The Skull (Anatomy 2300 Unit 4 OSU Spring 18)
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
How many bones make up the cranium?
8
How many bones make up the face?
14
Is the skull considered part of the axial or appendicular skeleton?
Axial
What bones make up the cranium?
Frontal bone (1)
Temporal bone (2)
Occipital bone (1)
Parietal bone (2)
Sphenoid (1)
Ethmoid (1)
What bones make up the face?
Maxillaee (2)
Palatine bones (2)
Nasal bones (2)
Inferior Nasal Conchae (2)
Zygomatic bones (2)
Lacrimal bones (2)
Vomer (1)
Mandible (1)
Occipital Bone
What bone is this?
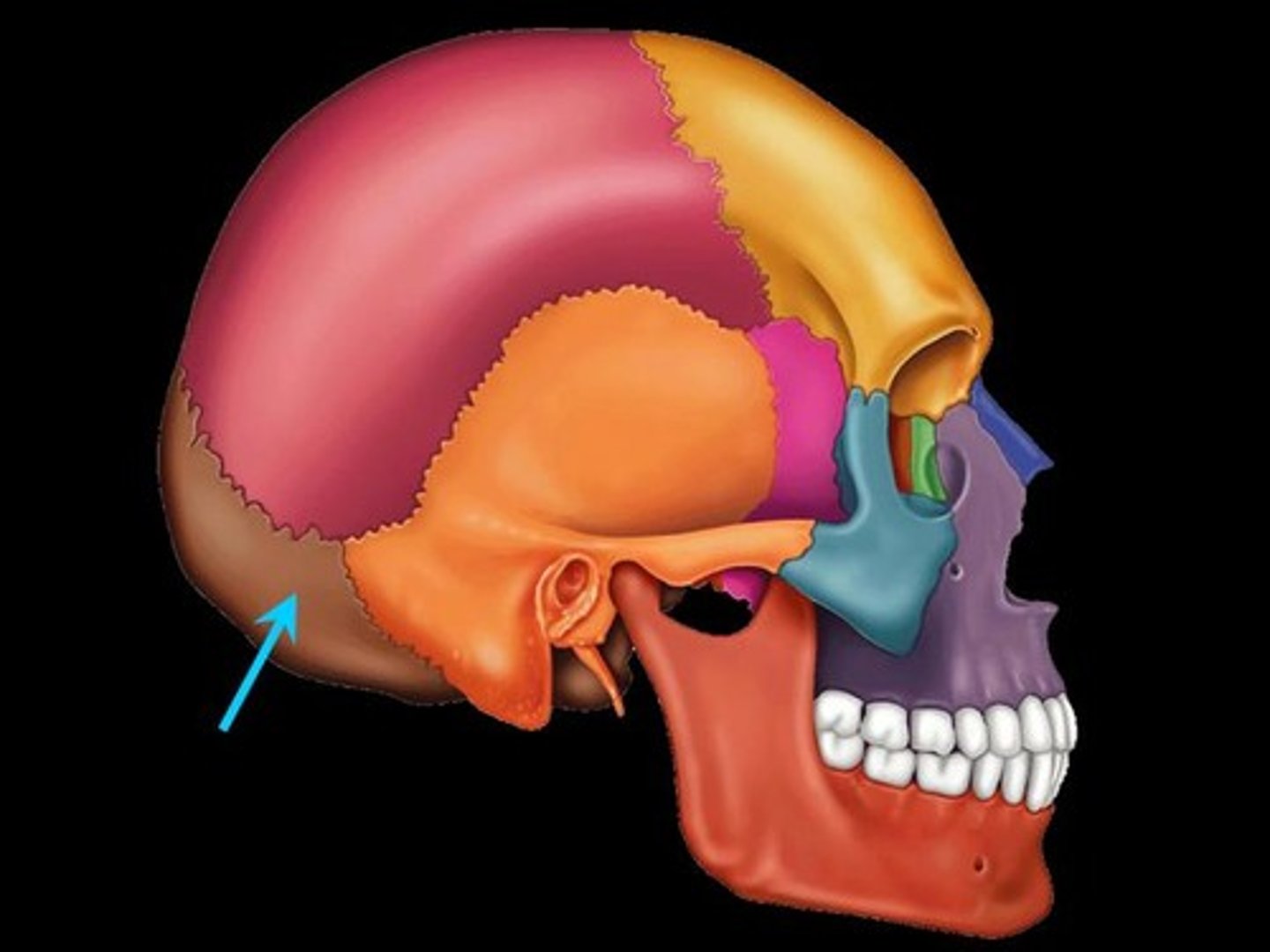
Parietal Bone (Note: There are two of them)
What bone is this?

Temporal bone (Note: There are two of them)
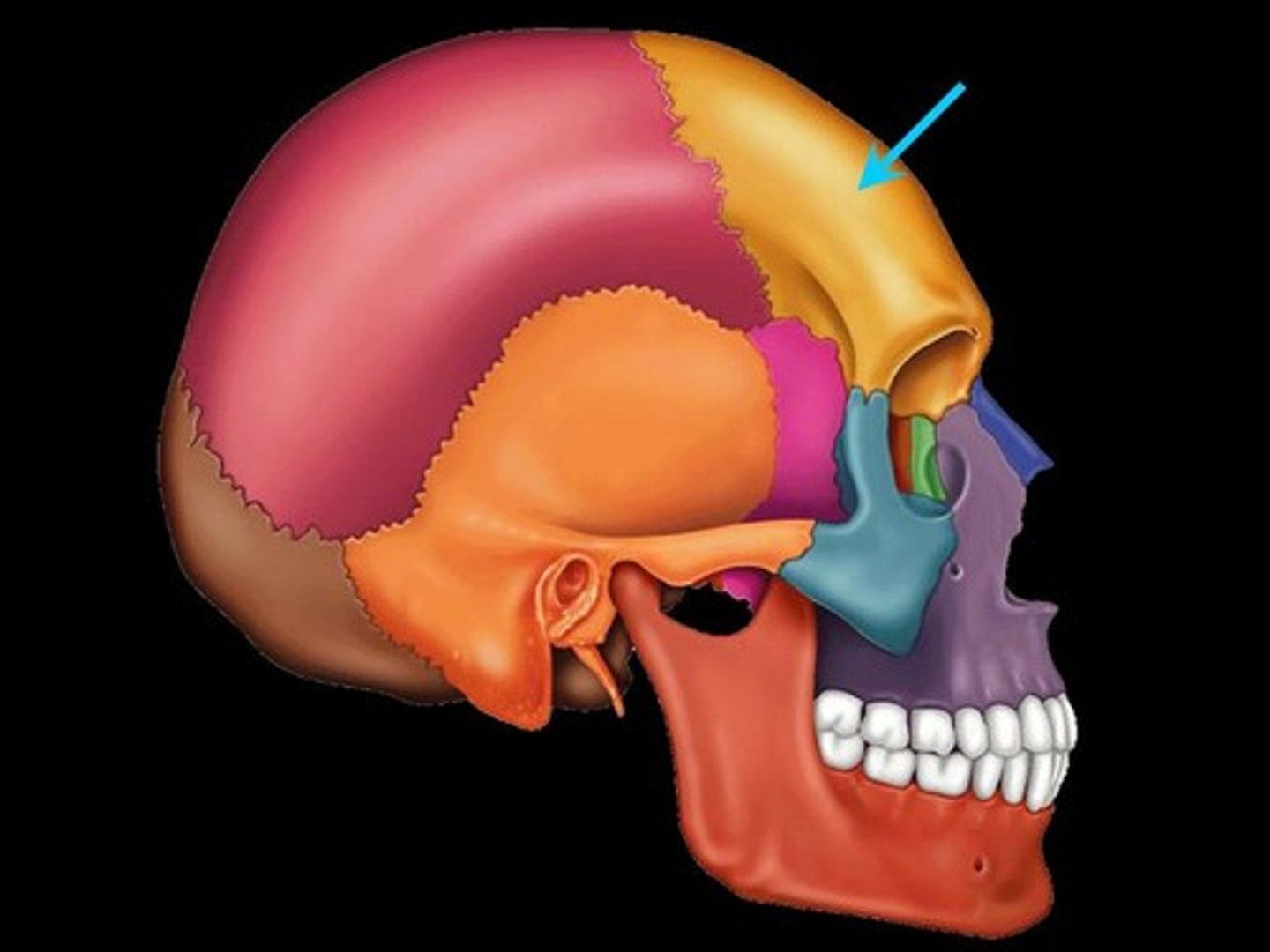
What bone is this?
Frontal bone
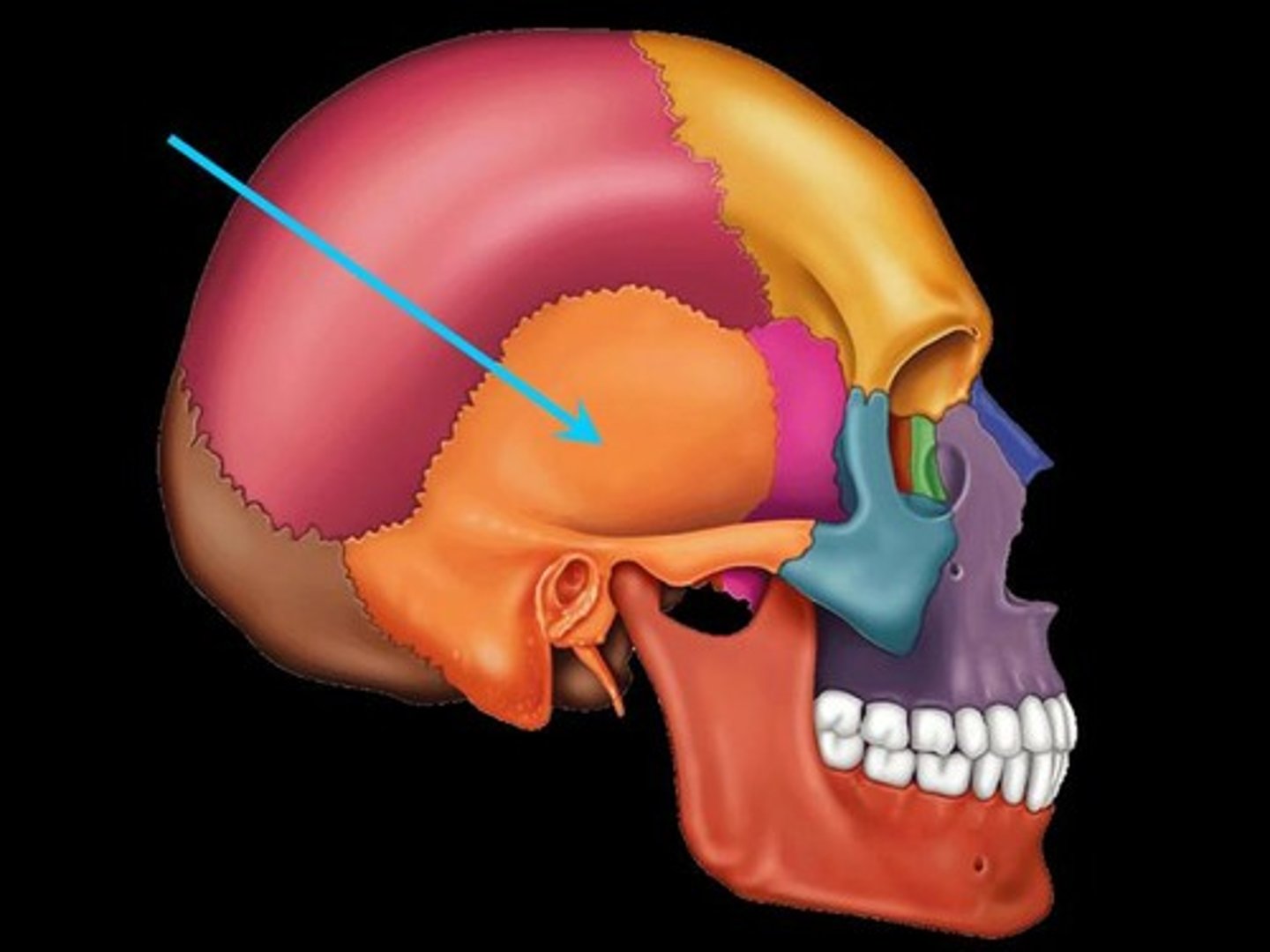
What bone is this?
Sphenoid
What bone is this?
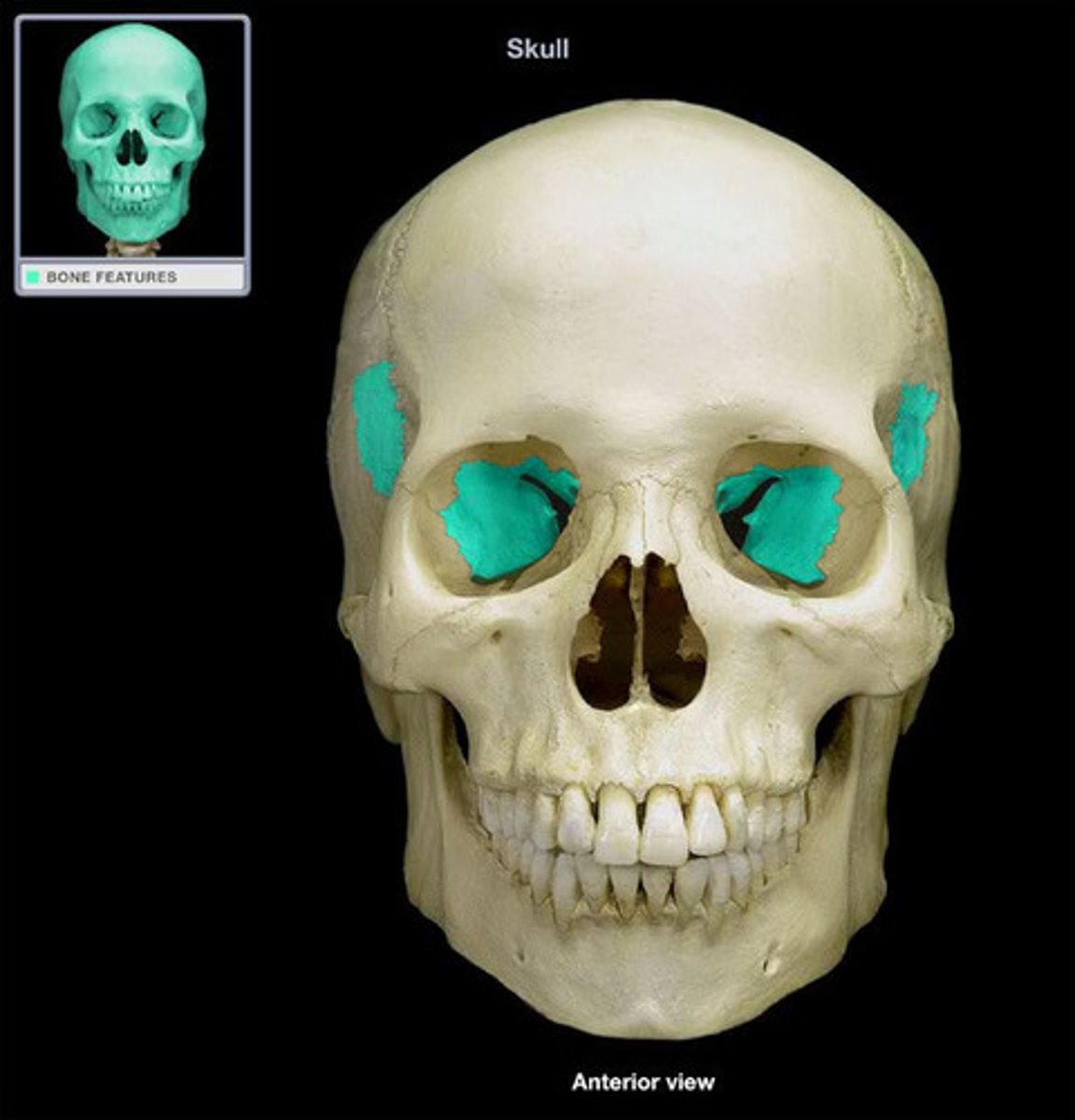
Ethmoid
What bone is this?
Maxillae (There are two bones)
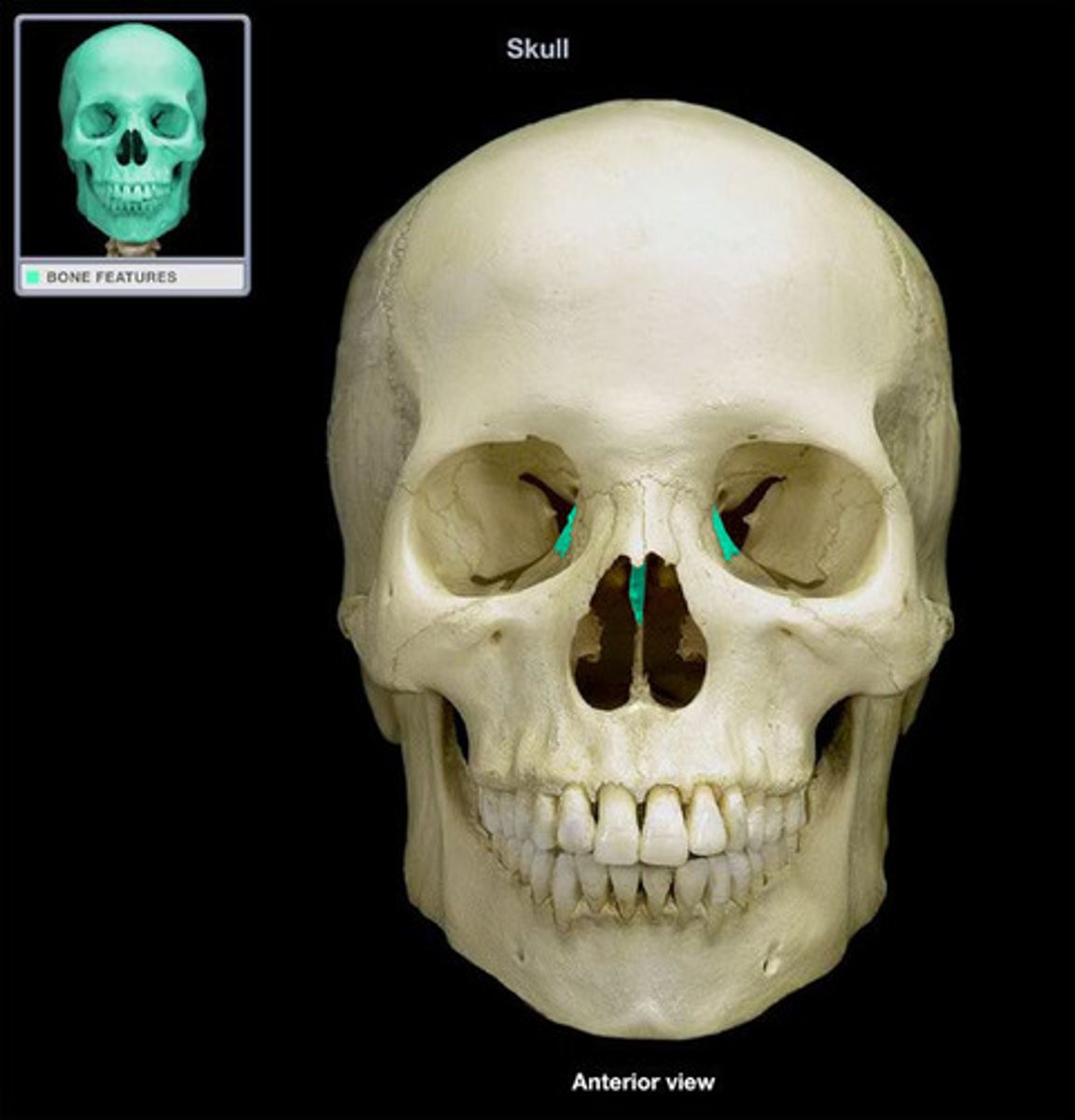
What bone is this?
Palatine bones (there are two bones)
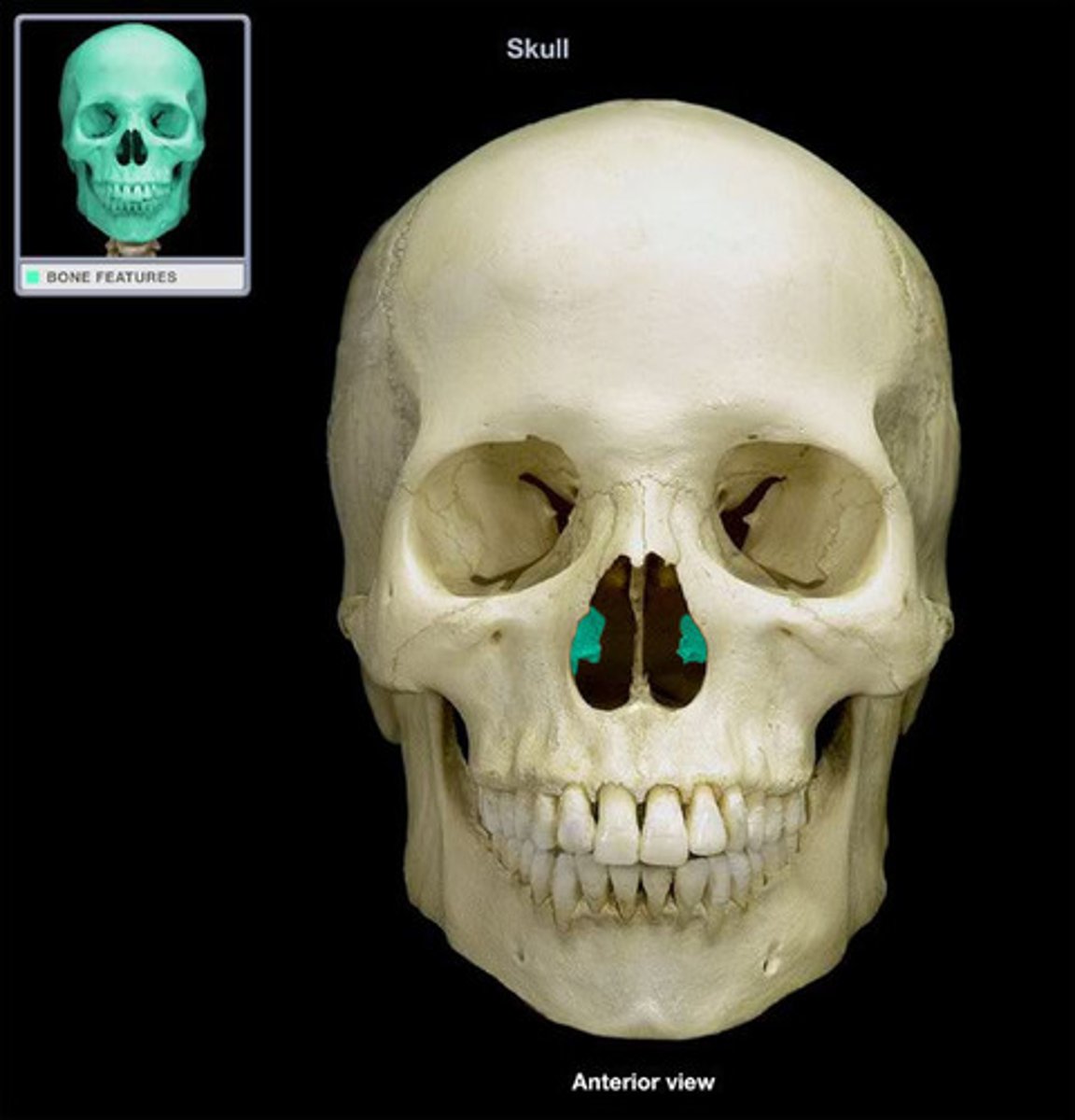
What bone is this?
Nasal bones (there are two bones)
What bone is this?
Inferior Nasal conchlae (there are two bones)
What bone is this?
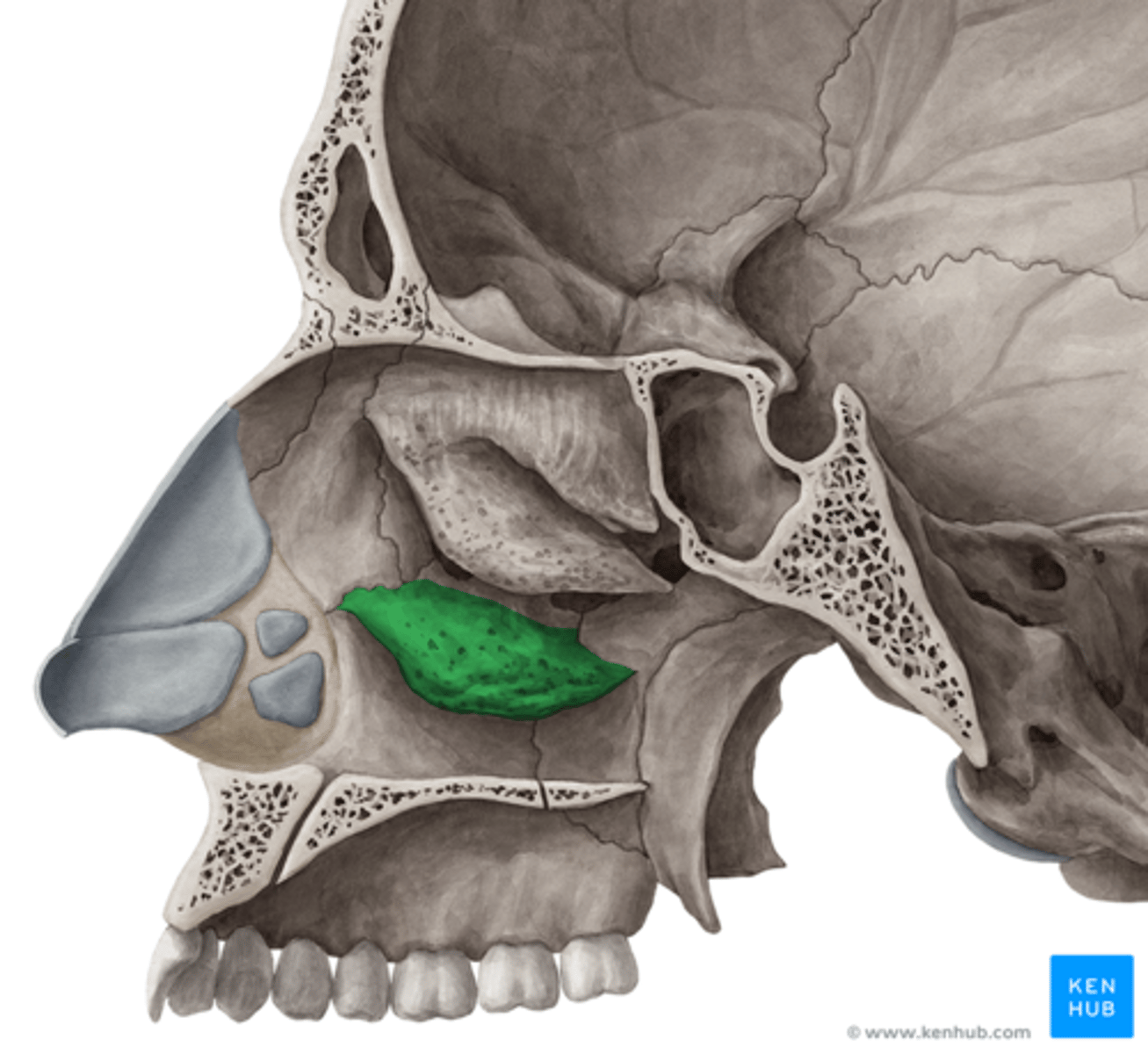
Zygomatic bones (there are two bones)
What bone is this?`
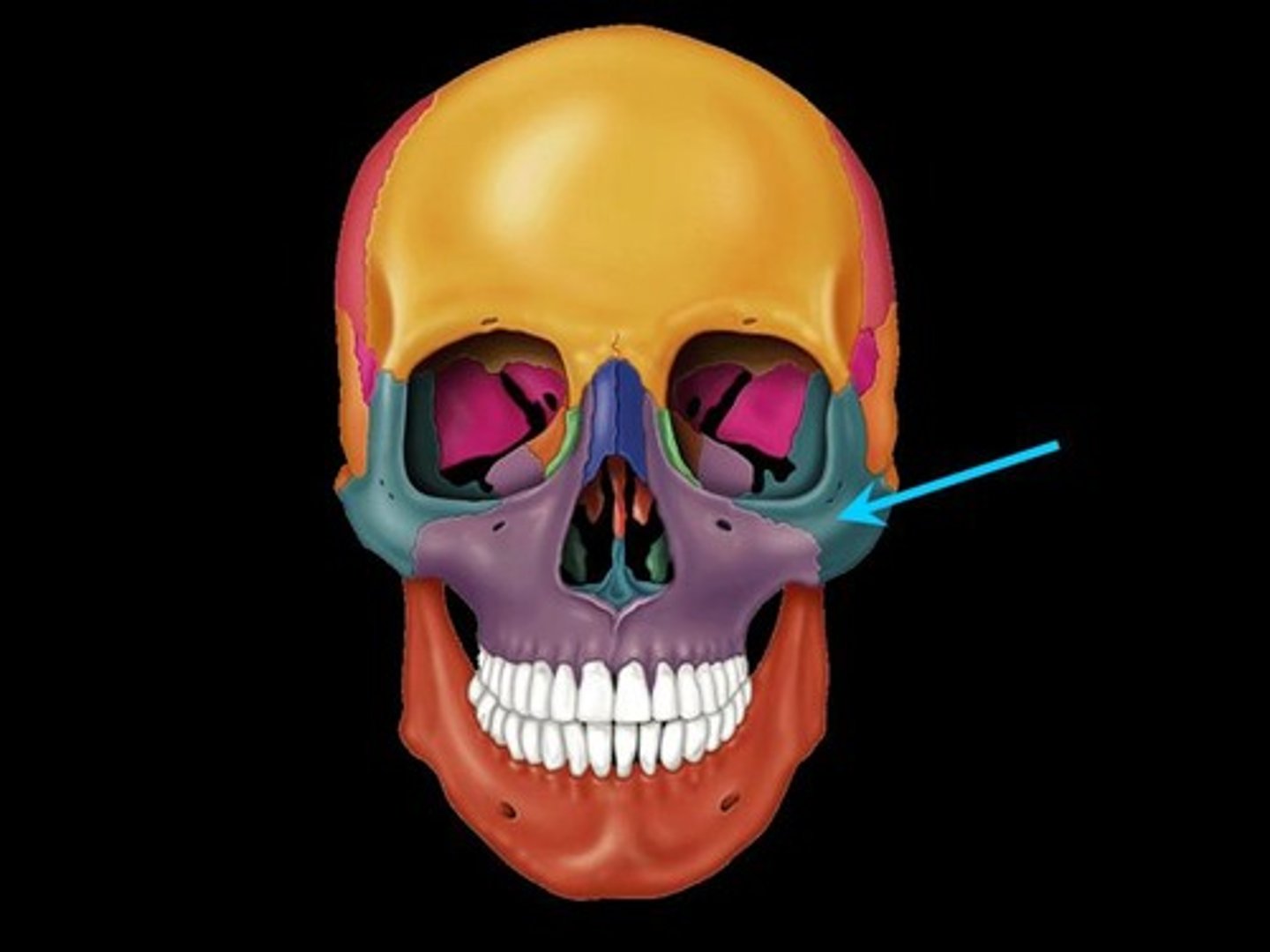
Lacrimal bones (there are two of these)
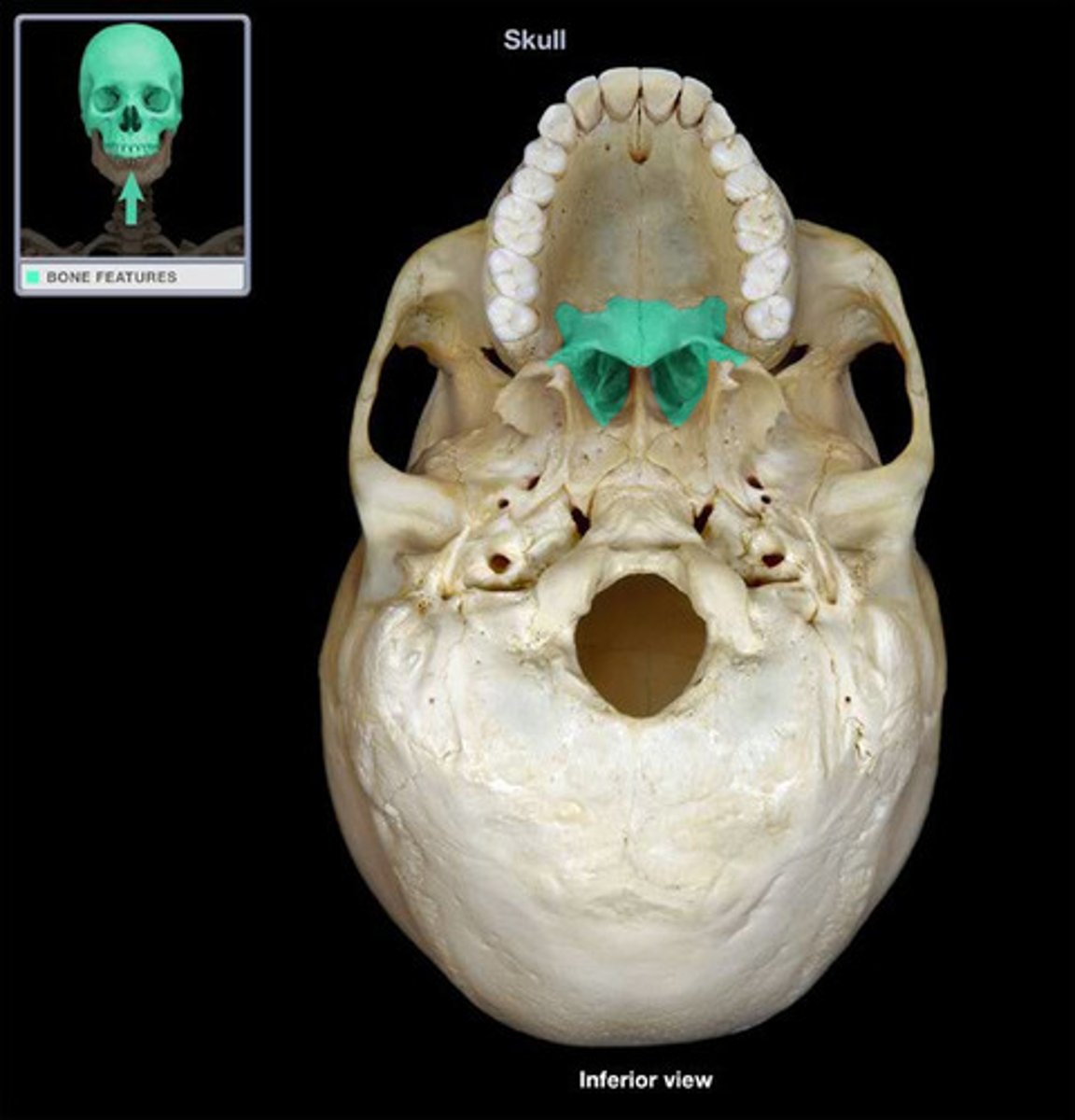
What bone is this?
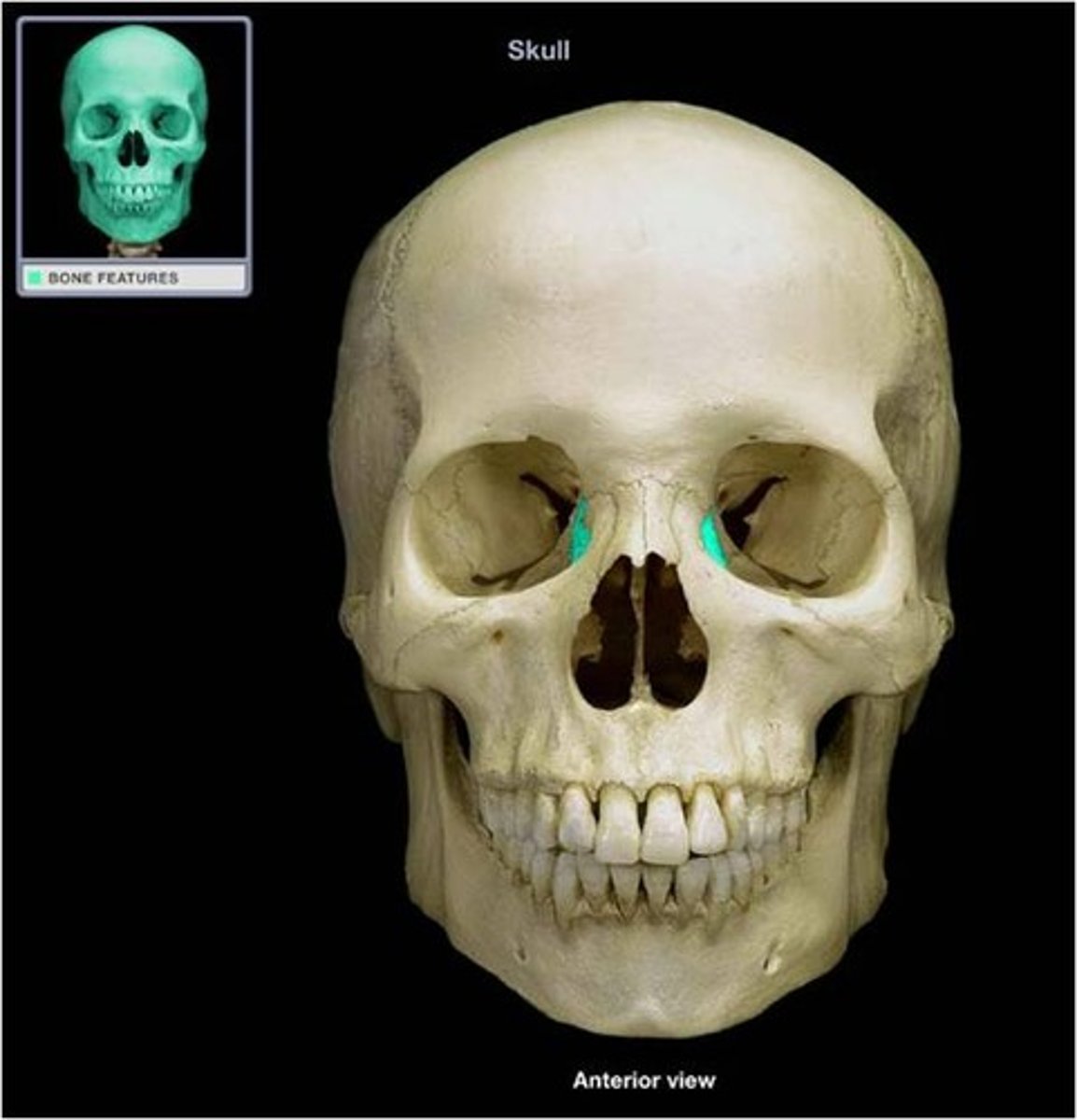
Vomer
What bone is this?
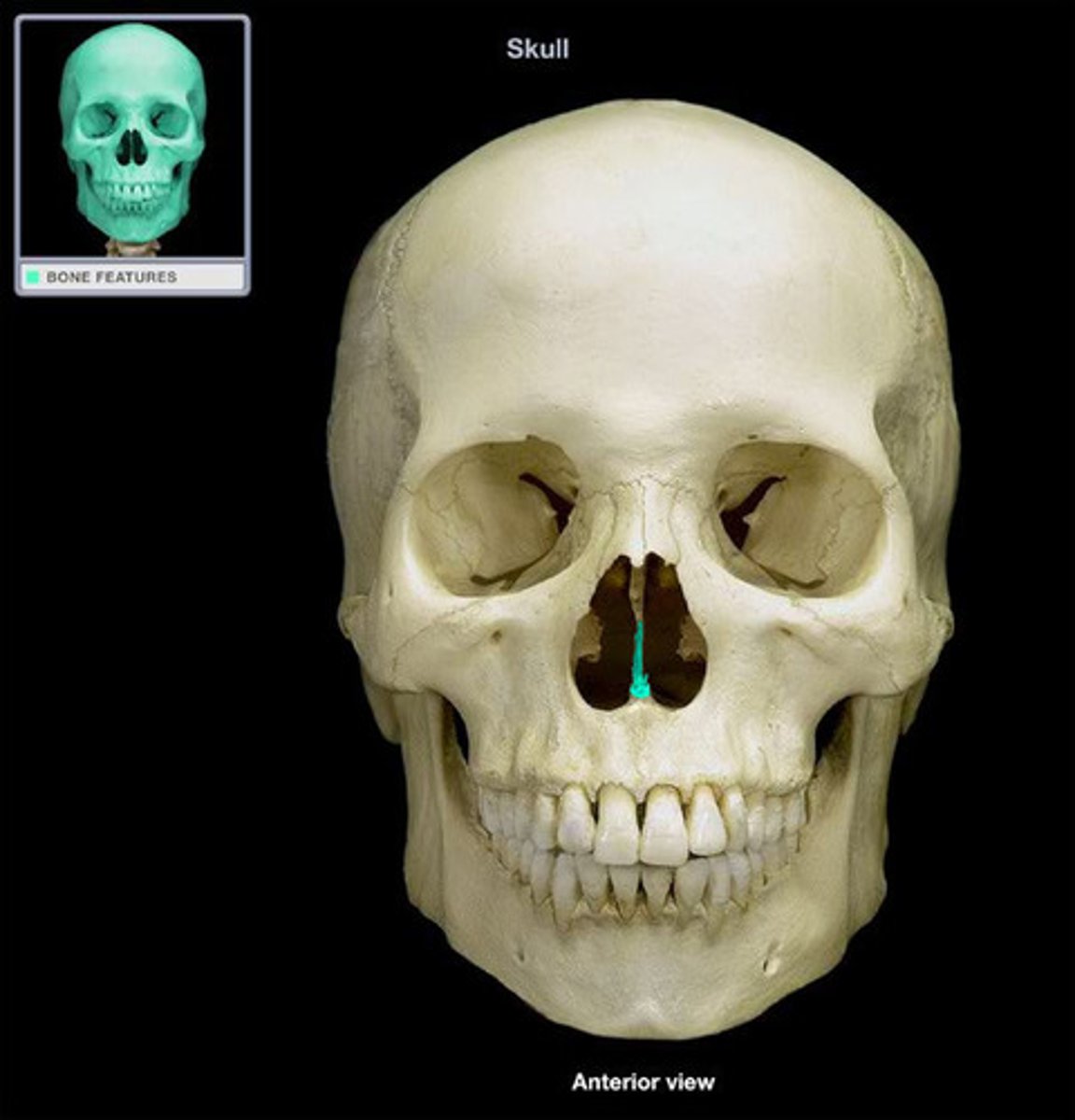
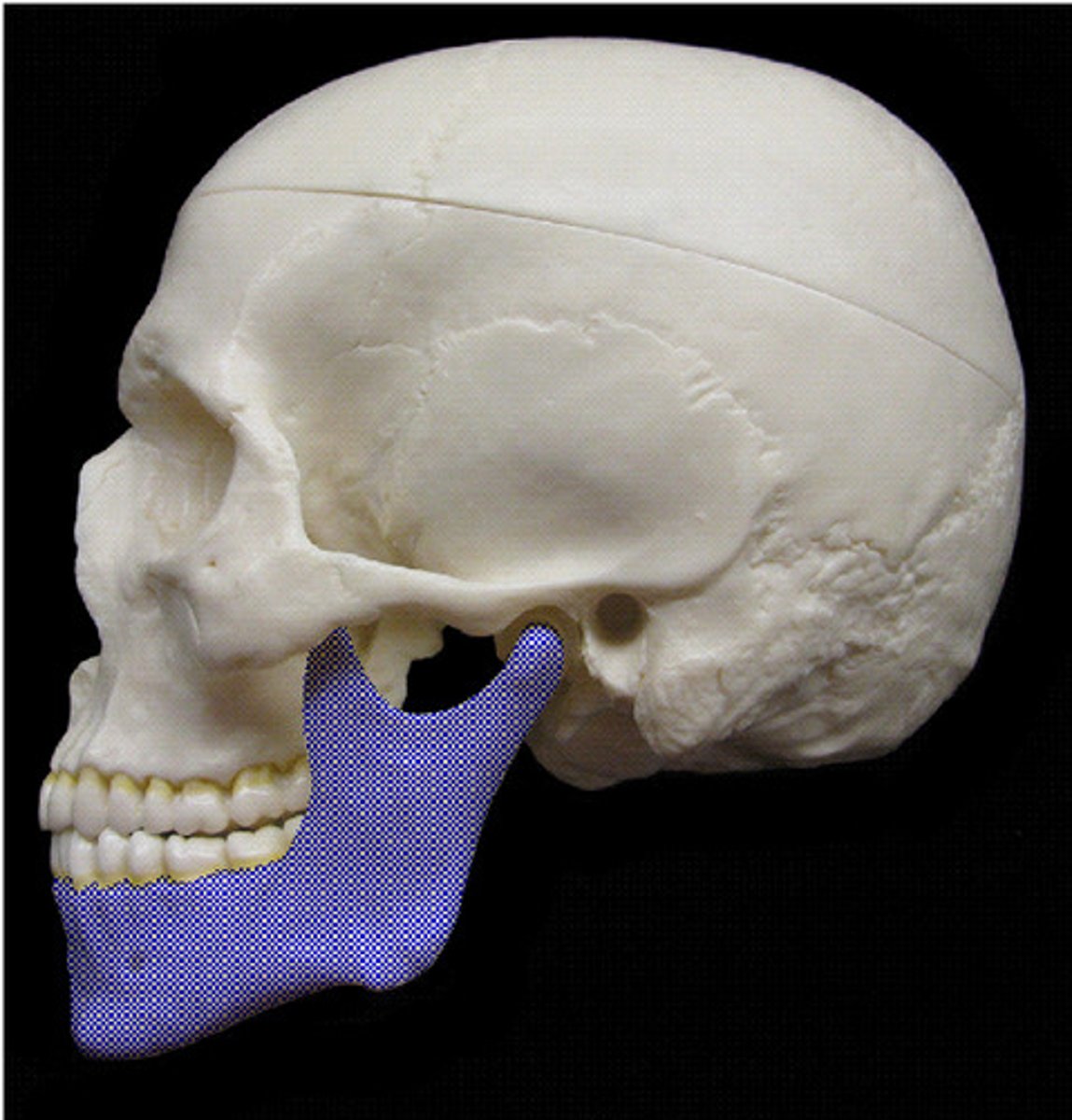
Mandible
What bone is this?
Cranium bones function?
Surround and protect the brain
Attachment sites for muscles
Which bones of the cranium make up the calvera (skull cap)?
Frontal Bone (1) (Superior aspect)
Parietal Bone (2) (Lateral aspect; major part of it)
Occipital Bone (1) (Posterior aspect)
Coronal suture
what suture is this?
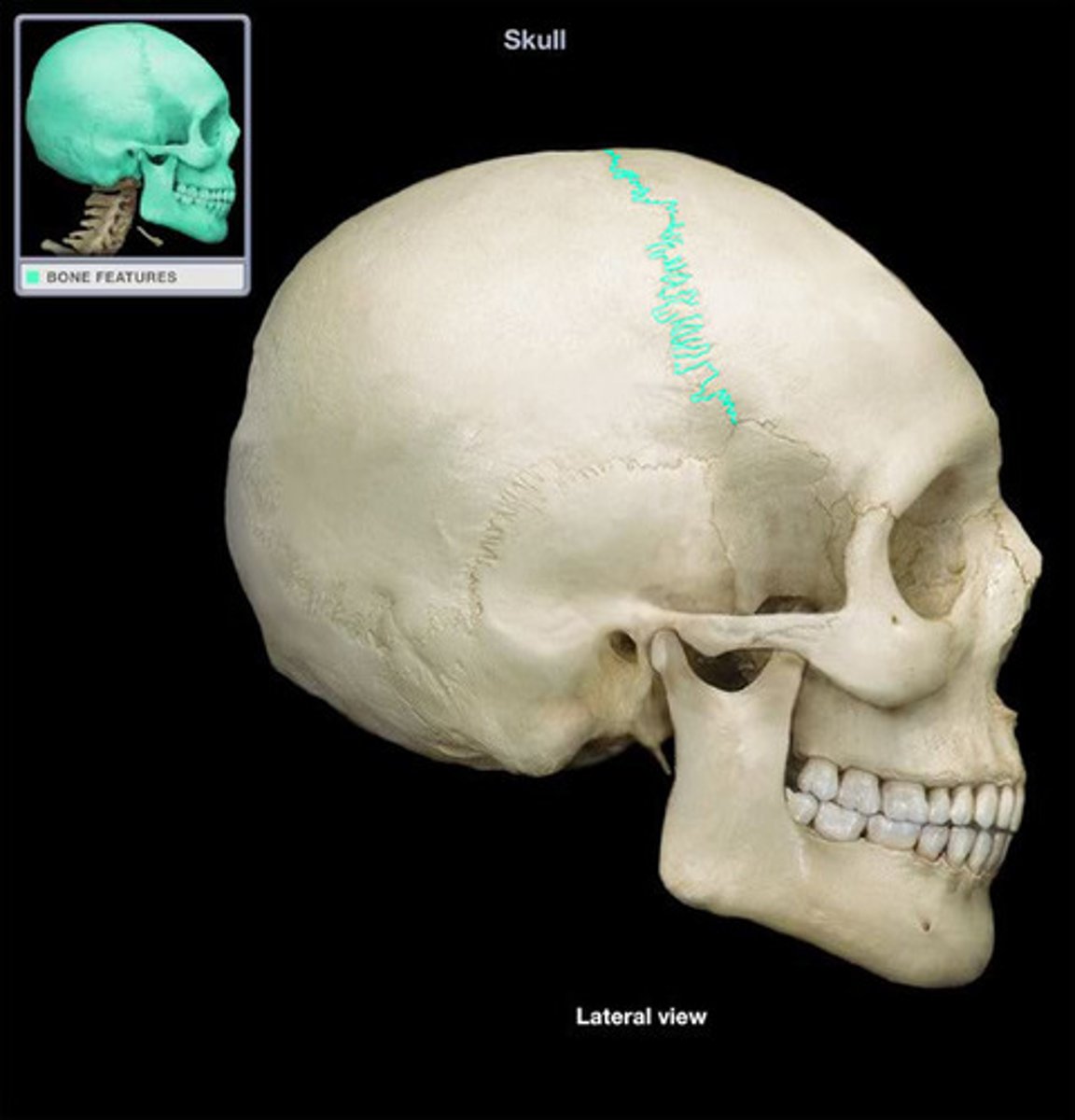
Squamosal Suture
what suture is this?
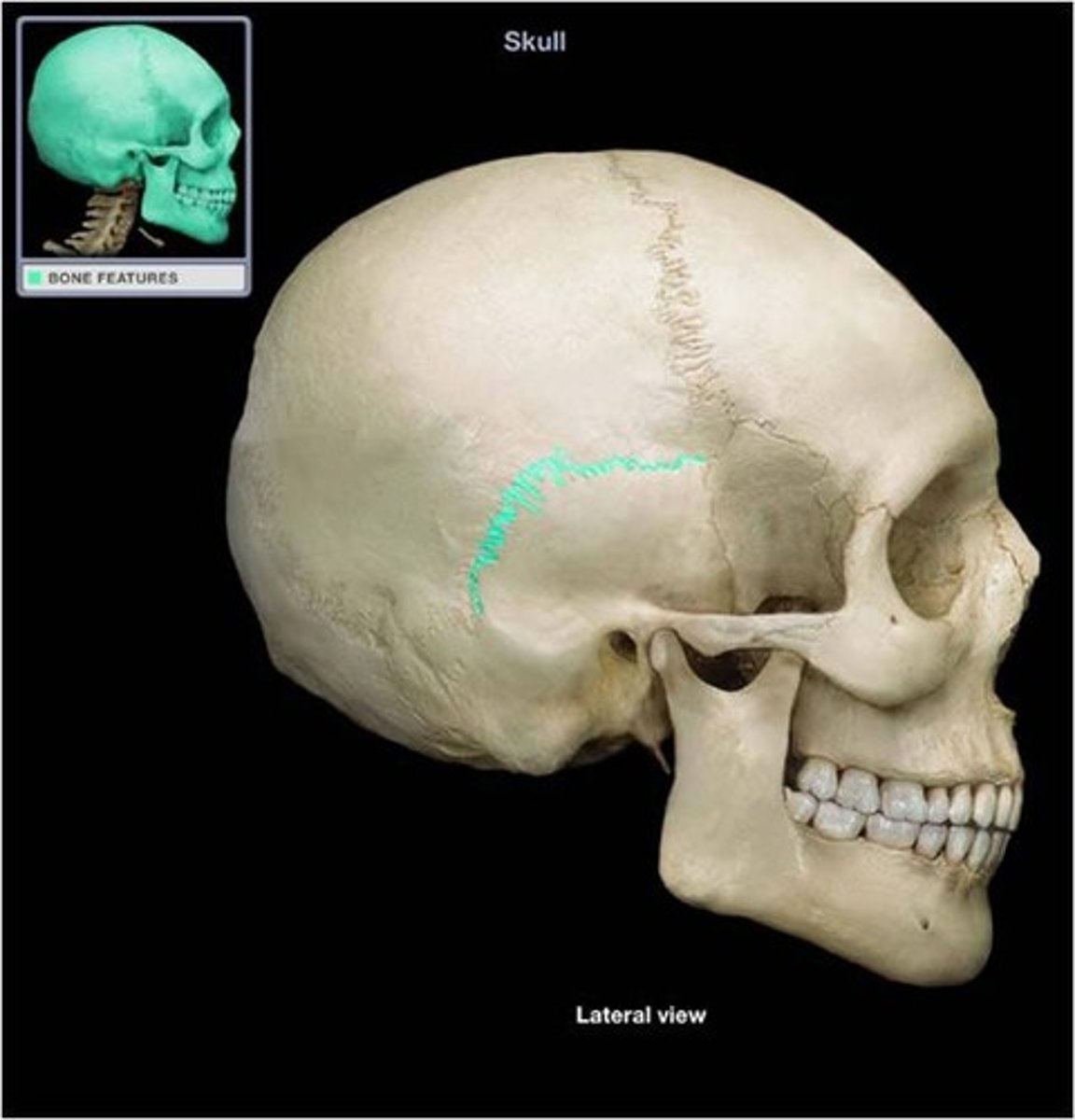
Sagittal suture
what sulture is this?

Lambdoidal sulture
Between parietal and occipital bones
What bones do coronal sulture seperate?
Frontal bone and parietal bones
what bones do squamosal suture seperate?
parietal and temporal (One is on each side of skull)
What bones do sagittal sulture seperate?
between parietal bones
What bones do lamboidal sulture seperate?
parietal and occipital bones
Sultures are considered ___ Joints based on structure and ___ joints baded on function?
Fibrous
Synarthrotic
Supra-orbital foramen (Frontal)
What is this?
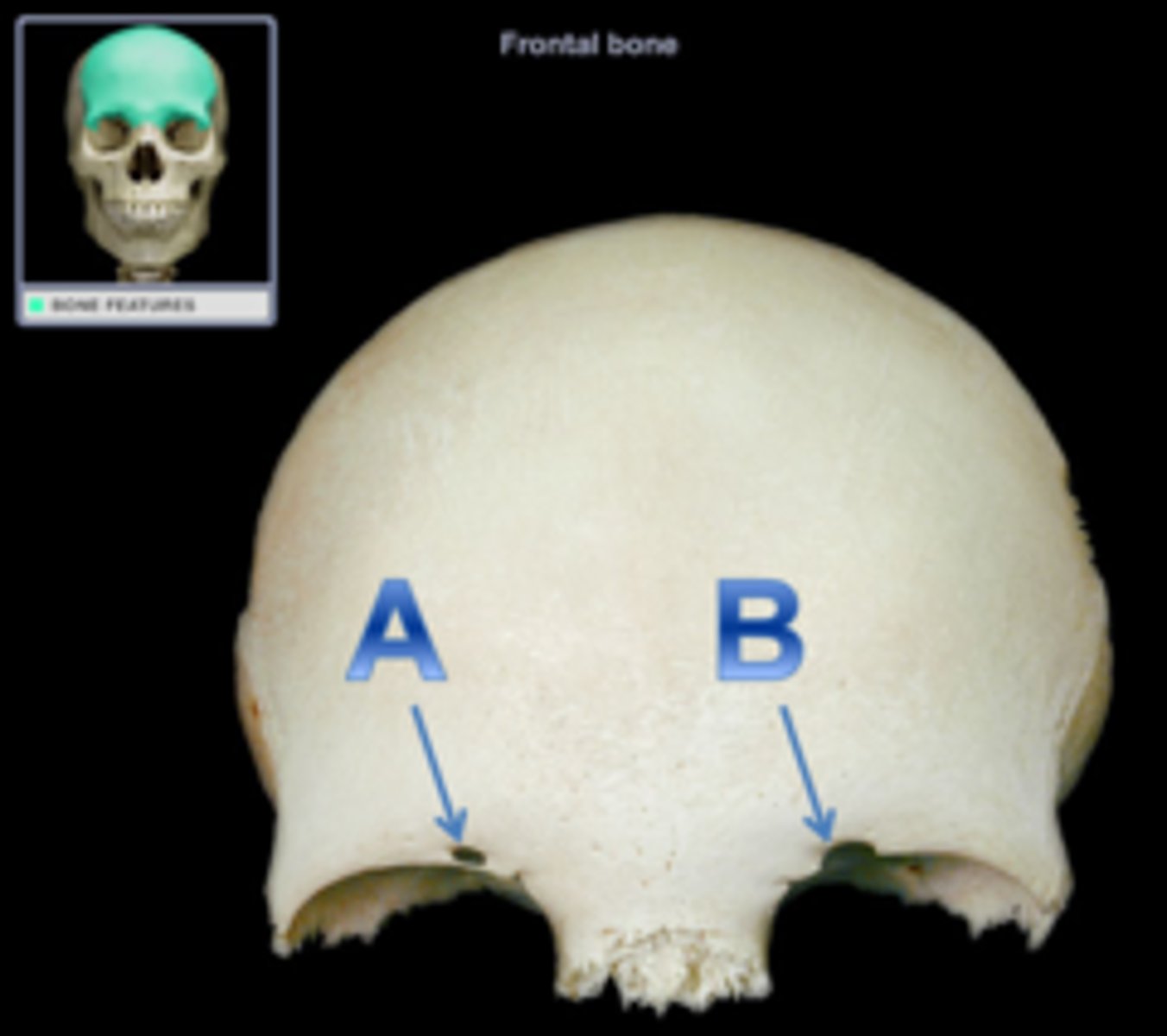
Supra-orbital notch (Frontal)
What is this?

Supra-orbital Margin (Frontal)
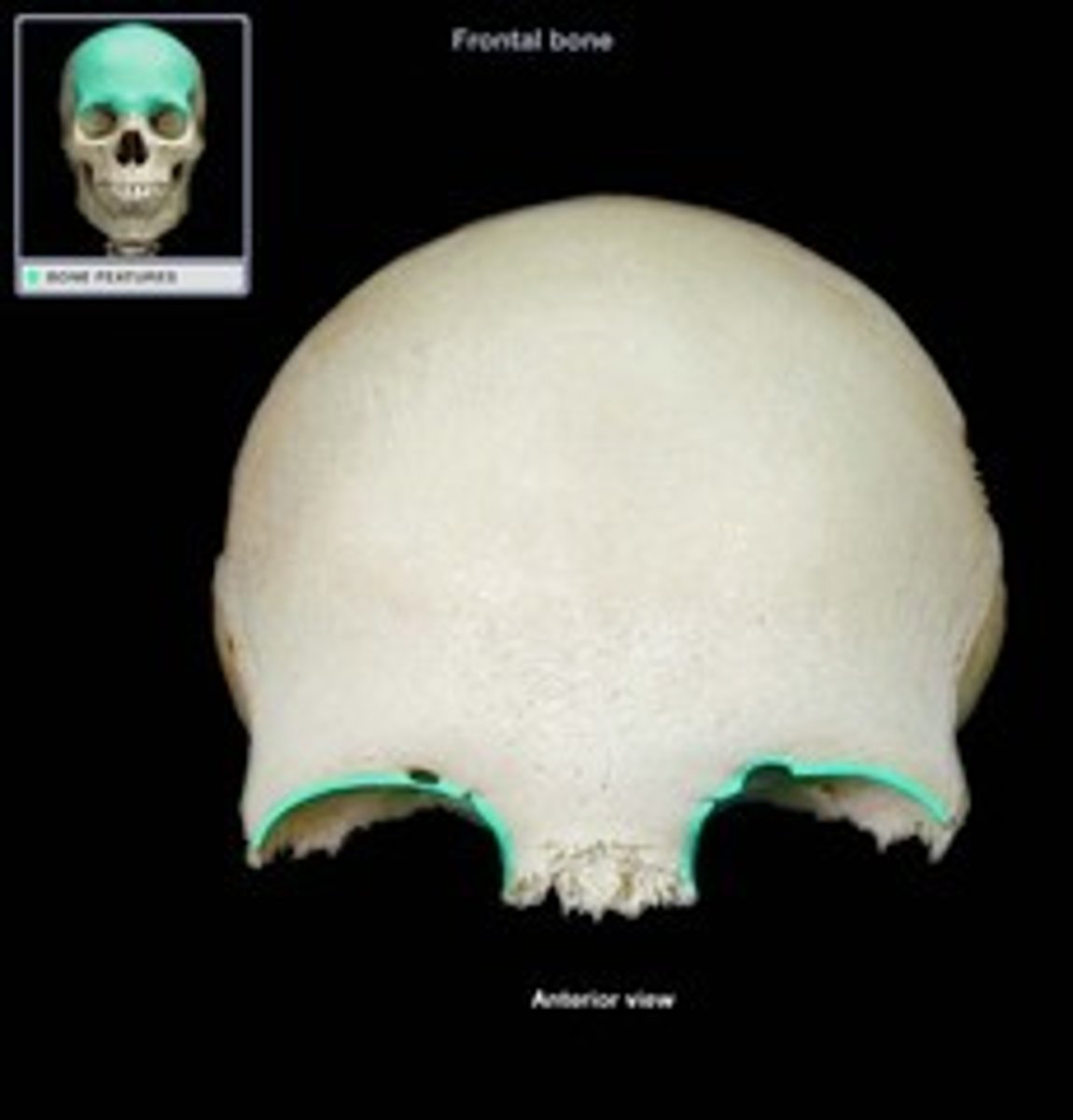
Notch for ethmoid (frontal)
What is this? (c)

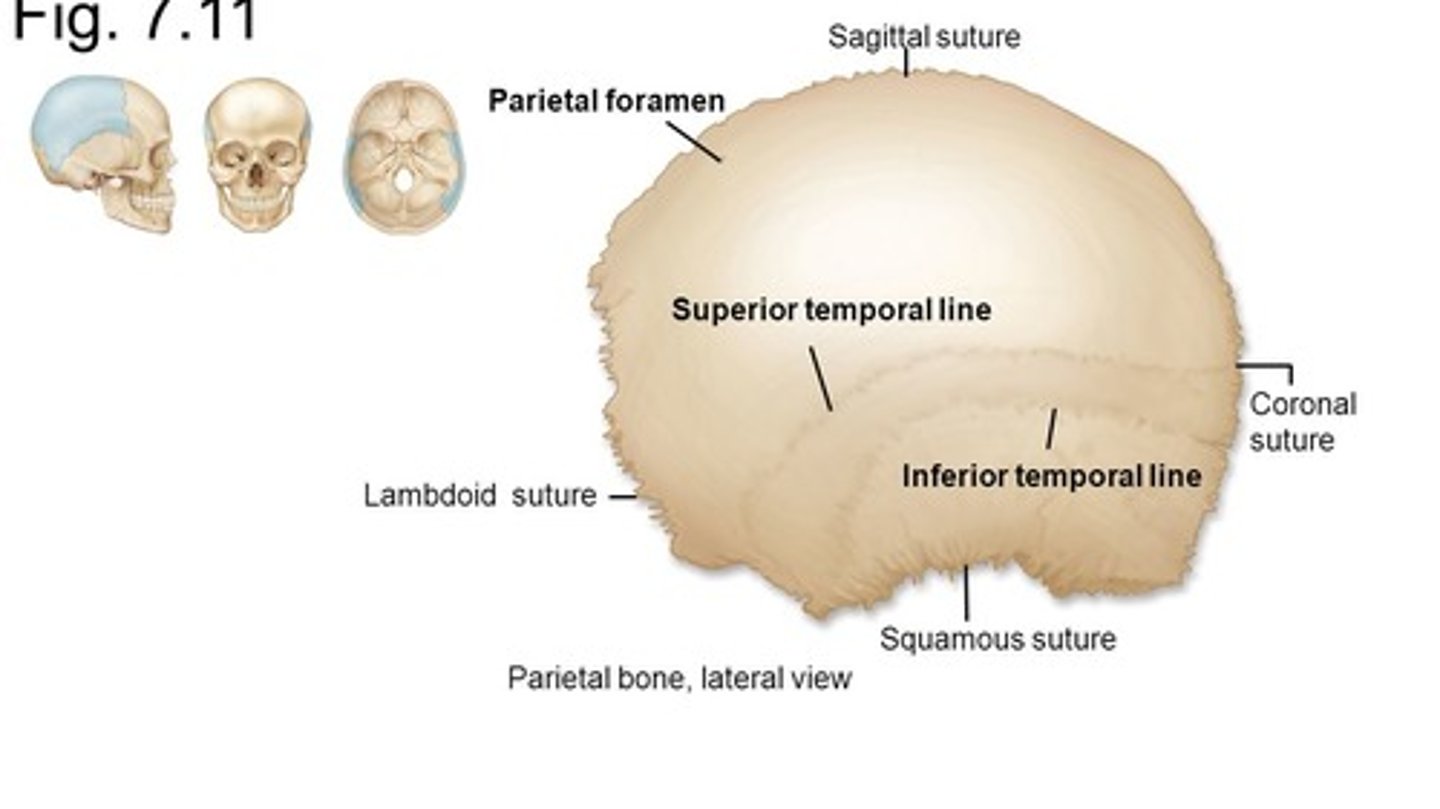
why are the temporal lines (parietal bone) important
Muscle attachment site
occipital condyle (occipital bone)
What is this?
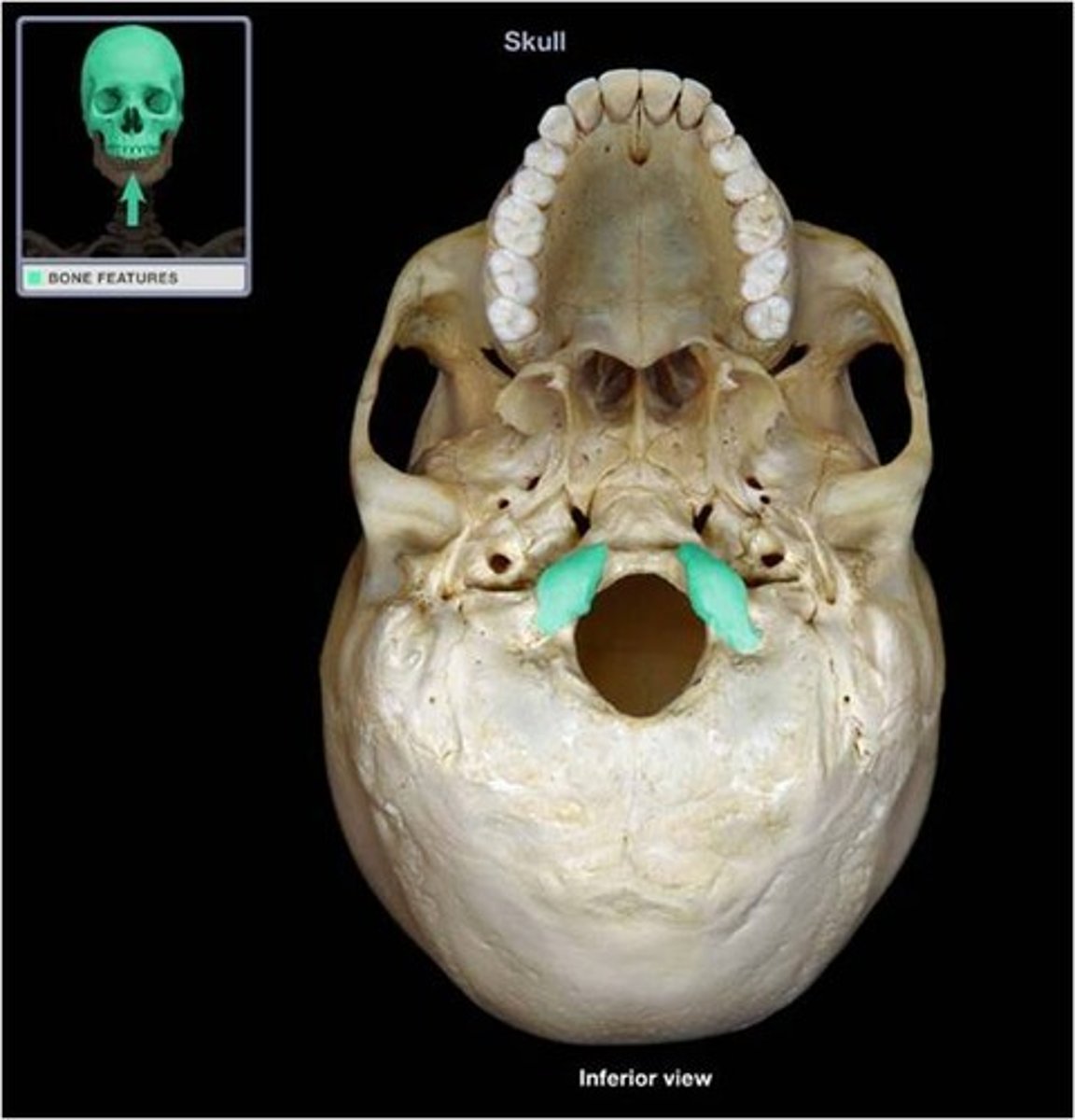
what does the occipital condyle articulate with?
Atlas (C1 vertebrae)
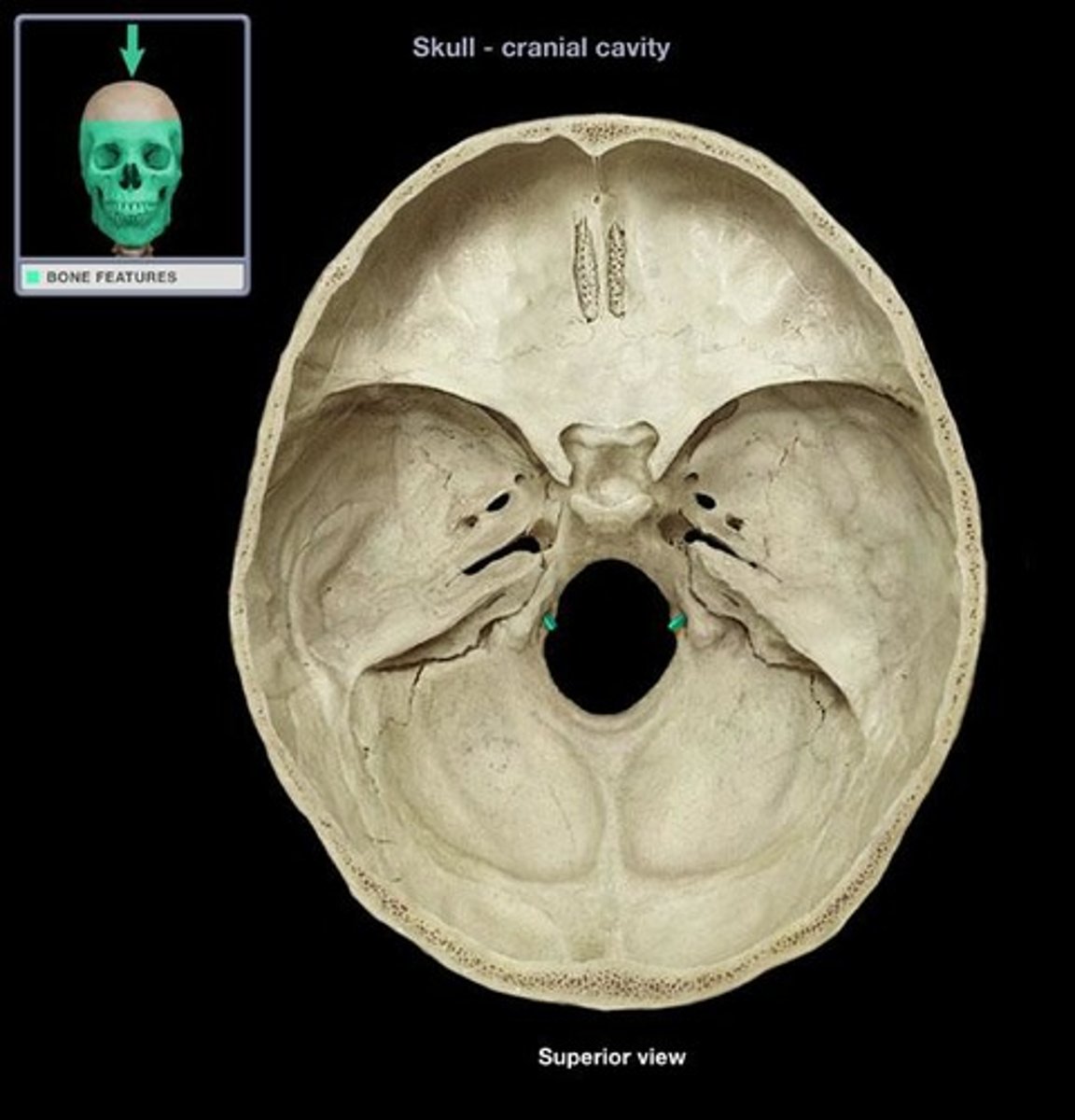
Foramen Magnum (occipital bone)
What is this?
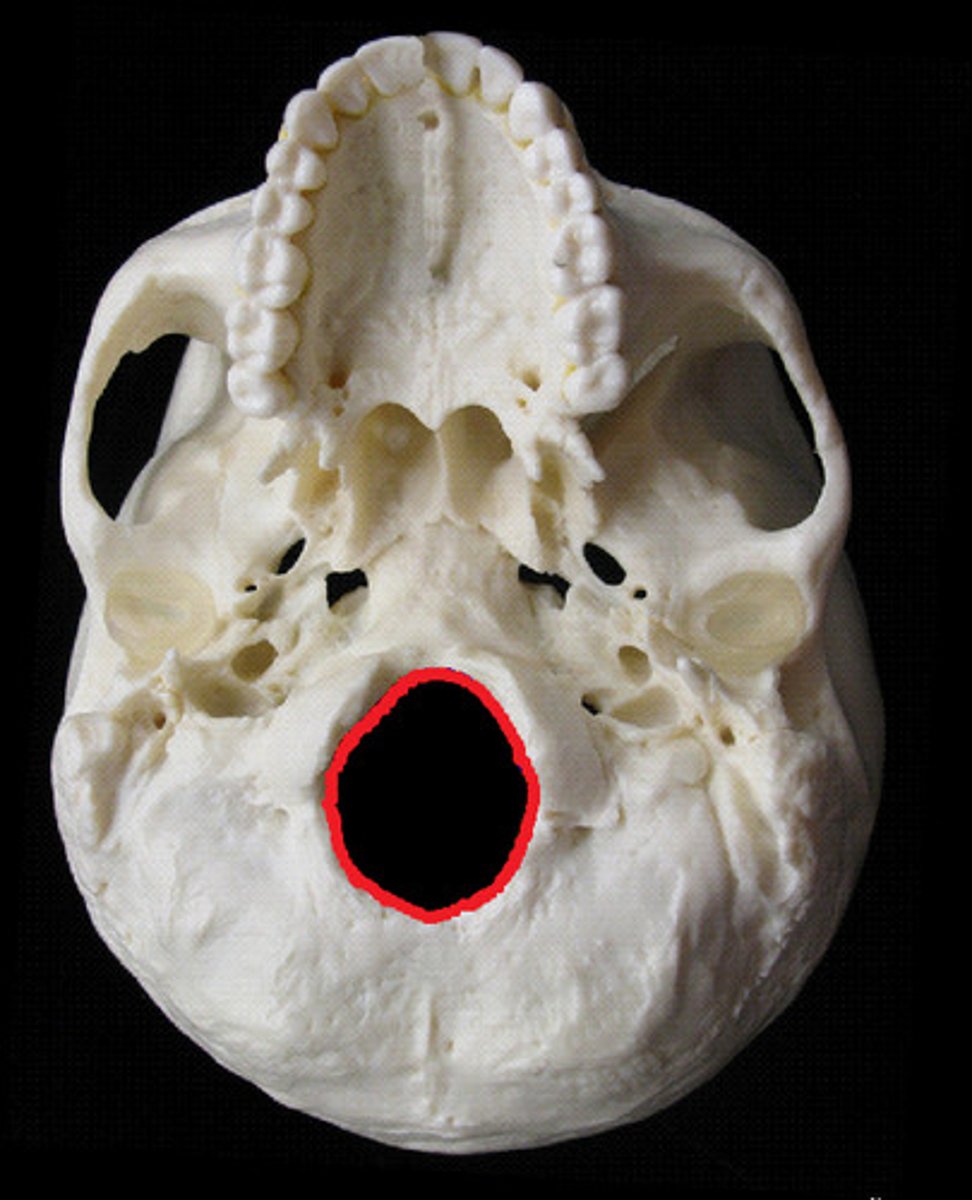
Hypoglossal canal (occipital bone)
Inferior nuchal line (occipital bone)
What is this?
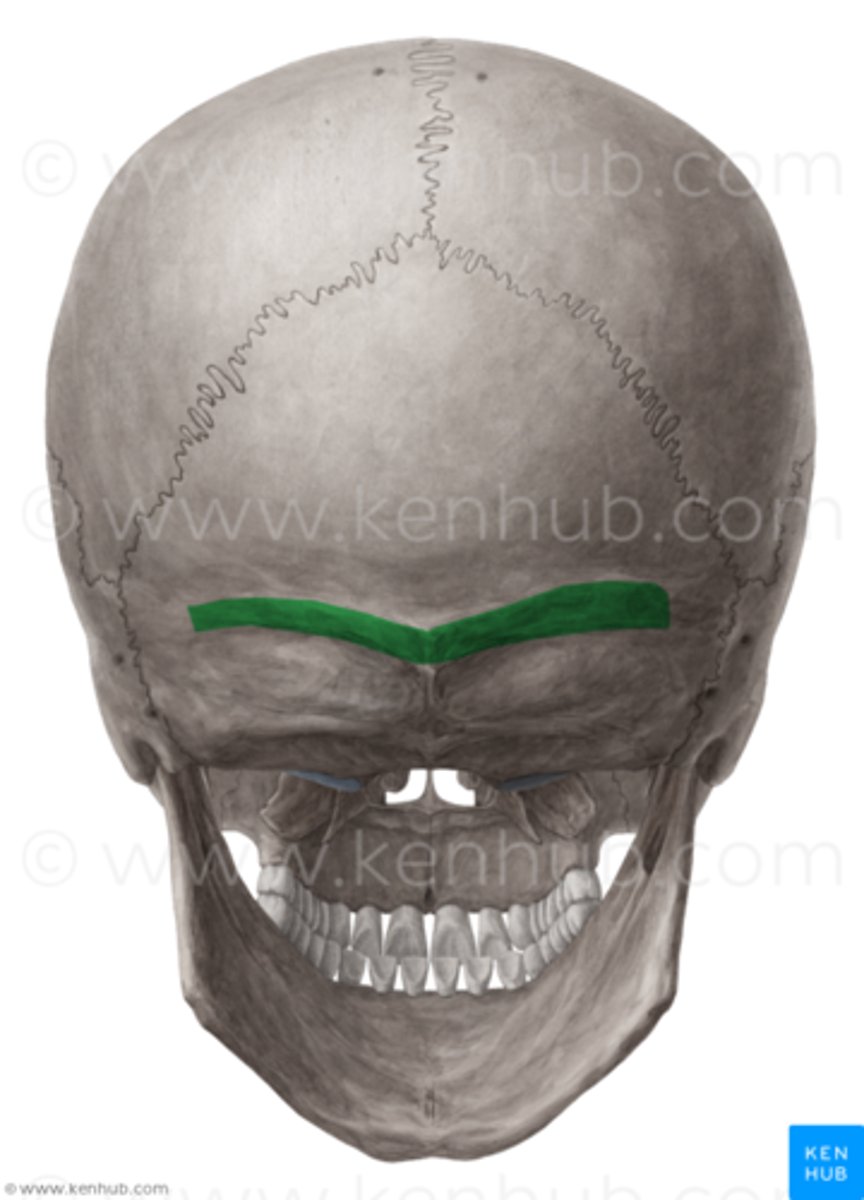
Superior nuchal line (occipital bone)
What is this?
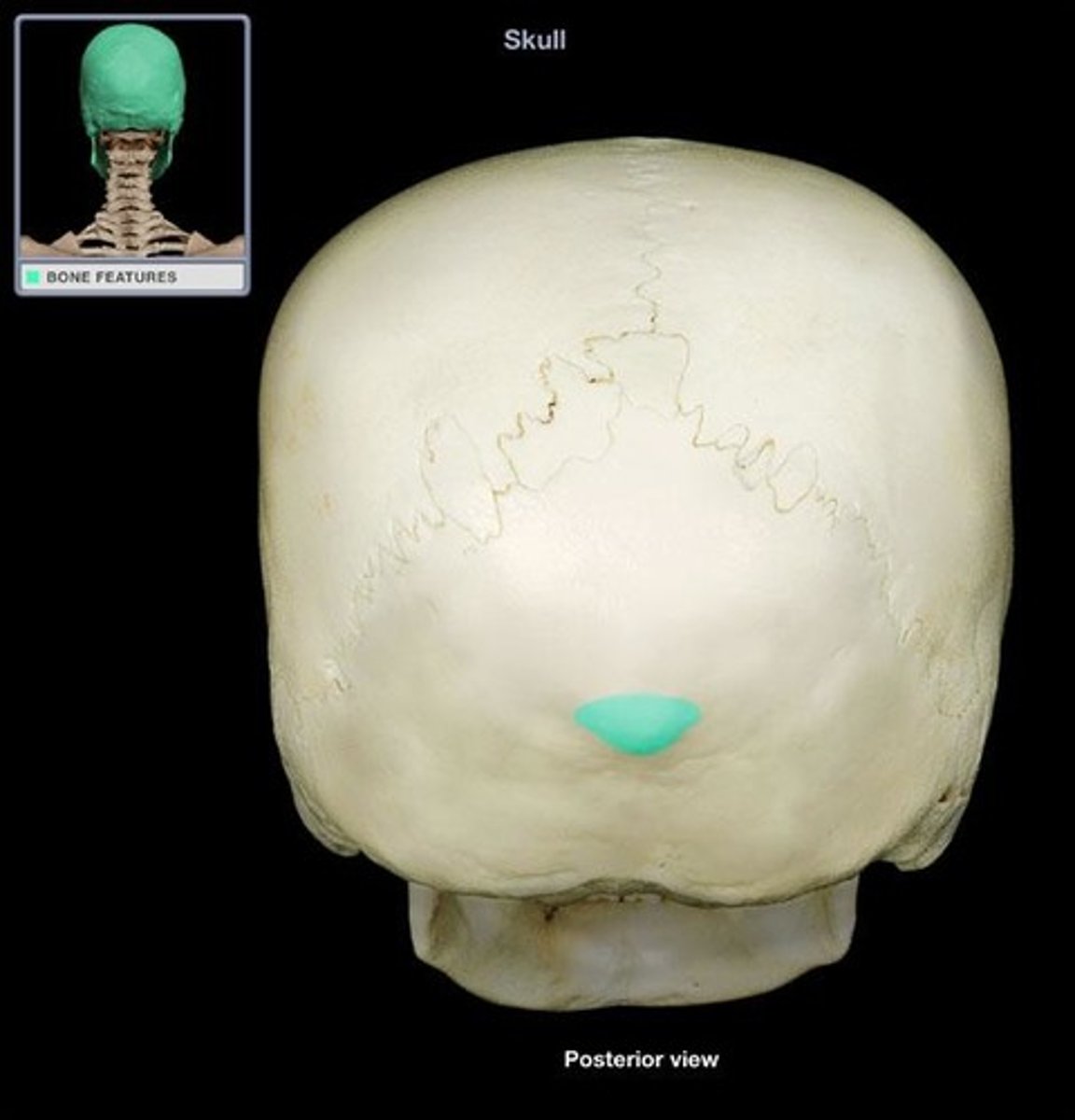
External occipital protuberance (occipital bone)
What is this?
Jugular foramen (Occipital bone)
What is this?
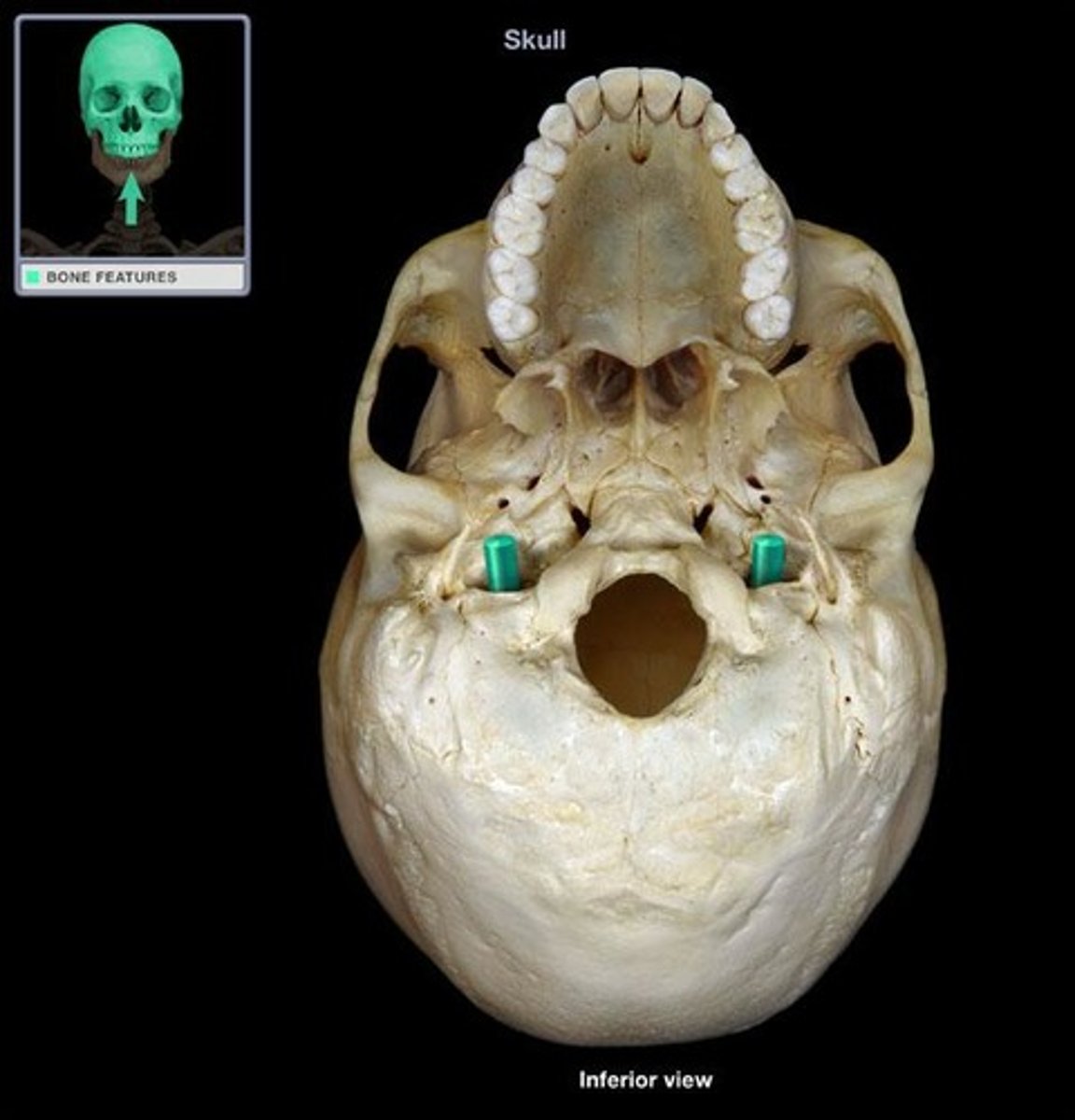
what lobes is the jugular foramen formed by?
Occipital and Temporal
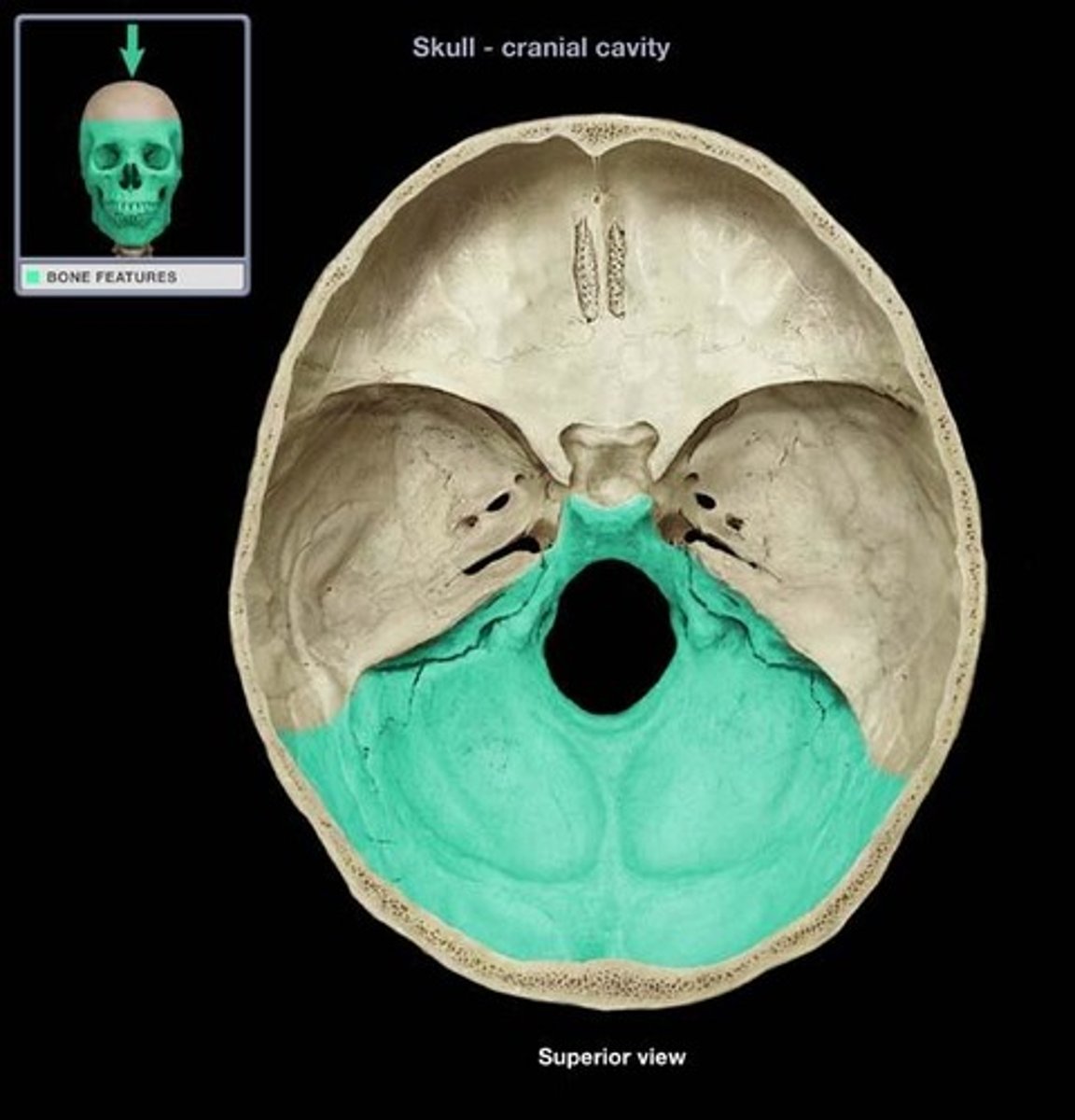
Where is the fossa for cerebellum located?
Occipital bone
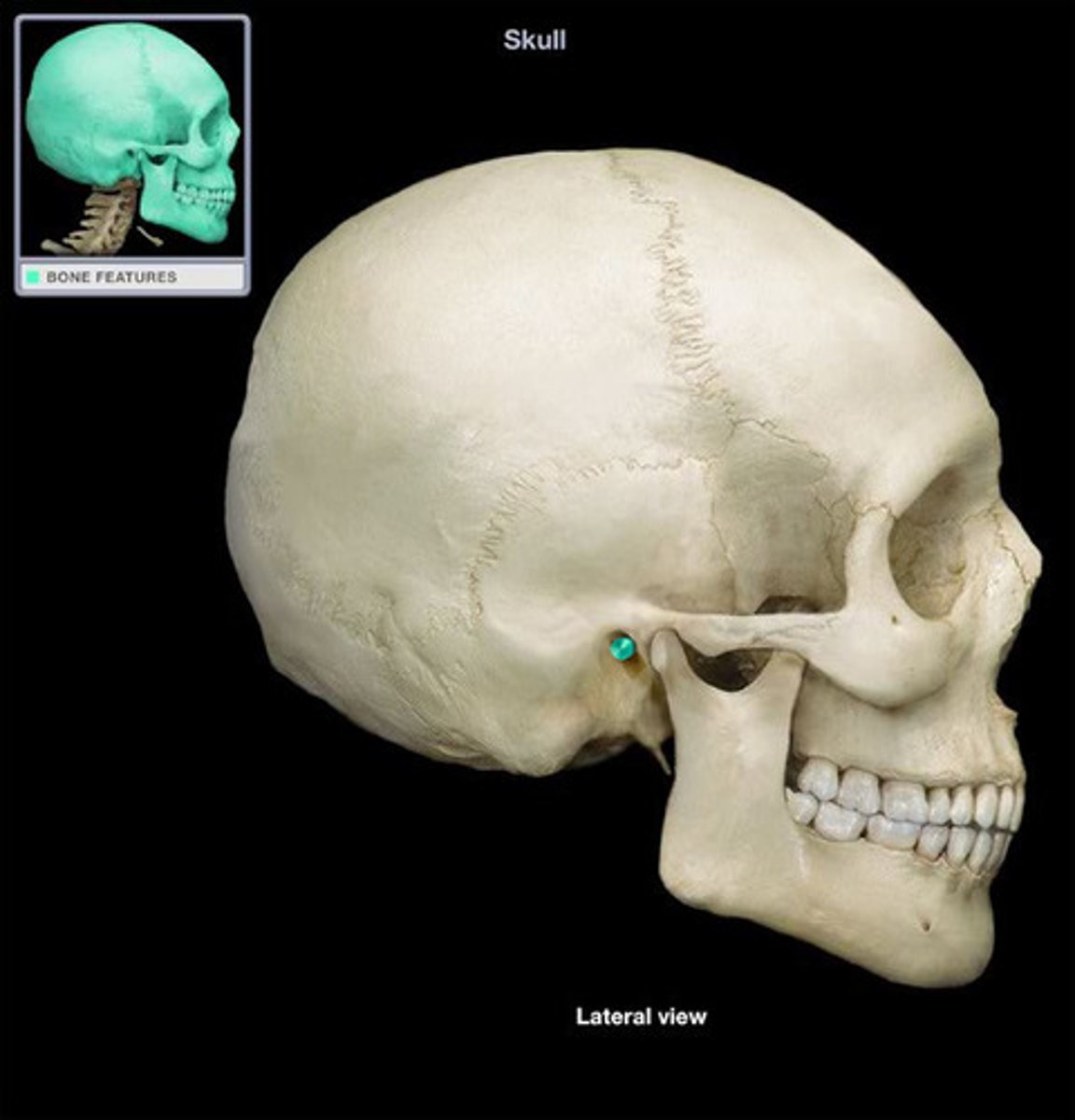
External acoustic meatus (Temporal bone)
What is this?
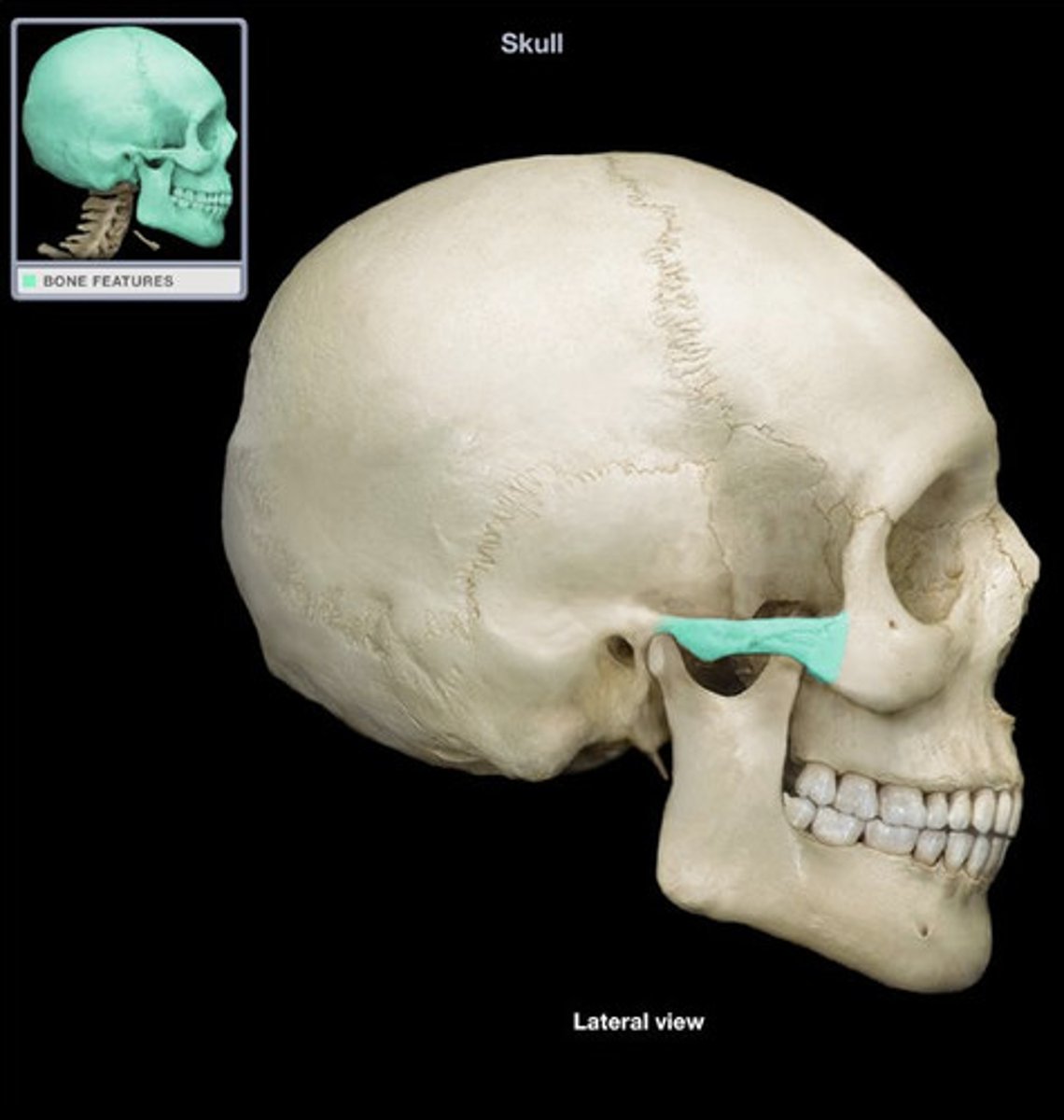
Styloid process (Temporal bone)
What is this?

Zygomatic arch (temporal bone)
What is this?
what makes up the zygomatic arch?
Zygomatic process of temporal bone
Temporal process of Zygomatic bone
Temporal fossa
Area superior and deep to zygomatic arch
Infratemporal fossa
Area inferior and deep to zygomatic arch
Carotid canal (temporal bone)
What is this?
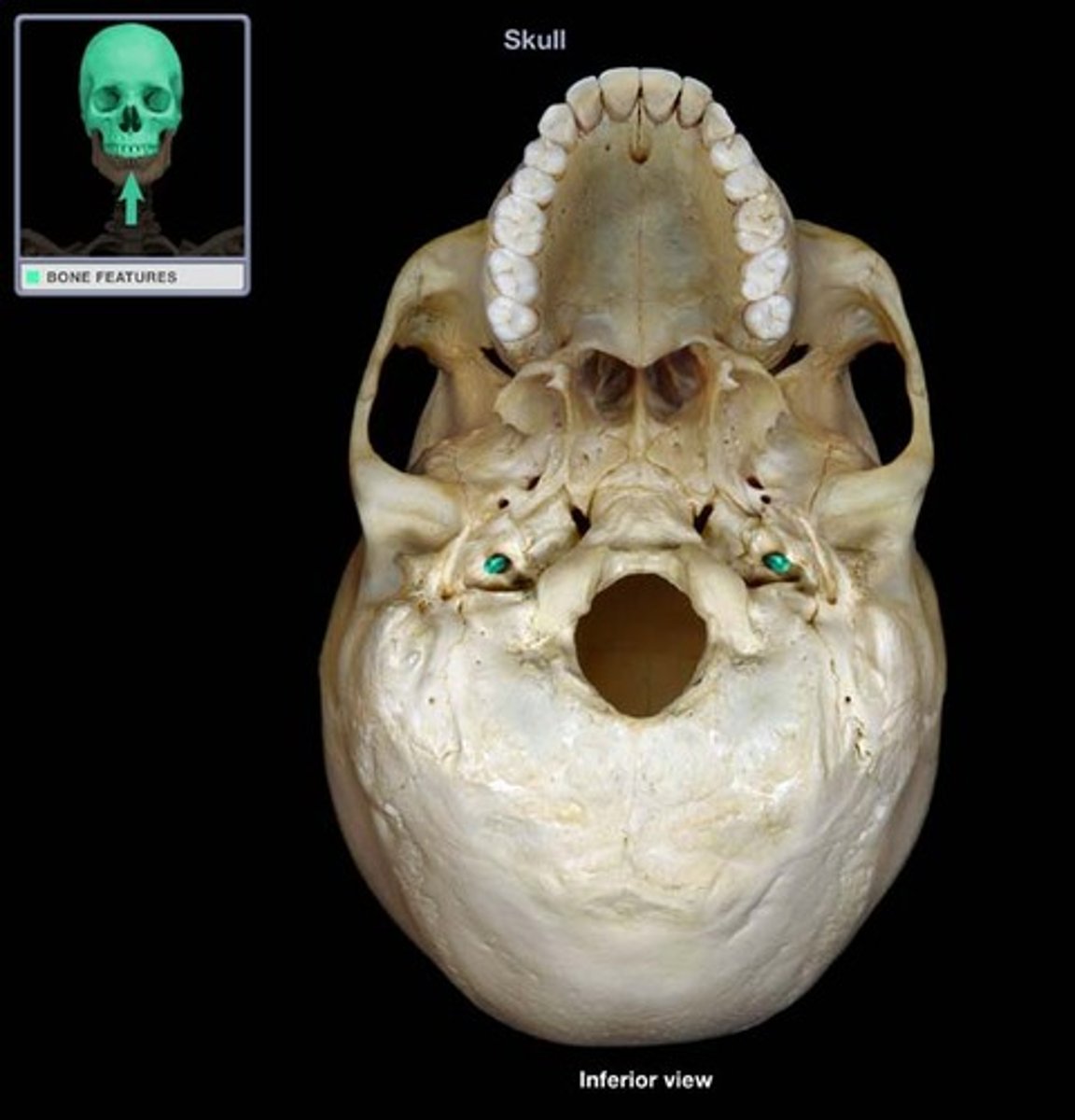
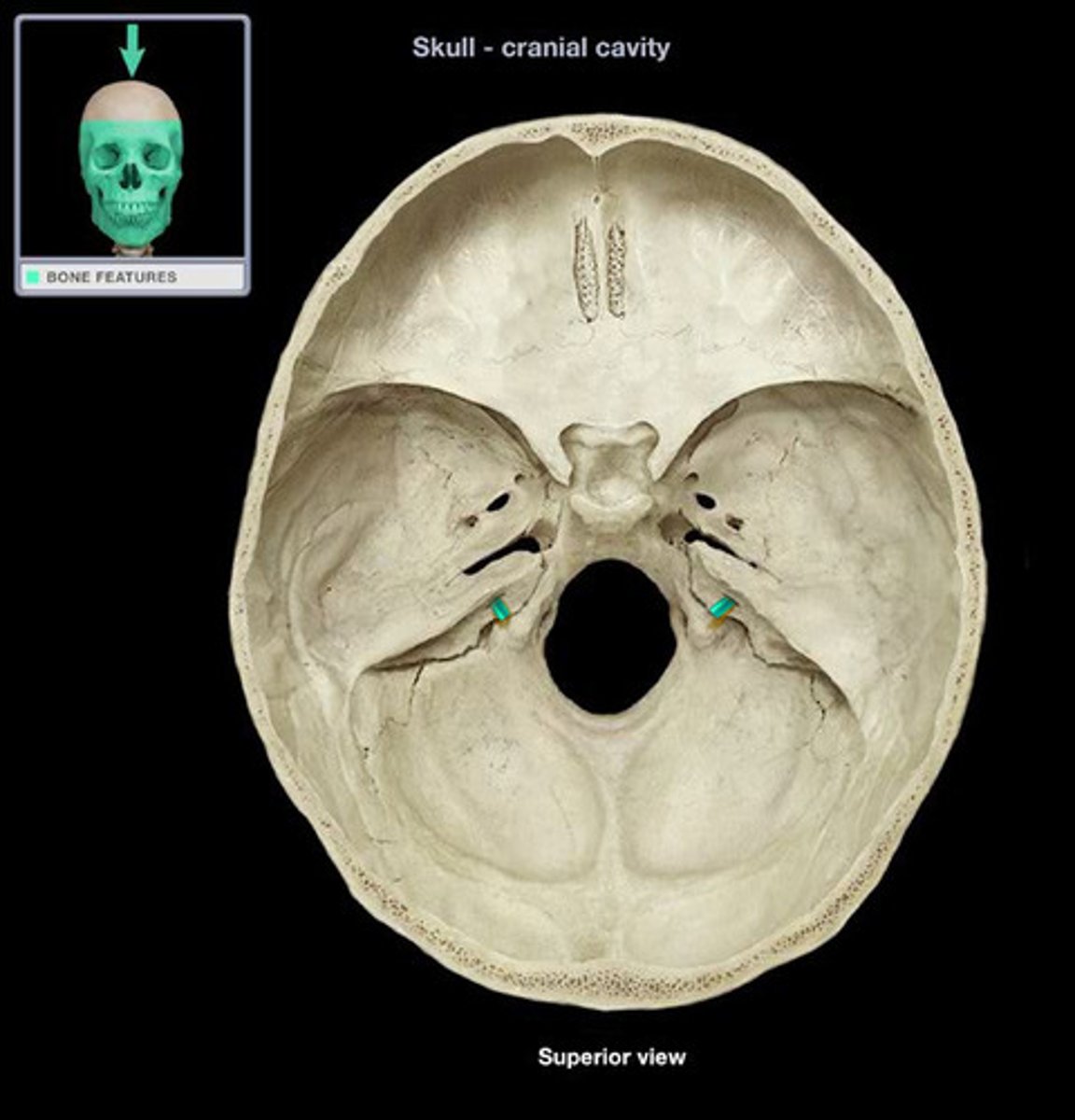
Internal acoustic meatus (temporal bone)
What is this?
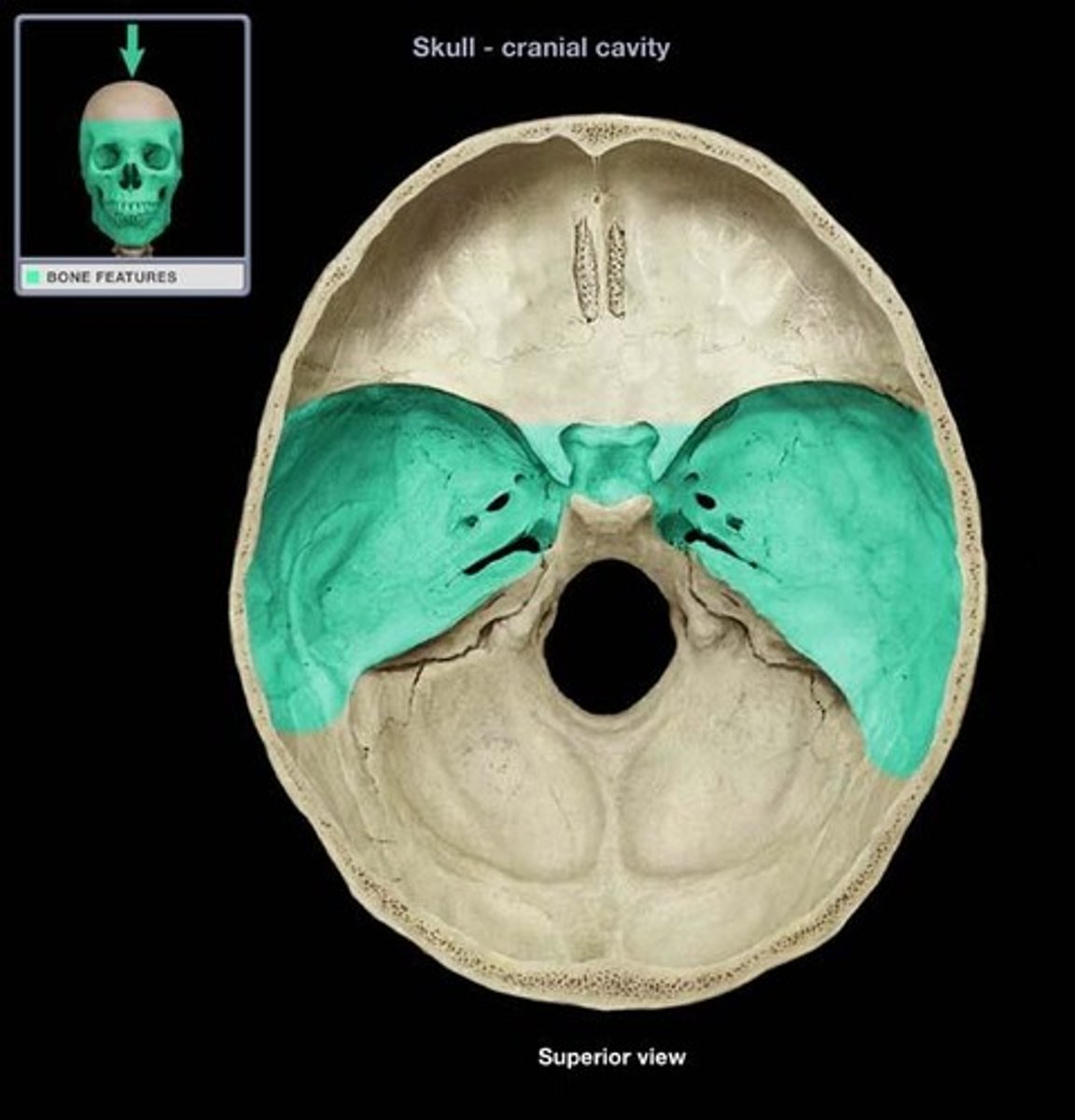
Middle cranial fossa (Temporal bone)
What is this?
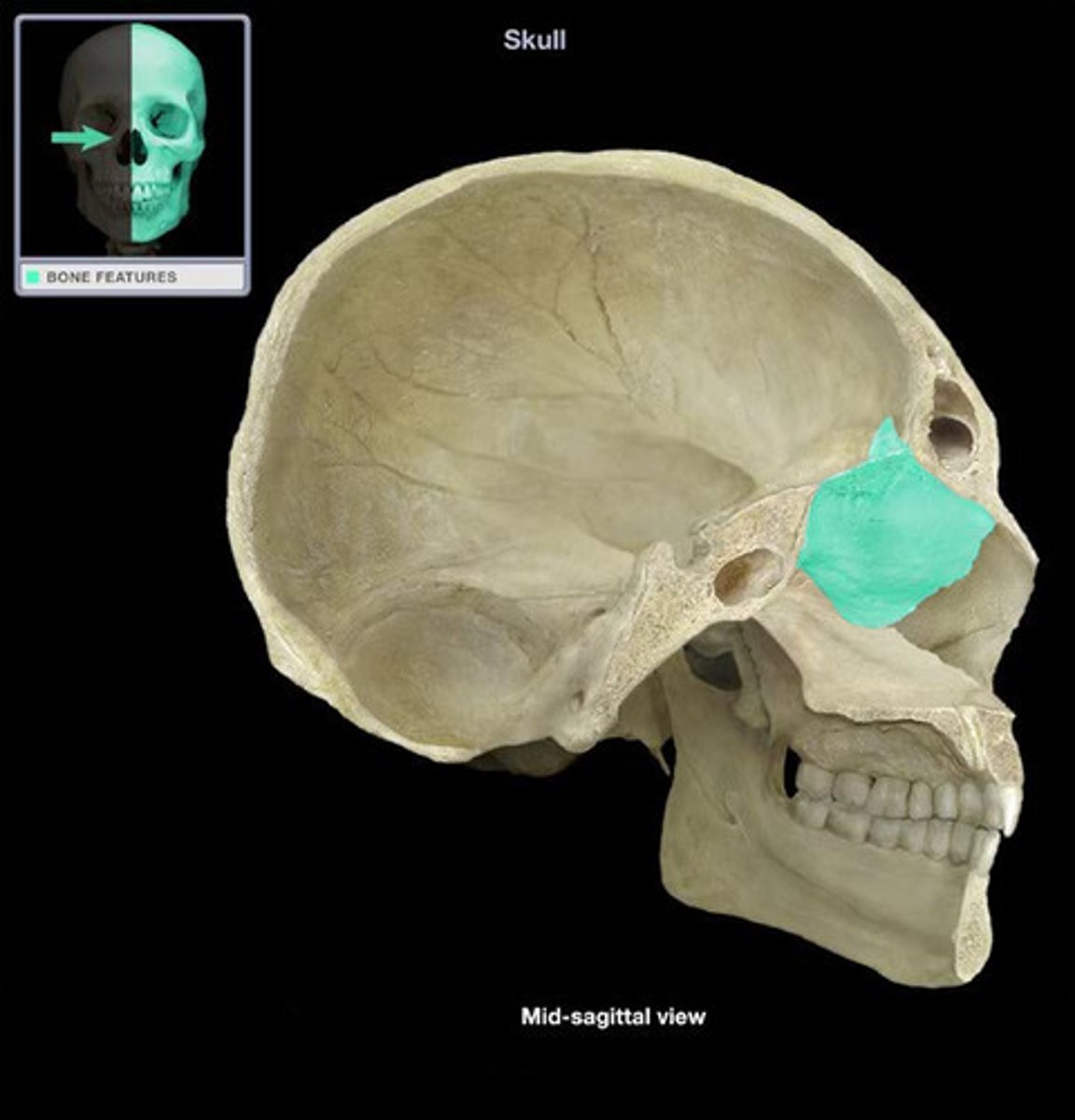
what bone is the roof of the nasal cavity?
Ethmoid
What is the only movable face of the bone?
Mandible
function of face bones?
Form framework of face
Cavities for special sense organs (sight, taste, and smell)
Openings for air (respiratory tract) and food (digestive track)
Secure teeth
facial expressions (anchor muscles)
Intra-orbital foramen (maxillae)
What is this?
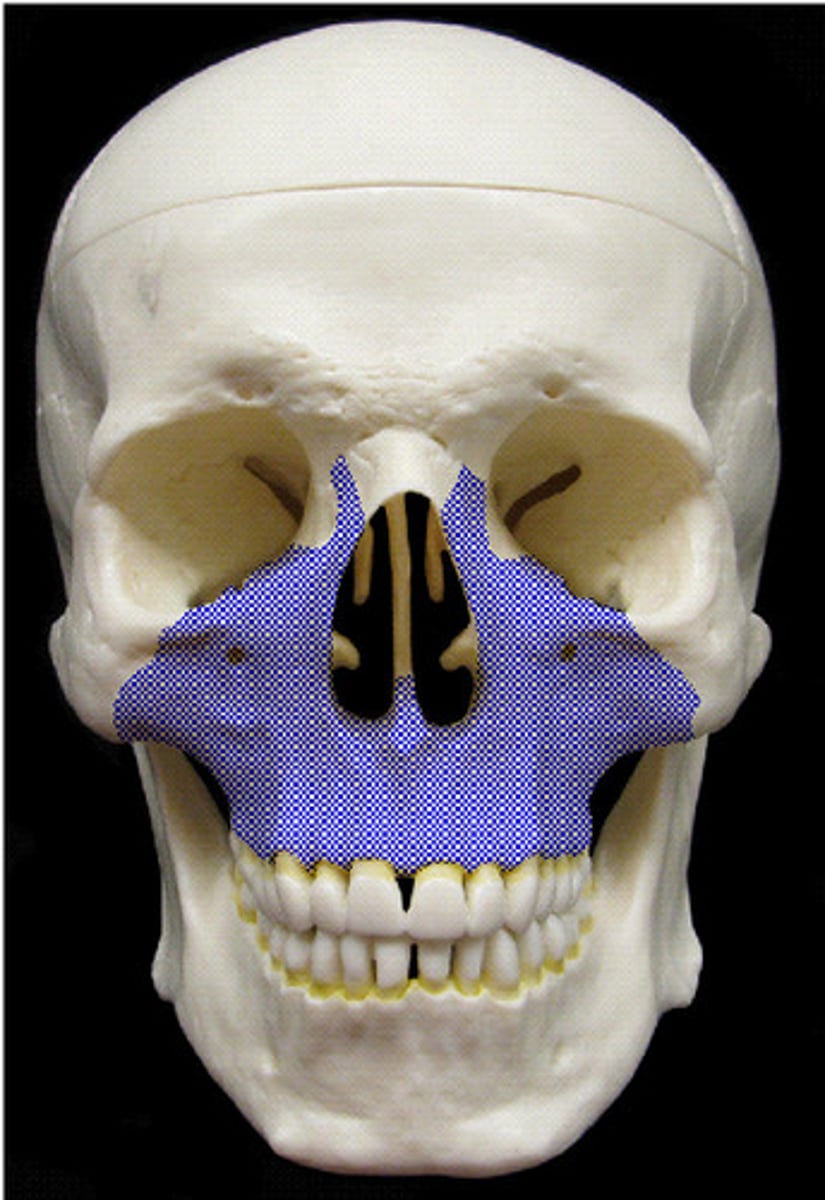
What makes up the hard palate?
Palantine process of maxillae
Horizontal plates of the palatine bones
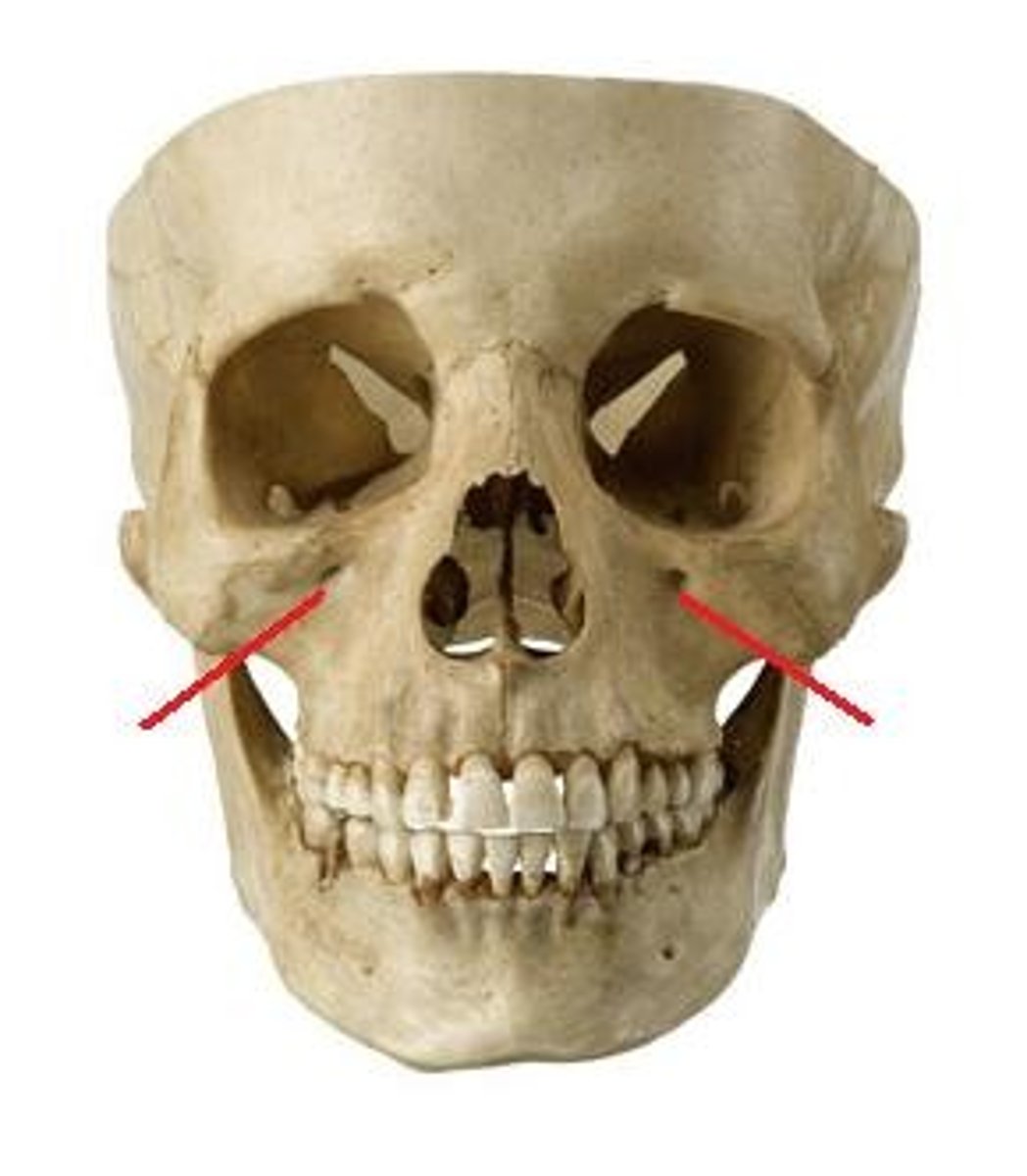
lacrimal groove (Lacrimal bone)
What is this?
What does the lacrimal groove contain?
Lacrimal sack
Coronoid process (mandible)
What is this?

Body (mandible)
What is this?
Ramus (mandible)
What is this?
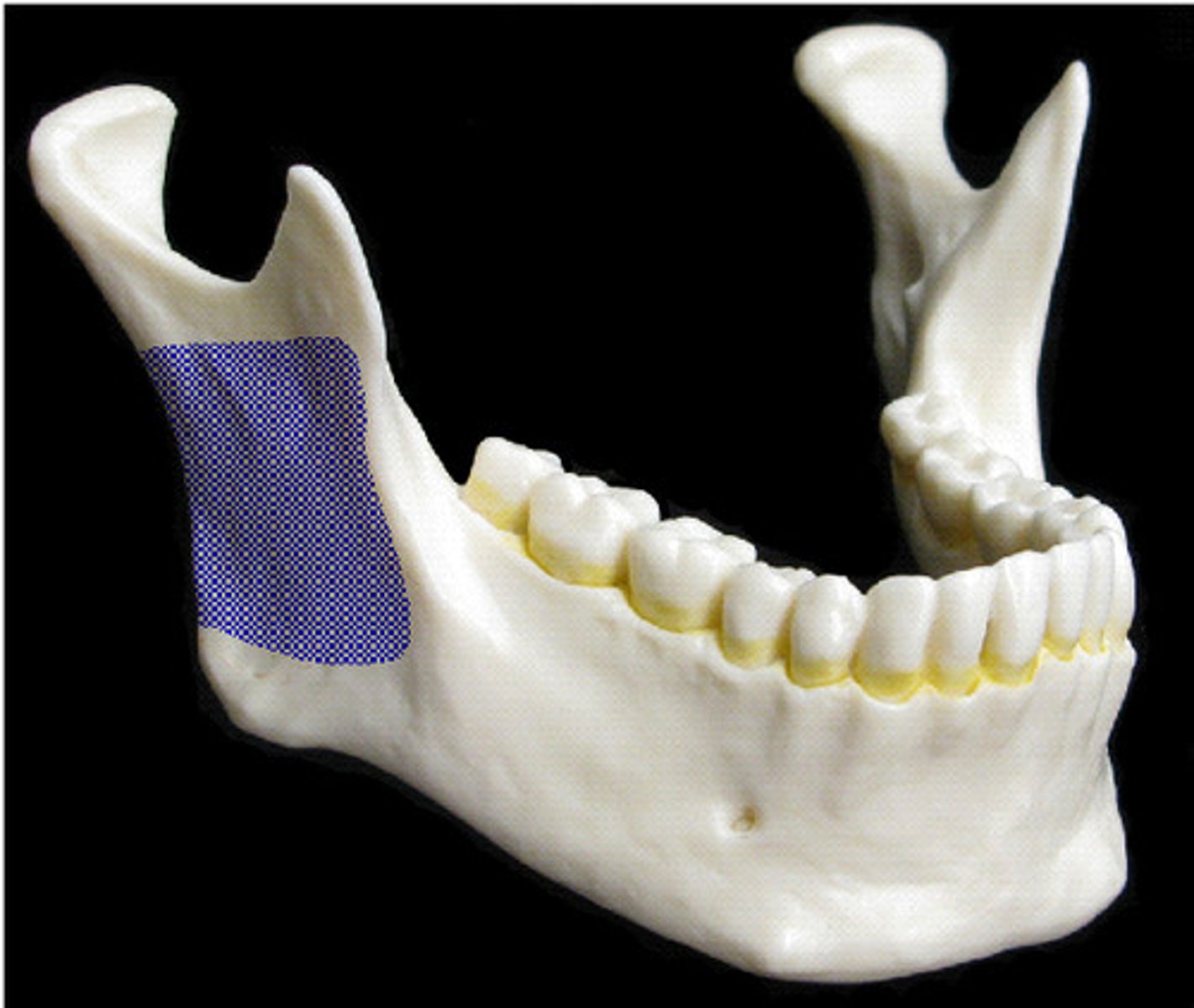
Angle (mandible)
What is this?

Mandibular notch (Mandible)
What is this?
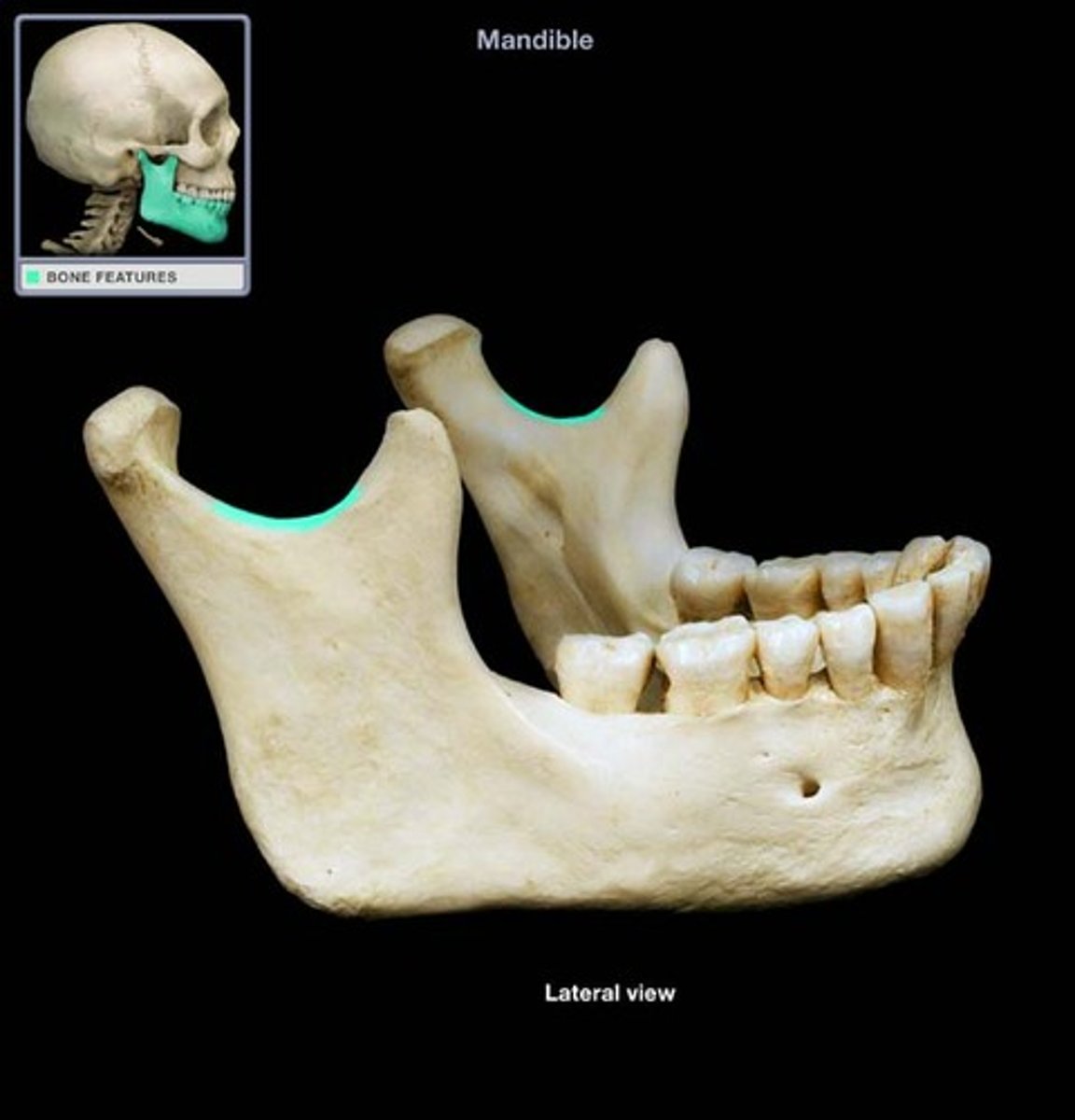
Mental foramen (Mandible)
What is this?
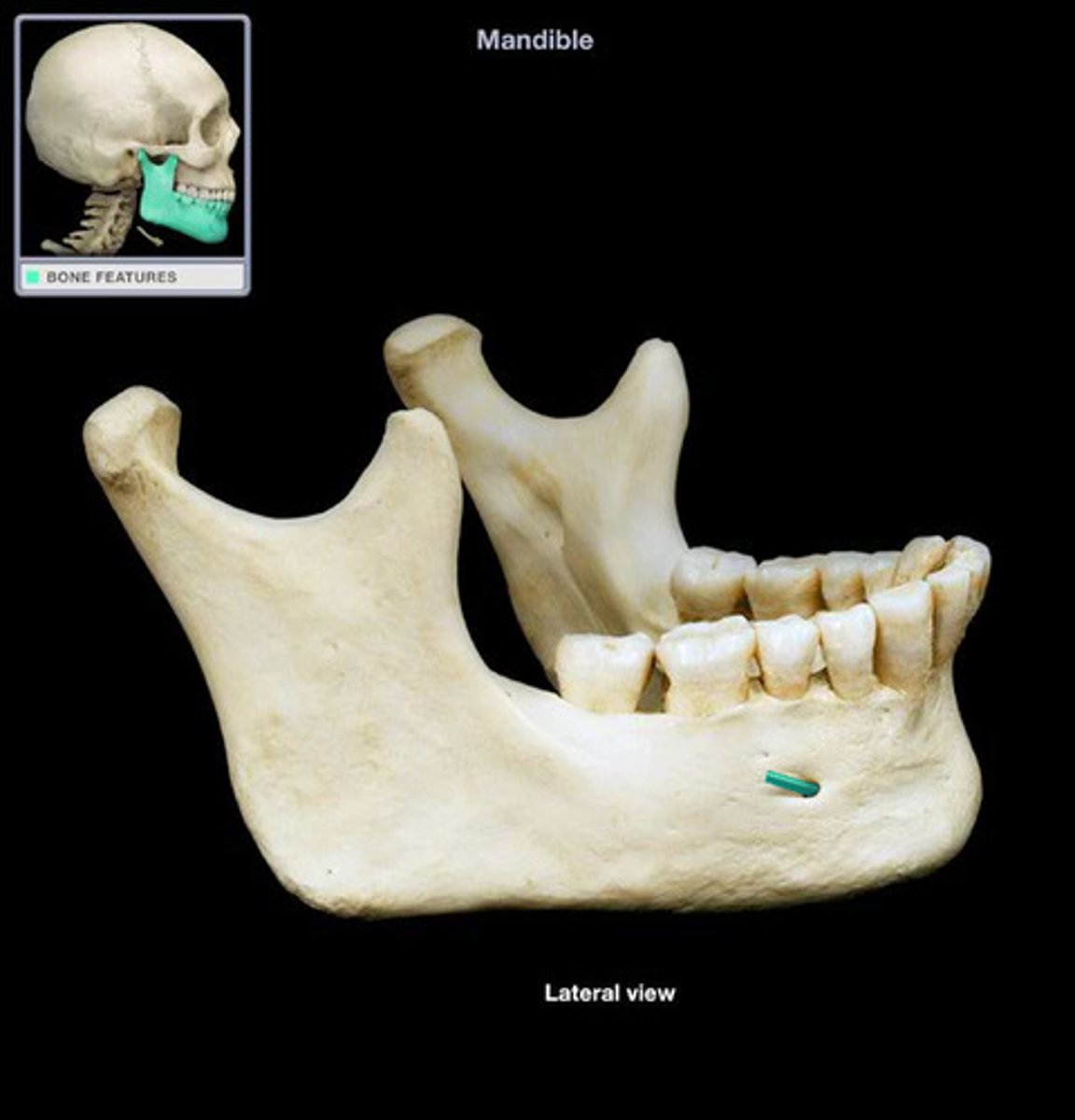
Genoid tubercle (mandible; muscles attach here)
What is this?

Mandibular foramen (mandible; nerve supply for teeth)
What is this?

The nasal septum is composed of?
Perpendicular plate of ethmoid bone
Vomer bone
Septal cartilage(made of hyelin cartilage)
What are the para-nasal sinuses?
frontal sinus
Ethmoid air cells (ethmoidal sinuses)
Sphenoid sinus
Maxillary sinus
Ethmoid air cells
What sinus is this?

Frontal Sinus
What sinus is this?
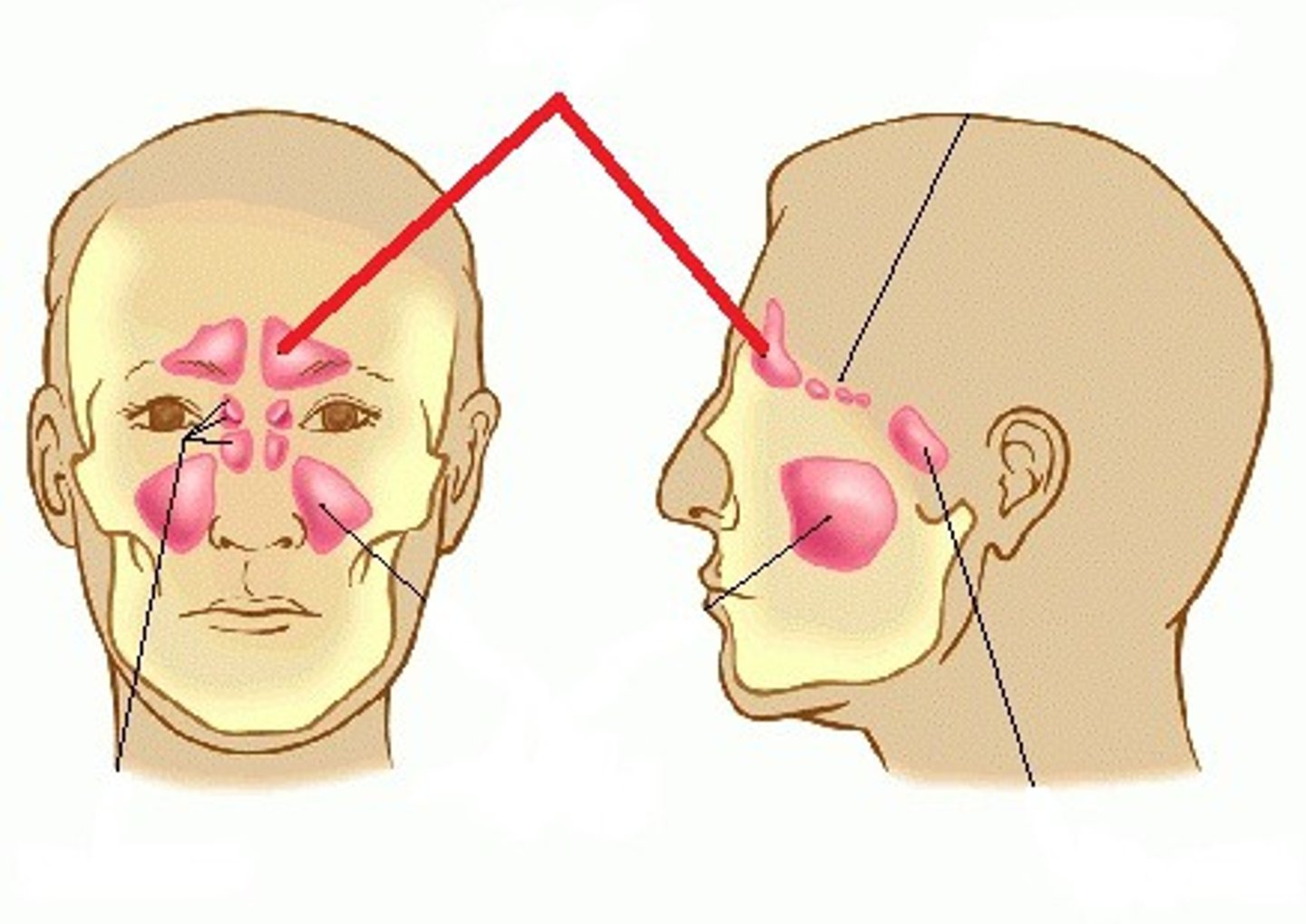
Sphenoid Sinus
What sinus is this?
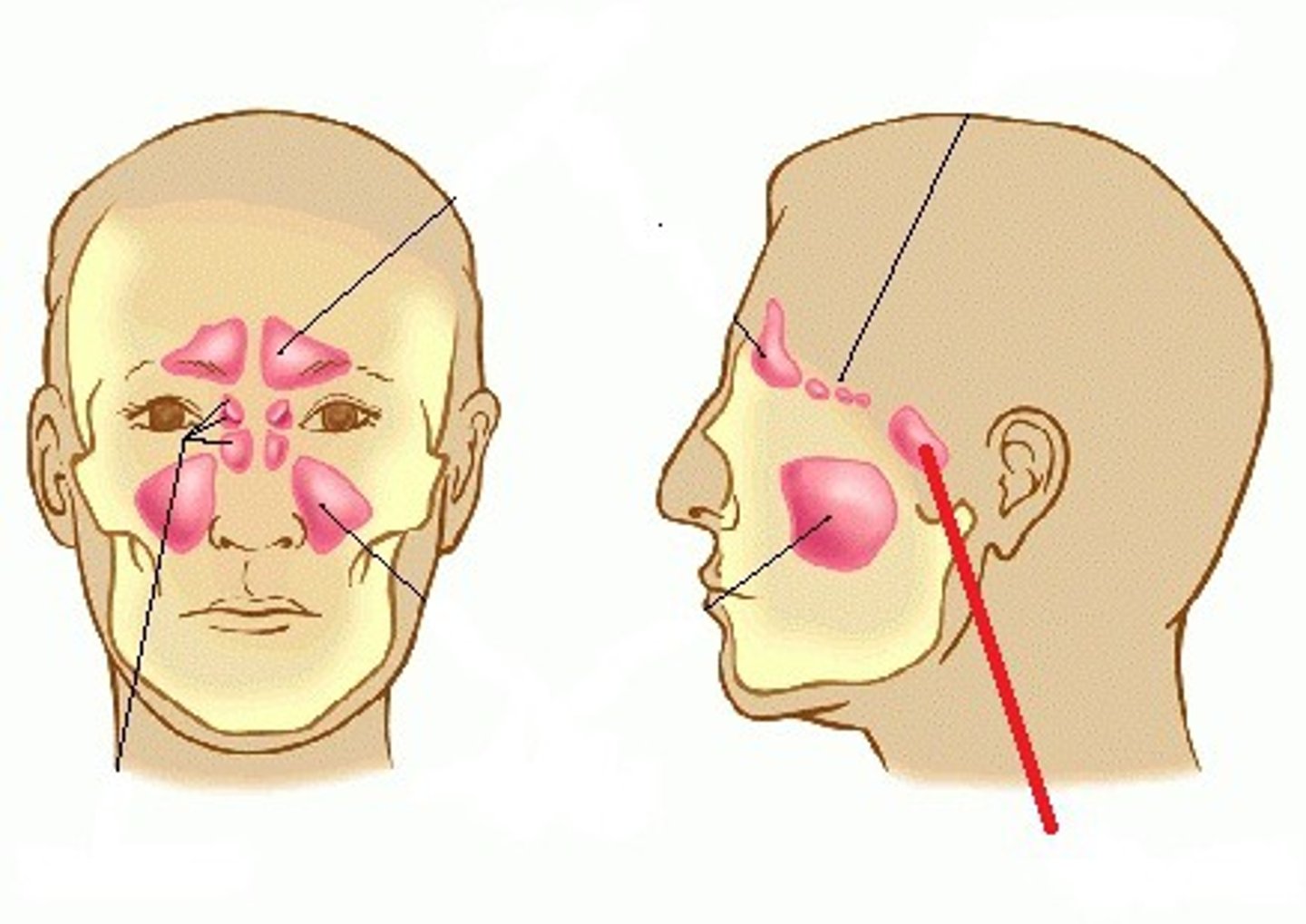
Maxillary sinus
What sinus is this?
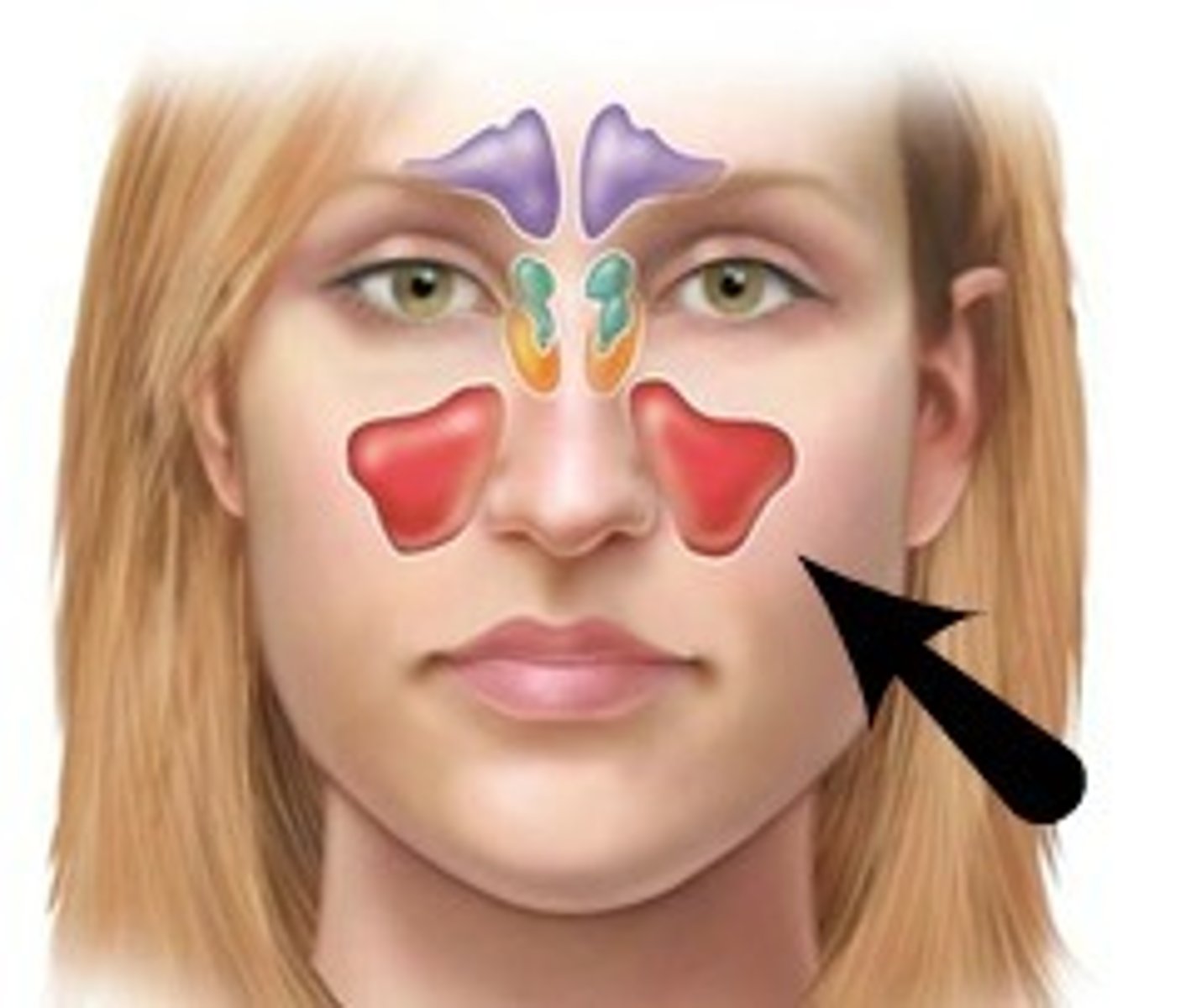
Which sinus collect the most mucus?
Maxillary sinus
What is a fontanel?
Space between skull bones (Seen in fetal and infant skulls)
What is the purpose of fontanels?
To allow head to flex through birth canal
Hyoid
What bone is this?

purpose of hyoid bone?
Swallowing
why is the hyoid bone unique?
Does not attach to any other bones
What does cranial nerve 1 (olfactory) pass through?
Cribriform foramina (in cribiform plate
what does cranial nerve 2 (Optic) pass through?
Optic canal (foramen)
what does cranial nerve 3 (Oculomotor),4 (trochlear), 5v1 (opthalmic division), and 6 (Abducens) pass through?
Superior orbital fissure
what does cranial nerve 5v2 (Maxillary division) pass through?
Foramen rotundum
what does cranial nerve 5v3 (mandibular division) pass through?
Foramen ovale
what does cranial nerve 7 (Facial) pass through?
Internal acoustic meatus (through facial canal, exits at stylomastoid foramen)
what does cranial nerve 8 (vestibulocochlear) pass through?
Internal acoustic meatus
What does cranial nerve 9 (glossopharyngel) cranial nerve 10 (vagus) and cranial nerve 11 (Accessory) pass through?
Jugular foramen
what does cranial nerve 12 (hypoglossal) pass through
Hypoglossal canal