Section 7.6 (Catabolism/Biosynthesis)
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
Fill in the diagram for the catabolism of various molecules from food.
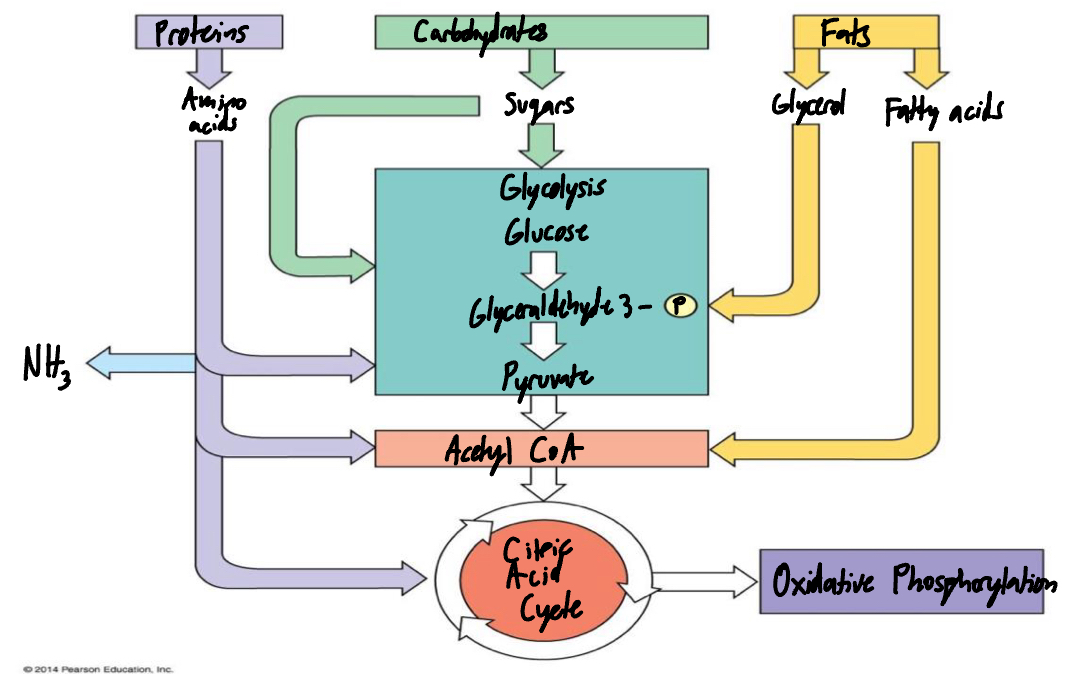
Where do carbohydrates enter aerobic respiration?
During glycolysis, the first stage that occurs in the cell’s cytoplasm
List what must happen to fats before they can enter cellular respiration. Then list where fats can enter aerobic respiration.
1) Lipolysis
2) Glycerol conversion: Glycerol —> Glyceraldehyde —> 3-phosphate
3) Fatty acid conversion: Fatty acids undergo beta-oxidation in mitochondrial matrix
1) Krebs cycle: Acetyl-CoA produced from beta-oxidation enters Krebs cycle
Entry point: Acetyl-CoA combines with a 4-carbon molecule (oxaloacelate) to begin cycle of reactions, which oxidizes the carbon groups and generates energy-carrying molecules like NADH and FADH_2
Lipolysis
Biological process where fats are broken down from stored triglycerides into free fatty acids and glycerol
Beta-oxidation
The metabolic process that breaks down FATTY ACIDS into two-carbon units called acetyl-CoA within the mitochondria
List what must happen to proteins before they can enter cellular respiration. Then list where proteins can enter aerobic respiration.
1) Hydrolysis
2) Deanimation
3) Carbon skeleton entry
1) Various points: the point at which a deaminated amino acid enters the pathway depends on the amino acid’s chemical structure
2) Pyruvate: Some amino acids can be converted to pryuvate, which enters the process after glycolysis
3) Acetyl-CoA: Other amino acids are converted into acetyl-CoA, which enters the Krebs (citric acid) cycle directly
4) Krebs cycle intermediates: Some amino acids can be converted into other intermediate molecules within the Krebs cycle
What is deanimation of proteins before entering cellular respiration?
Removing amino group (NH_2) from amino acid and then converting the removed amino group into ammonia
What is the carbon skeleton entry of proteins before they enter cellular respiration?
Remaining carbon skeletons of amino acid can be converted into a molecule that can enter cellular respiration
Remember that the stages of aerobic respiration are composed of many steps with many intermediate molecules and corresponding enzymes. Describe where your body could obtain the necessary precursors to make a non-essential amino acid.
Stages of cellular respiration are not only for generating ATP but also intermediates that serve as precursors for anabolic (biosynthesis) pathways
Many of intermediate molecules from glycolysis and Krebs cycle can be diverted from main catabolic pathway to construct bigger, more complex molecules