Key Concepts in Biology and Animal Behavior 3
1/428
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
429 Terms
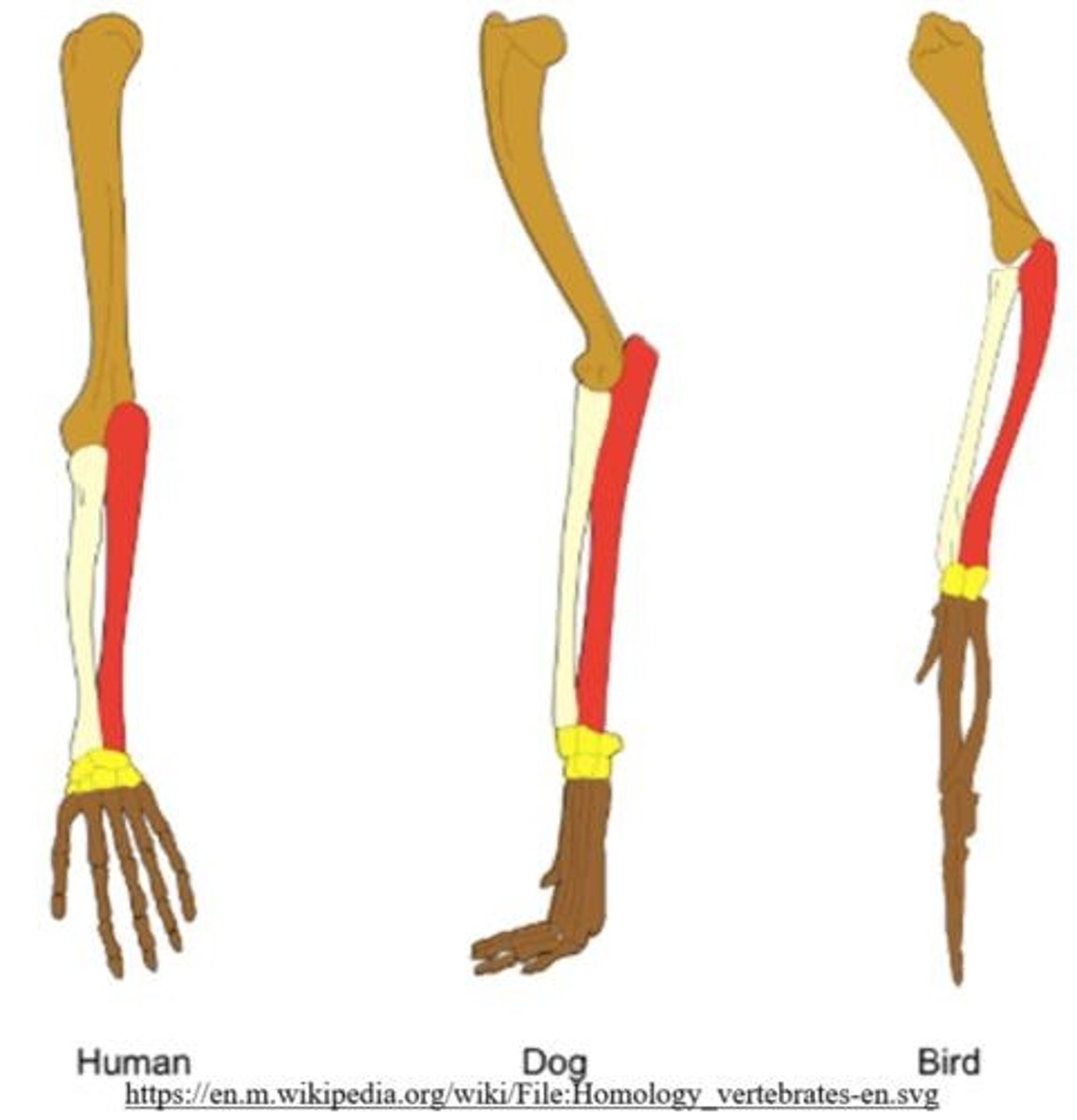
Homologous structures
Derived from a common ancestor, may differ functionally.
Genomics
Study of all genes within a genome.
Primary succession
Occurs after major disturbances on lifeless substrates.
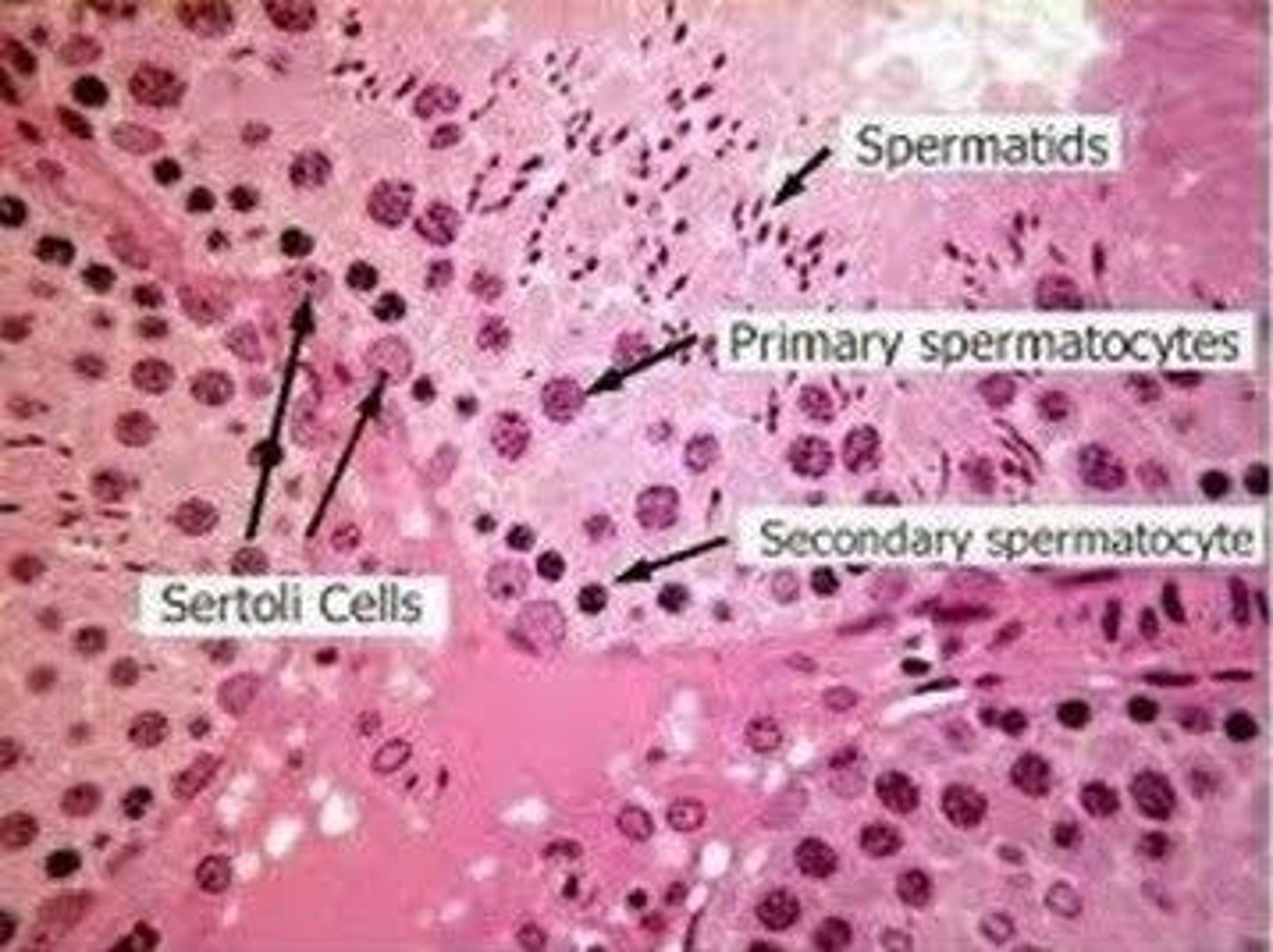
Sertoli cells
Nourish developing sperm cells during spermatogenesis.
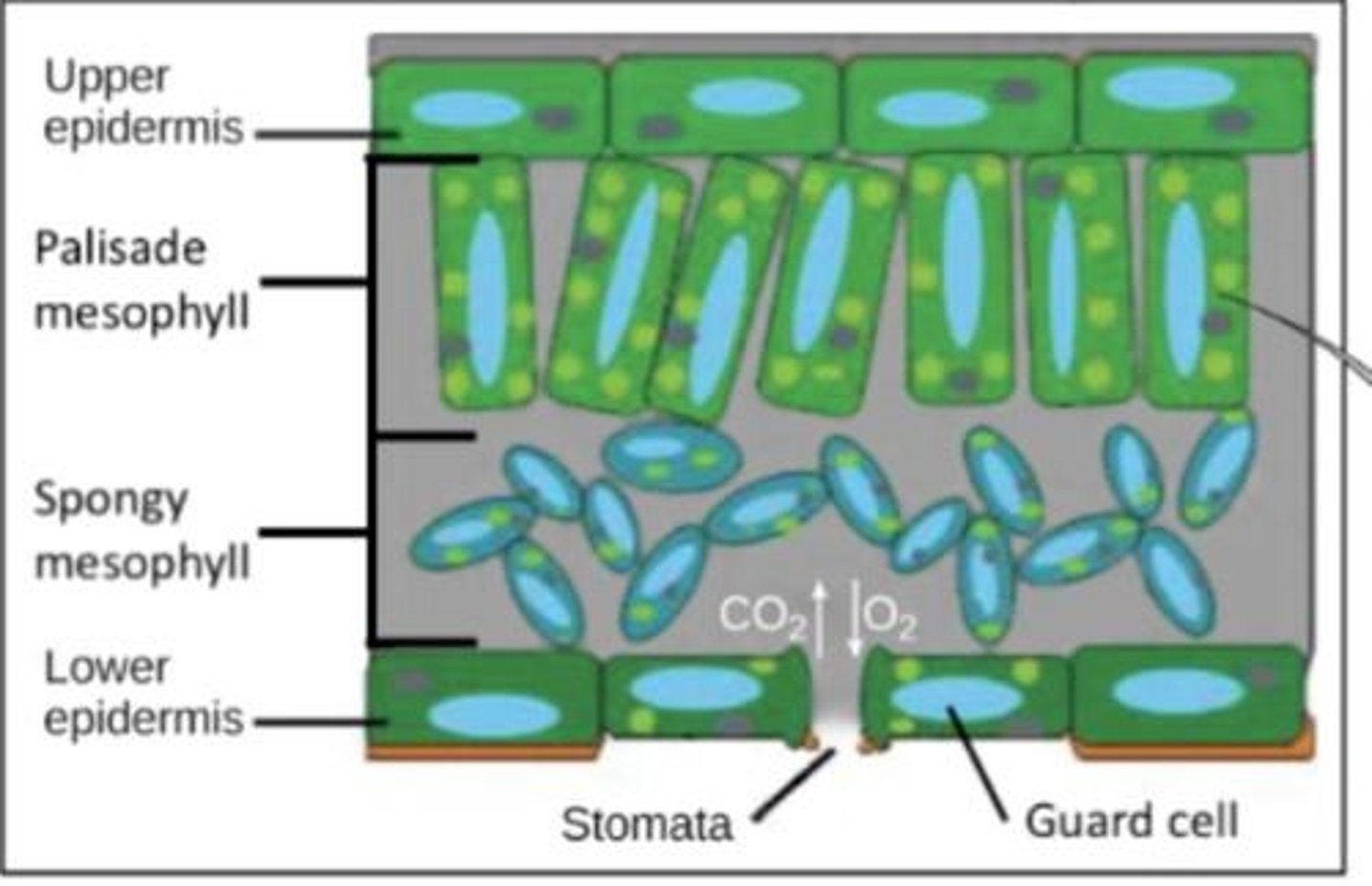
Guard cells
Control stomatal openings for gas exchange.
Bilateral symmetry
Organism has symmetrical right and left halves.
Epithelial tissue
Outer cell layer, protects and covers surfaces.
Epidermis
Outer layer providing protection and preventing water loss.
Radial symmetry
Symmetry around a central axis.
Autosomal dominant traits
Traits following a dominant inheritance pattern on autosomes.
Gene expression regulation
Turning on and off different gene expressions.
Autosomal recessive traits
Traits following a recessive inheritance pattern on autosomes.
Beta-oxidation
Process occurring in mitochondrial matrix for fatty acids.
Free fatty acids
Fatty acids that undergo beta-oxidation.
Homeotic genes
Genes determining body structure development.
Central vacuoles
Plant vacuoles acting like lysosomes and storage.
ATP synthase
Enzyme using gradient to synthesize ATP.
Substrate-level phosphorylation
Direct phosphorylation of ADP into ATP.
Food vacuoles
Temporary holders merging with lysosomes for digestion.
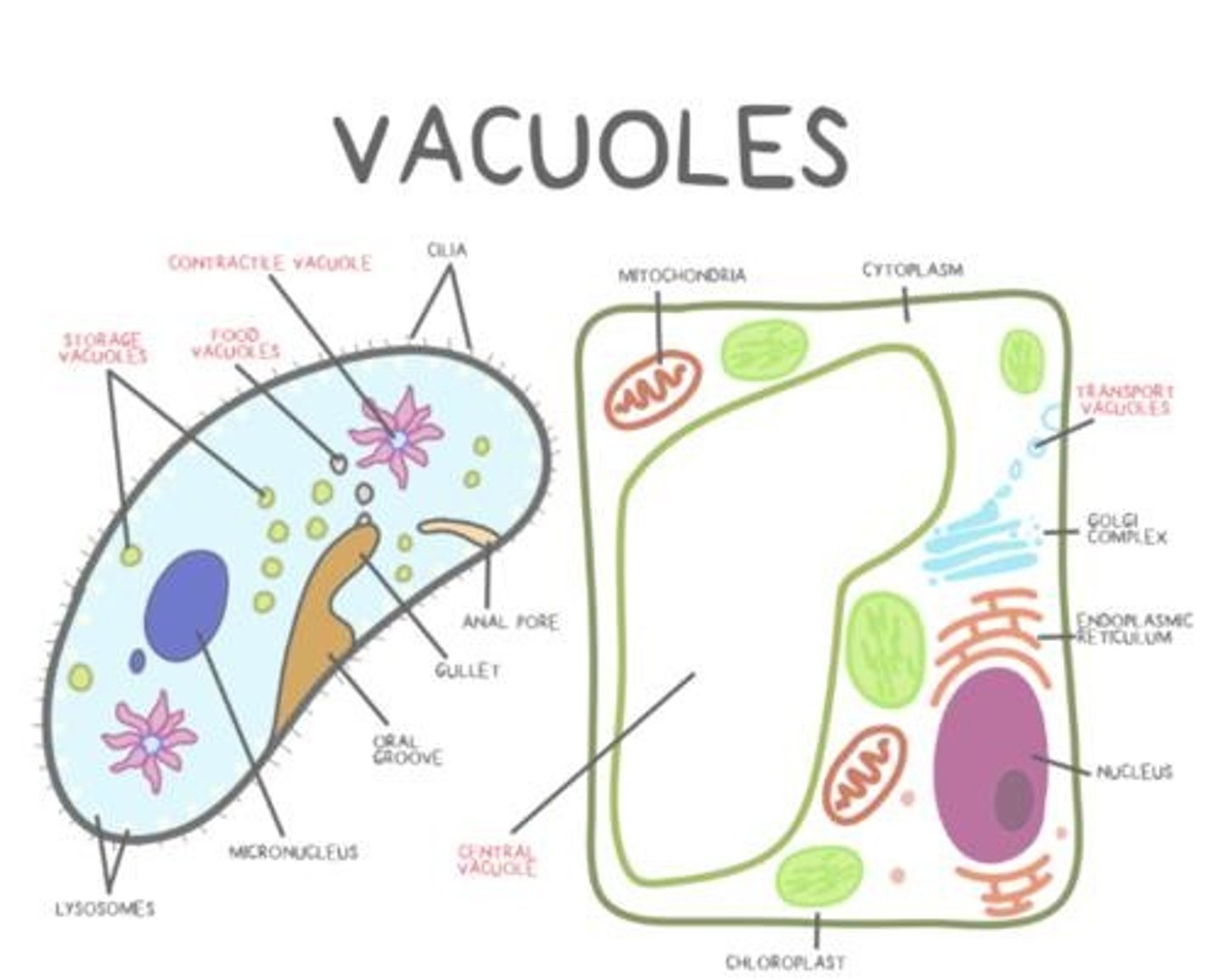
Transport vacuoles
Vacuoles moving materials between organelles.
Contractile vacuoles
Vacuoles pumping excess water out of cells.
Storage vacuoles
Vacuoles storing starches, pigments, and toxins.
Semilunar valves
Valves ensuring one-way blood flow from ventricles.
Complement system
Immune system component working with antibodies.
Search images behavior
Feeding behavior for locating safe, abundant food.
Scavengers
Animals consuming dead animals and plant matter.
Iteroparous
Animals caring for young as they mature.
Secondary consumers
Organisms one trophic level above primary consumers.
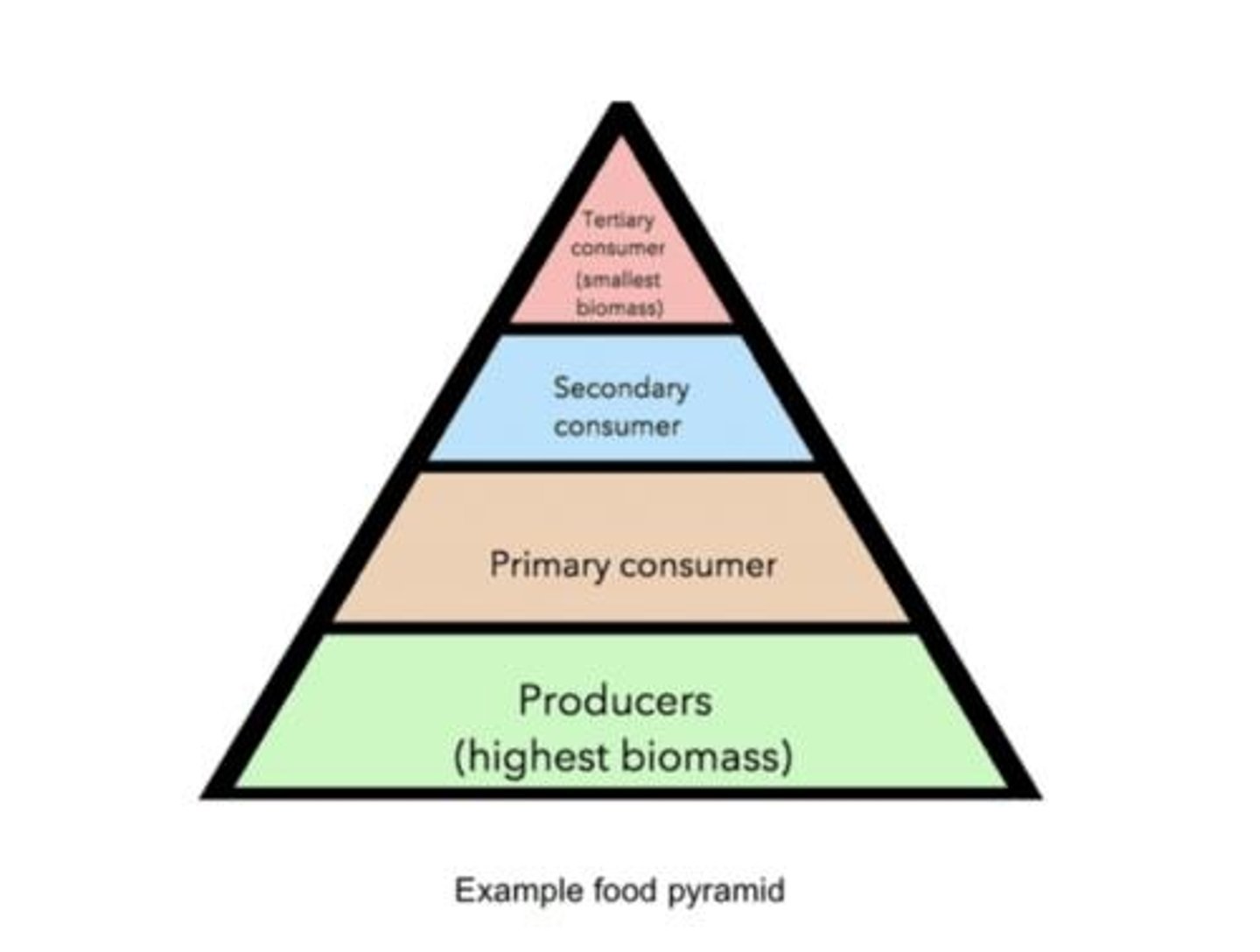
Primary consumers
Organisms feeding on primary producers.
Instincts
Innate behaviors occurring without conscious thought.
Tertiary consumers
Organisms one trophic level above secondary consumers.
Primary producers
Organisms at the lowest trophic level.
Cofactors
Non-protein molecules assisting enzyme functions.
Learned behaviors
Behaviors allowing adaptation to unexpected events.
Decomposers
Organisms breaking down and recycling dead material.

Social behaviors
Interactions for companionship, food, and protection.
Altruistic behaviors
Sacrifices made for the benefit of relatives.
Agonistic behaviors
Behaviors competing for resources like food and territory.
Intraspecific competition
Competition among individuals of the same species.
Exploitation competition
Indirect competition depleting a common resource.
Interference competition
Direct competition preventing resource establishment.
Apparent competition
Predation where one predator preys on two species.
Waxes
Esters of fatty acids and monohydroxy alcohols.
Detritivores
Consume detritus, aiding organic matter decomposition.
Semelparity
Mating only once in a lifetime.
Biotic factors
Living elements within an ecosystem.
Abiotic factors
Nonliving elements within an ecosystem.
Hair follicles
Generate hair and attach it to skin.
Mammary glands
Specialized glands that produce milk.
Apocrine glands
Glands that produce ear wax.
Sudoriferous glands
Main sweat glands important for thermoregulation.
Classical conditioning
Learning to pair a neutral stimulus with an unconditioned stimulus.
Savannas
Grasslands with diffuse trees, seasonal droughts, and fires.
Cooperation
Social behavior where animals group for mutual goals.
Detritus
Combination of feces and decomposing organic matter.
Sexual selection
Differential mating success based on traits.
Male competition
Males compete for mating opportunities.
Female choice
Females select mates based on attractive traits.
Spatial learning
Associating landmarks with specific locations.
Parasitism
One organism benefits at another's expense.
Mutualism
Both organisms benefit from the interaction.
Commensalism
One organism benefits, the other is unaffected.
Thermoregulation
Regulation of body temperature.
High quality mates
Mates with potential for producing high quality offspring.
Detritivores' role
Expose organic matter for fungi and bacteria.
Energy contribution in mating
Mating processes require varying energy levels.
Commensalism
One organism benefits; the other is unaffected.
Parasitism
One organism benefits at the expense of another.
Phototaxis
Movement in response to light stimulus.
Imprinting
Permanent learning of behaviors during a critical period.
Migration
Long-distance movement of animals instinctively.
Taxis
Movement towards or away from a stimulus.
Polygamy
Having multiple mating partners simultaneously.
Extinction
Loss of a species from an ecosystem.
Ecological Succession
Community development and change over time.
Biomass
Total mass of living organisms in an area.
Polyandry
One female mates with multiple males.
Polygyny
One male mates with multiple females.
Electroporation
Creating temporary holes in cell membranes.
Efferent
Motor neurons transmitting signals from CNS to muscles.
Keystone Predators
Species that maintain ecological balance through predation.
Sensitization
Increased response to a stimulus after repeated exposure.
Kinesis
Random movement in response to a stimulus.
Habituation
Decreased response to a repeated, meaningless stimulus.
Insight
Learning through understanding rather than trial and error.
Sexual Dimorphism
Differences in appearance between male and female species.
Observational Learning
Learning behaviors by watching others perform them.
Associative Learning
Connecting a stimulus with a behavior.
Alarm Pheromones
Signals to warn others of danger.
Releaser Pheromones
Attract mates or trigger immediate behaviors.
Biological Interaction
Close, long-term relationship between two organisms.
Primer pheromones
Chemical signals triggering long-term physiological changes.
Territoriality
Behaviors animals use to protect their territory.
Symbiosis
Interaction where different species live together.
Direct fitness
Genes passed directly from parent to offspring.
Indirect fitness
Genes passed through relatives enhancing inclusive fitness.
Kin selection
Evolutionary strategy favoring relatives' reproductive success.
Afferent neurons
Sensory neurons transmitting signals to the CNS.
Simple reflexes
Rapid reflexes with direct spinal cord connections.
Natural speciation
Speciation resulting from naturally occurring evolutionary processes.