Week 6: Precision Medicine
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Q: What is the goal of precision medicine in drug treatment?
A: To select drugs based on a patient's individual characteristics rather than trial and error.
Q: Why is the trial-and-error method insufficient?
A: Not all patients benefit, and some experience adverse effects.
Q: How does genetic classification improve treatment?
A: It allows personalized drug choices tailored to a patient’s molecular profile
Q: What determines the best breast cancer treatment?
A: Molecular type: ER+/PR+, HER2+, or Triple-negative.
Q: Which breast cancer type benefits most from standard chemotherapy?
A: Triple-negative breast cancer. Because nothing that it can specifically target like estrogen/progesterone receptors or HER 2
How to treat ER+/PR+ most specifically
Tamoxifen (binds to estrogen receptor causing proliferation of these cells)
How to treat HER2 most specifically?
Trastuzumab (Herceptin)(prevents from sending growth and proliferation signals)
Q: What is pharmacogenomics?
A: The study of how genes and DNA variants influence disease and drug response.
Q: Why are polygenic diseases harder to study?
A: They involve many genes contributing small effects.
Q: What does a GWAS (Genome-Wide Association Study) identify?
A: SNPs(single nucleotide polymorphis) associated with disease that are common in patients and uncommon in non-patients.
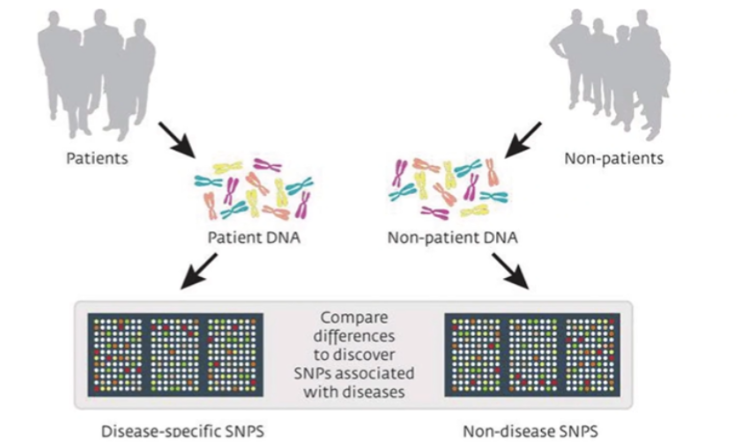
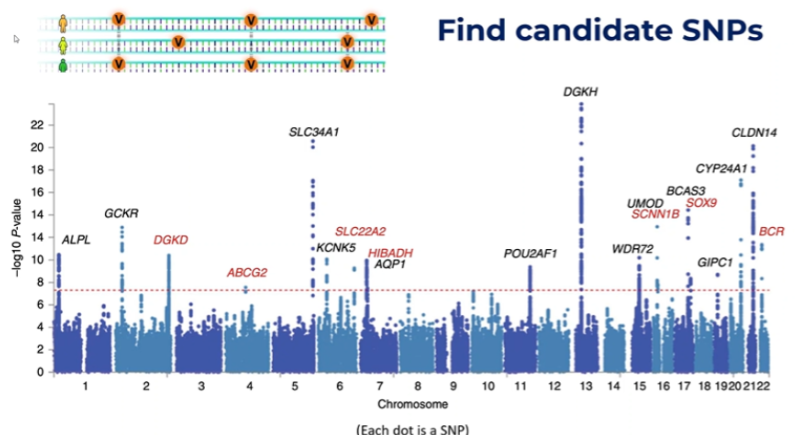
Q: What does the Manhattan plot display in GWAS?
A: Each dot represents an SNP; those above the significance line are candidate SNPs for investigation.
What is a SNP
single nucleotide polymorphisms
Q: What is a polygenic risk score?
A: A score representing cumulative risk based on multiple disease-associated SNPs

Q: How can polygenic risk scores help patients?
A: They guide preventive advice like yearly screenings or lifestyle counseling.
Q: What are the main steps after identifying candidate SNPs?
A: Validate genes in the lab, study gene-gene interactions, create risk scores, and inform patients/physicians. Then can use to make clinical decisions.
Q: Why is cost an important factor in precision medicine testing?
A: Sequencing ranges from one gene to whole genomes, with varying costs.
Q: Why consider the cost of adverse events?
A: Avoiding severe side effects can save money and improve patient safety.
Q: Why might insurance companies be reluctant to cover sequencing?
A: Benefits may appear years later, possibly after the patient has switched insurance.
Q: What risk comes with direct-to-consumer genetic testing?
A: Patients may misinterpret results without professional guidance. Genetic results can cause fear, confusion, or life-altering decisions.
Q: Why did Claire seek ApoE4 testing?
A: Family history: great-grandmother, grandmother, and mother had Alzheimer's.
Q: What difficulty did Claire face when seeking testing?
A: Turned away by multiple physicians because she had no symptoms.
Q: What happened after she got her results?
A: Received results without counseling, felt devastated, moved to a state with legal physician-assisted suicide.
Q: How did Josh learn he had two copies of ApoE4?
A: Through a workplace genetic testing study.
Q: Why did Josh struggle after receiving his results?
A: Felt unprepared; little medical guidance beyond “diet and exercise.”
Q: Why did Josh criticize direct genetic testing?
A: Believed it was unethical to give people alarming results with no actionable medical treatment.

What is V on here
Variants on the SNPs
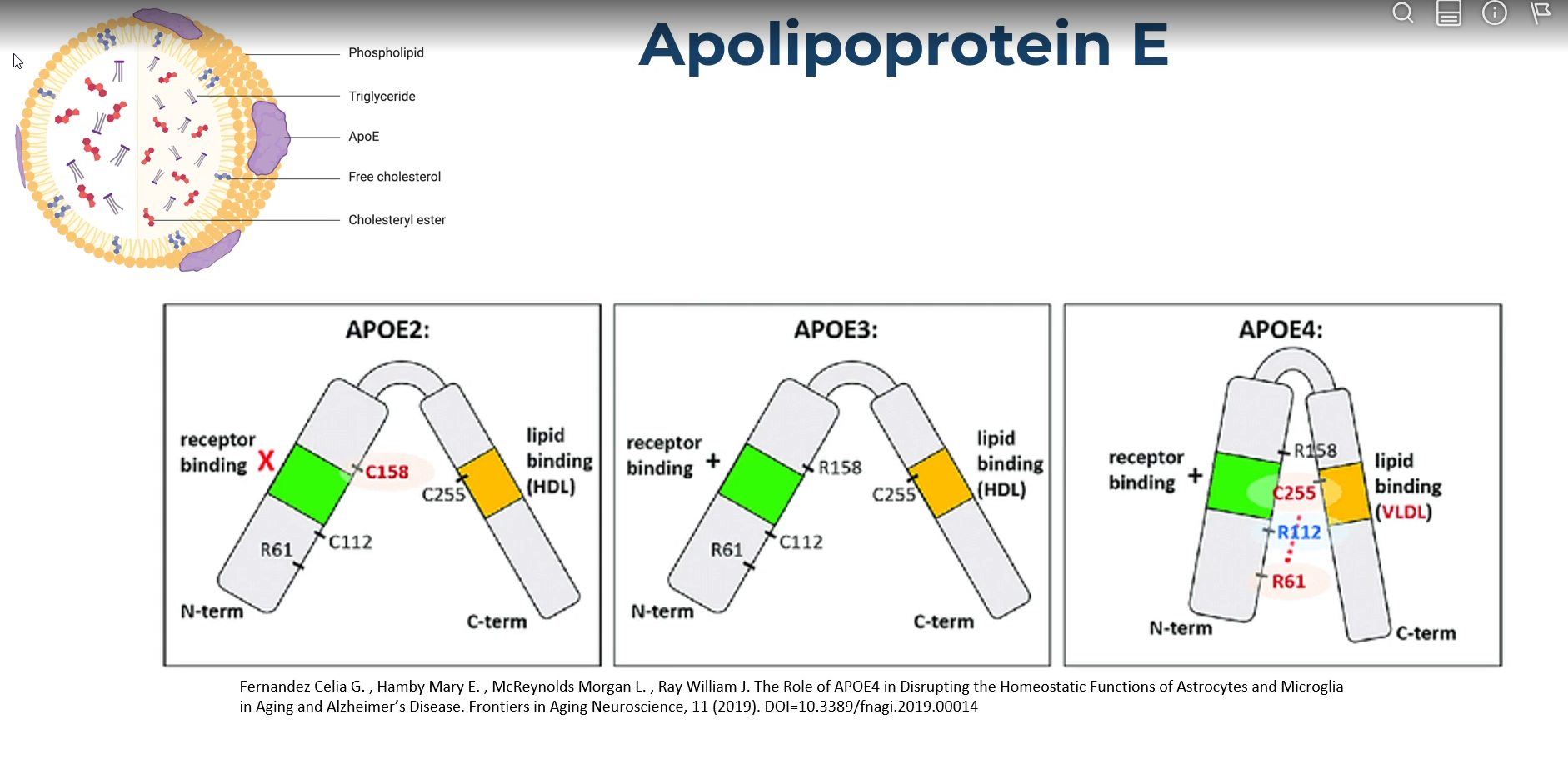
Q: What does ApoE do in the body?
A: Helps cholesterol particles dock and distribute lipids to cells.
Q: Which lipoprotein carries ApoE for healthy lipid regulation?
A: HDL (good cholesterol).
Q: How does ApoE2 affect Alzheimer’s risk?
A: Decreases risk (protective).
Q: How does ApoE2 affect cardiovascular risk?
A: Increases risk for early CVD due to having C158 (as opposed to standard R158) which inhibits receptor binding
Q: How does ApoE3 affect Alzheimer’s risk?
A: Neutral/average risk.
ApoE3 Alleles
R158, C112
ApoE2 Alleles
C158, C112,
ApoE4 Alleles
R158, R112; R112 variant causes interaction between C255 and R61
Q: How does ApoE3 affect cardiovascular risk?
A: Neutral/average risk.
Q: How does ApoE4 affect Alzheimer’s risk?
A: Greatly increases risk in a dose-dependent manner.
Q: How does ApoE4 affect amyloid-β (Aβ) in the brain?
A: Worst clearance; because it promotes very low density lipoprotein binding instead of standard high density lipoprotein binding
Apolipoprotein E image
Q: Risk of Alzheimer’s with 0 copies of ApoE4?
A: ~9%.
Q: Risk of Alzheimer’s with 1 copy of ApoE4?
A: ~30%.
Q: Risk of Alzheimer’s with 2 copies of ApoE4?
A: Up to ~90%.
Q: How many Americans have 1 copy of ApoE4?
A: ~75 million.
Q: How many have 2 copies of ApoE4?
A: ~7 million.