STRUCTURAL DESIGN MOCKBOARDS-MELODY
1/252
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
253 Terms
The procedures and limitations for the design of structures shall be determined by the following factors.
Zoning, site characteristics Occupancy, configuring structural system, and height
Minimum number of stories recommended to be provided with at least 3 approved recording accelerographs.
14
Maintenance and service of accelerographs shall be provided by the___.
Owner
Who shall be responsible for keeping the actual live load below the allowable limits and shall be liable for any failure on the structure due to overloading.
Occupant of the building
The period of continuous application of a given load or the aggregate of periods of intermittent application of the same load.
Load duration
Minimum area in square meters a member supports which the design live load may be reduced.
14 sqm.
Minimum height of any wall requiring structural design to resist loads onto which they are subjected.
1.50 mts.
Maximum deflection of a brittle finished wall subjected to a load of 250 Pascal applied
1/240 of wall span
Maximum deflection of a flexible finished wall subjected to a load of 250 Pascal applied perpendicular to said wall.
1/120 of wall span
Maximum floor area for a low-cost housing unit.
60 sqm.
The level at which the earthquake motions are considered to be imparted to the structure or the level at which the structure, as a dynamic vibrator, is supported.
Base
A member or an element provided to transfer lateral forces from a portion of a structure to vertical elements of the lateral force resisting system.
Collector
A horizontal or nearly horizontal system acting to transmit lateral forces to the vertical resisting elements, it includes horizontal bracing system.
Diaphragm
The total designed lateral force or shear at the base of a structure.
Base Shear, V
An element at edge of opening or at perimeters of shear walls or diaphragm.
Boundary Element
An essentially vertical truss system of the concentric or eccentric type which is provided to resist lateral forces.
Braced Frame
An essentially complete space frame which provides supports for gravity loads.
Building Frame System
A combination of a Special or Intermediate Moment Resisting Space Frame and Shear Walls or Braced Frames.
Dual System
That form of braced frame where at least one end of each brace intersects a beam at a point away from the column girder joint.
Eccentric Braced Frame (EBF)
The entire assemblage at the intersection of the members.
Joint
The horizontal member in a frame system, a beam.
Girder
An element of a diaphragm parallel to the applied load which collects and transfers diaphragm shear to vertical resisting elements or distributes loads within the diaphragm. Such members may take axial tension or compression.
Diaphragm Strut
The boundary element of a diaphragm or a shear wall which is assumed to take axial stresses analogous to the flanges of a beam.
Diaphragm Chord
Those structures which are necessary for emergency post-earthquake operations.
Essential facilities
That part of the structural system assigned to resist lateral forces.
Lateral Force Resisting System
Moment resisting space frame not meeting special detailing requirements for ductile behavior.
Ordinary Moment Resisting Space Frame
The displacement of one level relative to the level above or below.
Story Drift
The usable capacity of a structure or its members to resist loads within the deformation limits prescribed in this document.
Strength
The lower rigid portion of a structure having a vertical combination of structural system.
Platform
Horizontal truss system that serves the same function as a diaphragm.
Horizontal Bracing System
An assemblage of framing members designed to support gravity loads and resist lateral forces.
Structure
A structural system without complete vertical load carrying space frame. This system provide support for gravity loads. Resistance to lateral load is provided by shear walls or braced frames.
Bearing Wall System
A structural system with essentially complete space frame providing support for gravity loads. Resistance to lateral load is provided by shear walls or braced frames.
Building Frame System
A structural system with an essentially complete space frame providing support for gravity loads. Moment resisting space frames provide resistance to lateral load primarily by flexural action of members.
Moment Resisting Frame System
Is one in which the story strength is less than 80% of that of the story above.
Weak Story
An elastic or inelastic dynamic analysis in which a mathematical model of the structure is subjected to a ground motion time history. The structure's time-dependant dynamic response to these motion is obtained through numerical integration of its equations of motions.
Time History Analysis
The effects on the structure due to earthquake motions acting in directions other than parallel to the direction of resistance under consideration.
Orthogonal Effect
The secondary effect on shears and moments of frame members induced by the vertical loads acting on the laterally displaced building frame.
P-delta Effect
Material other than water, aggregate, or hydraulic cement, used as an ingredient of concrete and added to concrete before or during its mixing to modify its properties.
Admixture
Concrete that does not conform to definition of reinforced concrete.
Plain Concrete
Upright compression member with a ratio of unsupported height to average least lateral dimension of less than three.
Pedestal
Ratio of normal stress to corresponding strain for tensile or compressive stresses below proportional limit of material.
Modulus of Elasticity
In pre-stressed concrete, temporary force exerted by device that introduces tension into pre-stressing tendons.
Jacking Force
Length of embedded reinforcement provided beyond a critical section.
Embedment Length
Stress remaining in pre-stressing tendons after all losses have occurred, excluding effects of dead load and superimposed loads.
Effective Pre-stress
Length of embedded reinforcement required to develop the design strength of reinforcement at a critical section.
Development Length
Friction resulting from bends or curves in the specified pre-stressing tendon profile.
Curvature Friction
Concrete containing lightweight aggregate.
Structural Lightweight Concrete
Pre-stressing tendon that is bonded to concrete either directly or through grouting.
Bonded Tendon
Commonly used structural steel
ASTM A36
High-Yield Strength Quenched and Tempered Alloy Steel Plate, Suitable for Welding.
ASTM A514
True or False
Bar larger than 32mm in diameter shall not be bundled in beams.
TRUE
Minimum concrete cover for a pre-stressed concrete for beams and columns for primary reinforcements.
40 mm
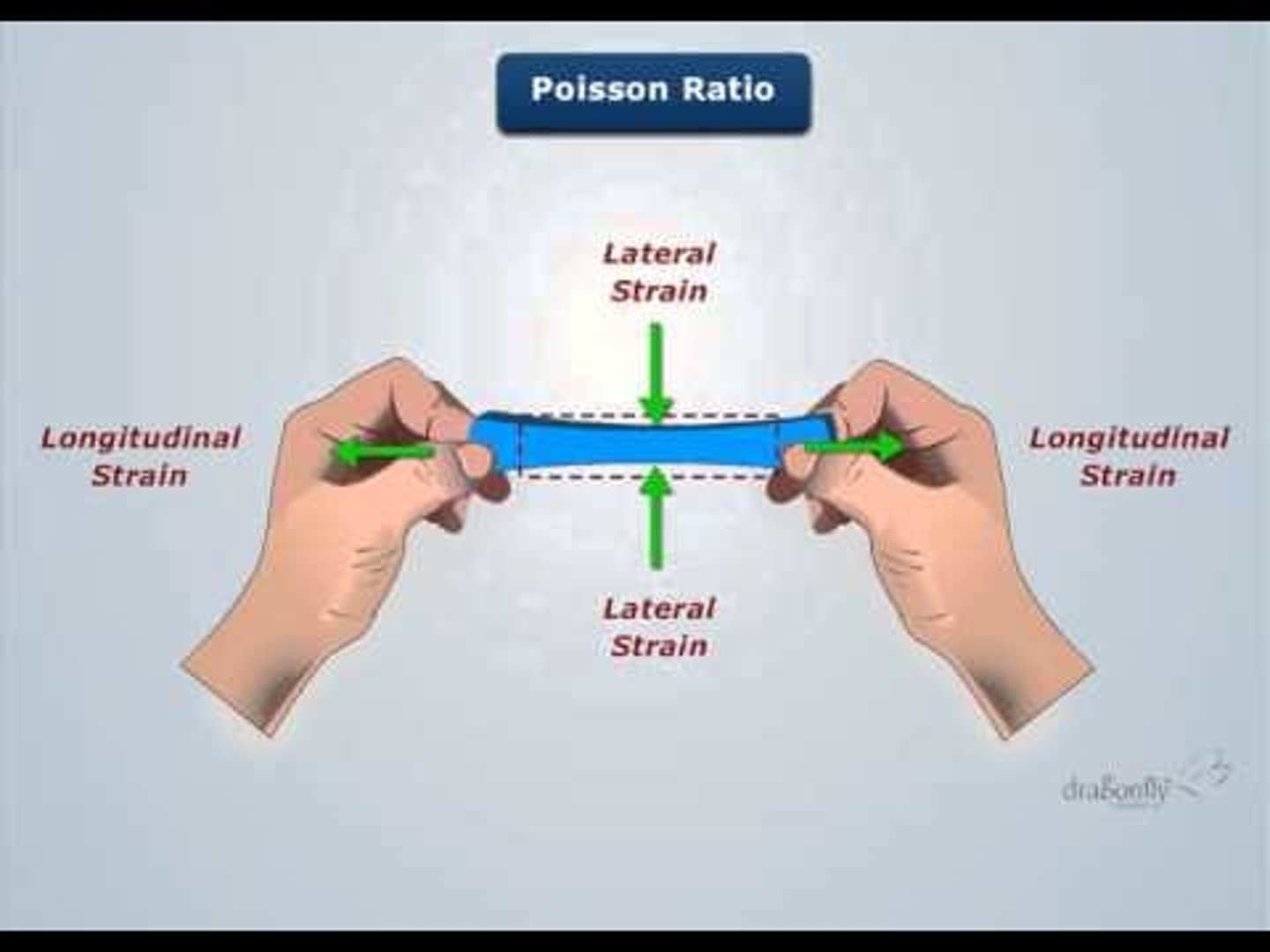
In a material under tension or compression, the absolute value of the ratio of transverse strain to the corresponding longitudinal strain.
Poisson's Ratio
In column, the ratio of its effective length to its least radius of gyration.
Slenderness Ratio
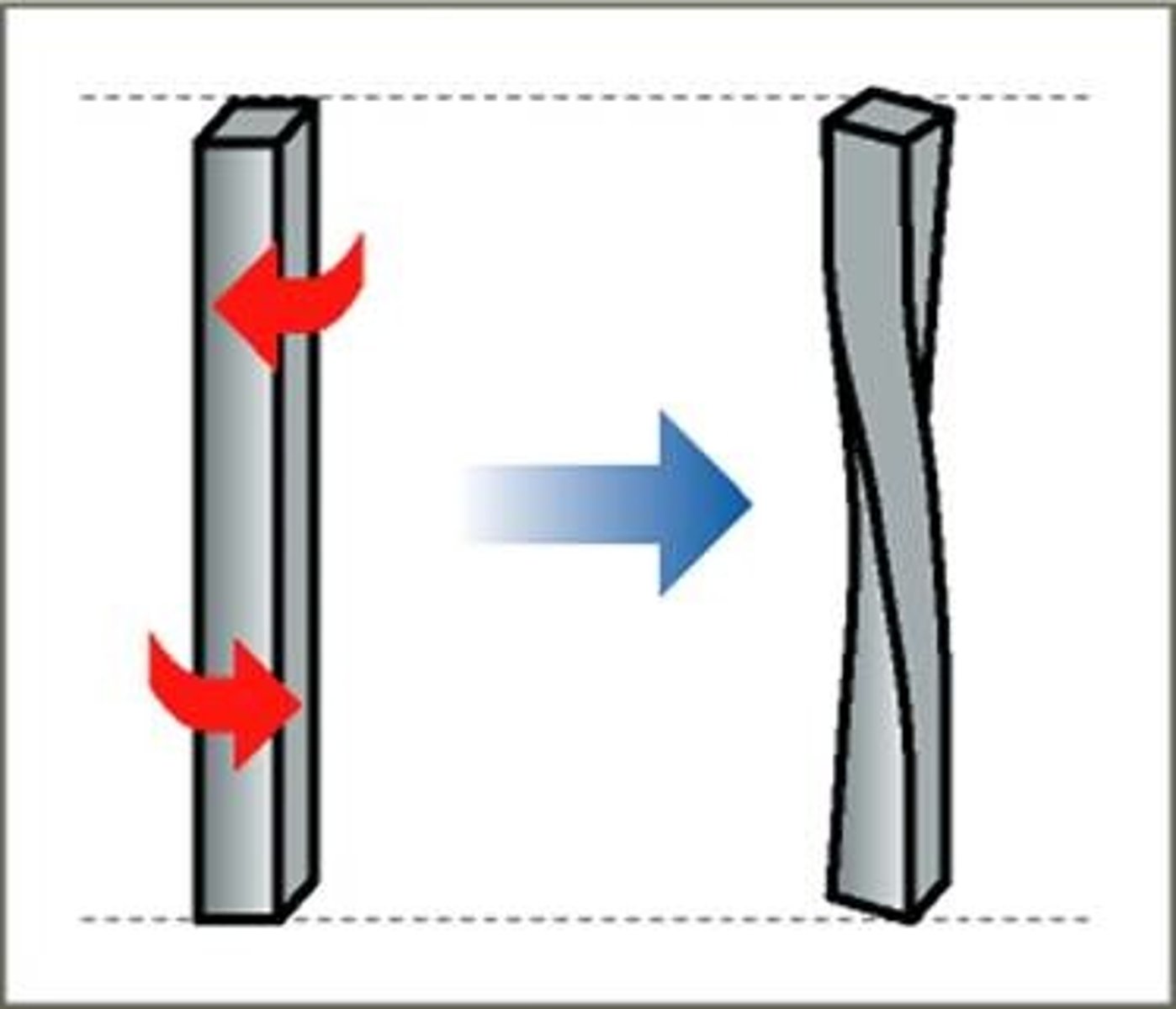
A quantity which measures the resistance of the mass to being revolved about a line.
Torsion
A type of concrete floor which has no beam.
Flat Slab

The tendency for one part of a beam to move vertically with respect to an adjacent part.
Shear
A change in shape of a material when subjected to the action of force.
Deformation
The maximum value of tension, compression, or shear respectively the material sustain without failure.
Yielding Stress
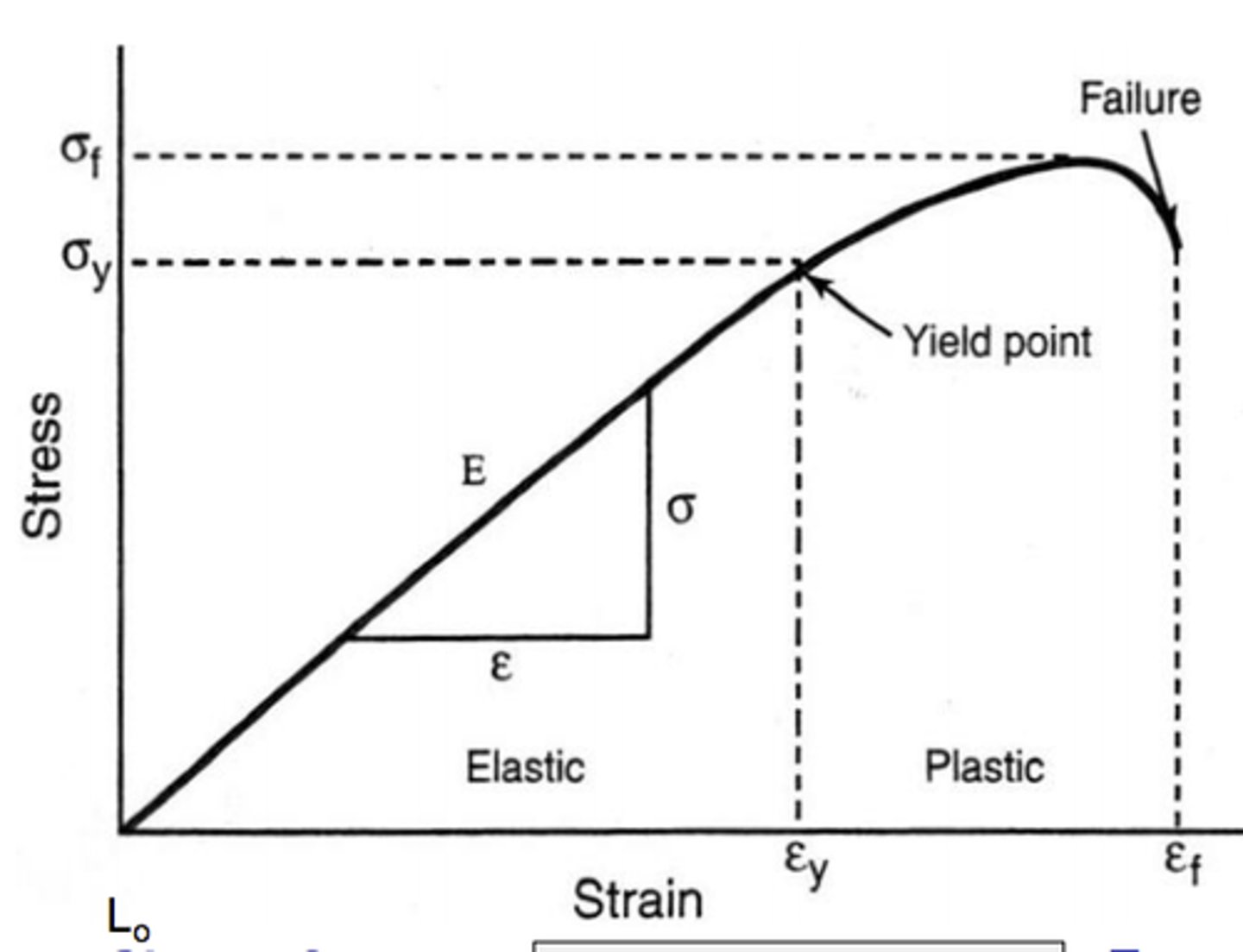
Intensity of force per unit area.
Stress
Loop of reinforcing bar or wire enclosing longitudinal reinforcement.
Tie / Stirrup
The measure of stiffness of a material.
Stiffness Ratio
The failure in a base when a heavily loaded column strikes a hole through it.
Punching Shear
The deformation of a structural member as a result of loads acting on it.
Deflection
Nominal thickness of of a timber.
6 inches
The sum of forces in the orthogonal directions and the sum of all moments about any points are zero.
Equilibrium
The complete records of tests conducted (slump, compression test, etc.) shall be preserved and made available for inspection during the progress of construction and after completion of the project for a period of not less than.
2 years
Wood board should have a thickness specification of.
not less than 1"X4"
The distance from the first to the last riser of a stair flight.
Run
A high-speed rotary shaping had power tool used to make smooth cutting and curving on solid wood.
Portable Hand Router
The major horizontal supporting member of the floor system.
Girder
Wood defects are: heart shake, cup shake, star shake, and___.
Knots
Dressed lumber is referred to ___.
Smoothed or planed lumber
The other kind of handsaw other than rip-cut saw.
Cross-cut saw
It refers to the occupancy load which is either partially or fully in place or may not be present at all.
Live load
The distance between inflection points in the span of a fixed-end or continuous beam, equivalent in nature to the actual length of a simply supported beam.
Effective length
The amount of space measured in cubic units.
Volume
In the formula e=PL/AE, E stands for___.
Modulus of Elasticity
An expansion joint of adjacent parts of a structure to permit expected movements between them.
Contraction joint
The total of all tread widths in a stair.
Total run
The force adhesion per unit area of contact between two bonded surfaces.
Bond Stress
A structural member spanning from truss to truss or supporting a rafter.
Purlin
Size of camber for a 25 meters steel truss.
Size of Dead Load Deflection
A connector such as a welded strut, spiral bar, or short length of channel which resists horizontal shear between elements.
Shear Connector
The force per unit area of cross section which tends to produce shear.
Shear Stress / Shearing Stress
The law that relates the linear relationship between stresses and strains.
Hook's Law
Minimum spacing of Bolts in timber connection measured from center of bolts parallel for parallel to grain loading is equal to ___.
4 X diameter of bolt
According to the provisions of the NSCP on timber connections and fastenings, the loaded edge distance for perpendicular to grain loading shall be at least ___.
4 X diameter of bolt
NSCP specifies spacing between rows of bolts for perpendicular to grain loading shall be at least ___ times bolt diameter for L/d ratio of 2.
2.5
Minimum diameter of bolts to be used in timber connections and fastening in accordance with NSCP specifications.
12 mm
Simple solid timber columns have slenderness ratio not exceeding ___.
50
Nails or spikes for which the wire gauges or lengths not set forth in the NSCP specifications shall have a required penetration of not less than ___.
11 diameters
Notches in sawn lumber bending members in accordance with the NSCP specifications shall not exceed.
1/6 depth of member
Notches in sawn lumber shall not be located in the ___.
Middle Third Span
Notches in the top and bottom of joists shall not exceed ___.
1/4 the depth
Allowable stresses for tension in structural steel in terms of gross area.
0.60 of specified min. yield stress
Allowable tensile stress of structural steel based on effective area.
0.50 of specified minimum tensile strength
Allowable stress for tension on pin connected members based on net area.
0.45 Fy
Allowable shear stress on structural steel on the cross sectional area effective in resisting shear.
0.40 Fy