Genotoxicity - toxicology slide 4
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
taught by Dr. Ramez Labib; 1.5hrs
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
what is the general objective of genetic toxicology?
Identification of materials with the potential to induce genetic damages in humans
provide support for the evaluation and interpretation of carcinogenicity and other toxicological results
provide support for regulatory decisions
alert producers and users of potential hazard
Mutagen
a substance that under the correct metabolic and cellular conditions has the ability to alter a cell’s genetic information (DNA) in a heritable manner
Carcinogen
a substance that under the correct metabolic and cellular conditions has the ability to transform a normal cell to a neoplastic cell (cancer)
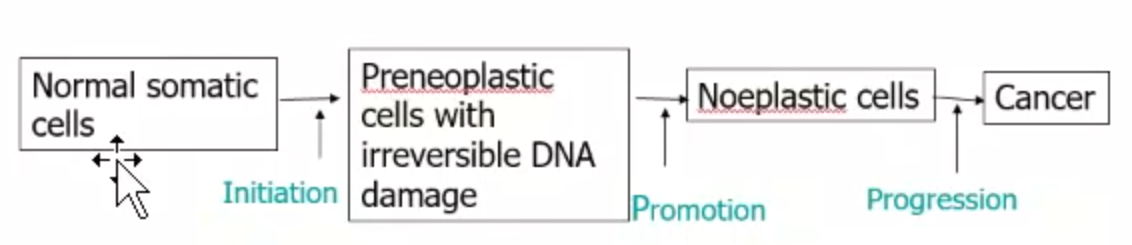
how does a genotoxic agent effect DNA?
it can go down 2 paths
microlesions - mutation type effect
error-free repair
no effect
Mis-repair or misreplication
point mutation
macrolesions - change in structure of chromosome(s)
chromosome rearrangement or deletion
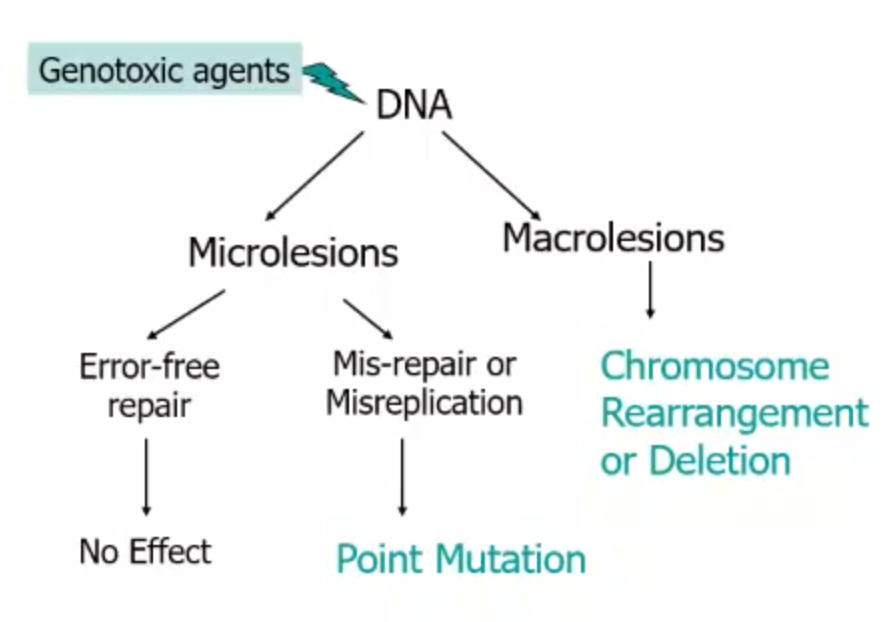
Outcome of Genetic Damage
mutation in somatic cells
Cancer
Aging
Mutation in Germinal Cells
Genetic Diseases
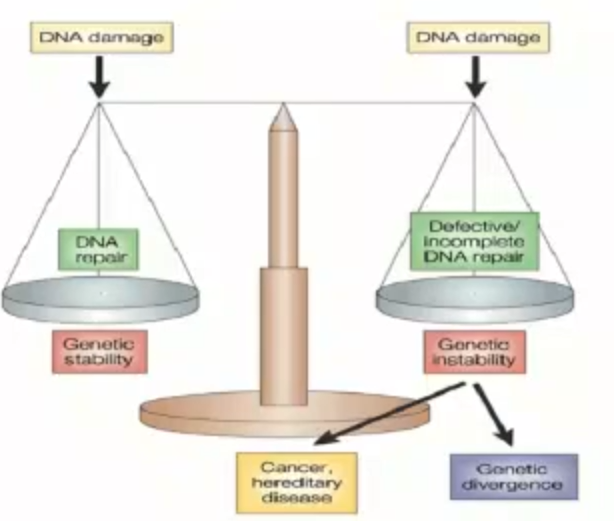
what does this diagram represent?
The Balance of DNA Damage and Repair
what are 3 major challenges to the integrity of the DNA molecule in vivo?
Lesions inflected by:
endogenous and environmental DNA-damaging agents and replication errors which have escaped the editing process during DNA synthesis
Exogenous sources
UV (sunlight)
Pollution (hydrocarbons
Smoking
Foodstuffs
Radiotherapy
Ionizing Radiation
X-rays
Chemotherapy (Alkylating agents)
Cisplatin
Mitomycin C
Cyclophosphamide
Psoralen
Melphalan
Endogenous Sources
Oxidative damage by free radicals
oxygen metabolism
Replicative errors
Spontaneous alternations in DNA
Alkylating agents (Malondialdehyde)
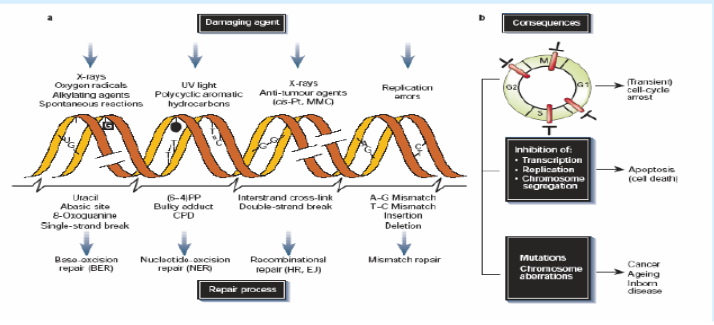
What are the common types of DNA Damage and Spontaneous Alterations
Exogenous Sources
Radiotherapy
Chemotherapy
Endogenous Sources
*look at pic for visual representations
transition
the substitution of an amino acid to another of the same amino acid (Val - Val)
transversion
the substitution of an amino acid to a different amino acid (Val-Pro)
Types of mutations - description
Point mutation (missense, nonsense, silent) - Change of base pair
Deletion mutation - removal of one or more bases
Insertion mutation - insertion of one or more bases
Frameshift mutation - deletion or insertion of a number of bases that cannot be divided by 3
Inversion mutation - inversion of a sequence of bases (may cause frame shift)
what are these mutations caused by?
Point mutation (missense, nonsense, silent) - Replication mistake, repair mistake, chemically altered base that mis-pairs
Deletion mutation - intercalating chemicals, DNA polymerase slips mobile genetic elements
Insertion mutation - intercalating chemicals, mobile genetic elements
Frameshift mutation - intercalating chemicals, mobile genetic elements
Inversion mutation - mobile genetic elements
Consequences of Point Mutations and Small Deletions
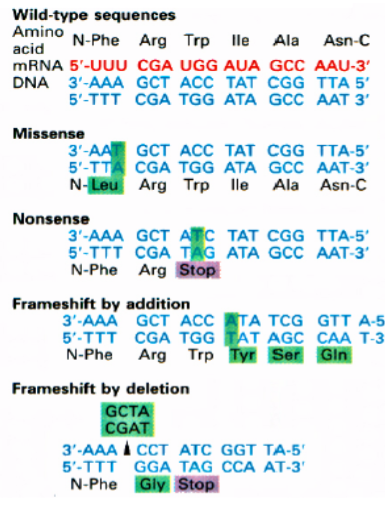
missense mutation
substitution of 1 amino acids for another. Most common type of mutation since most codons make an amino acid. usually (no always) relatively minor — often have no phenotype
nonsense mutation
single base change that generates a new stop codon causing truncation of protein synthesis. Often nonfunctional since many amino acids can be affected
what is human cancer linked to and is there any hope for cancer?
80% of human cancer is linked to chemicals
Primary event in cancer is DNA damage
The good news: DNA is the only macromolecule which can be repaired
;..;.;
What is some insight/info on DNA Repair?
All these others can be replaced, but DNA must be preserved
Importance of maintaining the integrity of the DNA is Highlighted by the Investment of Energy in DNA Repair
Less than 1/1000 Lesions become a mutation
Diverse DNA repair systems reflect diversity of DNA damage
Multiple systems recognize common lesions
Most DNA repair mechanisms rely on the complementary information in the DNA
what the mechanisms of DNA Repair?
Direct reversal repair: MGMT - O6-methylguanine DNA methyltransferase
Excision repair:
base excision repair (BER)
nucleotide excision repair(NER)
mismatch repair
what kind of repair is base excision repair and what does it do in basic terms?
Excision repair; fixes abnormal bases (uracil, hypoxanthine, alkylated bases)
what does (BER) stand for?
base excision repair
what kind of repair is nucleotide excision repair and what does it do in basic terms?
Excision repair; fixes large structural changes and helix distortions (pyrimidine dimers, bulky base adducts)
what does (NER) stand for?
nucleotide excision repair
what kind of repair is mismatch repair and what does it do in basic terms?
Excision repair; fixes mismatches
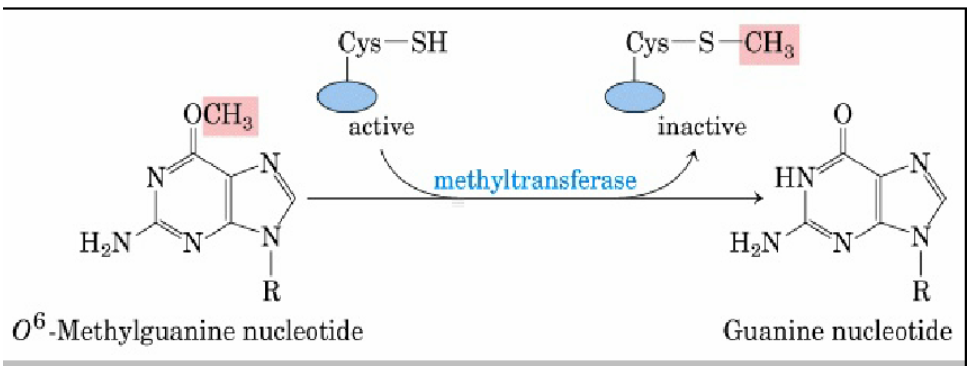
how does MGMT Direct Reversal Repair work? (google)
DNA repair pathway where the O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) enzyme directly reverses damage by transferring an alkyl group, such as a methyl group, from the damaged O6 position of guanine to its own cysteine residue
*look at pic for visual representation of mechanism
what does Base Excision Repair do? (list more detail)
damaged bases are removed by free bases
primarily responsible for removal or oxidative and alkylation damage
*most genes in this pathway are essential for it to work
*thought to have a important role in aging
what does Nucleotide Excision Repair do? (list more detail)
damaged bases are removed by oligonucleotides
primarily responsible for removal of UV-induced damage and bulky adducts
also removes ~ 20% of oxidative damage
*deficient in human disorders
what are Regulations for Mutagenicity Testing?
ICH - International Council for Harmonization (followed by FDA)
protocols that need to be followed to determine whether ur chemical(drug) is genotoxic
US EPA(environmental protection agency) - responsible for registration of new chemicals or pesticides
EU Dangerous Substance Legislation
Japan regulations
Redbook - guidelines for food regulations that need to be tested (followed by FDA)
ICH requires a S2B Genotoxicity Testing Battery, what does that entail?
a series of different tests that need to be run (going up in tiers) that lets u test to see if ur drug is carcinogenic
*all of these are required for submission of a new drug by the FDA
ICH S2B Genotoxicity Testing Battery tests (in order)
Ames test - testing for mutations in bacteria
must be done on 2 different strains
Salmonella and E.coli
Mammalian cell evaluation for mutation or chromosomal damage
In vitro cytogenetics (CHO, CHL, HPBL)
In vitro mouse lymphoma (TK ± assay)
In vivo evaluation for chromosomal damage
Micronucleus assay (mouse or rat)
Rat bone marrow chromosome aberration assay
US EPA Mutagenicity Testing Requirements
a series of different tests that need to be run (going up in tiers) that lets u test to see if ur pesticide is carcinogenic
*all of these are required for submission of a new pesticide by the EPA
US EPA Mutagenicity Testing Requirements tests (in order)
Ames test
Mouse Lymphoma TK +/- gene mutation assay
OR, u can do the CHO/HGPRT gene mutation assay AND in vitro chromosomal aberration assay if u want to do a different cell line (this is in place of mouse lymphoma)
Rodent micronucleus test
EU New Chemical Mutagenicity Testing
32:49
Japan Regulations on Mutagenicity Testing
32:49
32:49
32:49