monomers, polymers and carbohydrates
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
what are monomers?
smaller units from which larger molecules are made
small, identical or similar molecules that can be linked together to form larger molecules (called polymers)
what are polymers?
large molecules which are made from a large number of monomers
examples of monomers?
(alpha and beta) glucose
amino acids
nucleic acids
fructose
fatty acids
glycerol
what is a condensation reaction?
when monomers are joined together, it forms a polymer and a water molecule is eliminated
monomers are joined by a chemical bond in condensation reactions, where a water molecule is eliminated
what is a hydrolysis reaction?
the splitting of the chemical bond between 2 molecules, where a water molecule is added
how are larger carbohydrates made from monosaccharide monomers?
combining many monosaccharides results in the formation of a polysaccharide.
how are monosaccharides joined together to form a polysaccharide?
they are joined together with a glycosidic bond formed in a condensation reaction
examples of common monosaccharides?
fructose
glucose
galactose
how are disaccharides formed?
disaccharides are formed when a 2 monosaccharides undergo a condensation reaction (resulting in the elimination of water).
what is maltose?
maltose is a disaccharide that is formed by the condensation of two glucose molecules
this forms a glycosidic bond
what is sucrose?
a disaccharide that is formed by the condensation of a glucose and fructose molecule
what is lactose?
a disaccharide that is formed by the condensation of a glucose and galactose molecule
how are polysaccharides formed?
polysaccharides are formed from many glucose molecules joined together
formed by the condensation of glucose units
how are glycogen and starch formed?
they are both formed by the condensation of alpha-glucose
how is cellulose formed?
cellulose is formed by the condensation of beta-glucose
describe the structure of glycogen?
it is formed of many molecules of alpha-glucose joined together by 1,4 and 1,6 glycosidic bonds
it has a large number of side branches, which allows energy to be released quickly as enzymes can act simultaneously on these branches
it is relatively large, but compact, and therefore maximises the amount of energy it can carry
it is insoluble, which means it will not affect the water potential of cells and can diffuse out of cells.
what is the function of glycogen?
it is the main storage molecule in animals
how does glycogen act as a source of energy?
it is hydrolysed to glucose
glucose is used in respiration
structure of starch?
it is a mixture of 2 polysaccharides called amylose and amylopectin
it is insoluble so will not affect cell water potential
it is compact so a lot of energy can be stored in a samll space and when it is hydrolysed, the released alpha glucose can be transported easily
what is amylose?
amylose is an unbranched chain of glucose molecules joined by 1,4 glycosidic bonds
as a result, amylose is coiled and therefore a very compact molecules storing a lot of energy
what is amylopectin?
a branched chain and is made up of glucose molecules joined by 1,4 and 1,6 glycosidic bonds
due to the presence of many side branches, these can be acted upon simultaneously by many enzymes and thus broken down to release its energy.
function of starch?
it stores energy in plants
structure of cellulose?
composed of long, unbranched chains of beta glucose which are joined by glycosidic bonds
function of cellulose?
it is important in stopping the cell wall from bursting under osmotic pressure
this is because it exerts inward pressure that stops the influx of water.
this means that the cells stay turgid and rigid, helping to maximise the surface area of plants for photosynthesis
how are cellulose molecules adapted to their function in plant cells?
long and straight chains
become linked together by many hydrogen bonds to form fibrils
provide strength to the cell wall
what are the two glucose isomers called?
alpha glucose
beta glucose
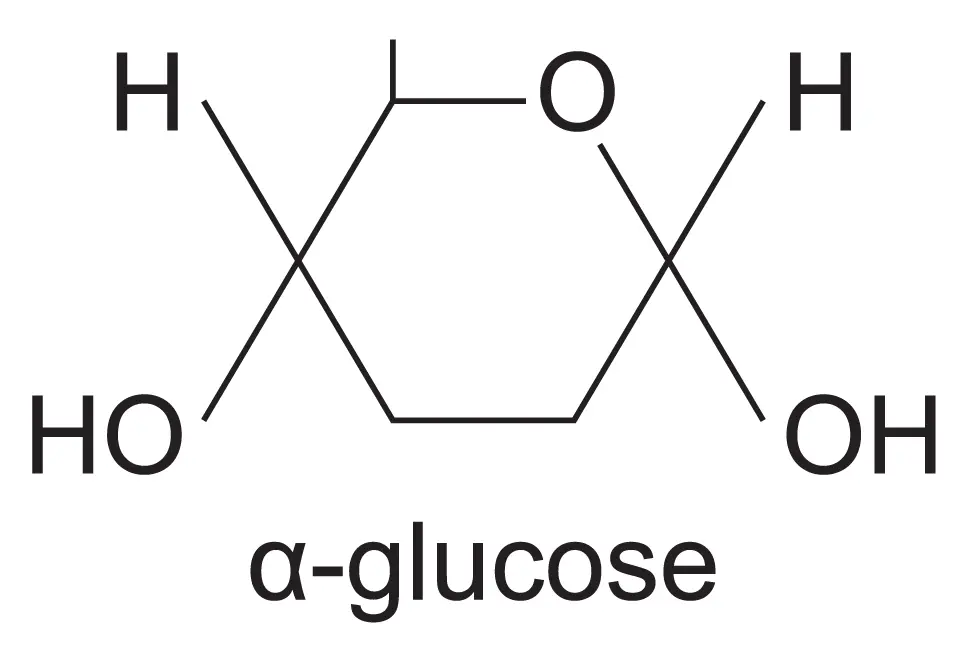
draw the structure of an alpha glucose isomer?
the hydroxyl group is at the bottom
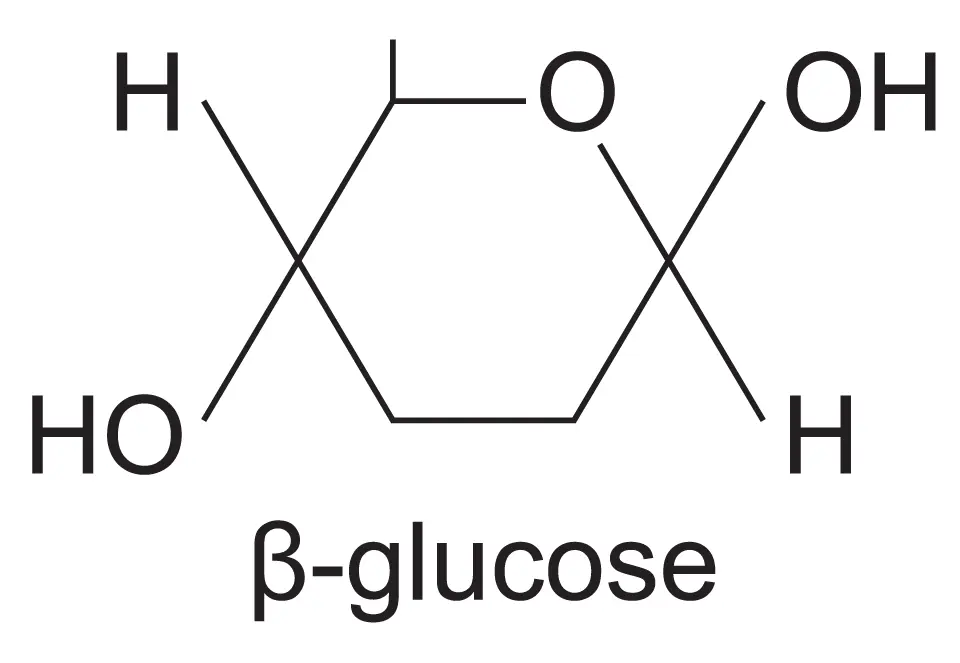
draw the structure of a beta glucose isomer?
they hydroxyl group is at the top
how to test for the presence of reducing sugars?
by using benedict’s reagent
add 2cm³ of the food sample to be tested into a boiling tube
add 2cm³ of benedict’s reagent
heat the mixture gently in water bath for 5 minutes
if the solution turns brick red, then a reducing sugar is present (positive results)
how to test for non-reducing sugars using benedict’s reagent?
add 2cm³ of food sample to 2cm³ benedict’s reagent in a boiling tube
then place this in a water bath for 5 minutes to gently warm
if the colour does not change from blue to brick red, then a reducing sugar is not present
then to another boiling tube, add 2cm³ of same food sample and 2cm³ of dilute hydrochloric acid.
place the test tube in a water bath for 5 minutes
the dilute hcl will hydrolyse the disaccharides and polysaccharides into their constituent monosaccharides
this is because all monosaccharides are reducing
after this, add some sodium hydrogen-carbonate to neutralised the test tube as the benedict’s reagent doesn’t work in acidic conditions. (pH paper is used to check that solution is neutralised)
now the solution can be tested by adding 2cm³ of benedict’s reagent to solution and placing in water bath for 5 minutes
if a non reducing sugar is present in the original sample, then there will be a colour change from blue to brick red (positive result)
biochemical test for starch using iodine/potassium iodide?
if the solution turns blue/black in colour from orange-brown, then starch is present
how does using a calorimeter increase the repeatability of a student’s results?
quantitative
standardises the result