Endocrine System: Pathophysio
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
homeostasis
the body's attempt to maintain a "balance" for optimal cell, organ and system functioning
2 systems maintaining homeostasis
nervous and endocrine
secreted by the endocrine system
hormones
primary endocrine organs
-Hypothalamus
-Pituitary gland
-Pineal gland
-Thyroid gland
-Adrenal gland
-Pancreas
-Gonads (ovaries/testicles)
secondary endocrine organs
-Heart
-Brain
-Stomach
-Liver
-Kidney
-Intestines
-Adipose tissue
hormones
regulatory molecules that are secreted by endocrine glands
target organs
organs that respond to hormones
goal of endocrine hormones
endocrine hormones travel through blood to target organs, and their action causes a "reaction" within the target organ
all organs in the body receive hormones, but only some respond because they have the corresponding receptors for that hormone. (T/F)
true
2 types of hormones
-non-polar (lipid soluble)
-polar (water soluble)
non-polar hormones
-insoluble in water (lipid soluble); does cannot dissolve in blood plasma
-soluble in other non-polar molecules (i.e. lipids)
-bound to carrier proteins in blood
-can be taken orally and absorbed through intestines into blood
types of non-polar hormones
steroids and thyroid
steroids
-secreted by adrenal cortex and gonads
-derived from cholesterol
thyroid
-primarily thyroxine
-derived from tyrosine and have iodine
how non-polar hormones work
-can cross plasma cell membrane of target cell
-receptor proteins are located inside the cell
-nuclear receptors: hormone binding triggers receptor to move to nucleus which binds to DNA, activating genes to produce proteins
polar hormones
-soluble in water = can dissolve in blood plasma
-able to be carried into their target organ
-cannot be taken orally or will be digested
types of polar hormones
catecholamines, polypeptides, proteins, and glycoproteins
catecholamines
epinephrine, norepinephrine, L-dopa
polypeptides
insulin
proteins
growth hormone
glycoproteins
luteinizing hormone
how polar hormones work
-cannot cross plasma cell mrbane of target cell
-plasma cell membrane has receptor proteins in it that bind hormones in extracellular fluid
-binding activates the secondary messenger systems--> caries out the hormone's effect
what is the medical implication of the secondary messenger system (with polar hormones)?
the secondary messenger is too polar to cross the cell membrane; therefore, hormone treatment is necessary (cannot simply activate the messenger)
hypothalamus
control center of the brain
hypothalamus functions
-controls anterior pituitary by hormones and posterior pituitary gland via neural input
-provides blood flow to the pituitary = hypothalamus-hypophyseal portal system
hormones of the hypothalamus
-corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH)
-thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH)
-gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)
-growth-hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH)
-somatostatin
-protein-inhibiting hormone (PIH)
corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH)
stimulates anterior pituitary to secrete ACTH
thyrotopin-releasing hormone (TRH)
stimulates anterior pituitary to secrete thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)
stimulates anterior pituitary to secrete gonadotropic hormone (FSH & LH)
growth-hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH)
stimulates anterior pituitary to secrete growth hormone (GH)
somatostatin
inhibits anterior pituitary gland from secreting growth hormone
protein-inhibiting hormone (PH)
inhibits anterior pituitary from secreting prolactin
pituitary gland location
-below hypothalamus
-attached to hypothalamus by infundibulum
pituitary gland is regulated by ____________
hypothalamus
pituitary glands
2 glands; anterior and posterior
anterior pituitary gland
-controlled by hormones secreted by the hypothalamus
-secretes its own hormones that regulate other endocrine glands
posterior pituitary gland
secretes hormones produced by neuron bodies in hypothalamus (which are transported into posterior pit. by axons)
organs affected by hormones of the posterior pituitary gland
-breast (mammary glands)
-uterus
-kidneys
organs affected by hormones of the anterior pituitary gland
-bones & soft tissues
-reproductive organs (gonads/ovary)
-thyroid gland
-adrenal gland
hormones of anterior pituitary
-produces and secretes "trophic" hormones
-if too high = causes excess growth of target organ
-if too low = causes target organs to shrink
types of hormones secreted by anterior pituitary
-growth hormone (GH)
-thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
-adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
-follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
-luteinizing hormone (LH)
-prolactin
growth hormone (GH)
stimulates protein synthesis and tissue/organ growth
thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
stimulates thyroid to secrete its hormones (T3 & T4)
adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)
stimulates adrenal cortex to secrete corticosteroids
follicle stimulating hormone (FSH)
stimulates growth of ovarian follicles and production of sperm
luteinizing hormone (LH)
stimulate ovulation and formation of corpus luteum in women; stimulates Leydig cells in men to produce testosterone
prolactin
stimulates milk production by mammary glands and inhibits ovulation
hormones of posterior pituitary
-produced, stored and secreted by hypothalamus
-antidieuretic hormone (ADH) and oxytocin
antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
aka vasopressin; acts on kidneys to promote water retention
oxytocin
stimulates contraction of uterus during labor and contraction of mammary ducts during lactation
how the hypothalamus controls the anterior pituitary gland
negative feedback loops to control homeostasis
pituitary pathologies
-inadequate GH
-over secretion of GH
inadequate GH pathologies
-Dwarfism: lack of growth in children
-Simmonds: premature aging in adults
over secretion of GH
-Gigantism: too much growth in children
-Acromegaly: thickening of bones and soft tissue growth in adults
pituitary cachexia (Simmonds disease) signs and symptoms
-progressive loss of skeletal muscles (without or with fat loss)
-low appetite
-unintentional weight loss/muscle wasting
pituitary cachexia (Simmonds disease) causes
-chronic inflammatory response
-cancer
-chronic illness (kidney disease, heart failure, COPD)
pituitary cachexia (Simmonds disease)
hypercatabolic syndrome affecting the pituitary gland
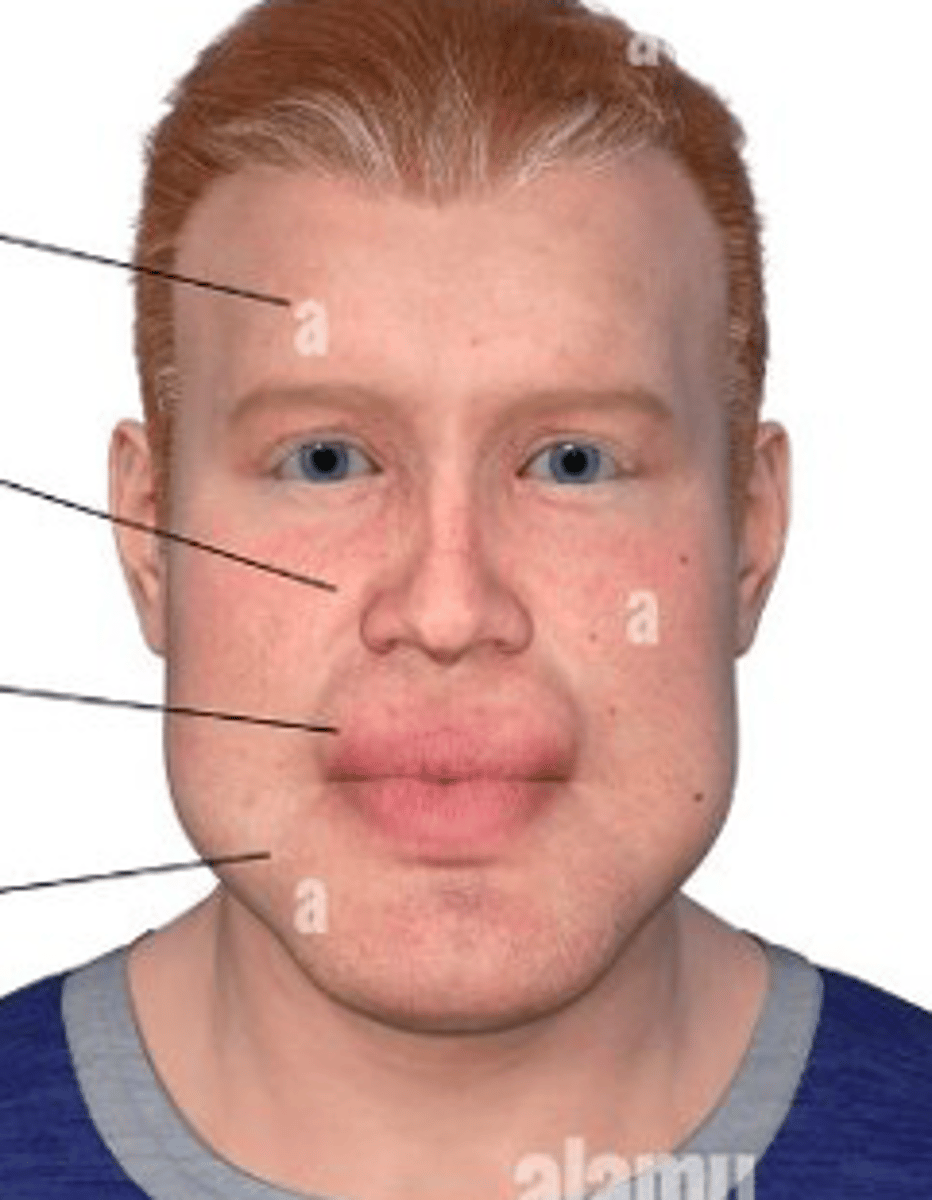
acromegaly
abnormal enlargement of the extremities (i.e. enlarged nose/lips/tongue, prominent forehead and chin/jaw)
adrenal gland basics
-located on top of kidneys
-two glands (one inside the other) --> adrenal cortex and adrenal medulla
adrenal cortex
-outer layers
-not innervated by axons
-secretes corticosteroids
-assist in regulating metabolism and electrolytes
adrenal medulla
-inner core
-innervated by sympathetic axons
-secretes epinephrine and norepinephrine
-assist in fight or flight
adrenal cortex hormones
glucocorticoids, mineralcorticoids, weak androgens
glucocorticoids
-increase blood glucose by breakdown of liver glycogen and conversion of non-carbohydrates to glucose)
-primarily cortisol (aka hydrocortisone)
mineralcorticoids
-regulate mineral and electrolyte concentrations in blood
-primarily aldosterone
weak androgens
-promote sex drive in women and puberty in men
-primarily androstenedione (converted to testosterone or esterone)
regulation of adrenal cortex
-negative feedback loop
-hypothalamus secretes CRH (corticotropin-releasing hormone)
-CRH triggers ACTH secrteted by anterior pituitary
-ACTH triggers adrenal cortex to release cortisol
-cortisol and ACTH provide negative feedback to slow or stop secretion of CRH by hypothalamus
cortisol (hydrocortisone)
suppresses inflammation and immune response
natural glucocorticoid
cortisol
man-made glucocorticoid
prednisolone & desamethasone
general adaptation syndrome (GAS)
-occurs in response to stress
-higher brain centers push increase of CRH secretion, thus ACTH when stressed
-increased cortisol means increased glucose for CNS and increased amino acids for tissue repair
medical implications of general adaptation syndrome (GAS)
-stress induced cortisol levels can be 6x as great as non-stressed levels
-can be detrimental as it suppresses immunity (increase risk of infection)
cortisol medication precuations
forms reduced natural cortisol secretion due to negative feedback loop -- drug must be tapered slowly
aldosterone
secreted by adrenal cortex
key functions of aldosterone
-retain sodium and water in blood (too little = dehydration)
-excrete potassium in urine (too much K+ in blood = heart fibrillation)
chemical regulators (chemical signals) leading to aldosterone secretion
-rise in K+ stimulates adrenal cortex to secrete aldosterone
-blood volume and pressure decrease triggers secretion of chemical, causes aldosterone to be secreted
adrenal pathologies
-Cushings
-Addisons
Cushing's disease
-oversecretion of ACTH
-sx: weakness, bone pain, back pain
-signs: moon face, hair growth, central obesity with abdominal/leg striae, easy bruising, thin extremities, personality changes, kyphosis
Addison's disease
-undersecretion of ATCH = electrolyte imbalance & dehydration
-sx: weak, hypotensive, weight loss, nausea, vomiting
-signs: "tanning" of pale skin, changes in distribution of body hair, weight loss
Emergent - addisonian crisis:
magnification of signs and symptoms in response to trauma, infection, and infarction which can lead to hypovolemic shock
PT concerns for Addison's disease
-no aquatic therapy
-monitor vitals
-watch for signs of infection
adrenal crisis (Addison's disease)
Profound fatigue, dehydration, vascular collapse (decrease BP), renal shut down, Na+ decrease and K+ increase
thyroid gland
-thyroid follicles trap iodine to make (thyroxine -T4, triiodothyronine-T3)
-non-polar: utilizes carrier protein to circulate blood
-thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) from anterior pituitary stimulates follicles to secrete hormone
thyroid gland and homeostasis
hormone levels rise = negative feedback turns off anterior pituitary stimulation
functions of thyroxine
-required for correct growth and development in kids, especially the CNS
-stimulates cell respiration to "set" basic metabolic rate (BMR)
Goiter pathology
growth of thyroid gland due to stimulation from high TSH
2 major causes of goiter
hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism
hypothyroidism
-insufficient iodine so thyroxine and T3 not, and TSH keeps elevating to send "signal" that blood levels are low and more should be made
-Hashimoto's disease (autoimmune)
hyperthyroidism
-antibodies stimulate thyroid to grow and overproduce thyroxine
-Graves disease
classic sign of Graves disease
bulging eyes
parathyroid glands
-4 on the back surface of thyroid glands
-secrete parathyroid hormone (PTH)
-regulates blood levels of Ca2+ and phosphate
how the parathyroid glands regulate blood levels of Ca2+ and phosphate levels
-absorption from food in intestine
-some deposited in bones
-some removed from bones
parathyroid function
-drop in blood Ca2+ triggers parathyroid to secrete PTH
-PTH stimulates osteoclasts to resorb bone and stimulates kidneys to retain Ca2+ (not lose it in urination)
-blood Ca2+ rises
pancreas gland
-pancreatic islets (islands of endocrine glands in pancreas)
-both hormones secreted regulate metabolism
pancreatic islets (Islets of Langerhans)
islands contain endocrine cells: alpha cells (secrete glucagon) and beta cells (secrete insulin)
basics of metabolism
-two processes acting antagonistaclly to one another
-anabolism
-catabolism
-hormones stimulating each side of metabolism
anabolism
conversion of smaller molecules into larger, complex molecules
examples of anabolism
-glucose becoming glycogen -- stored in liver
-fatty acids and glycerol become triglycerides -- stored in adipose cells
-amino acids become proteins
-insulin stimulates anabolism
catabolism
hydrolysis of molecules into subunits for use in cell respiration
examples of catabolism
glucagon stimulates catabolism of glycogen
how eating impacts blood glucose
rise in blood glucose; stimulate beta cells to secrete insulin and inhibit alpha cells from producing glucagon