IZA Test 4
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
114 Terms
What are some reasons why we manage populations?
-biodiversity
-ecosystem services
-genetic diversity (AZA)
-space in zoos (AZA)
What is biodiversity
Variety of ecosystems, species, populations within a species, and genetic diversity within a species
What are some examples of ecosystem services?
Oxygen production
Climate regulation
Pest/disease control
Carbon sequestration
Nutrient cycling
Pollination
What is genetic diversity?
The variety of alleles and genotypes present in a population, species, or group of concern
What 4 ways is genetic diversity generated?
-mutation
-migration
-selection (natural and artificial)
-genetic drift
T/F: Genetic diversity is usually reduced in small populations and species of conservation concern
true
What are the IUCN'S 3 reasons for conserving genetic diversity?
1. needed for populations to evolve and adapt to environmental change
2. Loss of genetic diversity is usually associated with inbreeding, reduction in reproduction, and survival
3. contributes to ecosystem diversity which makes ecosystems more resilient to environmental shocks
As genetic diversity decreases reproductive fitness ____?
decreases (positive correlation)
What is genetic drift?
Allele frequencies of a population change over generations due to chance
Is genetic drift more powerful in large or small populations?
small
What is genetic fixation?
100% frequency of an allele (no diversity for that allele)
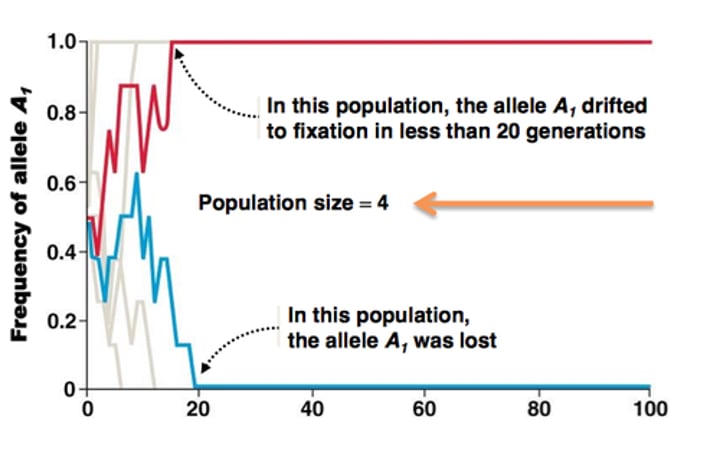
What are the two extreme outcomes of genetic drift?
-allele loss
-allele fixation
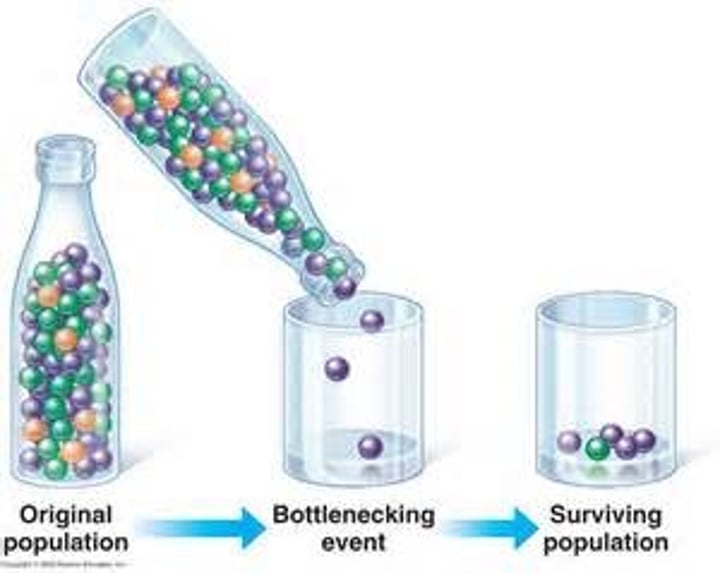
What is a genetic bottleneck?
drastic decrease in a population size and therefore the gene pool.
How many Mauritius kestrels are left?
4 birds (1 breeding pair)
What genetic factors are enhanced and reduced regarding the Mauritius kestrel's declining population?
genetic drift (enhanced)
selection (reduced)
What is the Isle Royale?
-national park in lake superior that is closed to hunting
-in winter creates an ice bridge from canada to michigan where animals cross
-predator prey observations
What happened with the Isle Royale wolves?
canine parvovirus hit the population of wolves causing a genetic bottle neck in the population and the inbreeding coefficient to increase drastically
How much genetic diversity does AZA aim to maintain in their captive managed populations?
>90% genetic diversity for 100+ years or 10 generations
what does the AZA do when genetic diversity is low?
-add founders
- genetic manipulation
What is the main reason for surplus animals?
space limitations
what are population managers main concern when it comes to surplus animals?
potential genetic contribution to population viability
what is the institutions main concern when it comes to surplus animals?
display and care of individuals in a physical setting
What are the 2 designations for surplus animals?
1. population managers: individuals not necessary for the long-term genetic and demographic management of a captive population
2. Institution: individuals held but no longer desired for display or breeding
What are the zoos 4 responsibilities when it comes to surplus animals?
-research and apply contraception
-population manage,.ment
-improve amount of higher quality off exhibit space
-develop retirement facilities
What are some ways surplus animals arise?
-number of males
What are some reasons why genetic value of an animal would change?
-animals having a high genetic representation
-# of males exceeds what is needed
-new imports lower the genetic value of existing animals
What is the appeal of babies in the zoo sphere?
babies = conservation success
increase attendance
media coverage
How do RCPs create surplus animals?
choosing to phase species out
What is an RCPs main focus on how they build sustainable populations?
keeping fewer species in order to have higher capacity to build sustainable populations
What is an RCPs success dependent on?
institutions following their recommendations when developing their ICPs
How can an institution reduce surplus animals?
Integration of both regional and institutional planning
Who is responsible for the disposition of the animals when they are phased out?
the holder institutions
What is one of the most sensitive public relations issues that zoos face?
surplus animals
What are some options for dealing with surplus animals?
-placement in other zoos
-dealers
-off exhibit holding
-population culling
-sanctuary placement
-research facilities
-non zoo facilities
-private breeders
-wild release
what is the most desirable option for dealing with surplus animals?
placing them in other AZA institutions
What is the issue with giving surplus animals to dealers?
-AZA member dealers not common
-hard to know where the animal will end up
What is the most common way to deal with surplus animals?
off-exhibit holding warehouses
T/F: Off-exhibit areas usually are as good as exhibit space.
false
What is the most controversial option when it comes to dealing with surplus animals?
culling
Where is culling prohibited?
germany
why would we cull an animal species in zoos?
Prevents animals from ending up at a facility that will not give animals proper care
why are sanctuaries not generally considered a viable option when it comes to placing surplus animals there?
Sanctuaries themselves have limited space and resources
Difficult to determine the level of care
What is translocation?
Movement of wild individuals from one part of their range to another for conservation purposes
where is translocation most common?
nature preserves
T/F: The effects of disease is greater is smaller populations than large?
true
T/F: Disease is a greater concern during translocation than it is between captive and wild populations.
false: Greater concern with captive to wild populations than withtranslocation
What are some ways we can lower disease risks?
Pre-release exam
Quarantine period before release
Avoid contact with/housing near similar or same species
Monitor necropsy results
How can an animal's/species behavioral competence change when kept in captivity?
-miss developmental opportunities
-genetic changes from adapting in captivity
-some become easier to train than others
What are some natural behavioral skills we teach animals in captivity?
Orientation and navigation
Foraging
Finding suitable nest/breeding sites
Predator avoidance
What are the three stages a captive breeding population goes through from least to most sustainable?
founder > growth > self sustaining
Reintroduction populations are typically ____?
small
What are small reintroduction populations greatly effected by?
stochasticity (random events)
-disease
-storms
-drought
what is the allee effect?
a population declines even though the numbers may seem healthy enough for breeding
What type of species does the Allee effect, effect the most?
social species
Members of an AZA Management Group must meet what criteria?
-Be a paid employee of their facility
-Uphold TAG business confidentiality
-Have proficiency in AZA web resources, internet, and email access.
-organization, communication, facilitation, conflict resolution skills
Who is required to create an institutional collection plan?
AZA zoos
Within an institution, collection plans are developed for each ____
taxa
ICP stands for
institutional collection plan
RCP stands for
Regional collection plan
This plan recommends species for management by TAGs
RCP
An ICP must be evaluated and submitted to AZA every ___ years
5
What is considered during the collection planning process?
AZA population status
IUCN status
public/zoo interest
This group oversees and supports AZA animal programs
APM committee
TAGs consider the needs of ____ when selecting species for management
AZA facilities
certified related facilities
sustainability partners
Surplus animals are defined as ____
off spring
animals no longer managed by a TAG
animals who are no longer reproducing
This group manages ~500 animal programs
APM committee
who creates RCPs
TAGs
This group creates specialist groups
IUCN
These populations are potentially sustainable
provisional SSPs
These populations are the most sustainable
secure ssp
Why do zoos need to manage populations?
limited space
maintain biodiversity
preserve genetic diversity
Genetic diversity is a measurement of ______ in a population
alleles
Who is the final authority on interpreting AZA standards?
accreditation committee
List some AZA accreditation standards
-animal care manuals must be available to staff
-zoos must have a records management system
-enrichment must be documented
What does BTP stand for
breeding and transfer plan
In order for a population to be considered for SSP designation what % of the managed population should be housed in AZA member facilities?
>50% of individuals
In order for a population to be considered for SSP designation the species must be held in at least how many AZA facilities?
15
How long do provisional SSP populations have to meet the eligibility criteria, develop goals, and make significant progress?
5 years
Signature SSP programs must publish at least _____ BTP every _____ years.
1, 3
A Secure SSP is a species we can be reasonably certain will still be present in zoos and aquariums in _____ years in a robust, viable, healthy, biologically sound population
100
What are some reasons why an animal may be deemed OUT of the SSP population?
age
reproductive status
demographic/genetic characteristics
institutional needs
global ex situ population management
Are government owned species eligible to be SSP programs?
no
What does GSMP stand for?
Global Species Management Plans
What does SMAART goal stand for?
Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Agreed upon, Realistic, Time
What does CPM stand for?
committee for Population Management
What does CRF stand for?
certified related facilities
T/F: CRFs also undergo a thorough accreditation review process?
true
TAGs work with SSP coordinators to set at least how many SMAART goals for each SSP program in its purview?
3
The first and second SMAART goals for the populations must relate to efforts to improve or maintain the population's ______ and ________.
viability and sustainability
The Time-bound element of SMAART goals for Provisional SSPs should not exceed ______ years, or one RCP cycle.
5
Provisional SSP goals must focus on which areas of the assessments to meet Signature SSP status?
genetics, demography, husbandry, and space and interest
What does AZA CMWS stand for?
AZA Conservation, Management, & Welfare Sciences Department
For SSPs, what is the ideal member capacity for the management group?
7-15 individuals
What does CGF stand for
conservation grants fund
Do SSPs manage in or ex situ species populations?
ex situ
at are some zoo research subjects?
behavioral
reproduction
nutrition
infectious disease
molecular/population genetics
enrichment
What group of animals are the primary focus of zoos historically?
mammals (non human primates & carnivores = 60% of published papers)
What groups of animals have research that typically appears in specialty journals?
birds & herps
Who was among one of the first scientists to contemplate the social psychology of animals in zoos?
Robert Sommer
How did robert sommer characterize zoo architecture?
either "hard" or "soft"