Amines, Amides, Amino Acids and Proteins
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Explain how the solubility of amines changes with increasing carbon chain length
solubility decreases
Hydrocarbon chains are polar so exhibit LDF only
LDFs disrupt hydrogen bonding network which forms between amine functional group and water molecyles
What is a Brønsted-Lowry base
A proton (H+) acceptor in aqueous solution
Give the equation for methylamine acting as a base
CH3NH2 + H+ ⇌ CH3NH3+
Give the equation for the reaction between methylamine and hydrochloric acid
CH3CH2NH2 + HCl → CH3CH2NH3C
What is the process in which a primary amine can be formed from a nitrile
Reduction of the nitrile
What is the reagent needed for the reduction of a nitrile to form a primary amine
LiAlH4 in a dry ether solvent
Explain the relationship between the availability of the lone pair on nitrogen and the base strength
The higher the electron density on the nitrogen atom, the more available the electron pair on the nitrogen atom and the more able the nitrogen atom can accept a proton
What is the general formula for the reduction of a nitrile
R-CN + 4[H] → R-CH2NH2
What is a use of nitrobenzene
To make aromatic amines
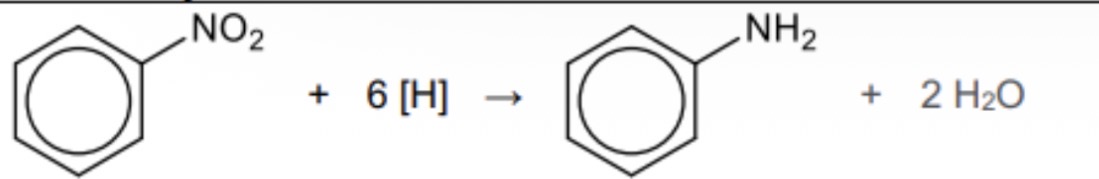
How can a phenylamine be prepared from nitrobenzene and what are the reagents used
In the reduction of nitrobenzene
Tin and concentrated HCl followed by dilute NaOH
Give the displayed formula for the reduction of nitrobenzene to form its products
What is a use for aromatic amines
Azodyes (synthetic dyes whose molecules contain two adjacent nitrogen atoms between two carbon atoms)
How can amines be prepared from halogenoalkanes
Heating the haloalkane in sealed container with excess ammonia dissolved in ethanol
Give the equation for the reaction between bromoethane and excess amonia
CH3CH2Br + 2 NH3 → CH3CH2NH2 + NH4B
Outline the mechanism for the reaction(s) of excess ammonia with bromoethane (multiple substitution)
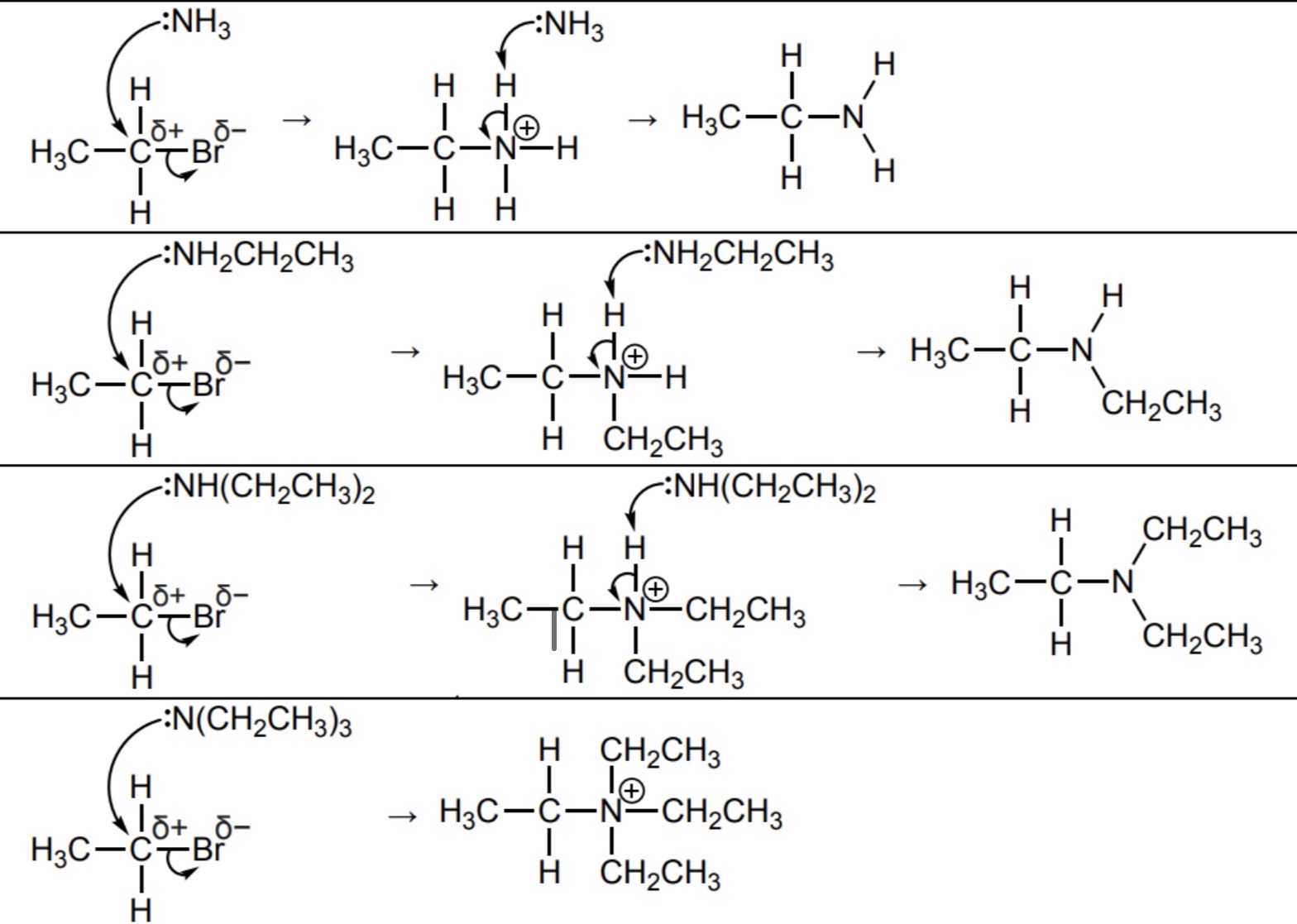
What is the final product that can be formed when excess ammonia is reacted with a halogenoalkane
Quaternary ammonium salt
What is a use for quaternary ammonium salts
Cationic surfactants (lower surface tension of a liquid)
Also conditioners, fabric softeners, detergents, wetting agents, dispersants, foaming agents
By what mechanism do amines react with acyl chlorides and what characteristic of amines allow this
react in a nucleophilic addition-elimination reaction
The amines act as a nucleophile as they are a lone pair donor
What is the produce formed when an amine reacts with an acyl chloride
An amide
Give the general formula for the reaction between an acyl chloride and an amine
R-COCl + H2N-R → R-CONH-R + HCl
What is the type of reaction between acyl chlorides and amines and why
condensation reaction
Forms HCl (small molecule)
What is the formula for aqueous hexaquacopper(II)
[Cu(H2O)6]2+(aq)
Give the equation for the reaction of ammonia added dropwise to hexaaquacopper (II)
[Cu(H2O)6]2+(aq) + 2 NH3(aq) → [Cu(OH)2(H2O)4](s) + 2 NH4+(aq)
Give the equation for the reaction of excess ammonia to hexaaquacopper (II)
[Cu(H2O)6]2+(aq) + 4 NH3(aq) → [Cu(NH3)4(H2O)2]2+(aq) + 4 H2O(l)
Give the equation for the reaction of butylamine added dropwise to hexaaquacopper(II)
[Cu(H2O)6]2+(aq) + 2 CH3CH2CH2CH2NH2(aq) → [Cu(OH)2(H2O)4](s) + 2 CH3CH2CH2CH2NH3+(aq)
What is the observation made when butylamine is added dropwise to hexaaquacopper (II)
Pale blue precipitate of [Cu(OH)2(H2O)4](s)
What is the butylamine acting as in the reaction when butylamine is added dropwise to hexaaquacopper (II)
Brønsted-lowry base
Give the equation for the reaction of excess butylamine and hexaaquacopper(II)
[Cu(H2O)6]2+(aq) + 4 CH3CH2CH2CH2NH2(aq) → [Cu(CH3CH2CH2CH2NH2)4(H2O)2]2+(aq) + 4 H2O(l)
What is the observation made in the reaction of excess butylamine and hexaaquacopper(II)
Deep blue solution of [Cu(CH3CH2CH2CH2NH2)4(H2O)2]2+(aq)
What is the butylamine acting as in the reaction of excess butylamine and hexaaquacopper(II)
Ligand
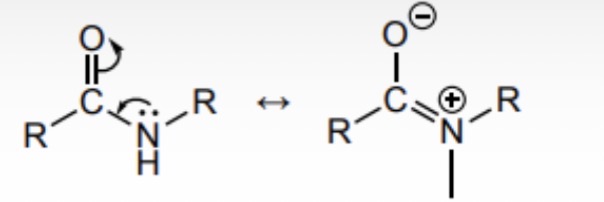
Draw an annotated formula to show why the lone pair of electrons on the N of an amide may not be as available as may be thought
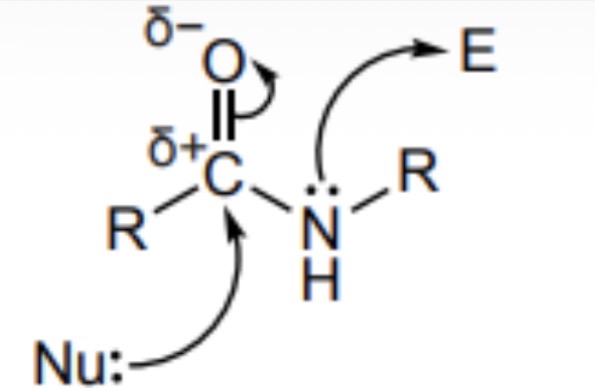
Draw an annotated formula to show where a nucleophile would attack an amide and where the amide could act as a nucleophile from
Why are amides unreactive carbpxylic acid derivatives
C-N bond strong due to slight delocalisation of nitrogen lone pair so unlikely to break
What are amides neutral/don’t act as bases
Lone pair on nitrogen delocalised slightly due to adjacent C=O bond so unavailable to accept a proton
How can an amide be formed
reacting acyl chlorides with concentrated ammonia
(Also reacting acyl chlorides with amines)
Describe the reaction between acyl chlorides and concentrated ammonia, giving the products
vigorous reaction
Hydrogen chloride (condensation reaction)
Solid amide
Give the equation for the reaction of ethanoyl chloride with concentrated ammonia
CH3COCl + NH3 → CH3CONH2 + HCl
Give the equation for reaction of the hydrogen chloride (produced from the recaction with the ethanoyl chloride) and the concentrated ammonia
NH3 + HCl → NH4Cl
Give the overall equation for the reaction of ethanoyl chloride and concentrated ammonia
CH3COCl + 2 NH3 → CH3CONH2 + NH4Cl
How can nitriles be hydrolysed/undergo hydrolysis
heated under reflux
Dilute hydrochloric acid (dilute = water present)
Give the general equation for the hydrolysis of a nitrile
R-CN + 2H2O + HCl → RCOOH + NH4Cl
What is needed for the reduction of nitriles and what is formed
reducing agent - lithiumtetrahydridoaluminate (LiAlH4) in dry ether
Primary amide formed
Give the equation for the reduction of butanenitrile
CH3CH2CH2CN + 4 [H] → CH3CH2CH2CH2NH2
Give the structural formula for paracetamol
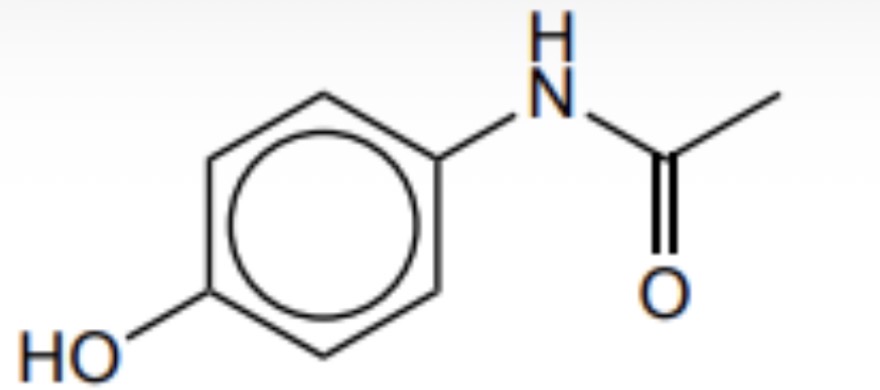
How can paracetamol be synthesised from phenol
Nitration/electrophilic substitution using conc H2SO4/conc HNO3 below 50˚ forming phenol nitride (NO2)
Reduction using Sn/conc HCl forming phenol nitrile (NH2)
Condensation reaction using ethanoyl chloride forming paracetemol
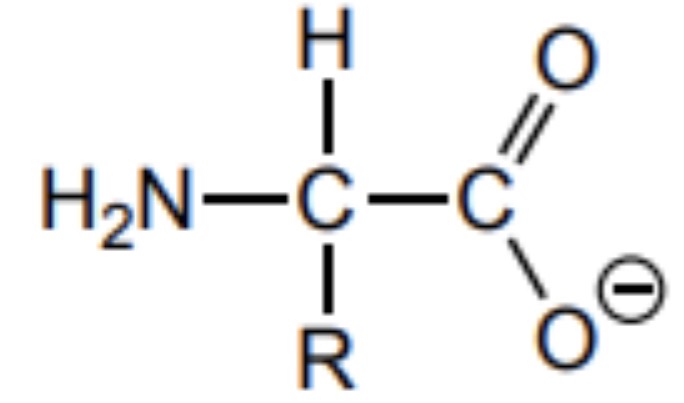
Draw the structure of an amino acid at high pH (very basic)
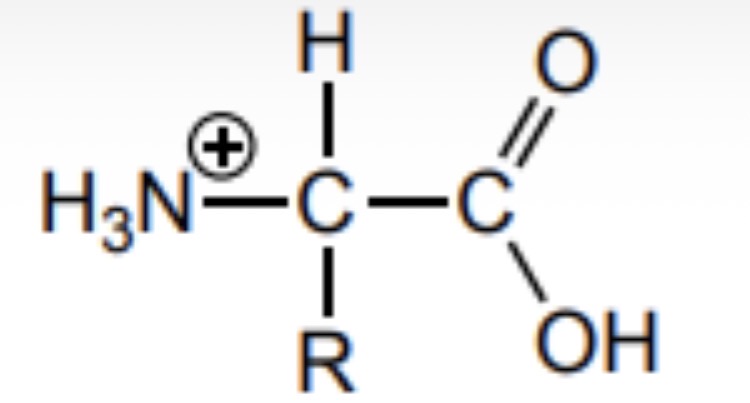
Draw the structure of an amino acid at a low pH (very acidic)
What is formed from an amino acid at the isoelelectric point
A zwitterion containing both the acidic and basic functional group
Draw the structure of an amino acid at the isoelectric point
The R group is unaffected
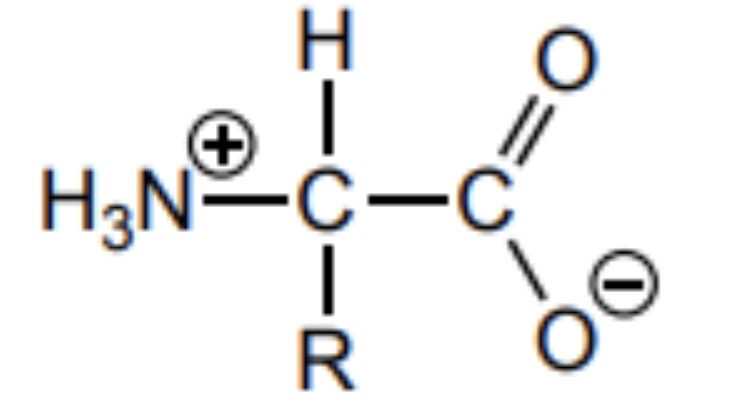
Why do all amino acids form crystalline structures at room temperature
ionic bonding holds together amino acid zwitterions
Lots of energy required to overcome strong electrostatic attractions between oppositely charged ions
What is needed for the hydrolysis of proteins/ peptide bonds
Dilute hydrochloric acids (H2O + H+ for every amine group to form -NH3+)
What is formed when proteins are hydrolysed
The constituent amino acids with acidic amine groups (-NH3+)
What is the process by which constituent amino acids are separated after a protein has been hydrolysed
chromatography
ninhydrin used as a contrast agent to make spots of colourless amino acids visible
Makes amino acids purple in colour