biological molecules (WHOLE)
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
2 amino acids
dipeptide
what are one or more polypeptides
proteins
what is polypeptide
lots of amino acids
how are peptides formed?
via condensation reactions between an amine group of one amino group and the carbonyl group of another
a molecule of water is realeased
the bonds formed is called a peptide bond
the reverse happens during digestion
what’s the enzyme that catalyses the condensation reaction between two amino acid called
peptidyl transferase
amino acids and their condensation reaction
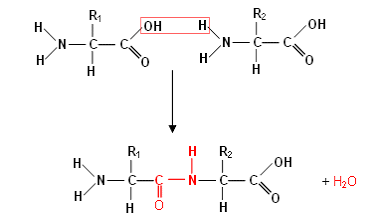
why do the polypeptides fold into complex structures?
the different R groups of the amino acids interact with each other which form different bonds.
The different sequences of amino acids present lead to different structures with different shapes,
the primary structure of proteins
simple long chains with no intermolecular bonds or interactions
the secondary structure of proteins
hydrogen bonds form causing the molecule chain to either fold or coil
the primary sequence is what determines weather it folds or coils
what are the two secondary structure of protein?
Alpha helix (α-helix) and beta pleated sheet (β-sheet)
They form due to hydrogen bonding between the backbone atoms of the polypeptide chain
These hydrogen bonds stabilize the structure and help the protein fold into regular, repeating patterns
the tertiary structure of proteins
the 3D shape of the polypeptide chain.
It creates a specific shape due to the sequence of amino acids in the haon
hydrogen bonds, ionic one, disulphide bridges form between R groups
a change to the sequence of amino acids would effect the secondary and tertiary structure as these bonds would form in different
All enzymes, antibodies and some hormones have a tertiary structure
quaternary structure of proteins
if proteins are made of more than one polypeptide chains they then are joined together to create quaternary structure.
Antibodies and haemoglobin are examples.
why are lipids non polar
because elections are evenly distributed
what is the biological roles of lipids
controlling fluidity of the cell membrane
electrical insulation
hormone production
waterproofing
what are triglycerides made off
one glycerol and 3 fatty acids
what is the general formula of triglycerides
CnH(2n+1)COOH
what’s the function of triglycerides
energy storage
thermal insulation (buoyancy, and around vital organs cushioning)
the long fatty acids chains release lots of energy when broken down.
what is glycerols
a small 3 carbon molecule with three alcohol groups (C3H8O3)
why are triglycerides good for energy store
they yield more energy per unit mass than other compounds so are good for energy storage
properties of fatty acids
fatty acids have a carboxyl group and a hydrocarbon chain
the chain can be from 14-22 carbon long
fatty acids have the same basic structure but the hydrocarbon tail varies
the tails are hydrophobic (they repel water molecules) therefore lipids are insoluble
what are saturated fats
they have no C=C bonds in the chain
this makes them saturated and straight chains
what are mono saturated fats
they have one C=C bond in the chain
this causes a kink and bends in the chain
bending in the chains means they cannot pack closely together
this makes them liquid at room temp
what are poly saturated fats
they have several C=C bonds
this makes them unsaturated
this causes kinks and bends in the chain
the bends lower the melting point
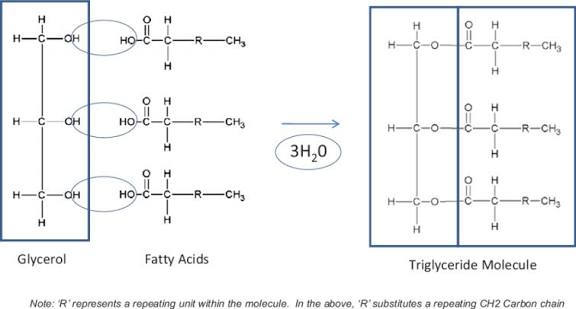
how are triglycerides formed
triglycerides are made of one glycerol and 3 fatty acids joined together
each hydroxyl group interacts to form an ester bond between the glycerol and each fatty acid
during the ester bond formation three water molecules are released
this reaction is called esterification
when triglycerides are broken down, 3 water molecules are needed to be supplied to reverse the reaction
structure of triglycerides
what are phospholipids
lipids with a phosphate group rather than a fatty acid chain.
what’s the property of the phosphate group in phospholipids?
it’s hydrophilic
what’s micelle
when mixed with water, phospholipids form droplet spheres
the hydrophilic head gave the water
the hydrophobic tails gave each other
this is called micelle
what’s a phospholipid bilayer
Made of phospholipids (hydrophilic heads + hydrophobic tails)
In water, tails hide from water, heads face water
Two layers form: tails inside, heads outside → bilayer
Basis of cell membranes; creates a semi-permeable barrier
what are sterols also known as
steroid alcohols
what are sterols
complex alcohol molecules based on a 4 carbon ring structure with a hydroxyl group at the end of
the hydroxyl group is polar and therefore hydrophilic
the rest of the molecules is hydrophobic
where is cholesterol made
it’s manufactured in the liver and intensifies.
what’s the function of cholesterol
it positions itself between the phospholipids in the membrane,
it adds stability to the membrane (fluid at low temp and not too fluid at high temp)
vitamins D, steroid, hormones and bile at
produced using cholesterol
what’s the steps for the emulsion test for lipids?
lipids do not dissolve in water but they do in ethanol to find out if there is fats in a sample, you do an emulsion test.
add ethanol to a test substance and shake throughly for about a minute so it dissolves
add water to the solution
if lipid is present, it will show as a milky emulsion. The more lipids, the more noticeable the milky colours will be.
(the rest can be improved by adding dye Sudan III, which will stain the lipids red)
what’s a carbohydrate
molecules which contain Hydrogen, carbon and oxygen only. The general formula is Cx(H2O)y
Molecular formula of glucose
C6H12O6
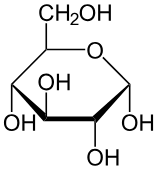
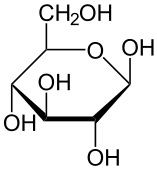
what are the two structures of glucose
• alpha glucose
• beta glucose
What happens to glucose in aqueous structures
forms a ring structure- a hexose monosaccharide.
alpha glucose
beta glucose
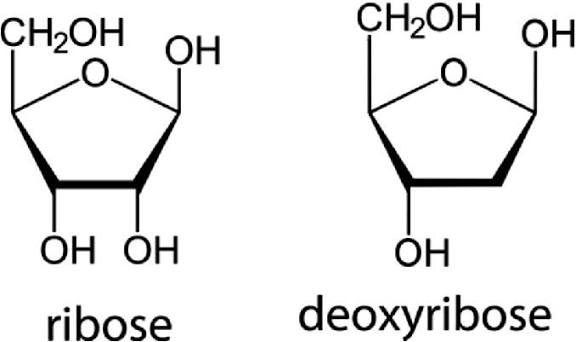
what are sugars that contain five carbon molecules called
pentose monosaccharides
ribose and deoxyribose
How are disaccharides formed
when two monosaccharides are joined together by a glycosidic bond
what is a glycosidic bond
a covenant bond between 2 monosaccharides
How does the condensation reaction occur between two sugars
It is formed when two hydroxyl groups on diffrent monosaccharides interact to form a strong covenant bond called glycosidic bond. (The oxygen link that holds the two molecules together) Every glycosidic bond results in one water molecule being removed.
The opposite is an hydrolytic reactions.
What are the two classification of sugars
• reducing sugar
• non-reducing sugar
what is a reducing sugar
• can donate electrons, the sugar becomes the reducing agent.
• they can be detected using benedict test
• the sugar reduces the soluble copper sulphate to insoluble copper oxide
• therefore turning it brick red
What are examples of reducing sugars?
1. glucose
2. fructose
3. galactose
4. galactose-fructose
what’s non-reducing sugar?
• sugars that cannot donate electrons
• therefore they cannot be oxidised
• to detect non reducing sugars you must first hydrolyse it to break the disaccharides
an example: sucrose
What is starch
glucose that’s photosynthesised and stored as starch in excess
starch is an energy store for plants and is insoluble.
Why is starch a good storage molecules?
• because its insoluble
• makes it an ideal storage molecule as it prevents water entering cells my osmosis which would make them swell
what are the two polysaccharides known as starch
1. Amylose
2. amylopectin
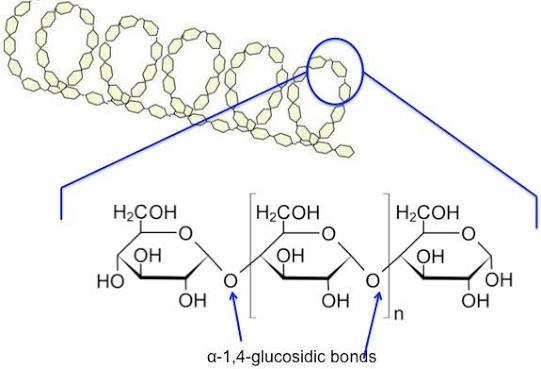
how is amylose formed
formed by alpha glucose molecules forming a 1-4 glycosidic bonds.
properties of amylose
due to the angle of the bonds the long chains twists to form a helix
it is further stabilised by hydrogen bonding
therefore it is very compact, insoluble and good for storage.
amylose structure
twists and form a helix structure
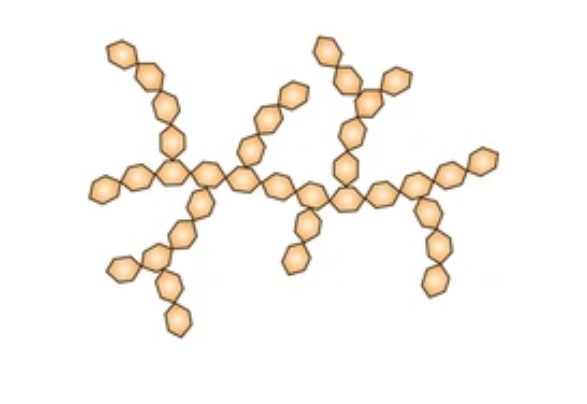
how is amylopectin formed
by alpha glucose molecules forming a 1-6 and 1-4 glycosidic bond.
properties it amylopectin
branched chains
the branches occur every 25 units
allows the enzyme to break down molecule to get to the glycosidic bonds easily.
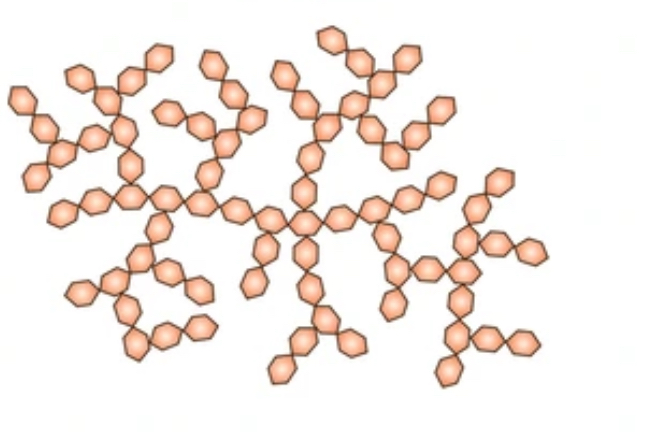
What is glycogen
the equivalent energy storage molecule found in animal and fungi.
animals store excess glucose as glycogen
it’s stored in the liver and some muscles
properties of glycogen
made of alpha glucose
forms more branches- 10 every subunits
the branching of glycogen makes it very compact, therefore ideal for storage
branches means there is many free ends where glucose can be added or removed
this speed up process of storing and releasing glucose molecules required by the cells.
what is cellulose
the major component of cell walls in plants
properties of cellulose
made from beta glucose
long unbranded chains
1-4 beta glycosidic bond
the subunit are oriented alternatively upwards and downward
therefore cellulose is a straight chain
the straight chain are linked with hydrogen bonds.
amylopectin structure
glycogen structure
cellulose structure

What is an OH group called
hydroxyl group
Why does water have a high boiling point
Due to the hydrogen bonding between water molecules. It takes a lot of energy to increase the temperature and water and cause water to become gaseous
Why is water less dense in its solid state?
Water molecules are held further apart when they are solid than when they are liquid, therefore density decreases as water becomes solid. This is because as water cools the hydrogen bonds become fixed in position. Which produces a giant rigid but open structure.
What does polar mean?
A molecule with a uneven distribution of charge. with a positive pole<latex>\delta</latex>+ and a negative <latex>\delta</latex>-
Why does water have high electronegativity
Because it has higher affinity for electrons.
What is an advantage of oxygen being slightly negative and hydrogen slightly positive in water
it makes it polar which means it can form weak electrostatic associations with other polar molecules. This is called an hydrogen bond.
What is a property of hydrogen bonds
Hydrogen bonds are weak when they are few so they are constantly breaking and reforming. When a large number is present they form a strong structure.
properties of water: high specific heat capacity
• heat capacity is the energy needed to increase the temp of 1kg of water by 1 celcius.
• Hydrogen bonds between the water molecules absorb a lot of energy so the specific heat capacity of water is high
• this means there is no rapid temp changes
• This makes water a great habitat
• Also mean optimal temp is maintained within cells and bodies
properties of water: high latent heat of evaporation
• HLHE is the energy needed to make water evaporate.
• Hydrogen bonds use a lot of energy when water evaporates which makes it great for cooling
• an example: thermoregulation such as sweating
• allows for temp to be maintained in cellular environments since enzymes only work within a narrow range.
Property of water: cohesion
• Cohesion is the attraction between molecules of water.
• water flows, which shows water molecules stick together
• water is adhesive: it sticks to other polar molecules. The cohesion-adhesion properties of water are important in the transport of water in plants-capillary action.- in the transpiration stream.
• the cohesion nature of water also causss surface tension when a body of water meets the air.
• these hydrogen bonds occur between the top layer of water molecules to create a ‘ film’ on the body of water.
why is water a good solvent
water is polar so slightly. positive end of the water molecule will be attracted to negative ion and the slightly negative end of water will be attracted to the positive ion. In this way, ions will be completely surrounded by water molecule. (dissolve)
This allows chemical reactions to occur in cells and also molecules and ions to be transported