These type of primary bone lesions destroy normal bone and show up dark on film
Osteolytic
This is the most common truly osseous cancer
Osteogenic sarcoma (osteosarcoma)
This cancer from this oncology section best represents the classic "moth-eaten pattern" with respect to bone destruction
Multiple Myeloma
FYI: Could also be Ewing’s sarcoma but MM is best answer
Kaposi’s sarcoma is more commonly seen in all of the following population except: (list them instead)
Ture Kaposi’s: Mediterranean & North African men
AIDS patients
While soft tissue sarcoma can arise anywhere in the body, they most commonly occur in what area?
Lower extremities
Soft tissue sarcomas most commonly metastasize to what organ?
Lung
True or False: The single most important factor in the outcome of soft tissue sarcoma patients is the size of the tumor
False: The most important single factor is the histologic grade of the tumor
grade is more important cuz they are already radioresistant, so grade matters??
Soft tissue sarcomas are best diagnosed using what imaging tool?
MRI
FYI: Cuz it is soft tissue
When treating soft tissue sarcomas with radiation, treat the GTV (gross tumor volume) plus how many centimeter margin?
4 cm
T/F: Sarcomas tend to spread via the hematologic route rather than the lymphatic route
True:
FYI: The periosteum keeps primary bone tumors contained in a manner that generally prevents lymphatic spread.
The most common type of soft tissue sarcoma
Liposarcoma
These are the most lethal type of soft tissue sarcomas
Rhabdomyosarcoma
The most common type of genitourinary sarcoma
Leiomyosarcoma
Which of the following is NOT one of the etiologies described for soft tissue sarcoma? (list instead)
Previous RTT- breast & HD
Von Recklinghausen or Li-Fraumeni syndrome
What is the most common presentation of Hodgkin’s disease?
enlarged mass in the neck
The peak incidence for Hodgkin’s disease is
adolescence (11-30)
The xiphoid is at the level of:
T-10
How would a stage lll Hodgkin’s disease be treated?
(i.e field arrangement)
Mantel & Inverted Y
(treats stages 3 and 4) at stage 3 there is + nodes in both sides of the diaphgram
T / F HD shows a second "peak" of incidence in old age.
True
T/F: Older Hodgkin disease patients generally have a poorer prognosis than younger patients.
True
Pruritis is
itching
Involvement of two or more lymph nodes on the same side of the diaphragm is classified as what stage of Hodgkins disease?
Stage II
A benign tumor made of fat cells would be called a/an:
lipoma
A patient presenting with HD in the cervical, axillary and para-aortic lymph node groups would be what clinical stage?
stage lll
Cuz it’s in both sides of the diaphragm
Clinically, what anatomical landmark may be used as the inferior border of a mantle field?
xiphoid
Kaposi’s sarcoma is commonly associated with all of the following demographic groups EXCEPT: (list instead)
North African
Mediterranean
AIDS patients
The lymphatic organs are the
spleen, tonsils, thymus, and lymph nodes
STTL
Structures in Waldeyers ring are seldom involved in patients with HD. However, with such involvement, what nodes must be treated in the Waldeyers ring field?
pre-auricular
The most commonly occurring soft tissue sarcoma is:
liposarcoma
A typical dose for HD would be how many Gray?
35-45
Sarcomas tend to spread via:
hematologic route
T / F Radiation therapy is the definitive treatment modality for most soft tissue sarcomas.
False because most sarcomas are radioresistant
The single most important factor in the outcome (prognosis) of soft tissue sarcoma patients is:
histological grade (degree of cellular differentiation)
Though soft tissue sarcomas can arise anywhere in the body, they are most likely to occur in what area?
lower extremities
Why may mantle fields may require extended SSD calcs?
Need field sizes larger than the maximum field size of the machine.`
Subdiapgragmatic fields are most commonly used to treat what stage(s) of HD?
3 & 4
FYI: cuz after stage 3 and 4 there is positive lymph nodes in both sides of the diaphragm
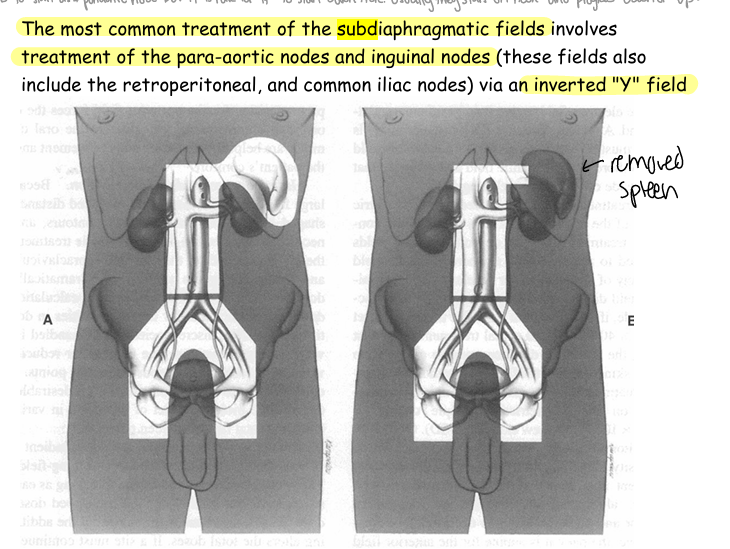
The Cisterna Chyli is located at the level of
L2
A "mini-mantle" might be used to treat patients with involvement of all of the following nodes except: (list them instead)
cervical
supraclav
axilla
Treatment fields used to treat Hodgkins disease (TNI) are known as
Mantel and inverted Y
Which of the following is most clearly associated with the etiology of soft tissue sarcomas: (list it)
Previous RTT: breast cancer and HD
Von Recklinghausen disease Li-Fraumeni Syndrome
Multiple myeloma is a neoplastic proliferation of
Plasma cells
The lateral borders of a mantle field must include the: (just list all instead)
Superior:
Inferior:
Lateral:
Superior: a line from mental point to mastoid tip
Inferior: xiphoid tip; spinal level: T10
Lateral: must include axilla
FYI: What structures does mantle field block
throat block
humoral heads
lungs
safety block/ cord block
Some places add: heart block
What tumors appear almost anywhere fat is present?
Liposarcoma
T / F MM is invariably an incurable disease but it can usually be controlled for long periods of time.
True
T / F Multiple Myeloma (MM) occurs most commonly in childhood/adolescence.
False: Most occur after age 40
T / F Chondrosarcoma is common in childhood, but rare in adulthood.
False: Chondrosarcoma is rare in childhood but becomes more prevalent with advancing age.
FYI: chondrosarcoma is cartilage sarcoma
i guess adults cartilage deteriorates or something
What is the most frequent site of metastatic involvement of a soft tissue sarcoma?
Lung
What is the most common presenting symptom of multiple myeloma?
back pain
What is the primary modality in the treatment of multiple myeloma?
chemotherapy
FYI: makes sense, since it goes everywhere
Which of the following is the least common site of incidence for Ewing’s sarcoma and osteogenic sarcoma? (list it instead)
A proximal tibia
B distal femur
C ribs
D humerus
C ribs
osteosarcoma- distal femur & proximal tibia (bones around knee), fast growing bones
Ewing’s: diaphysis on lower half of body
A possible late effect of MOPP chemotherapy for HD would most likely be:
secondary malignancy (particularly acute leukemia)
The overall 5 year survival rate for HD is about ___%.
80%
Mycosis fungoides is a type of
T cell lymphoma
(nothing is lympoid)
The prognosis of lymphoma is least influenced by (list them instead)
stage- biggest prognostic factor, tumor size
age
histology
What ethnic group is multiple myeloma most common in?
African descent
The most common site of primary bone tumors is near the:
epiphyseal line (the growth plate)
The staging system for Hodgkins disease is
Ann Arbor staging
A staging system for lymphoma is the
Rappaport system
Hodgkins disease patients with “A” symptoms are
asymptomatic
A Hodgkins patient presents with a 4 cm. mass in the left supraclavicular area, what is the clinical stage?
IA
I- single node
A- no symptoms: weight loss, fever, nigh sweats
Which of the following primary bone tumors is most radiosensitive?
Ewing’s sarcoma
This is the life support sheath providing nutrient blood for bone cells and a source of bone developing cells during growth and after fracture:
periosteum
What is the most common site of presentation for soft tissue sarcomas?
lower extremity
Most primary bone cancers are:
A carcinomas
B sarcomas
C lymphomas
D melanomas
sarcomas
The incidence of primary bone tumors is highest in what age group:
adolescent
What study best shows a soft tissue sarcoma?
MRI
With what type of bone tumor do radiographs show a classical "moth-eaten" pattern to the cortex of a the bone?
Multiple Myeloma
What sarcoma originates in connective tissue of nerve sheaths?
Fibrosarcoma
What will therapeutic doses of radiation to growing bone and cartilage result in for children:
A marked retardation of bone growth
What is the most frequent primary bone tumor?
Osteosarcoma
Which is the most radiosensitive of the soft tissue sarcomas?
liposarcoma
FYI: while Ewings can appear in soft tissue, it most commonly appears in the bone so that is why liposarcoma is the best answer
T / F There is thought to be a viral etiology for NHL.
True
Which of the following is NOT a common site for NHL? (list instead)
lymph nodes
Waldeyer’s ring
GI tract (most common extranodal location)
What lesions are the most lethal of the soft tissue sarcomas?
Rhabdomyosarcoma