VCU DPT - Biomechanics (Lecture 15)
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
does the type of load impact the bone's response
YES
tension vs compression vs torsion
bone is better at handling ___________ compared to ______ and ________
compression
tension, torsion
does bone like to be loaded fast or slow
FAST
injuries:
at faster load, is it ligament or bone
at slower load, is it ligament or bone
faster, ligament
slower, bone
t/f: bone behaves viscoelastically
truwe
- harder you push the more it resists
what 3 things make up bone
identify the component that makes up the biggest piece
orgnaic material
water
minerals (majority)
mineral gives bone its _____
strength and stiffness
organic material gives bone its ______
flexibility and resiliance
difference in plastic and elastic deformation
elastic will return to before, plastic is permanent change
if a system is perfectly resiliant, what is it
it returns as much work put into the system that was strained upon it
which kind of break had more energy
crack
explosion
explosion
bone is surrounded by _________
describe whatever term you put in the blank
periosteum
an outer layer that is filled with vessels and nerves
t/f: periosteum covers the ENTIRE bone
false
all of bone except joint surfaces
what is contained in the inner layers of bone?
what is the term for all inner layers
bone cells to help repair and grow (osteoblasts)
osteogenic layer
the endosteum is where?
what is it filled with
the center of the bone, medullary cavity
filled with marrow, osteoblasts and osteoclasts
osteoblasts _____, osteoclasts _____
build
destroy
cortical/compact bone is ___________
trabecular/cancellous bone is ________
outer
inner
match the pairs
a) cortical bone
b) trabecular bone
c) 5-30% porosity
d) outer bone
e) inner bone
f) 30-90% porosity
g) compact bone
h) cancellous bone
a, c, d, g
b, e, f, h
what is a structural unit of bone
osteon
what is an osteon
lamallae surrounding in concetric rings
functional unit of bone
what are volkmanns canal
path from the surfaces
wht are haversian canals
canals for blood vessels and nerves
what is a lacunae
these are at the boundaries of lamalle, and contain a SINGLE bone cell
we store energy in the __(outer/inner)___ layer of bone, and get strength from the __(outer/inner)___ layer of bone
inner
outer
stress-strain is a ______________
normalized verison of load deformation
what is a normalized version of a load-deformation plot
stress-strain plot
why is stress-strain nromalized version of load-deformation
because
stress = Force/area
strain = change Length/initial length
what does the area under the curve represent in a load-deformation curve
energy being stored in the system
stress = _____
strain = ______
force/area
change length/length
with the load-deformation curve in bone, the elastic region slope is very steep. what does this mean
you can apply a lot of load to the bone before it begins to change its shape
severity of break is related to amount of ________
energy
- aka the area under load-deformation curve
with a load deformation curve, the further right you are the ___ energy is stored in system
what happens if system fails farther to right
energy
hhigher severity of break
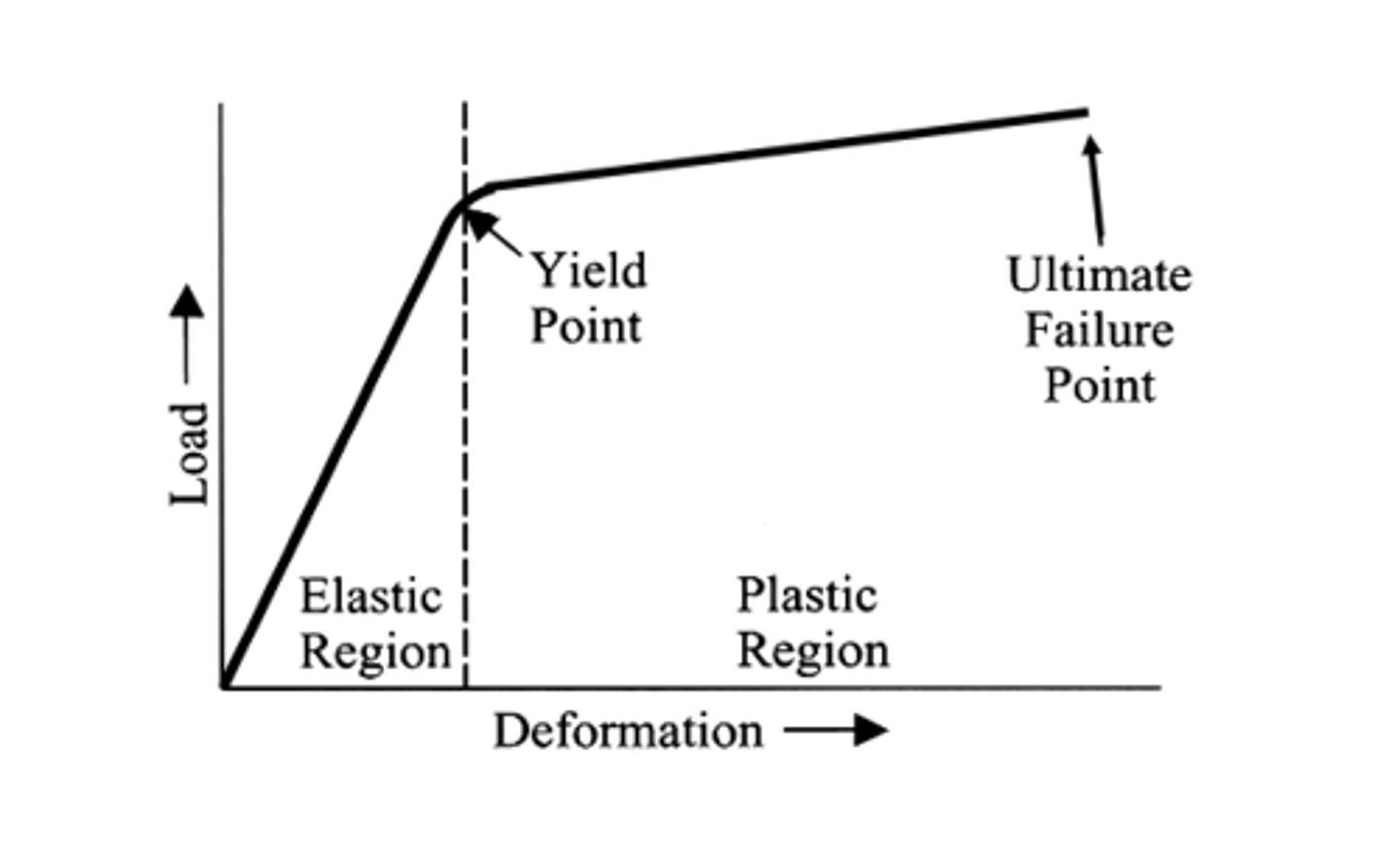
what does the ultiate failure point represent in a load-deformation curve
for y-axis
for x-axis
for area under curve
Y: the total amount of load a system can take before it fails, and breaks
X: the total amount of deformation the system can undergo before it breaks
AUC: amount of energy system can handle before it fails
the slope of a load-deformation curve is related to young's modulus of elasticity. the steeper it is, the more ______ it is
stiff
what are the three paramters for structure strength
1. ultimate failure point
2. deformation before failing
3. energy (area under curve)
stress-strain helps us see different mechanical properties when loaded along different axes, due to it being Force/area
what property is this referred to as
ansiotropy
what would indicate a stiff system in a stress strain curve
a steep slope
_______ curve takes into consideration the amount of change in length in relation to original position
stress strain curve
which direction is bone best loaded
- straight up and down
- at angle
- at side
straight up and down
what does it mean when i say bone is biphasic
minerals/collagen and GS
stronger in combination than its indivual parts
cortical bone is ___(stiffer/less stiff)___ than canellous bone
therefore, it has higher __(stress/strain)__ but less __(stress/strain)___
stiffer
stress, less strain
stress refers to force, strain is change in length
which has higher strain
cortical bone
cancellous bone
what does this mean
cancellous (75% strain before failure)
cortical (2% strain before failure)
cancellous bone can change length from starting length more than cortical before failing
which has higher stress
cortical bone
cancellous bone
what does this mean
cortical bone can withstand higher force per area than cancellous bone
put these into position: shear, compression, tension
bone strongest in (a) > (b) > (c)
bone strongest in (compression) > (tension) > (shear)
bone is _______ when laoded at higher speeds
brittle
which conforms to original shape, ductile or brittle
brittle does
is younger bone or older bone ductile? which is brittle?
younger bone is ductile
- can change shapes
older bone is brittle
- returns to shape
t/f: after a period of immobilization, the bone NO LONGER deforms before failing
false! it will still deform
what happens to bone after period of immobilization:
- load to failure
- energy storage
- stiffness
all decrease
load-deformation curve is shorter, less area under curve, and flatter
does all trauma result in reverisble bone loading or bone fracture
no!
rate of loading changes, also how much into plastic region we go
bone is stiffer at _____ rate of loading
bone can absorb more load at _____ rate of loading
less deformation of failure at _____ rate of loading
bone can take more energy at _____ rate of loading
all HIGHER
t/f: bone is stiffer, can absorb energy better, deforms less, and can take more energy at higher rate of loading
true
fracture can be result of single load greater than ultimate material strength OR ________
repeated lower loads, causing micro fractures
with cyclic loading, we see reversible/nonreversible behavior
nonreversible
things change over time!!
this is good, meaning if we can load the bone over time it gets stronger
what does cyclic loading produce?
micro structural damage to bone tissue
damage in bone tissue accumulates faster at ______ intensity of cyclic loading
higher
transverse patellar fracture is example of what type of load causing fx
tension
bending causes _____ on one side and _______ on the other
which side breaks
compression
tension
the tension side breaks
the butterfly fragment is always located on the (compression/tension) side of the leg
compression
as a long bone gets bent over a point, what gets created on either side
tension on the side bending
compression on side acting as fulcrum
when there is compression on bone due to bending happening on other side, what happens to compression site over time
it gets smaller as bone bends more
- leads to butterfly fx
when we get to a certain level of energy, the bone will break. the type of fracture is reliant on the ________
type of load the bone gets
there is often more soft tissue injury with __(bending/torsion)____
bending
- happens at higher load, quicker
which takes less load to cause fracture
torsion
bending
torsion
what kind of fracture is seen with torsional force
spiral fracture
axial compression and bending is reuslt of what force
torsion
torsion/spiral fractures break _______ with ___ force
heal _______, why?
easier with less force
quicker due to larger surface area and less soft tissue involvement
the butterfly fragment is on the
a) tension side
b) compression side
B
the greater the force's magntiude, the ____ its energy
implication for soft tissue?
higher
more soft tissue destruction
the more complex the fracture pattern, the ____ energy needed to produce fracture
greater
low energy is dissapated through ___ cracks than high energy load
fewer
t/f: following fractue, ductile bone does not reutrn to original form
true, brittle does
t/f: bone is stiffer when loaded at higher rates
true
a sudden change in material shape will change the way stress is distributed in the structure, giving rise to ___________
stress concetrations/risers
after material has changed shape and there are __________, these can be thought of as rocks interrupting water flow
stress concetration/risers
pathological fx through tumor
refracture near area of callus
fracture at end of internal fixation device
fracture through screw hole
these are all exmaples of fractures due to what
a stress concetraction/riser changing the distribution ability of the tissue
it takes bone roughly 8 weeks to get to normal after healing. what happens to bone strength, with 100% being normal, after you go back to get screw out
bone back at 50% strength
- like it was newly fractureed
when the stress riser defect is less than bone diameter, does bone return to normal quickly
what about when stress riser is greater than diameter
in 8 weeks yeah it gets back
no, 90% reduction and stays very low
an open section defect is when the defect is ______ than bone diameter
greater than
explain why area moment of intertia is related to bone
a larger area moment of intertia means hardest to bend
area segments further from the axis contrubte signficntly more to area moment of intertia
why does area segments further from axis contribute more to area moment of intertia than closer?
what does it mean
contribution is proportional to square of distance from neutral axis
the larger it is, harder it is to bend
describe bone's ability to resist twisting force, and relate it to polar moment of inertia
around a pole, a larger moment of inertia is more resistant to move
therefore, if a bone is thicker and as result has larger moment of inertia, it is less likely to twist than a skinnier bone (which has less resistance)
with same thickness of cortical bone, which one would break easier from a twisting force
thicker bone
skinnier bone
explain your answer
skinnier
has a smaller moment of inertia, so it would take less resistance to get it to rotate
rotating is bad for bone!
which has better mechanical advantage to resist torque
thicker bone
skinnier bone
thicker
relate how bone heals to polar moment of inertia
bone heals thicker
therefore, it will be more resistant to twisting force because higher polar moment of inertia
when does bone mineral content peak?
who get affected by resoprtion from hormonal changes mostr
30s
women
through the third decade, we have
_____ elastic modulus
______ in yeild strength
increase
increase
older bone is _______ than younger bone
stiffer, stronger
the ability of bone to elongate more until failure _________ throughout life
decreases
- deformation to failure is higher when young
old bone is ____ brittle, with _____ energy capacity
more
less
how does stress strain curve differ from load-deformation
stress strain is normalized, can compare types of bone across specturm
effect of immob on bone
decreases its strength, deformation ability, stiffness
how is ____ related to bone strength
a) polar moment of inertia
b) area moment of inertia
a) farther from axis, stronger
b) area from axis is stronger