Attention
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Input attention
Alertness/arousal, orienting reflex, spotlight attention & search
What does controlled attention include?
Selective attention, mental resources/conscious processing, supervisory attentional system
Alertness/Arousal: What is vigilance/sustained attention?
Maintaining focus over prolonged periods of time. Our alertness decreases over time.
Effectiveness is influenced by:
Length of signal, frequency of signal, busyness of background/noise
The Central Executive
Attentional controller with two components: semi-automatic conflict-resolution system and supervisory attentional system (SAS)
Semi-automatic conflict-resolution system
Without conscious awareness
Supervisory attentional system (SAS)
-crucial, intervenes when automatic conflict resolution is not possible
Perseveration
-repeatedly performing the same action or mistake
-failure to focus resulting in utilizing behaviors
-indiscriminately make use of cues in environment
-failure to monitor behavior
-inappropriate for situation
-suggests that the SAS relies on the frontal lobes
Orienting Reflex
Reflexive redirection of attention towards an unexpected, novel stimulus
Attention as a Mental Process
Much of our cognitive processing requires attention, concentrating effort on a stimulus or mental event
Attention as a Resource
Attention is limited and must be divided between ongoing tasks
Default Mode Network
-set of brain structures that are more active when we are idle than when we are actively processing information
-medial prefrontal cortex
-posterior cingulate cortex
-angular gyrus
Pre-attentive processing
Processing before the focus of attention is brought to a stimulus
Post-attentive processing
Processing once attention is focused on a stimulus
Selective Attention
The ability to select certain stimuli in the environment to process, ignoring other irrelevant information
Zoom Lens Model
Attention can be 'zoomed' in or out; broad attention slows processing, narrow attention speeds it up
Spotlight Model
Spotlight can be aimed at stimuli of interest; area outside of the spotlight is unattended
Dual Task Methods
Requires participants to do two tasks simultaneously to observe the effects on attention
Dual Task vs. Multitasking
Dual task requires two tasks to be performed concurrently; multitasking allows shifting back and forth between tasks
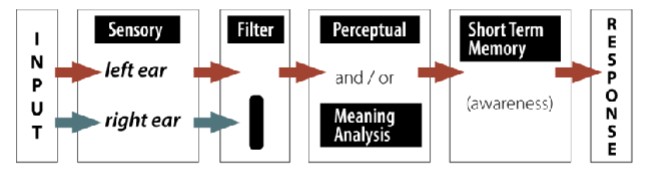
Broadbent's Filter Model
Proposes that information is filtered early in the processing stream based on physical characteristics. Cannot account for phenomena like the cocktail party phenomenon
Divided Attention
Splitting your attention between multiple tasks
Dual-Task Interference
Cost to performance when doing 2+ tasks simultaneously
Psychological Refractory Period
Period of time after presentation of a stimulus where a second stimulus cannot be processed
Capacity Theory
We have a set capacity for attention; exceeding limits results in task failures
Divided Attention and Aging
General decline in performance when using multiple types of targets and increasing number of tracked items
How can we improving multitasking?
Practice tasks, use less speed, find tasks that are less similar
Controlled vs. Automatic Processing
Automatic processing requires little to no conscious processing; controlled processing requires conscious effort
Action Slips
Absentminded mistakes made while engaged in automatic processing
Attentional Blink
Period of time after detection of a visual stimulus during which another stimulus can't be detected
Change Blindness
Failure to notice a change in the environment
Inattentional Blindness vs. Change Blindness
Single scene vs. subsequently presented scenes; both highlight coherence and attentional set

What is the Stroop effect?
A cognitive phenomenon where naming the color of a word is hampered by the word's meaning. This effect demonstrates the interference of conflicting information in verbal tasks.
Automatic vs Controlled Processes: Quantitative
Automatic and controlled processes are fundamentally the same, automatic are just faster.
Automatic vs Controlled Processes: Qualitative
Automatic and controlled processes are fundamentally different. When processes become automatic the way in which we accomplish them changes.

Change Blindness: Flicker task
Experiment where you are repeatedly shown two nearly identical images and you have to try to spot the difference but will fail because we struggle to notice big changes during brief visual interruptions like eye movements or cuts.