BSC2085L practical 2 exam ₍^. .^₎⟆
1/156
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
157 Terms
location of hyaline cartilage connective
ends of long bones
function of hyaline cartilage
reinforcement, cushioning of structures
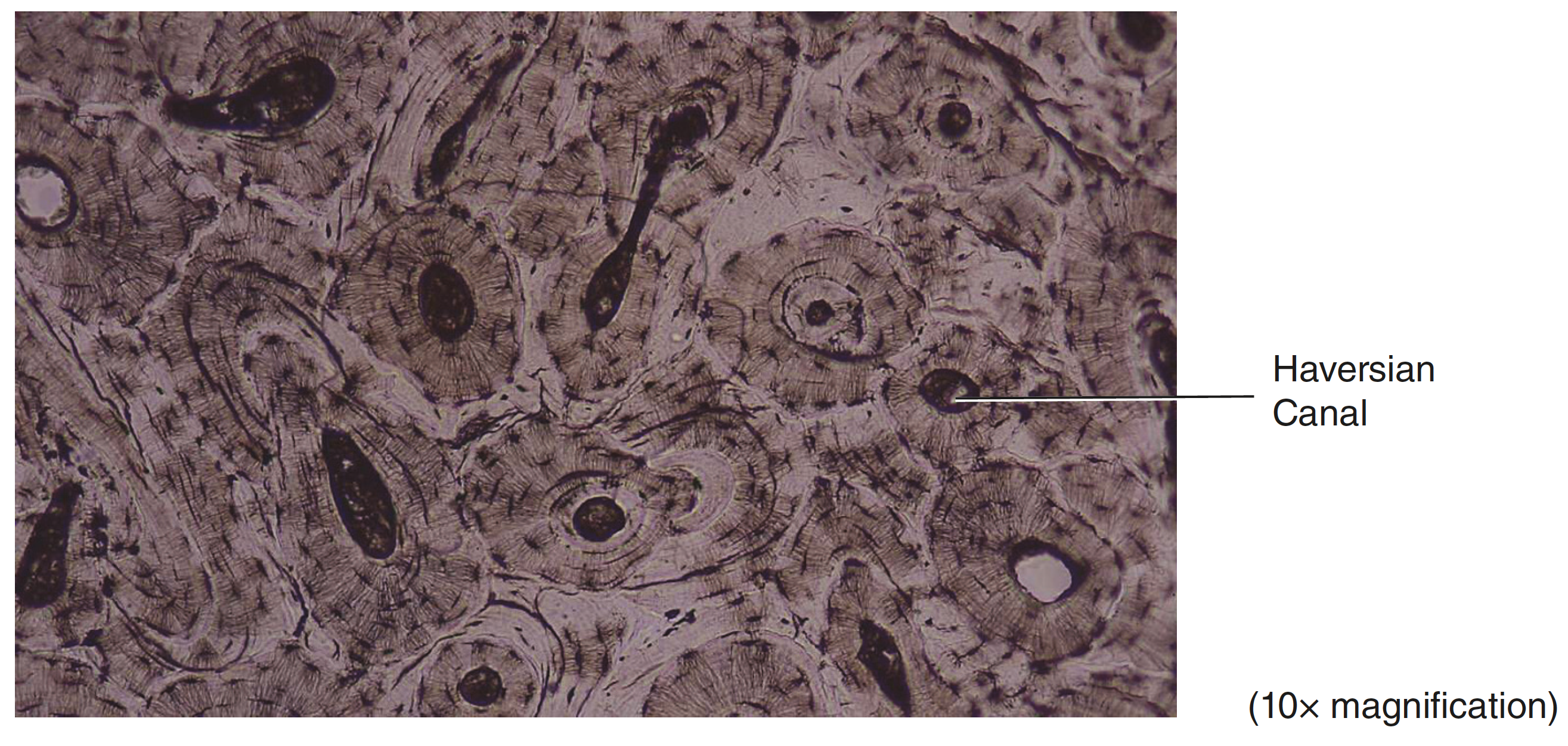
location of connective compact bone
found in all bones, forms the hard external covering of all bones
function of connective compact bone
provides strength and support, facilitates movement and weight bearing. houses bone marrow, calcium and fat
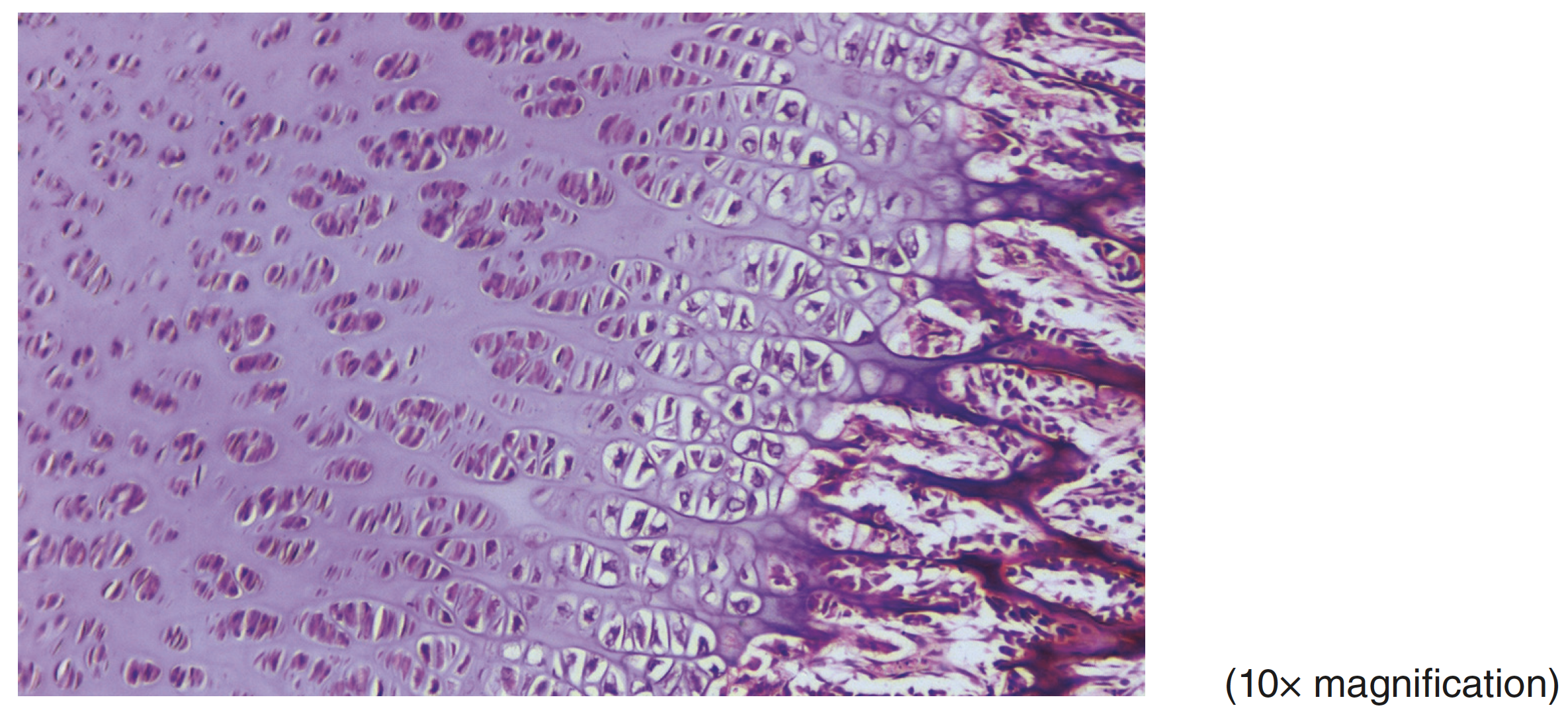
hyaline cartilage connective is composed of
chondrocytes, collagen fibers, and a semisolid ECM
connective compact bone is composed of
osteocytes, collagen fibers, calcium carbonate
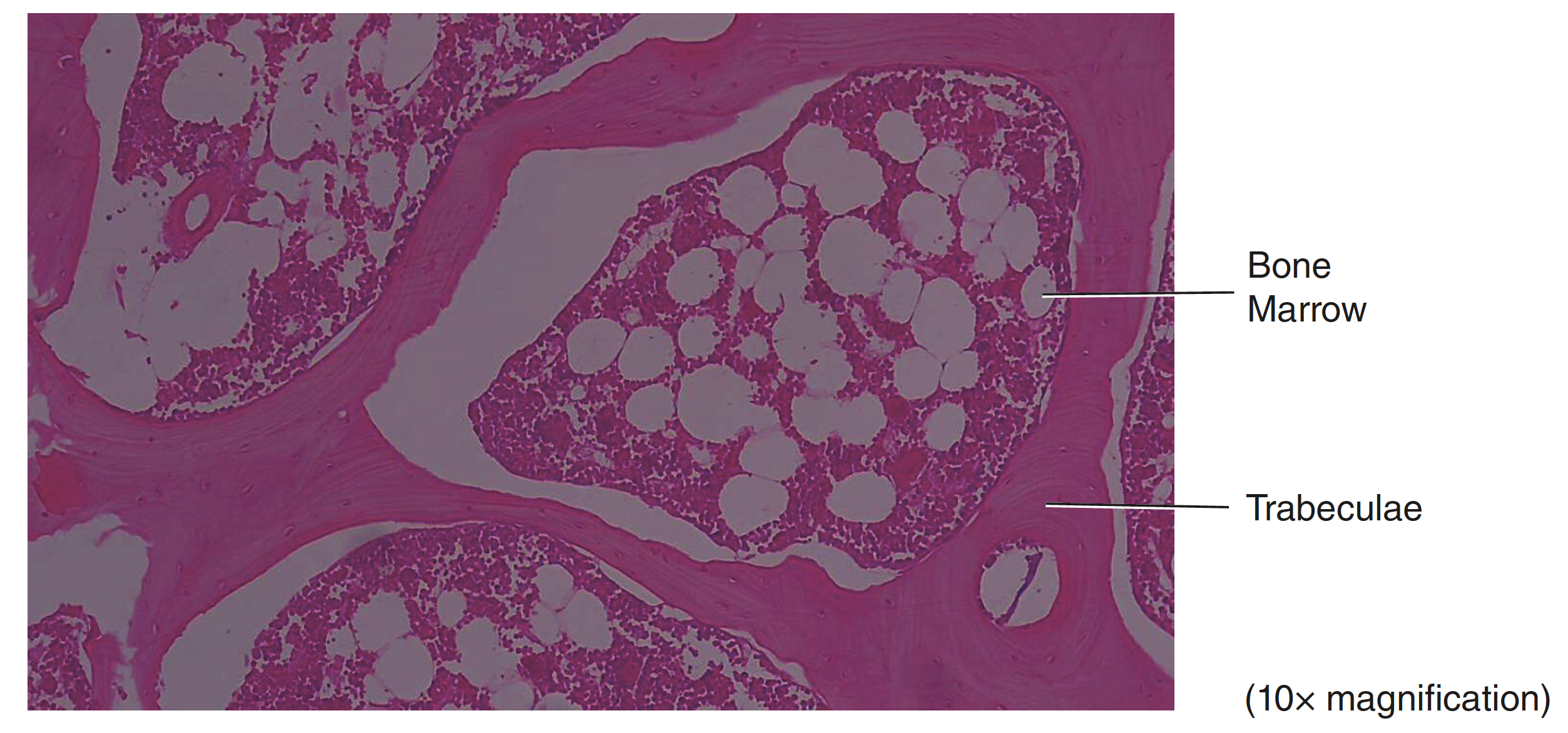
connective spongy bone is composed of
osteocytes, trabeculae, red bone marrow
connective hyaline cartilage
connective compact bone
connective spongy bone
long bones
length of the bone is greater than the width
short bones
length and width are about equal, sometimes cube shaped
flat bones
thin, plate-lite structures
irregular bones
have a variety of shapes
examples of a long bone?
femur
humerus
tibia
examples of a short bone?
carpals
tarsals
examples of flat bones?
parietal bones
sternum
ribs
examples of irregular bone?
vertebrae
pelvic bones
facial bones
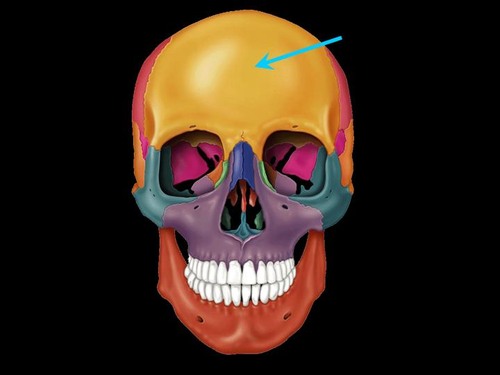
frontal bone
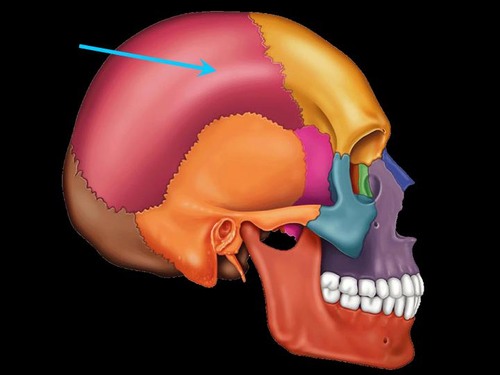
parietal bone
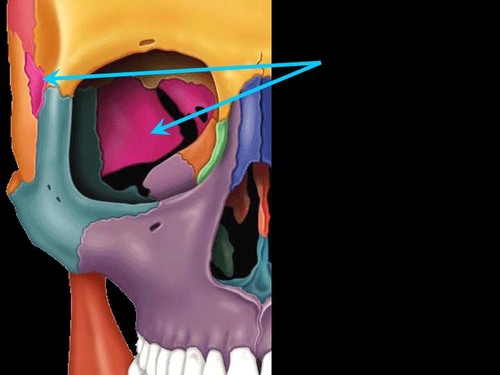
sphenoid bone
nasal bone
zygomatic bone
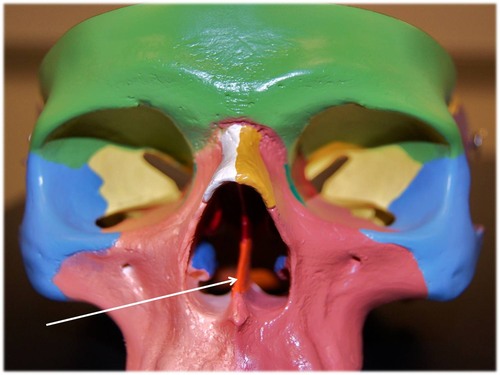
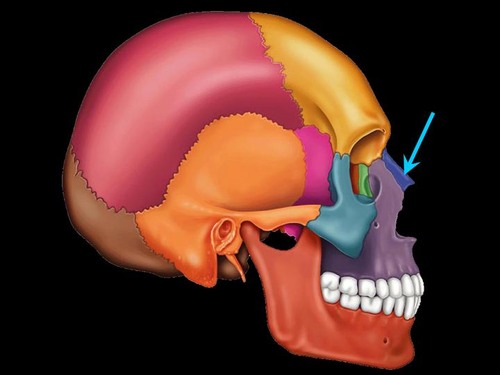
vomer bone
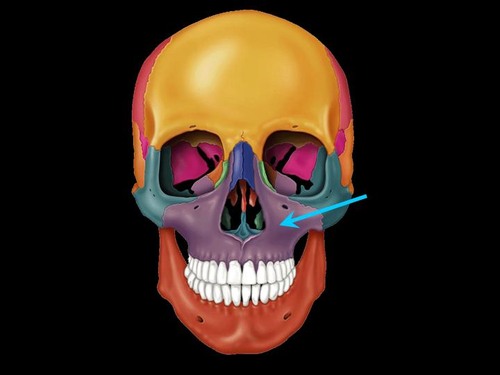
frontal maxilla
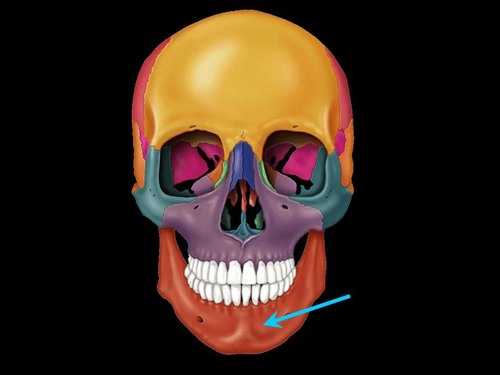
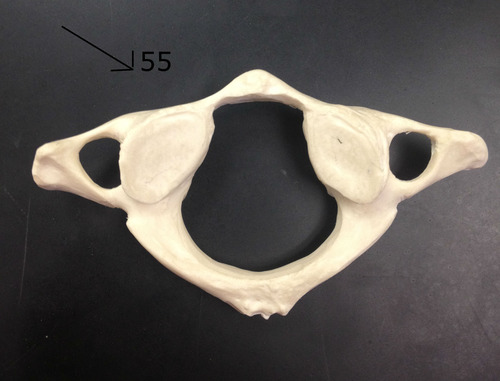
mandible
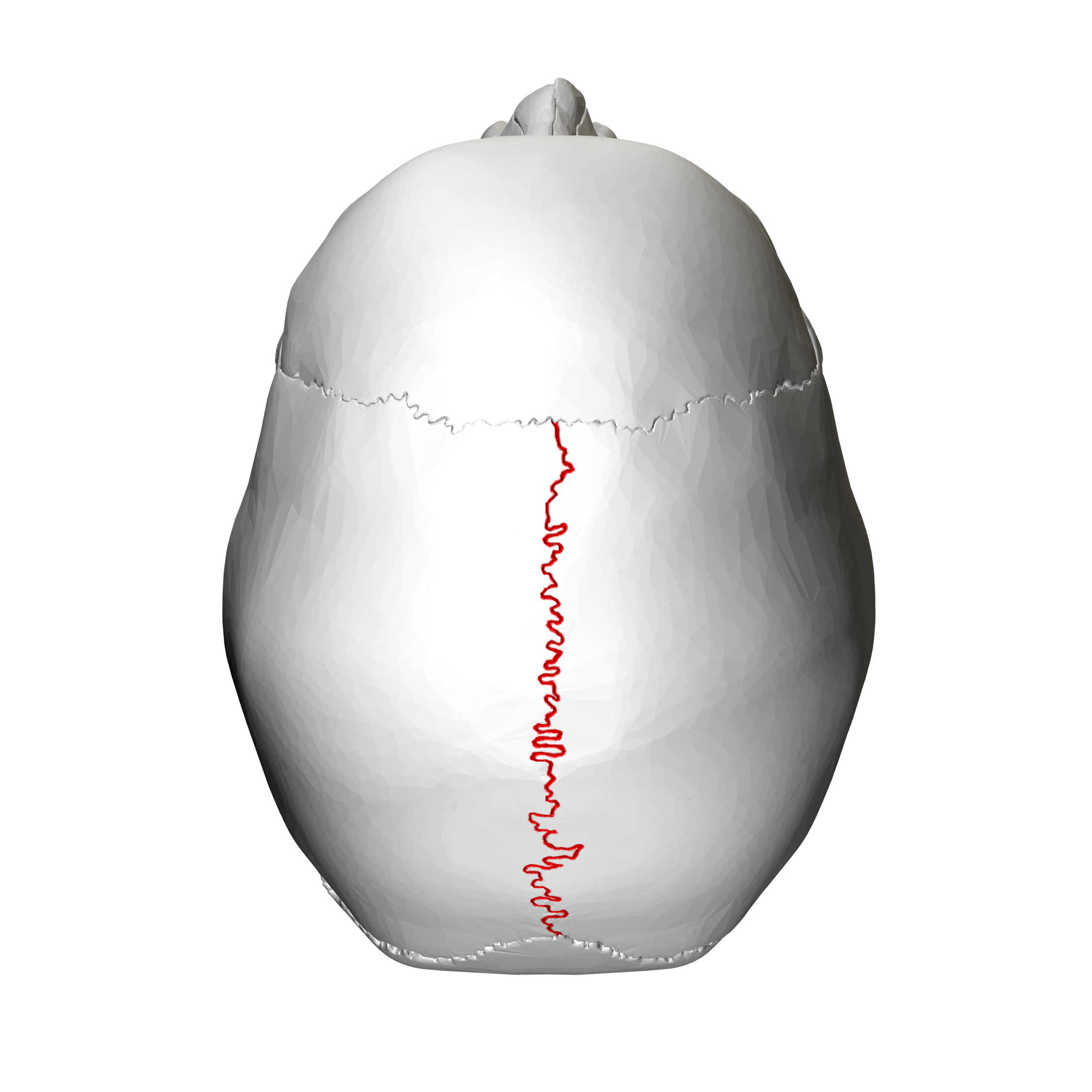
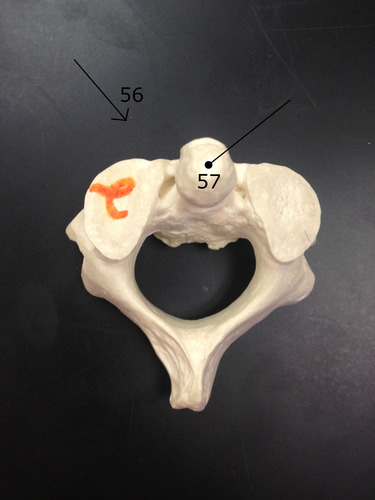
saggital suture
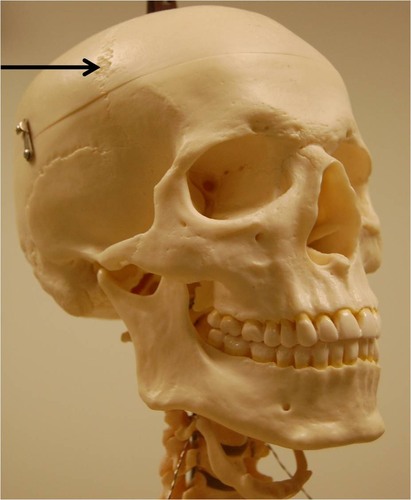
coronal suture
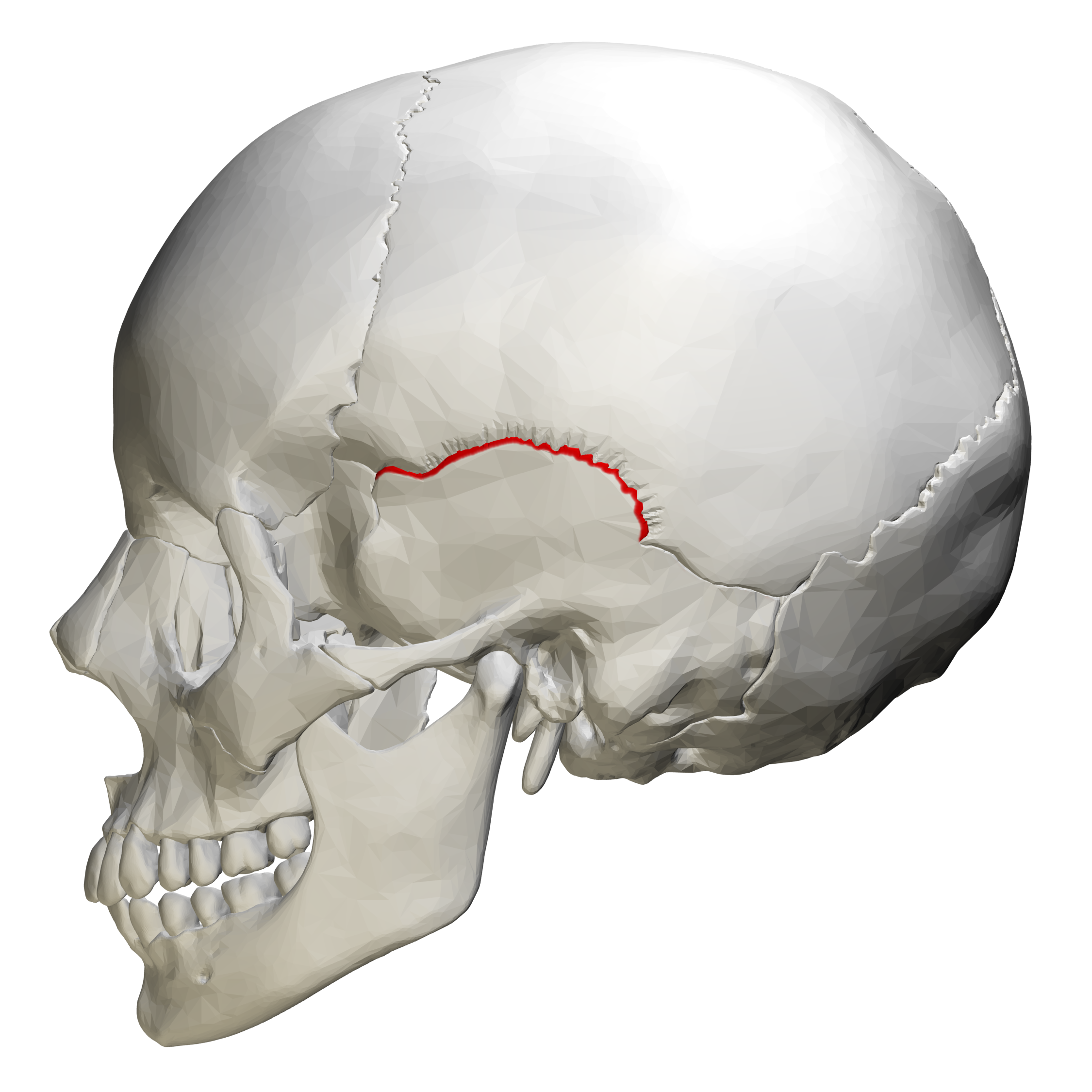
squamous suture
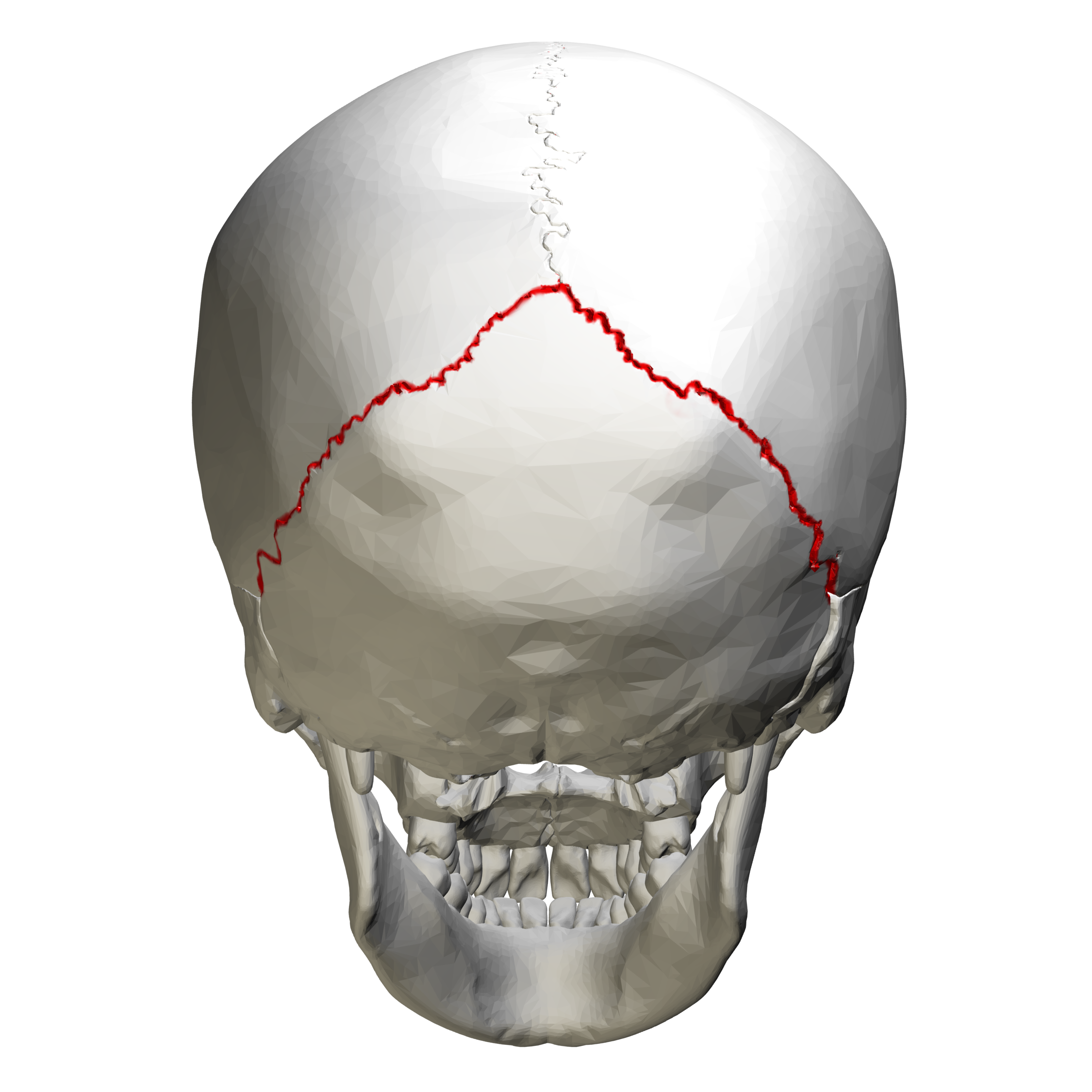
lambdoid suture
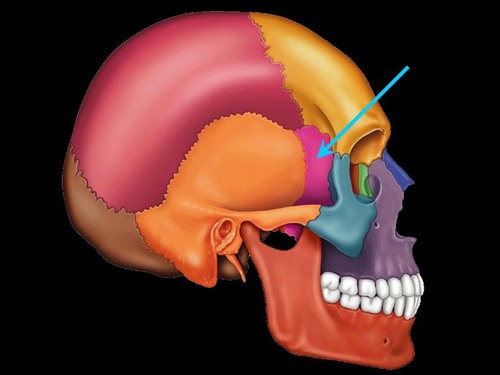
sphenoid bone (lateral view)
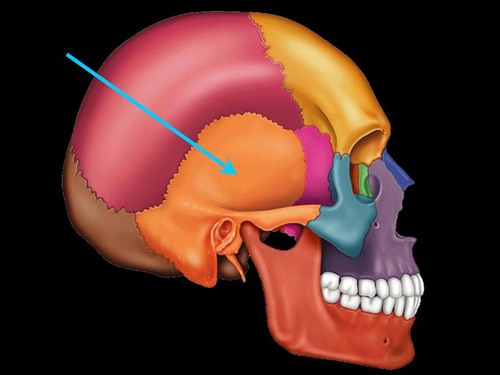
temporal bone
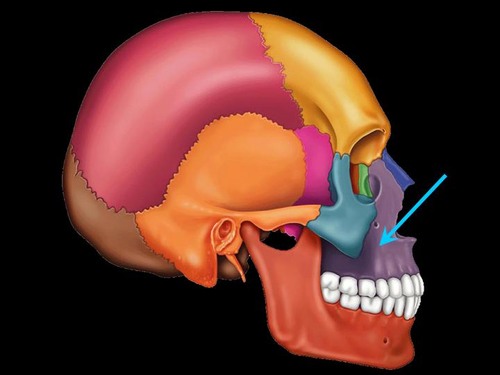
maxilla (lateral view)
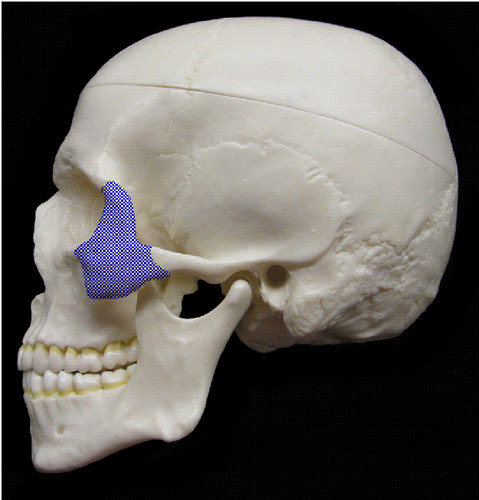
zygomatic bone (lateral)
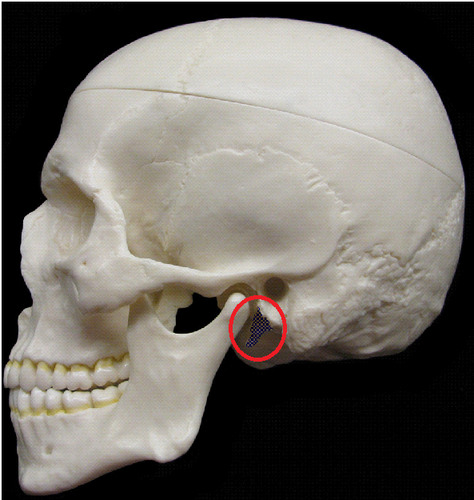
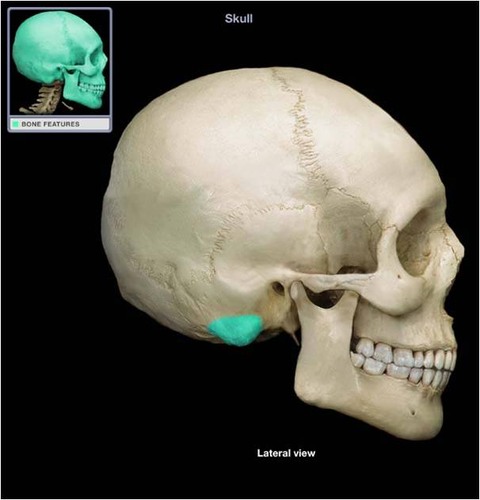
styloid process
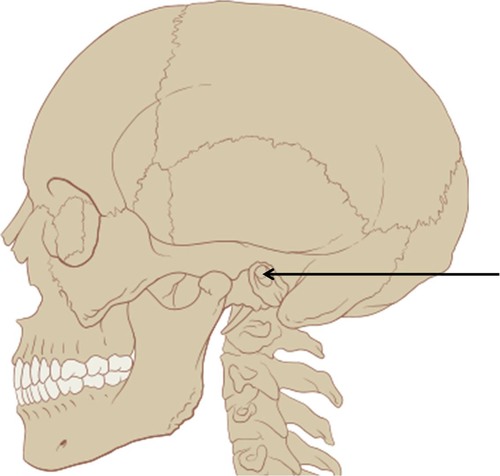
external auditory meatus
mastoid process
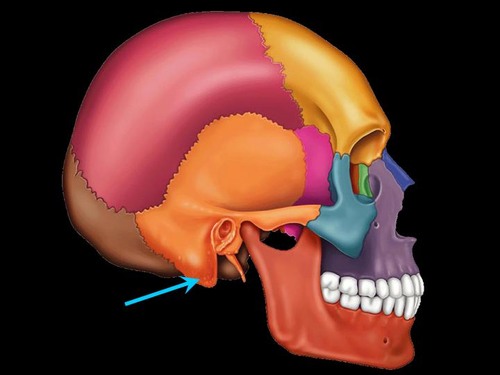
lingual bone
palatine process
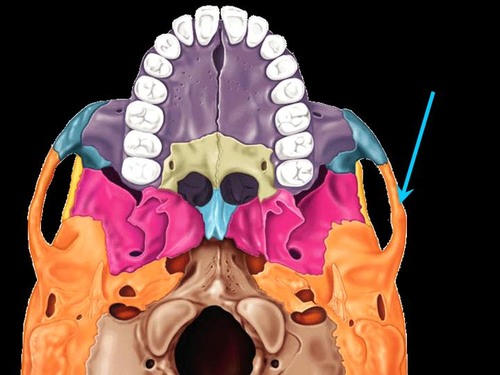
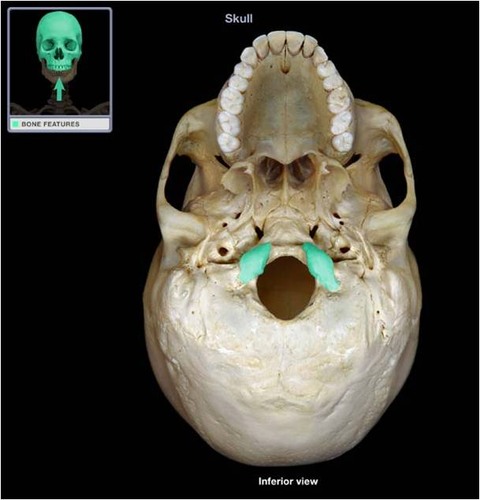
zygomatic bone (inferior)
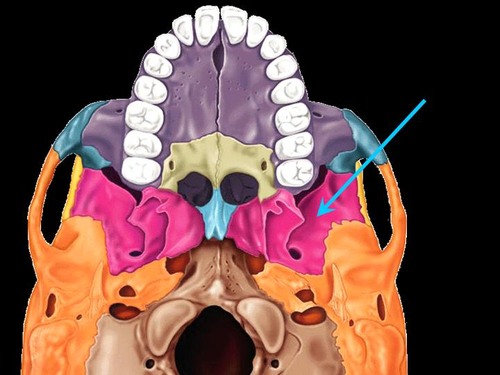
sphenoid bone (inferior)
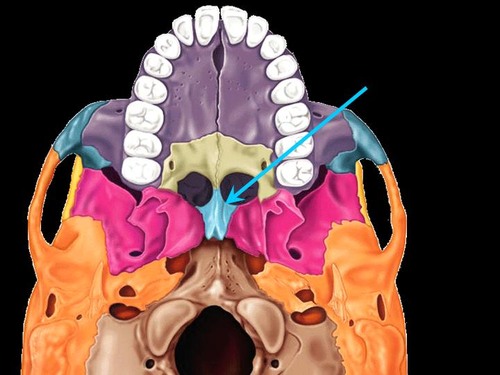
vomer (inferior)
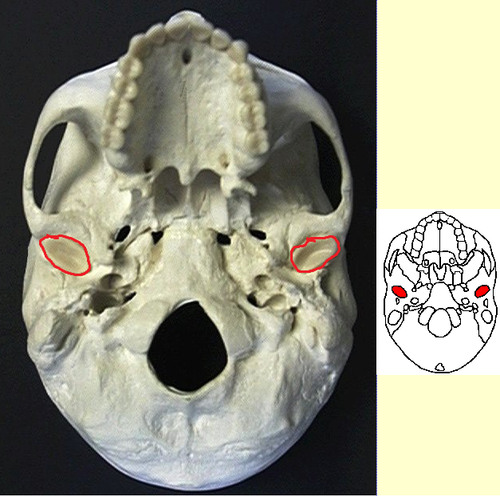
mandibular fossa
mastoid projection
occipital condyle
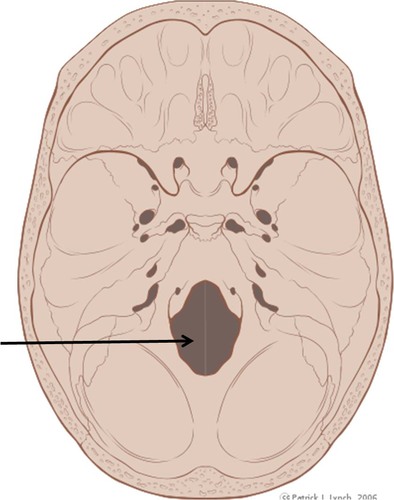
foramen magnum
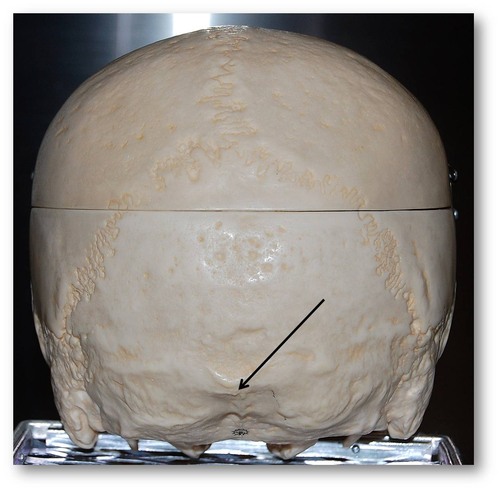
occipital bone
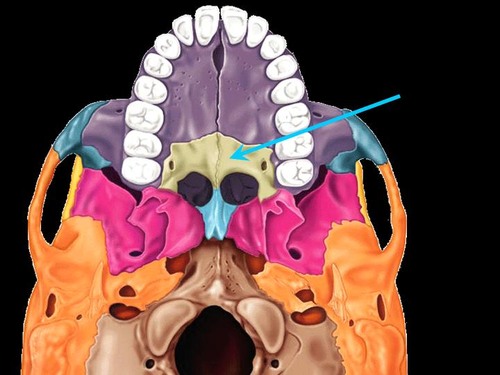
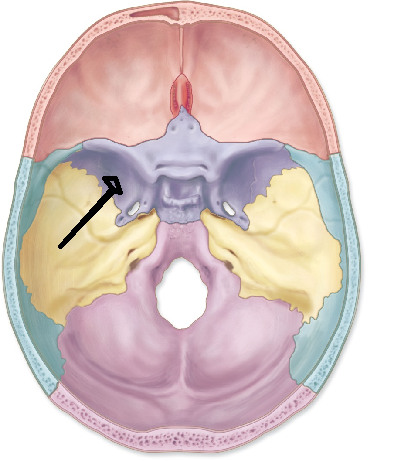
palatine bone
crista galli
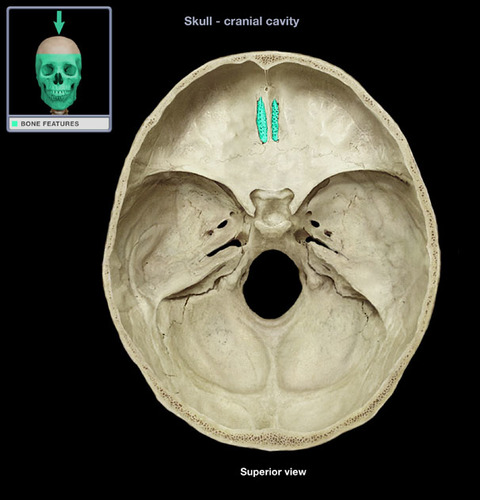
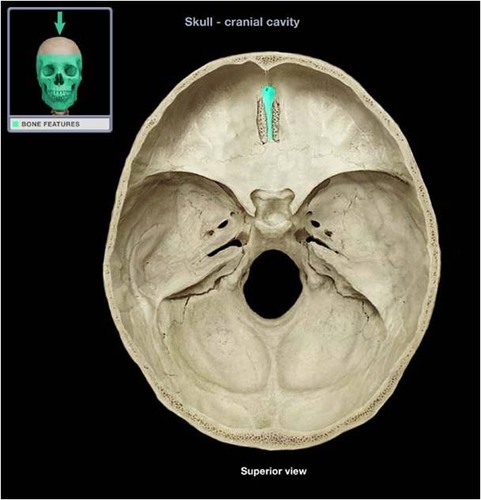
cribriform plate
greater wing of sphenoid
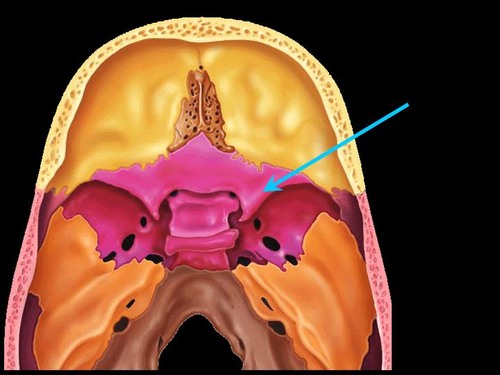
lesser wing of sphenoid
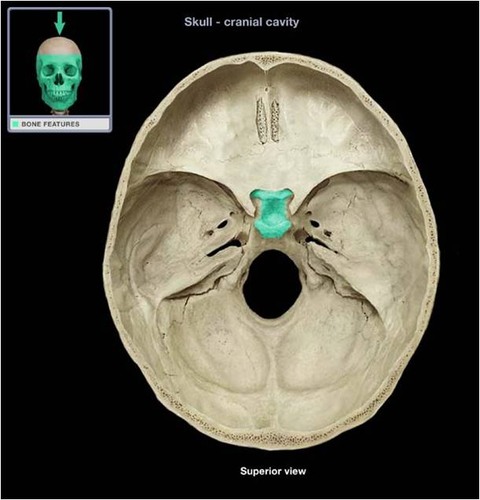
sella turcica
the axis
the atlas
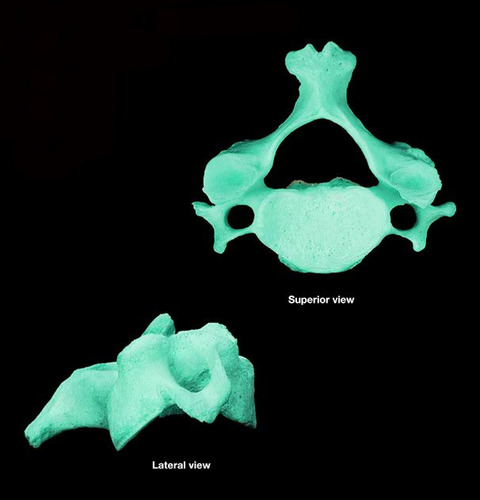
cervical vertebra
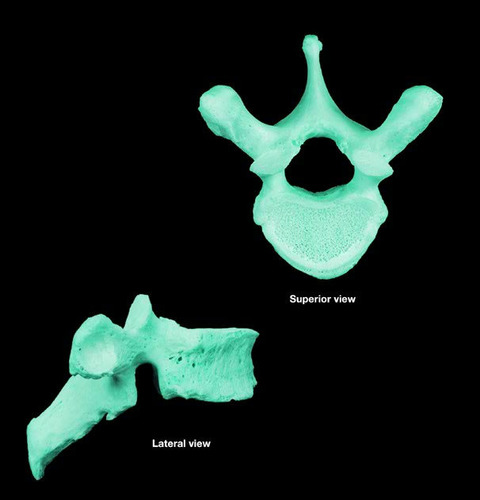
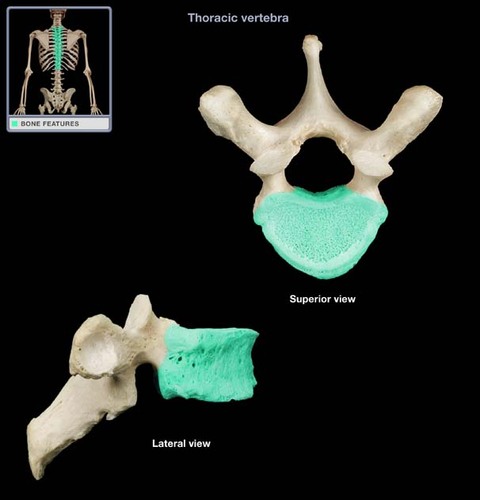
thoracic vertebra
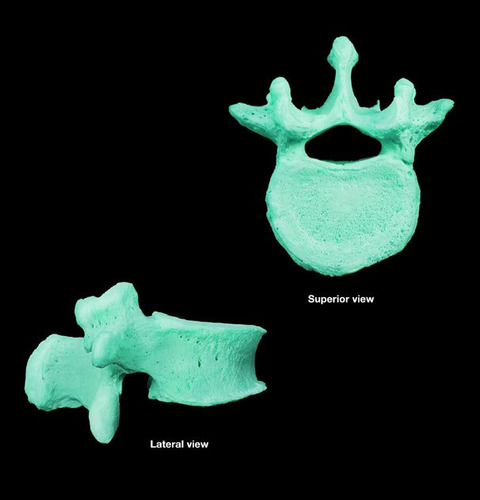
lumbar vertebra
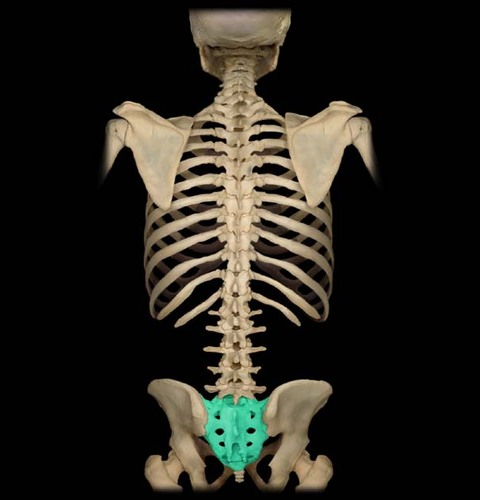
sacrum
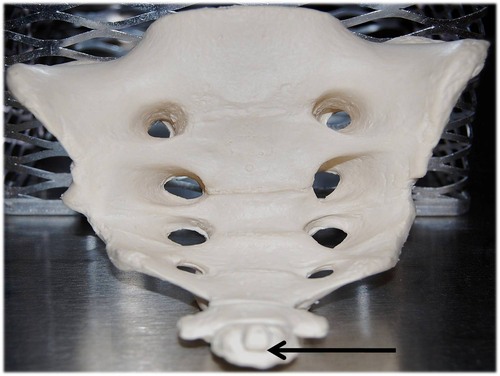
coccyx
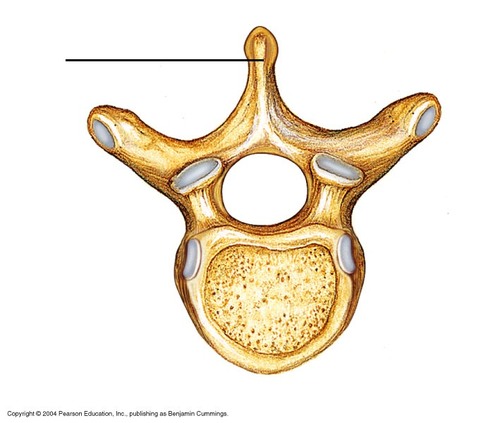
spinous projection
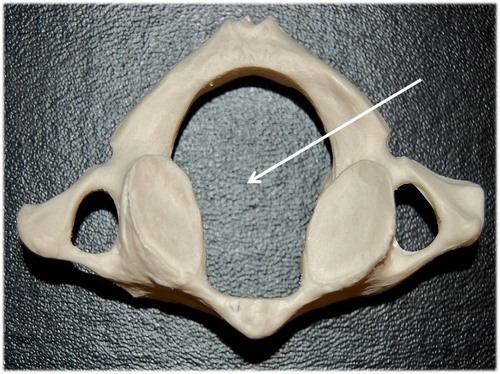
vertebral foramen
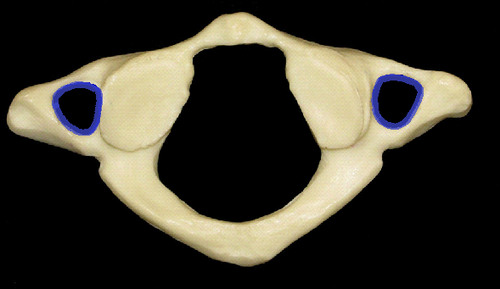
transverse foramen
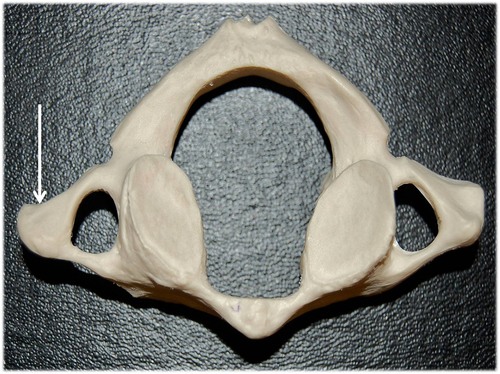
transverse projection
body
dens (odontoid projection)
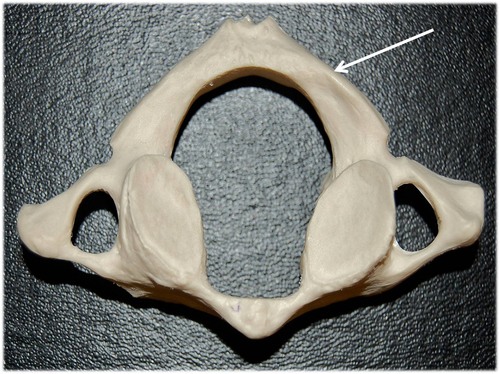
posterior arch
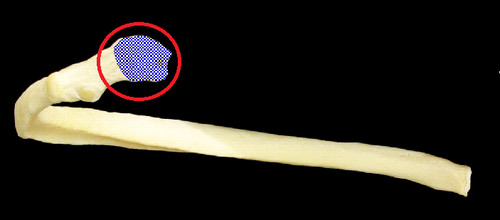
vertebral end
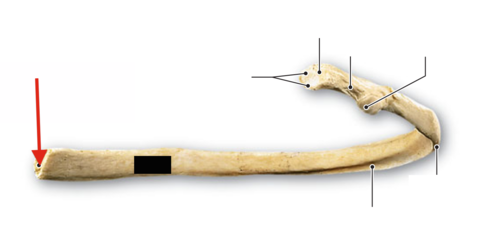
sternal end
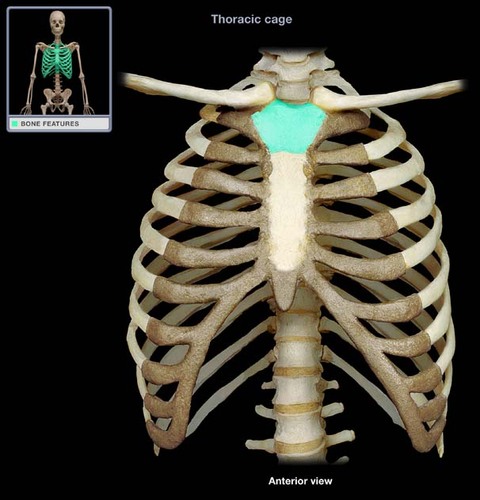
manubrium
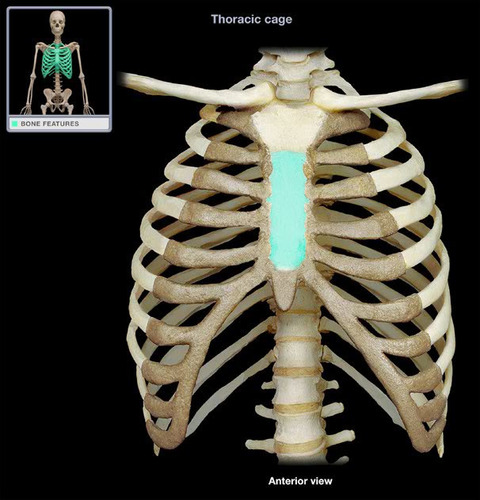
body of the sternum
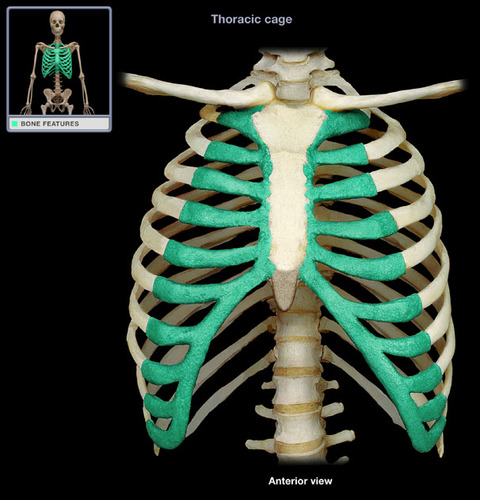
costal cartilage
which skull bone connects to all the other skull bones?
sphenoid bone
the inner ear is contained in which bone?
temporal bone
the spinal cord and brainstem connect through what hole, in which bone?
magnum foramen, skull
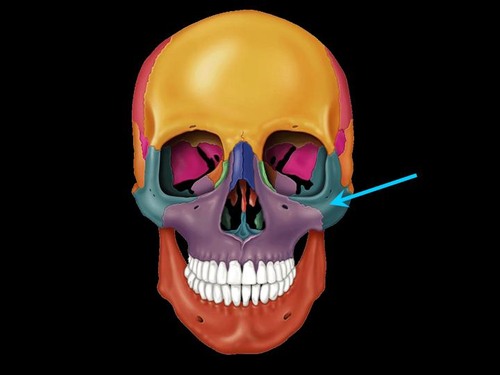
bones that make up the bony orbit of the eye socket?
frontal, lacrimal, ethmoid, maxilla, zygomatic, palatine, sphenoid
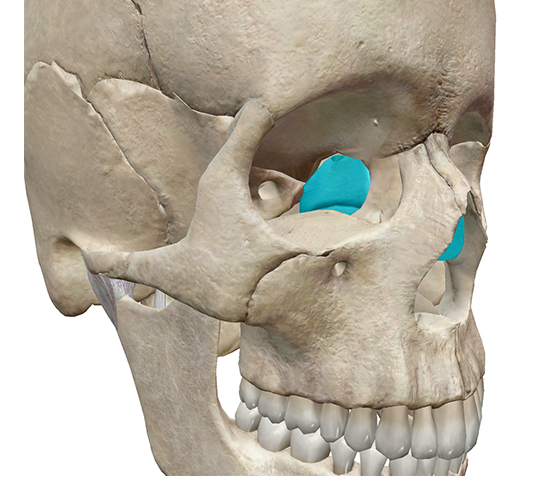
ethmoid bone
what is the master gland?
pituitary gland
which bone surrounds the master gland?
sphenoid bone
what features make the cervical vertebrae different than other vertebrae?
short, bifurcated spinous process
transverse foramen for vertebral artery (unique in cervical)
transverse processes are shorter
have the smallest body because they bear the least amount of weight
how many cervical vertebrae are there in the vertical column?
7
names of the first two cervical vertebrae?
c1 - atlas
c2 - axis
what movement does c1 allow?
anterior/posterior arches - nodding “yes”
due to unique articulation between atlas and occipital condyles of skull
what movement does c2 allow?
shaking head - “no” motion
dens process allows for articulation with atlas
what structure does c1 articulate with?
occipital condyles of skull, c2 (axis)
what structures does c7 articulate with?
t1 thoracic vertebra
c6 vertebra
what are the purposes of the transverse foramen?
allows for verebral artery and vein to pass through cervical vertebrae
features of the thoracic vertebrae?
larger than cervical vertebrae
body has 2 small articular facets on each side to articulate with ribs
long spinous pprocess w/ downward hook
only vertebrae to articulate with ribs
how many thoracic vertebrae are there?
12
what do the throacic vertebrae articulate with?
the ribs
how many pairs of ribs are there?
12 pairs
how do the ribs articulate with the throacic vertebrae?
articulate posteriorly
what do the throacic vertebrae articulate with superiorly?
cervical vertebrae
what do the throacic vertebrae articulate with inferiorly?
lumbar vertebrae
features of lumbar vertebrae?
large, block-like bodies
short, thick spinous processes
articular facets are oriented differently
recieves most stress, strong
how many lumbar vertebrae are there?
5
what other vertebrae do the lumbar articulate with?
thoracic vertebrae (T12)
sacrum
what bone does the sacrum articulate with superiorly?
5th lumbar (L5)
what bone does the sacrum articulate with on its lateral surface?
illium
what joint is formed between the sacrum and the lateral bones?
iliosacral joint