CH7: Immunohematology and blood transfusion medicine
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
1. Which immunodominant sugar confers A antigen
specificity?
a. D-Galactose
b. L-Fucose
c. N-Acetylgalactosamine
d. Both A and C
c. N-Acetylgalactosamine
2. If a patient has an A2 ABO type, which of the following
statements is true?
a. The patient's red cells will react with anti-A1 lectin
b. The patient's serum will react with A2 cells
c. The patient's red cells will react with anti-A2 lectin
d. The patient's serum will react with A1 cells if
anti-A1 is present
d. The patient's serum will react with A1 cells if
anti-A1 is present
3. Which genotype confers the Bombay blood type?
a. Hh
b. hh
c. Sese
d. Lele
b. hh
4. Which genes encode for Rh antigens?
a. RHDCE
b. RHD
c. RHCE
d. Both b and c
d. Both b and c
5. Testing for the D antigen was conducted at the IAT
phase. A control was included in the testing. Both
the patient's red cells and the control tube reacted
at 4+. How would you interpret this test?
a. The test is invalid because the control tube was
positive
b. The patient is D positive
c. The patient is D negative
d. The test should be repeated and the control tube
omitted
a. The test is invalid because the control tube was
positive
6. Of the red cells listed, which has the most D antigen
present?
a. Rh null
b. D positive
c. dce/dce
d. D--
d. D--
7. Which is true of the Duffy blood group system?
a. Antigens are resistant to enzyme treatment
b. Antibodies never show dosage
c. Fya and Fyb are codominant alleles
d. The majority of whites are Fy(a-b-)
c. Fya and Fyb are codominant alleles
8. Which antibody is typically considered to be an autoantibody
if found in the serum of an adult?
a. Anti-K
b. Anti-I
c. Anti-D
d. Anti-Fya
b. Anti-I
9. Which reagent destroys all of the Kell blood group
system antigens?
a. DTT
b. Chloroquine diphosphate
c. AHG
d. LISS
a. DTT
10. Which is true of antibodies to Kidd blood group system
antigens?
a. They are enhanced by enzymes
b. Titers can quickly drop in patients
c. Both A and B
d. None of the above
c. Both A and B
11. Which of the following is true of the Lewis system?
a. Lewis antigens are found on type II precursor cells
b. Lewis antigens are well developed at birth
c. Antibodies to Lewis antigens always cause HTRs
d. Antibodies to Lewis antigens rarely cross the
placenta
d. Antibodies to Lewis antigens rarely cross the
placenta
12. Which of the following is true of antibodies to MNS
blood group system antigens?
a. Anti-U is directed at a high-incidence antigen
b. Anti-N is commonly found
c. Anti-M is always clinically significant
d. Anti-S is reactive with enzyme-treated cells
a. Anti-U is directed at a high-incidence antigen
13. Which of the following antibodies is classified as
"biphasic" and an autoantibody?
a. Anti-B
b. Anti-P
c. Anti-H
d. Anti-Lea
b. Anti-P
14. You have performed an antibody screen using the
tube method. All three screening cells tested negative.
The Coombs check cells in all three tubes are also
nonreactive. What should you do?
a. Respin the tubes and reread them
b. Report the antibody screen as negative
c. Repeat the antibody screen
d. Perform an antibody identification panel
c. Repeat the antibody screen
15. An antibody panel has six 2+ reactive cells at AHG
phase. Panel testing using enzyme-treated cells
showed no reactivity. Which is the most likely antibody
that is present?
a. Anti-Fya
b. Anti-e
c. Anti-k
d. Anti-Lua
a. Anti-Fya
16. A patient has a currently nonreactive antibody screen
but has a history of anti-Jka in the patient file. Which
type of crossmatch must be performed on this patient?
a. Immediate spin crossmatch
b. IAT crossmatch
c. Electronic crossmatch
d. Both a and c
b. IAT crossmatch
17. A recently transfused patient has a 3+ reactive DAT
with anti-IgG. Which procedure should be used to
identify the specificity of the IgG antibody attached
to the red cells?
a. Adsorption
b. Neutralization
c. Titration
d. Elution
d. Elution
18. An O-negative mother gave birth to an O-positive
baby. Her rosette test was positive. Which of the following
is true?
a. The test is invalid because of the mother's
ABO type
b. A Kleihauer-Betke test should be performed to
quantify the fetal maternal hemorrhage
c. The mother should be given a 300-mg dose
of RhIG
d. A weak D test should be performed on the baby
b. A Kleihauer-Betke test should be performed to
quantify the fetal maternal hemorrhage
19. In which of the following settings are platelet transfusions
not indicated?
a. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
b. Immune thrombocytopenic purpura with severe
intracranial hemorrhage
c. Massive transfusion
d. Vascular catheter placement, platelet count
24,000/mL
e. Brain biopsy, platelet count 62,000/mL
a. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura
20. An obstetric patient presents to the hospital with
marked vaginal bleeding and severe lower abdominal
pain. During placement of an intravenous catheter,
she was noted to have marked oozing. She is diagnosed
with disseminated intravascular coagulation
as a complication of her primary problem. She is
given cryoprecipitate and fresh frozen plasma before
going to the operating room. What element of cryoprecipitate
is important in treating this patient?
a. Factor I
b. Factor II
c. Factor VIII:c
d. Factor VIII:vWF
e. Factor XIII
a. Factor I
21. A patient's ABO blood type is determined by which
of the following?
a. Genetic inheritance and environmental factors
b. Genetic inheritance
c. Environmental factors
d. Immune function
e. Maternal blood type
b. Genetic inheritance
22. A trauma patient with type AB is seen at a rural hospital.
The hospital only has 3 units of type AB RBCs.
What blood type of RBCs can the patient receive as
an alternative?
a. Type O
b. Type B
c. Type A
d. None of the above
e. All of the above
e. All of the above
23. A genetic state in which no detectable trait exists is
called:
a. Recessive
b. Dominant
c. Incomplete dominance
d. Amorph
d. Amorph
24. Most blood group antigens are expressed as a result
of which of the following?
a. Autosomal recessive inheritance
b. X-linked dominant inheritance
c. Y-linked recessive inheritance
d. Autosomal codominant inheritance
d. Autosomal codominant inheritance
25. What blood type is not possible for the offspring of
AO and BO parents?
a. AB
b. A or B
c. O
d. All are possible
d. All are possible
26. How many molecules of IgM are needed to fix
complement?
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
a. 1
27. For lysis of red blood cells to occur after antigen-
antibody reaction, which compound is required?
a. Albumin
b. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD)
c. Complement
d. Antihuman globulin (AHG)
c. Complement
28. An end-point of tube testing other than agglutination
that must also be considered a positive reaction is
called:
a. Clumping
b. Mixed field
c. Hemolysis
d. Microscopic
c. Hemolysis
29. Mixed-field (mf) agglutination can be observed
in the:
a. DAT on a person undergoing delayed hemolytic
transfusion reaction
b. IAT result of a patient who has anti-Lea
c. DAT on a patient on high doses of penicillin
d. Typing result with anti-A of a patient who is A2
subgroup
a. DAT on a person undergoing delayed hemolytic
transfusion reaction
30. In which situation(s) may the ABO serum grouping
not be valid?
a. The patient has hypogammaglobulinemia
b. IgM antibodies are present
c. Cold autoantibodies are present
d. All of the above
d. All of the above
31. If you knew the DAT is positive, what would you
expect the Rh control to be when doing a weak D test
through AHG?
a. Negative
b. Positive
c. Mixed field
d. Hemolysis at 37 C would be seen
b. Positive
32. How can IgG antibodies be removed from red cells?
a. Elution
b. Adsorption
c. Prewarming
d. Neutralization
a. Elution
33. Testing needs to be done with an antiserum that is
rarely used. The appropriate steps to take in using this antiserum include following the manufacturer's
procedure and:
a. Performing a cell panel to be sure that the antiserum
is performing correctly
b. Performing the testing on screen cells
c. Testing in duplicate to ensure the repeatability of
the results
d. Testing a cell that is negative for the antigen and
one that is heterozygous for the antigen
d. Testing a cell that is negative for the antigen and
one that is heterozygous for the antigen
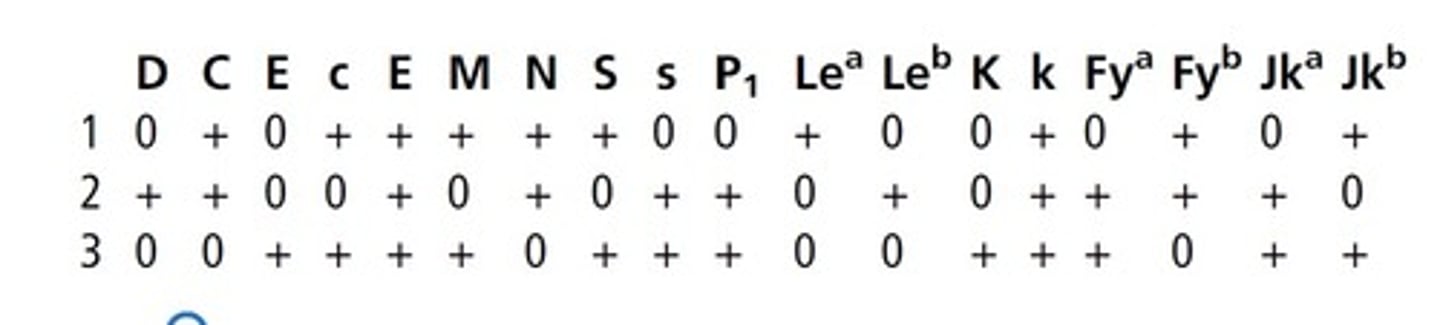
(see pic) 34. Based on the following antigram, which cell is heterozygous
for M?
a. Cell 1
b. Cell 2
c. Cell 3
d. None of the above
a. Cell 1
35. Which antibody can be neutralized with a specific
reagent?
a. Anti-D
b. Anti-Jka
c. Anti-M
d. Anti-Lea
d. Anti-Lea
36. Group O red blood cells are used as a source of commercial
screening cells because:
a. Anti-A is detected using group O cells
b. Anti-D reacts with most group O cells
c. Weak subgroups of A react with group O cells
d. ABO antibodies do not react with group O cells
d. ABO antibodies do not react with group O cells
37. The use of EDTA samples for the direct antiglobulin
test prevents activation of the classical complement
pathway by:
a. Causing rapid decay of complement proteins
b. Chelating Mg2+ ions, preventing assembly of C6
c. Chelating Ca2+ ions, preventing assembly of C1
d. Preventing chemotaxis
c. Chelating Ca2+ ions, preventing assembly of C1
38. Check (Coombs control) cells are:
a. Added to every negative antiglobulin test
b. Added to negative direct antiglobulin tests only
c. Used to confirm a positive Coombs' reaction
d. Coated with both IgM and C3d
a. Added to every negative antiglobulin test
39. What type(s) of red cells is(are) acceptable to transfuse
to an AB-negative patient?
a. A negative, B negative, AB negative, O negative
b. O negative only
c. AB negative only
d. AB negative, A negative, B negative only
a. A negative, B negative, AB negative, O negative
40. A nonbleeding adult of average height and weight
with chronic anemia is transfused with 2 units of
red blood cells. The pretransfusion Hgb is 7.0 g/dL.
What is the expected posttransfusion Hgb?
a. 8 g/dL
b. 9 g/dL
c. 10 g/dL
d. 11 g/dL
b. 9 g/dL
41. An IgA-deficient patient with clinically significant
anti-IgA requires which of the following?
a. Leukocyte-reduced fresh frozen plasma
b. CMV-seronegative RBCs
c. Irradiated RBCs and platelets
d. Washed RBCs
d. Washed RBCs
42. Anti-H will react weakest with blood from a person
with _____________.
a. Group O
b. Group A1
c. Group A2
d. Group A2B
b. Group A1
43. Which of the following antibodies do not match the
others in terms of optimal reactive temperature?
a. Anti-Fya
b. Anti-M
c. Anti-K
d. Anti-S
b. Anti-M
44. What antibody can an R1r patient make if transfused
with R2R2 blood?
a. Anti-D
b. Anti-C
c. Anti-E
d. Anti-c
e. Anti-e
c. Anti-E
45. What is the probability of finding blood negative for
the Jka and Fya antigens (23% of population is Jk
[a-] and 34% of population is Fy[a-])?
a. 5.1%
b. 51%
c. 7.8%
d. 78%
c. 7.8%
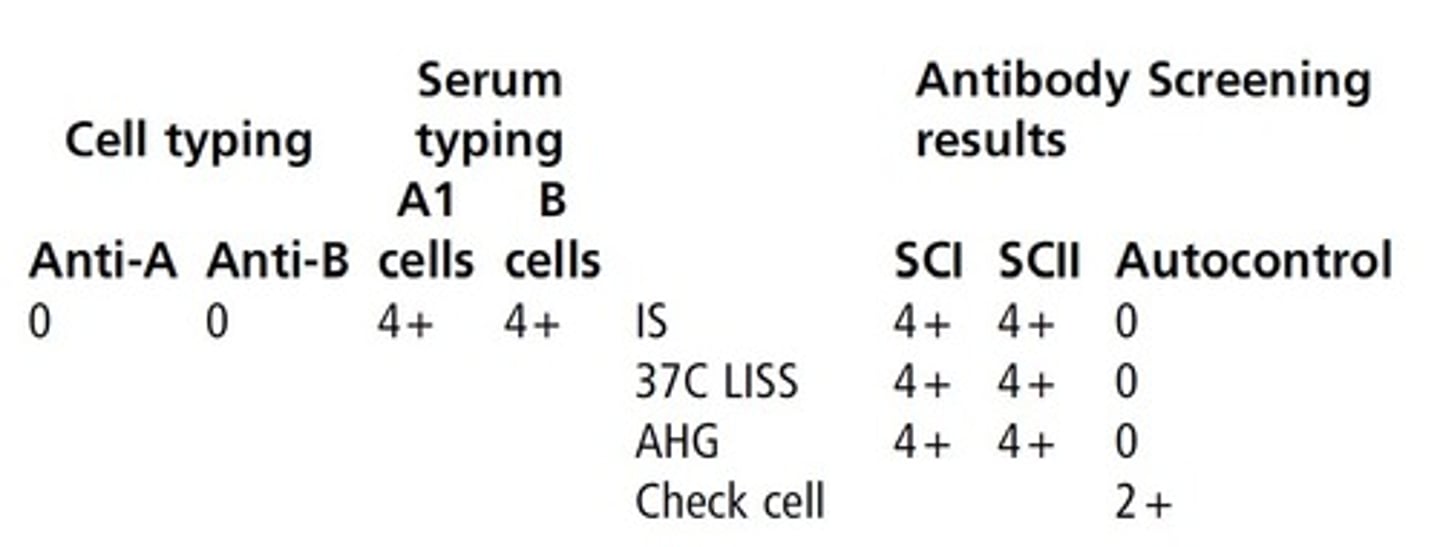
(see pic) 46. If the following patient's RBCs were tested against
anti-H lectin and did not react, this person would
be identified as a(an):
a. Acquired B
b. Secretor
c. Oh phenotype
d. Subgroup of A
c. Oh phenotype
47. If a person has the genetic makeup Hh, AO, LeLe,
sese, what substance will be found in the secretions?
a. A substance
b. H Substance
c. Lea substance
d. Leb substance
c. Lea substance
48. Before A and B antigens can be expressed, the precursor
substance must have the terminal sugar
_______________.
a. d-Galactose
b. N-Acetylgalactosamine
c. Glucose
d. L-Fucose
d. L-Fucose
49. A white female's RBCs gave the following
reactions: D+, C+, E-, c+, e+. The most probable
Rh genotype is:
a. DCe/Dce
b. DCe/dce
c. DCe/DcE
d. Dce/dCe
b. DCe/dce
50. If a D-positive person makes anti-D, this person is
most likely:
a. Partial D
b. D negative
c. Weak D as position effect
d. Weak D because of transmissible genes
a. Partial D
51. A serum containing anti-k is not frequently encountered
because of which of the following?
a. People who lack the k antigen are rare
b. People who possess the k antigen are rare
c. The k antigen is not a good immunogen
d. Kell-null people are rare
a. People who lack the k antigen are rare
52. A characteristic of the Xga antigen is that the Xga
antigen:
a. Has a higher frequency in women than in men
b. Has a higher frequency in men than in women
c. Is enhanced by enzymes
d. Is usually a saline reacting antibody
a. Has a higher frequency in women than in men
53. Which of the following is a characteristic of the Kidd
system antibodies?
a. The antibodies are usually IgM
b. The corresponding antigens are destroyed by
enzymes
c. The antibodies are usually strong and stable during
storage
d. The antibodies are often implicated in delayed
hemolytic transfusion reactions
d. The antibodies are often implicated in delayed
hemolytic transfusion reactions
54. Anti-E will react with which of the following cells?
a. RoRo
b. R1R1
c. R2R2
d. rr
c. R2R2
55. Which statement is not true concerning anti-Fya and
anti-Fyb?
a. Are clinically significant
b. React well with enzyme-treated panel cells
c. Cause hemolytic transfusion reactions
d. Cause a generally mild hemolytic disease of the
newborn
b. React well with enzyme-treated panel cells
56. Which of the following antibodies can be neutralized
with pooled human plasma?
a. Anti-Hy and anti-Ge:1
b. Anti-Cha and anti-Rga
c. Anti-Coa and anti-Cob
d. Anti-Doa and anti-Jsb
b. Anti-Cha and anti-Rga
57. Donors who have received RBC transfusion within
the last 12 months are deferred because:
a. Blood could transmit hepatitis or HIV
b. Donor red cell hemoglobin level may be too low
c. Donor health would prohibit the donation
process
d. There will be two cell populations in this
donor
a. Blood could transmit hepatitis or HIV
58. Autologous presurgical donations are not allowed
for which of the following patients?
a. Weigh less than 100 lb
b. Under the age of 14
c. With hemoglobin of 13 g/dL
d. With bacteremia
d. With bacteremia
59. Which of the following viruses resides exclusively in
leukocytes?
a. HCV
b. HBV
c. CMV
d. HIV
c. CMV
60. Which product is least likely to transmit hepatitis?
a. Cryoprecipitate
b. Plasma protein fraction
c. RBC
d. Platelets
b. Plasma protein fraction
61. In preparing platelets from a unit of whole blood, the
correct order of centrifugation is:
a. Hard spin followed by a hard spin
b. Light spin followed by a light spin
c. Light spin followed by a hard spin
d. Hard spin followed by a light spin
c. Light spin followed by a hard spin
62. Which antibody could cause hemolytic disease of the
fetus and newborn?
a. Anti-I
b. Anti-K
c. Anti-Lea
d. Anti-N
b. Anti-K
63. A group A, D-negative obstetric patient with
anti-D (titer 256) is carrying a fetus who needs an
intrauterine transfusion. The blood needed
should be:
a. Group A, D-negative RBC
b. Group A, D-negative whole blood
c. Group O, D-negative RBC
d. Group O, D-negative whole blood
c. Group O, D-negative RBC
64. Which of the following mothers should receive
RhIG?
a. A-negative mother; O-negative baby; no prenatal
care, anti-D in mother
b. AB-negative mother; B-positive baby; anti-D
in mother
c. O-negative mother; A-positive baby; no anti-D
in mother
d. A-positive mother; A-positive baby; no anti-D
in mother
c. O-negative mother; A-positive baby; no anti-D
in mother
65. How many doses of RhIG are indicated for a
Kleihauer-Betke reading of 0.6%?
a. 1
b. 2
c. 3
d. 4
b. 2
66. What should be done first if a mother types as O and
the baby types as AB?
a. Report the results with no further testing
b. Try to get a sample from the father
c. Recheck all labels, get new samples, if necessary,
and retest
d. Retype using all new reagents
c. Recheck all labels, get new samples, if necessary,
and retest
67. A newborn has a positive DAT.What is the best procedure
to determine the antibody causing a positive
DAT in this newborn?
a. An antibody titer on the mother's serum
b. An antibody panel on the mother's serum
c. An antibody panel performed on the eluate of the
mother's cells
d. An antibody panel performed on the eluate of the
baby's cells
b. An antibody panel on the mother's serum
68. Which of the following is(are) an example(s) of a
record-keeping error?
a. Use of correction fluid or tape
b. Using pencil
c. Documentation after the fact
d. All of the above
d. All of the above
69. Which of the antigens below is considered low
incidence?
a. Fya
b. S
c. C
d. Kpa
d. Kpa
70. Which of the antigens below is considered high
incidence?
a. Fyb
b. Vel
c. E
d. S
b. Vel
71. In performing tube testing, you see many mediumsized
agglutinates in a clear background. How would
you grade this reaction?
a. 2+
b. 1+
c. 4+
d. 3+
a. 2+
72. Of the following, which genotypes would result in
the B phenotype?
a. BB
b. AB
c. BO
d. a and b
e. a and c
e. a and c
73. How would you interpret the following reactions?
Forward Type Reverse Type
Anti-A Anti-B A1 Cells B Cells
0 0 4+ 4+
a. Blood type A
b. Blood type O
c. Blood type B
d. Blood type AB
b. Blood type O
74. Noting these reactions, if they patient needed blood
now, what type of blood should be transfused?
Forward Type Reverse Type
Anti-A Anti-B A1 Cells B Cells
4+ 0 1+ 4+
a. Blood type A
b. Blood type O
c. Blood type A2
d. Blood type A
b. Blood type O
75. Blood group antibodies made by type A and type B
people are predominantly which class?
a. IgE
b. IgA
c. IgG
d. IgM
d. IgM
76. Based on these reactions,what should be the next step?
Forward Type Reverse Type
Anti-A Anti-B A1 Cells B Cells
4+ 0 1+ 4+
a. Test the serum with A2 cells
b. Report the patient as type A
c. Test the cells with anti-A1 lectin
d. Both a and c
e. Request a new specimen
d. Both a and c
77. A "directed donor" unit of blood is defined as a unit
of blood from a person who gives blood for:
a. Relief of polycythemia or other blood disorder
b. His or her specific use only
c. First-degree blood relative
d. Another person he or she has specified
d. Another person he or she has specified
78. Before the patient can receive a directed donation
unit, the patient requires which of the following tests
to be completed?
a. Type and screen only
b. Type and screen and compatibility testing
c. Retype of patient and donor unit
d. No additional testing is required
b. Type and screen and compatibility testing
79. An 18-year-old female with a hematocrit of 38%,
temperature of 37 C, and blood pressure of 175/
90 mm Hg presents for whole blood donation. Based
on this information, would you accept, permanently
defer (PD), or temporarily defer (TD) the donor?
a. Accept
b. TD, blood pressure is too high for a person of
her age
c. TD, temperature is too high
d. PD, for all values listed
a. Accept
80. A 63-year-old man with a hemoglobin value of
130 g/dL and pulse of 80 beats/min, who received
human pituitary growth hormone (PGH) when he
was 10 years old, presents for whole blood donation.
Based on this information, would you accept, permanently
defer (PD,) or temporarily defer (TD) the donor?
a. Accept the donor
b. TD, because of the human PGH
c. PD, because of the human PGH
d. PD, because of the high hemoglobin value
c. PD, because of the human PGH
81. A 38-year-old female weighing 153 lb, who received
the rubella vaccine 2 months previously, presents to
donate whole blood. She also received 2 units of
packed cells after the delivery of her eighth child
8 weeks ago. Based on this information, would you
accept, permanently defer (PD), or temporarily defer
(TD) the donor?
a. Accept the donor
b. TD because of the packed cells 8 weeks ago
c. PD because of receiving blood products
d. TD because of the rubella vaccine
b. TD because of the packed cells 8 weeks ago
82. A22-year-old female witha cousinwithAIDSwhohad
taken aspirin the day before and with needle marks on
both arms presents to donate whole blood. Based on
this information,would you accept, permanently defer
(PD), or temporarily defer (TD) the donor?
a. PD, needle marks on both arms
b. TD, needle marks on both arms
c. PD, cousin with AIDS
d. TD, because of the aspirin
a. PD, needle marks on both arms
83. Each unit of blood must be tested for all of the following
except:
a. Anti-HIV 1/2
b. HBsAg
c. Anti-HCV
d. Antigen to HCV
d. Antigen to HCV
84. The principle of the HBsAg test is to detect which of
the following?
a. Antigen in patient's plasma
b. Antigen on the patient's RBCs
c. Antibody in patient's serum
d. Antigen and antibody in patient's serum
a. Antigen in patient's plasma
85. Cryoprecipitate is prepared by first thawing:
a. Fresh frozen plasma at 1 to 6 C, and then doing
a cold centrifugation to pack the cryoprecipitate
to the bottom so the plasma may be removed
b. Fresh frozen plasma at room temperature, then
placing in the freezer for 2 hours, then centrifuging
and removing the cryoprecipitate
c. Cryoprecipitate at 1 to 6 C, then pooling the
thawed cryoprecipitate in batches of 10 units,
then quickly refreezing
d. Cryoprecipitate at room temperature, then centrifugation
in the cold to concentrate the cryoprecipitate
to the bottom before adding more plasma
to reconstitute
a. Fresh frozen plasma at 1 to 6 C, and then doing
a cold centrifugation to pack the cryoprecipitate
to the bottom so the plasma may be removed
86. Platelets must be kept in constant motion for which
of the following reasons?
a. Maintain the pH so the platelets will be alive
before transfusion
b. Keep the platelets in suspension and prevent
clumping of the platelets
c. Mimic what is going on in the blood vessels
d. Preserve the coagulation factors and platelet
viability
a. Maintain the pH so the platelets will be alive
before transfusion
87. After thawing and pooling cryoprecipitate for transfusion
to a patient, the product should be stored at:
a. Room temperature
b. 1 to 6 C
c. 37 C
d. 0 C
a. Room temperature
88. Fresh frozen plasma must be thawed at which
temperature?
a. 1 to 6 C
b. Room temperature
c. 37 C
d. 40 C or higher
c. 37 C
89. Frozen red blood cells are prepared for transfusion
by thawing at:
a. Room temperature and then washing with saline
b. 37 C in a water bath and then washing with different
concentrations of saline
c. 37 C control incubator and then mixing well
before transfusion
d. 1 to 6 C for 2 days and then washing with different
concentrations of dextrose
b. 37 C in a water bath and then washing with different
concentrations of saline
90. Which is the most likely reason frozen deglycerolized
red blood cells would be used?
a. A patient with antibodies to a high-frequency
antigen
b. Pregnant women requiring intrauterine
transfusions
c. Emergency transfusion situations
d. Group AB Rh-negative patients
a. A patient with antibodies to a high-frequency
antigen
91. One indication for transfusion of thawed/pooled
cryoprecipitate would be replacement of which of
the following?
a. Factor X in hemophiliacs
b. Factor VIII in massively transfused patients
c. Fibrinogen
d. Volume
c. Fibrinogen
92. A contraindication for transfusing red blood cells to
a patient is if the patient:
a. Is massively bleeding
b. Has well-compensated anemia
c. Has bone marrow failure
d. Has decreased red blood cell survival
b. Has well-compensated anemia
93. Concerning the component and the required quality
control results, which of the following is a true
statement?
a. FFP must have 80 international units of fibrinogen
in 7 units tested
b. Cryoprecipitate must have 80 international units
of factor VIII
c. Leukocyte-reduced red blood cells must have
fewer than 3.3x1011 WBCs in each unit
d. Platelets must have no red blood cells
b. Cryoprecipitate must have 80 international units
of factor VIII
94. Fresh frozen plasma must be stored at:
a. Colder than -18 C for no longer than 1 year
from donation
b. Colder than -38 C for no longer than 1 year
from donation
c. Exactly -18 C for no longer than 1 year from
donation
d. -18 C to -38 C for up to 10 years from
donation
a. Colder than -18 C for no longer than 1 year
from donation
95. The storage temperature for packed red blood cells is
_______________.
a. 1 to 10 C
b. 1 to 4 C
c. 1 to 6 C
d. 20 to 25 F
c. 1 to 6 C
96. Platelets made from a single whole blood donation
should contain which of the following?
a. 3x1011 platelets in 90% of samples
b. 3.3x109 platelets in 75% of samples
c. 5.5x1010 platelets in 90% of samples
d. 10x1010 platelets in 75% of samples
c. 5.5x1010 platelets in 90% of samples
97. Frozen red blood cells must be stored at
__________________.
a. 180 C or less
b. 18 C or less
c. 32 C or less
d. 65 C or less
d. 65 C or less
98. The temperature for incubation of the indirect antiglobulin
test (IAT) should be ____________.
a. 24 C
b. 6 C
c. 37 C
d. 3710 C
c. 37 C
99. The temperature of a blood refrigerator without a
continuous recording device should be recorded:
a. Daily
b. Every 4 hours
c. Once every 24 hours
d. Every 30 minutes
b. Every 4 hours
100. When should quality control be performed on routine
blood typing reagents?
a. At the beginning of each shift
b. Once daily
c. Weekly
d. Only when opening a new vial
b. Once daily