Glencoe World History Chapter 4
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Minoan Civilization
a civilization that existed on the Mediterranean island of Crete
Mycenaean
of or relating to or characteristic of ancient Mycenae or its inhabitants

Homer
ancient Greek epic poet who is believed to have written the Iliad and the Odyssey (circa 850 BC)

Ionia
region of western Asia Minor colonized by Ancient Greeks

Epic Poem
a long narrative poem telling of a hero's deeds
Polis
a city state
Acropolis
served as a place of refuge during an attack and sometimes came to be a religious center on which temples and public buildings were built
Agora
served as a place where people could assemble and as a market
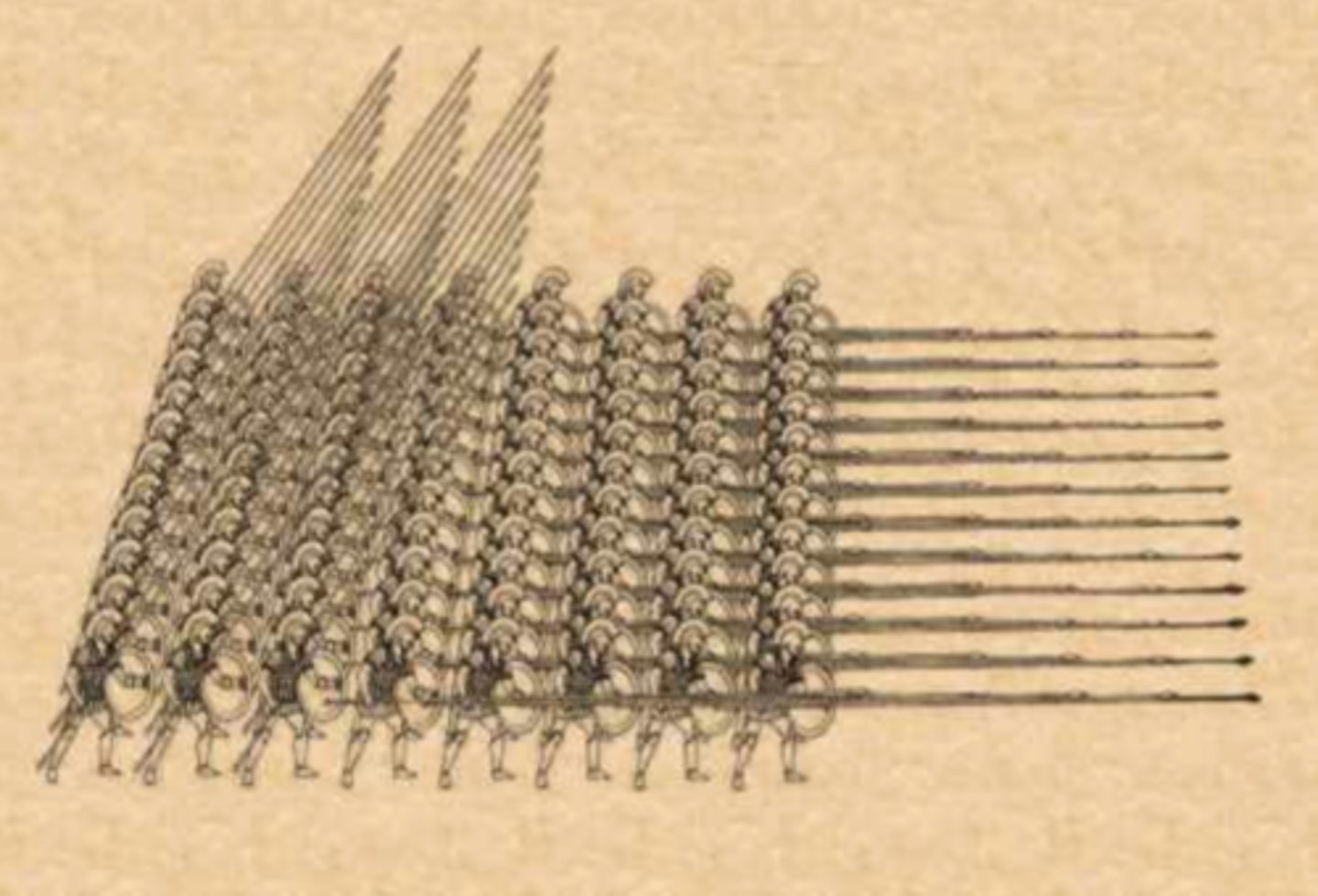
Hoplites
heavily armed infantry soldiers or foot soldiers

Phalanx
a military formation of foot soldiers armed with spears and shields
Democracy
A government by the rule of the many

Oligarchy
a political system governed by a few people
Sparta
an ancient Greek city famous for military prowess; seized more land when needed

Helots
Slaves to the Spartans that revolted and nearly destroyed Sparta in 650 B.C.E.
ephors
a group of five men who were elected each year and were responsible for the education of the youth and conduct of the citizens
Athens
the capital and largest city of Greece; enemy of Sparta

Solon
a reform-minded aristocrat
Cleisthenes
An aristocrat, created a council of 500 and helped form Athenian democracy

Darius
Persian ruler that seeked revenge on the Athenian navy

Xerxes
son of Darius; became Persian king. He vowed revenge on the Athenians. He invaded Greece with 180,000 troops in 480 B.C.

Delian League
Pact joined in by Athenians and other Greeks to continue the war with Persia
Pericles
Athenian statesman whose leadership contributed to Athen's political and cultural supremacy in Greece

Age of Pericles
a period of classical Athenian and Greek history in which Athens reached its highest power
Direct Democracy
system of government in which people gather at mass meetings to decide on government matters

Ostracism
procedure used by Athenian assembly in 5th century B.C. to banish a citizen for 10 years without revoking their rights; 6,000 votes were needed for banishment
Macedonia
an ancient kingdon ruled by Alexander the Great that conquered Greece and the Persian empire in the 300s BC
Rituals
another name for ceremonies or rites
Oracle
a sacred shrine where a god or goddess revealed the future through a priest or a priestess
Tragedies
the first Greek dramas; presented in a trilogy ... serious drama about common themes such as love, hate, war or betrayal
Aeschylus
writer of tragedies; wrote Oresteia; proposed the idea of having two actors and using props and costumes

Sophocles
Greek writer of tragedies; author of Oedipus Rex

Herodotus
the ancient Greek known as the father of history

Thucydides
considered the greatest historian of the ancient world

Philosophy
an organized system of thought
Pythagoras
Greek philosopher and mathematician who proved the Pythagorean theorem

Socrates
Athenian philosopher (ca. 470-399 B.C.E.) who shifted the emphasis of philosophical investigation from questions of natural science to ethics and human behavior.

Socratic Method
a method of teaching by question and answer
Plato
Philosopher (429 BC-347 BC) who studied under Socrates and questioned reality. He believed that studying ideas and forms held the truth to what is real and wrote the Republic, which described an ideal state with philosopher-kings, warriors, and masses. He also creates the Academy, an ancient school of philosophy. "How do we know what is real" "Philosophy begins in wonder"

Aristotle
Greek philosopher; teacher of Alexander the Great; knowledge based on observation of phenomena in material world

Philip II
king of ancient Macedonia and father of Alexander the Great (382-336 BC)

Alexander the Great
son of Philip II; received military training in Macedonian; conquered much land in Asia Minor, Syria, Egypt, and Mesopotamia; goal was to conquer the known world

Hellenisitic Era
the era in which the Greeks were imitated in other parts of the world due to spread of Greek ideals during the reign and conquests of Alexander the Great
Eratosthenes
Greek mathematician and astronomer who estimated the circumference of the earth and the distances to the moon and sun (276-194 BC)

Euclid
He is the father of geometry and wrote a book explaining geometry (the Elements)

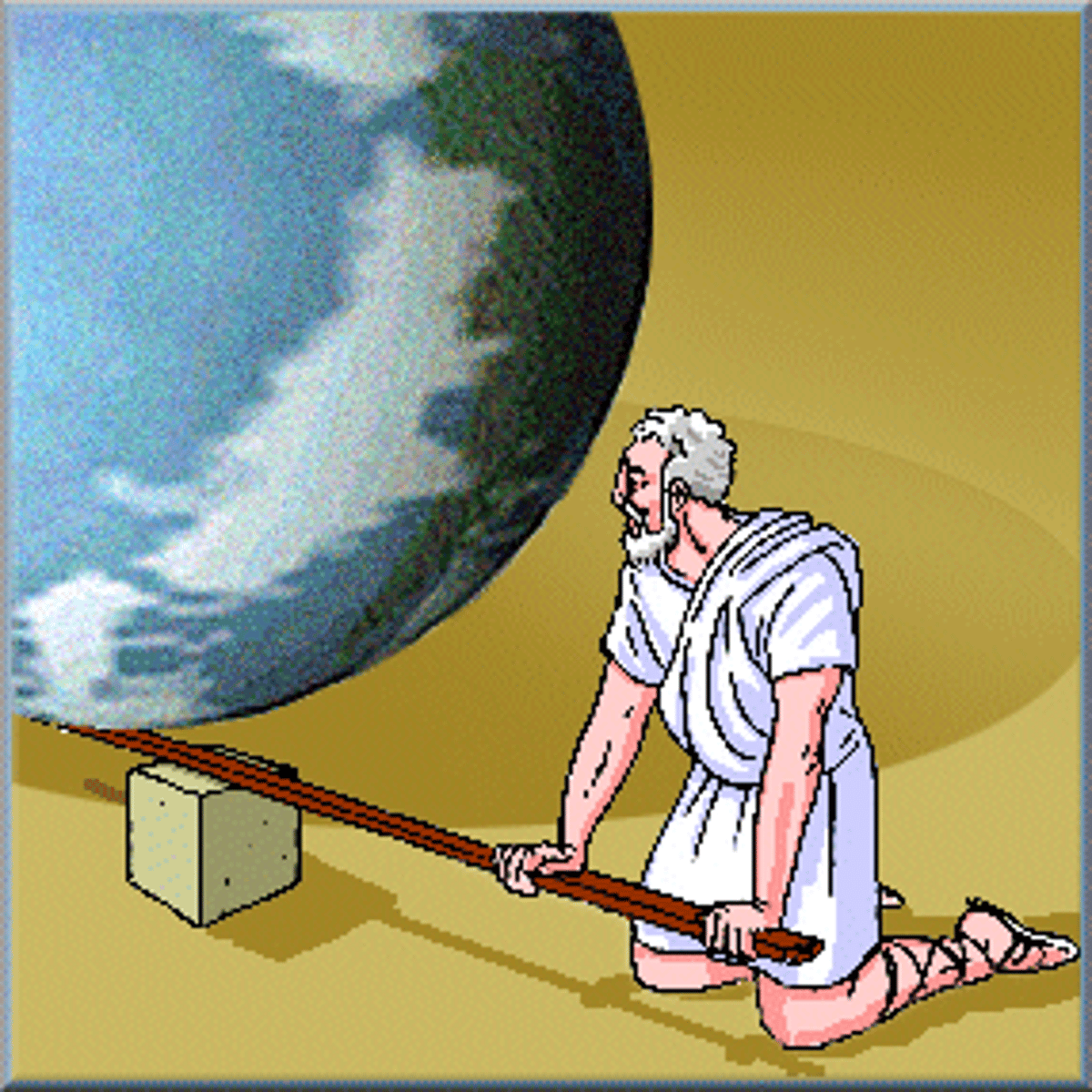
Archimedes
(287-212 BCE) Greek mathematician and inventor during the Hellenistic Era. He wrote works on plane and solid geometry, arithmetic, and mechanics. He is best known for the lever and pulley.
Epicureanism
philosophy founded by Epicurus in Hellenistic Athens; taught that happiness through the pursuit of pleasure was the goal of life

Stoicism
(philosophy) the philosophical system of the Stoics following the teachings of the ancient Greek philosopher Zeno

arete
excellence that is won in a contest or struggle.