CHM 1060 ~ CHP 9-11
1/143
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
144 Terms
IUPAC rules for naming alcohols
Name longest carbon chain which the hydroxyl group is attached.
Drop final -e and add suffix -ol.
Number the chain starting at the end nearest the hydroxyl.
Use appropriate number to indicate the position.
How do you number alcohols where the oh group is attached to a carbon atom in a ring?
The ring is numbered beginning with —OH group.
One 1 is omitted.
How are alcohols classified?
According to number of carbons attached to the carbon directly attached to the —OH.
Alcohols have higher boiling points than what because of what?
Higher boiling points than similar molecular weight hydrocarbons due to hydrogen bonding.
Nucleophilic substitution reactions
Capable of producing several families of compounds.
Nucleophile replaces an atom or group of atoms that is easily replaced usually Br and Cl.
Combustion.
CO2 + H2O
(True / false) alcohols are not flammable
False.
Alcohol dehydration
An alcohol molecule loses water to produce an alkene.
—OH and —H from a neighboring carbon is lost during dehydration.
How is the major product formed in alcohol dehydration?
Formed from losing —H from carbon atom that has fewer H atoms.
Oxidation
Gaining of oxygen atoms
Loss of hydrogen
Reduction
Loss of oxygen atoms
Gaining of hydrogen atoms
Organic oxidation. What are the oxidizing agents? What alcohols can do this reaction?
Increases the number of c—o bonds and / or decreases the number of c — h bonds.
KMnO4, K2Cr2O7, H2CrO4
Only primary and secondary alcohols can perform this reaction.
What happens when alcohols are oxidized by K2Cr2O7 in organic oxidation?
Carbonyl group is formed with a double bond.
The —OH and a —H on the carbon carrying the —OH are lost.
Ketones
Have a carbonyl carbon that is attached to two other carbon atoms.
Aldehydes
Have a carbonyl which is attached to one hydrogen atom and either a second hydrogen or a carbon atom.
How do name aldehydes and ketones.
Parent numbered from end nearest the carbonyl.
Aldehyde carbonyls are always the first carbon counted, but not indicated in the name.
Aldehyde: drop “e” and add “al”
Ketone: drop “e” and add “one”
Do ketones and aldehydes and ketones have higher or lower boiling points than alcohols and why? What forces do they have?
No they have lower boiling points than alcohols because they cannot hydrogen bond. They do have LDFS and dipole forces.
What can aldehydes be oxidized into?
Aldehyde can be directly oxidized into carboxylic acids.
What will strong oxidizing agents oxidize alcohols into?
Aldehydes.
Catalytic hydrogenation
Can reduce the carbonyl of aldehydes and ketones.
Biochemistry
Study of chemical substances found in living organisms and the chemical interaction of these substances with each other.
Biochemical substances
Chemical substances found within a living organism
Bioinorganic substances
Water and inorganic salts
Bioorganic substances
Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
What would happen to biochemical substances if they were isolated compounds?
The substances have no life in and of themselves.
What happens when these chemical substances are gathered together in a cell?
Their chemical interactions are able to sustain life.
Carbohydrates. Why are they broken down? How do plant produce it?
Broken down to produce energy
Plants produce majority through photosynthesis
How much do carbohydrates account for in dry plant material?
75%
Functions of carbohydrates in the human body. (5 + 2 exs)
Provide energy through process called oxidation
Short term energy reserve.
Ex: glycogen
Provides carbon atoms for synthesis or proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids.
Can link with lipids to become structural components of the cell membrane.
Can also be linked to proteins.
Glycoproteins: Function in cell-cell recognition and signaling processes.
Monosacchardies. Empirical formula? How many? What there function? What functional group(s) do they contain? How many carbons? How soluble are they in water? What state are they in at room temp? Examples (2)?
Empirical formula: CnH2nOn.
1
Building blocks of other sacchardies,
Contain a ketone or aldehyde functional group.
6-C or 3-C.
Highly soluble in water.
Crystalline solid at room temp.
Ex: glucose + fructose
Carbohydrate
Polyhydroxy aldehyde, ketone, or a compound that produces such substances upon hydrolysis.
Disaccharide. How many monosaccharide residues? What are they linked by? Shape? Are they water soluble? Examples (2)?
Contain 2 monosaccharide residues.
Linked via glycosidic bond.
Crystalline.
Water soluble substances.
Ex: Sucrose, lactose.
Oligosaccahardies. How many monosaccharide residues? How often are free oligosaccharides encountered in biochemical systems? Example?
3 to 10 monosaccharide residues.
Free oligosaccharides are not often encountered in biochemical systems.
Ex: Raffinose.
Polysaccharides. How many monosaccharide residues? How do the number of monosaccharides vary? Examples (3)?
Contains more than 10 monosaccharide residues.
Number of monosaccharide units varies from a few 100 units to 50,000 units.
Ex: starch, cellulose, glycogen.
Aldoses
Contain an aldehyde.
Ketoses.
Contain a ketone.
How are monosaccharides classified?
Number of carbon atoms.
3-C atoms.
Trioses.
4-C atoms.
Tetroses.
5-C atoms.
Pentoses.
6-C atoms.
Hexoses.
Stereoisomers.
Same molecular formula,
Same atomic connections.
Different 3-D shape.
Only interchangeable only by breaking bonds.
Mirror image
Reflection of an object in a mirror classes of objects base on images.
Non-superimposable mirror images. Does it have a chiral center or not?
Images where not all the points can coincide when images are laid upon eachother.
Chiral center.
Superimposable mirror images. Does it have a chiral center or not?
Coincide when images are laid upon each other,
Achiral center (w/o chiral center)
Enantiomers. How can you intercovert?
Non-superimposable mirror image forms of a molecule.
Only way to intercovert is to break bonds.
Chiral.
Used to describe objects that cannot be superimposed on their mirror images.
Chiral carbon center
Carbon that is attached to four different atoms or groups of atoms.
Pairs of enantiomers. Are they similar? Are they properties the same? Are the difficult to separate? How hard is to to tell which is present?
Nearly identical.
Physical properties are the same. Make them hard to separate.
Hard to tell which enantiomer is present.
As the number of chiral carbon atoms increases… the total possible number of stereoisomers. ____
increases.
How to find maximum # of stereisomers?
2n
Diastereomers.
Stereoisomers that are not enantiomers.
How are carbohydrate usually drawn drawn as?
Fischer projections.
What do horizontal lines in Fischer projections represent?
Bonds towards viewer.
What do vertical lines in Fischer projections represent?
Bonds away from viewer.
D isomer
—OH on the stereocenter to the right
L isomer
—OH on the stereocenter to the left.
Are D or L isomers most common?
D isomers
How are D and L isomers counted and determined?
Counting begins at the carbonyl group.
The highest numbered chiral center is used to determine D or L configuration.
D-Sugars
—OH attached to chiral carbon atom furthest from the carbonyl points right.
L- sugars
—OH points left.
Majority of monosaccharides have how many carbons?
Pentoses and hexoses
Where do D-ribose and D-2-deoxyribose differ at?
C-2.
D-ribose has a OH at C-2.
D-2-Deoxyribose has a H at C-2.
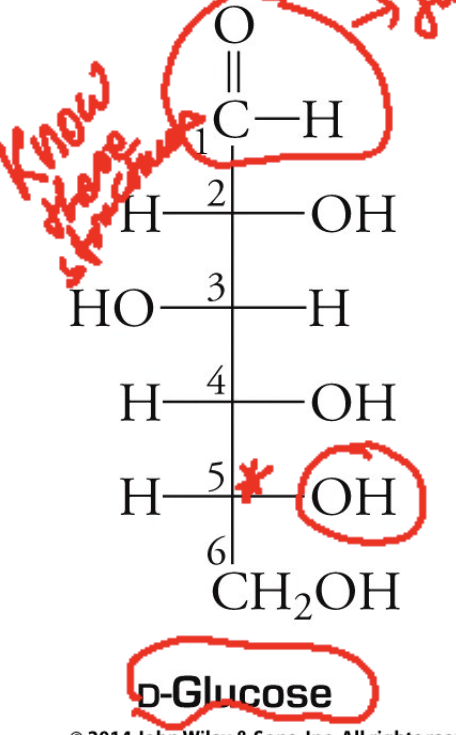
D-glucose. What is it? When it is released? What is it a key reactant in?
Dextrose or blood sugar.
Released when starch and glycogen are broken down.
Key reactant in reactions that produce compounds used to drive non-spontaneous biochemical reactions.
D-glucose structure
L-glucose structure

D-galactose structure
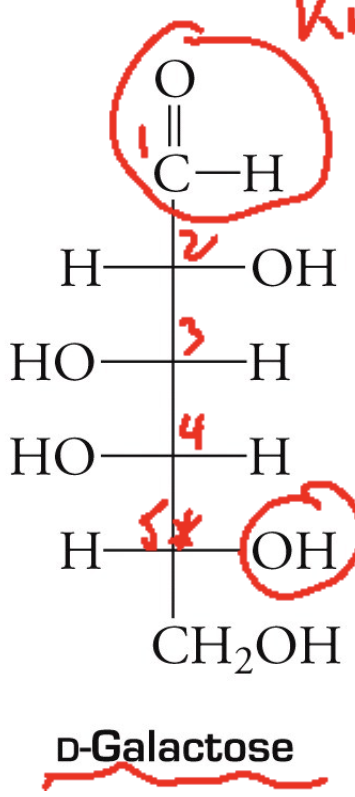
D-galactose. What does it combine with to make lactose? What does lactose do? What does galactose convert to when lactose is digested? What can inhibit this transformation?
Glucose + galactose = lactose
Lactose gives milk its sweetness.
Galactose is converted to glucose.
Genetic disorder can inhibit the transformation.
D-fructose. What is it? What is found in nature? What is it present in? How much of honey does it make up? What it is a key role in?
Fruit sugar.
Ketose most often found in nature.
Present in fruit.
40% of honey.
Key role in energy production.
D-fructose structure

Reduction
C=O of an aldehyde or ketone react with hydrogen + Pt catalyst or appropriate enzyme. Produce an alcohol.
Benedict’s reagent. What does it oxidized? What does it oxidize in the reaction, what does it reduce? What is a compound called when a benedict’s test is positive? What are ketones able rearrange into? What does this cause? What is it useful for?
Oxidizes aldehydes.
Sugar is oxidized while Cu2+ is reduced.
+ Benedicts~ Reducing sugar.
Ketones are able to rearrange into aldehydes to give a positive Benedict’s test.
Useful for monitoring diabetes and tests for sugars in urine.
What happens when a aldehyde and alcohol react?
Hemiacetal forms.
What do monosaccharides form? How many can they form? What is carbon 1 always?
Cyclic hemiacetals.
Form 2.
Carbon 1 is always the one that is the aldehyde or ketone in the linear forms.
Anomers.
Cyclic monosaccharides that differ only in the position of substituents on the anomeric carbon atom.
What are the 2 forms of D-glucose?
alpha-form
beta-form
Alpha-form of D-glucose.
Where the —OH of the Cl and CH2OH of C5 are on the opposite sides.
Beta-form of D-glucose.
Where —OH of Cl and CH2OH of C5 are in the same side.
How to fully name monosaccharides?
Specify if alpha or beta and its ring size.
Furanose.
5 membered ring
Pyranose
6 membered ring
What happens when a hemicetal and alcohol react?
Acetal forms.
When can a acteal be formed? What is the acteal referred to? What is the bond to the new —OC group called?
When a cyclic monosaccharide reacts with another sugar.
Acteal referred to as glycoside.
The bond to new —OC group is glycosidic bond.
How are glycosidic bonds named? What does alpha and beta refer to? What is then listed?
Named systematically.
Alpha or beta refers to the oxygen connecting to two residues.
The connected carbons are then listed.
What is sucrose the disaccharide of?
D-glucose and d-fructose.
Lactose. What is it made up of? Joined by what? What is milk rich in? What does the enzyme lactase hydrolyzes?
Beta-D-galactose unit and D-glucose unit.
Joined by a beta(1-4) glycosidic linkage.
Milk is rich in the disaccharide lactose.
Enzyme lactase hydrolyzes beta(1-4) glycosidic linkages.
What are the two types of polysaccharides?
Homopolysaccharides
Heteropolysaccharides
Homopolysaccharides. Examples (2)?
Composed of just one type of mono.
Cellulose and starch.
Heteropolysaccharide. Examples (2)?
Composed of more than one type of mono.
Glycogen and hyaluronic acid.
Cellulose. Important to what? What do humans lack?
Important to structure of plants.
Humans lack the enzyme to hydrolyze cellulose.
Starch. What do the glycosidic bonds help the molecule do?
Energy storage for plants.
Glycosidic bonds cause the molecule to coil up into helical shapes.
Glycogen.
Animal starch. Energy storage molecule.
Hyaluronic acid.
Lubricating fluid surrounds joints and the vitreous humor present inside the eye.
Lipids
Organic compounds that are insoluble or partially soluble in water + highly soluble in polar solvents.
How do you classify lipids?
Biochemical function.
Saponification
Classification of lipids based on biochemical function give examples for each.
Energy storage lipids (Triacylgylerols)
Membrane lipids (Phospholipids, glycolipid, cholesterol)
Messanger lipids (steroid hormones, eicosanoids, vitamins)
Emulsification lipid (Bile acids, bile salts)
Protective coating lipids (waxes)
Classification of lipids based on saponification function give examples for each.
saponifiable lipids (Triacylglycerols, waxes, phospholipids)
Nonsaponifiable lipids (Cholesterol, eicosanoids, steroids hormones, bile acids, and bile salts).
Fatty acids. Do they have an even or odd number of atoms? How many C atoms do short, medium, and long chain fatty acids have?
Naturally occurring mono carboxylic acids with linear carbon chains.
Have an even number of atoms
Short chain fatty acids contain 4-6 C atoms.
Medium chain fatty acids contain 8-10 C atoms.
Long chain fatty acids contain 12-26 C atoms.
Saturated fatty acid. Where does numbering start? What is the structural notation and what is an example? How are there boiling and melting points? How packed are there hydrocarbon tails together? As you increase LDFS what increases also? As number of carbons increase what also increases?
Only single C bonds.
Numbering starts from end of —COOH group.
Structural notation: Indicates number of C atoms
Example: (16:0) 16 C atoms and 0 double bonds.
High boiling and melting points.
Hydrocarbon tails closely packed together.
Increase LDFS, increase hydrocarbon chain length
Increase number of carbons, increase boiling and melting point.
Unsaturated fatty acid. Monounsaturated? Polyunsaturated? Up to how many double bonds are found in biochemically important PUFAS? What type of bonds cannot pack tightly together? What is the result of this?
Have 1 or more C=C bond.
Mono: 1 C=C bond.
Poly: 2 or more C=C bond.
Up to 6 double bonds are found in biochemically important PUFAS.
Cis-double bonds cannot pack tightly, this results to lowering the amount of intermolecular forces and also leads to decreased melting and boiling points.