Session 1: Energy Reactions in Cells
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Homeostasis
A dynamic equilibrium of steady internal, physical and chemical conditions maintained by living organisms.
Homeostatic mechanisms act to ___ imbalance in the internal environment
counteract
Give example of homeostatic mechanism at cellular level
regulation of intracellular calcium concentration
Give example of homeostatic mechanism at tissue level
balance between cell proliferation and cell death (apoptosis)
thermogenesis
Give example of homeostatic mechanism at organ level
regulation of water and ion concentrations in blood by the kidney
Give example of homeostatic mechanism at organism level
maintenance of body temperature
Plasma glucose
~5mM
Functions of blood
- Transportation
- Coagulation
- Immune function = WBC
- Regulation of body pH (CO2 concentration)
- Regulation of core body temperature
- Hydraulic function

Benefits of blood testing compared to biopsy
1) Could be dangerous to biopsy - invasive
2) Biopsy is expensive
4) Blood obtained readily
All living cells constantly require energy for what types of work?
1) Biosynthetic work = synthesis of cellular components
2) Transport work = movement of ions/nutrients across membranes
3) Mechanical work = muscle contraction
4) Electrical work = nervous conduction
5) Osmotic work = osmosis in kidney
All cells use ___ bond energy to drive energy-requiring activities
chemical
Reactions in which more energy is released than used
RELEASED - EXORCIZED
Exergonic
Reactions in which more energy is used than released
USED - ENDERMAN
Endergonic
Free energy (Gibbs Free Energy)
underlined
Energy released in an exergonic reaction, which is available to do work _
Exergonic reactions occur ___ and provide the energy to drive endergonic reactions
spontaneously
Gibbs free energy, G
Energy released in exergonic reaction which is available to do work
Negative ΔG
- Net loss of energy and reaction occurs spontaneously
- Exergonic
Positive ΔG
- Needs input of free energy
- Endergonic
- Must be coupled with exergonic reaction
Two main types of METABOLIC reaction
1) Catabolic
2) Anabolic
Catabolic reactions
- Breakdown larger molecules into smaller ones
- Exergonic
- Oxidative
Anabolic reactions
- Synthesise larger molecules from smaller ones
- Uses energy released from catabolism
- Reductive
Redox reaction
reduction-oxidation reaction
H-carrier molecules
- Carriers of 'reducing power' for ATP or biosynthesis
Name the major H-carrier molecules
1) NAD
2) NADP
3) FAD
Which vitamins primarily provide nicotinamide (H-carrier molecules)
think: niacin and pellagra!
Vitamin B3
Which vitamins primarily provide flavin (H-carrier molecules)
think: ariboflavinosis!!
Vitamin B2
Four stages of catabolism and where they occur in the body
1) Digestion of macronutrients to cellular fuel molecules = extracellular (gut)
2) Transformation of fuel molecules to metabolic intermediates = intracellular (cytosol)
3) TCA cycle = intracellular (mitochondria)
4) Oxidative phosphorylation = intracellular (inner mitochondrial membrane)
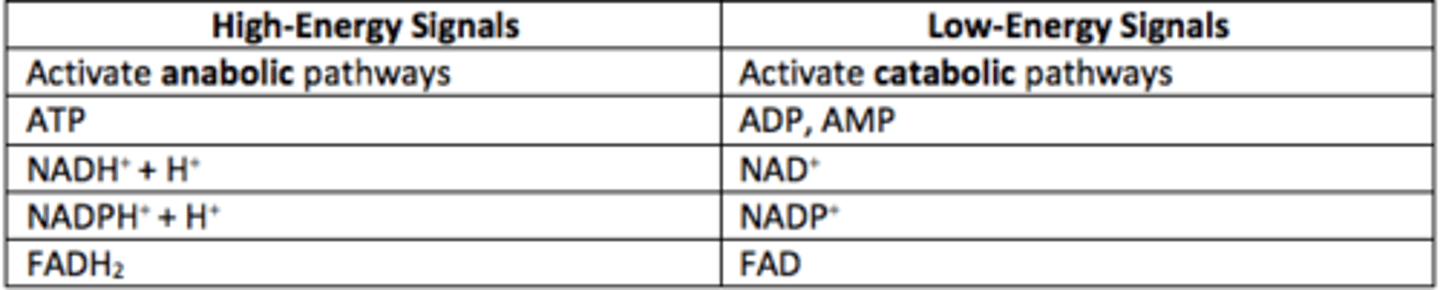
What are high-energy signals?
ATP, NADH, NADPH, FADH2
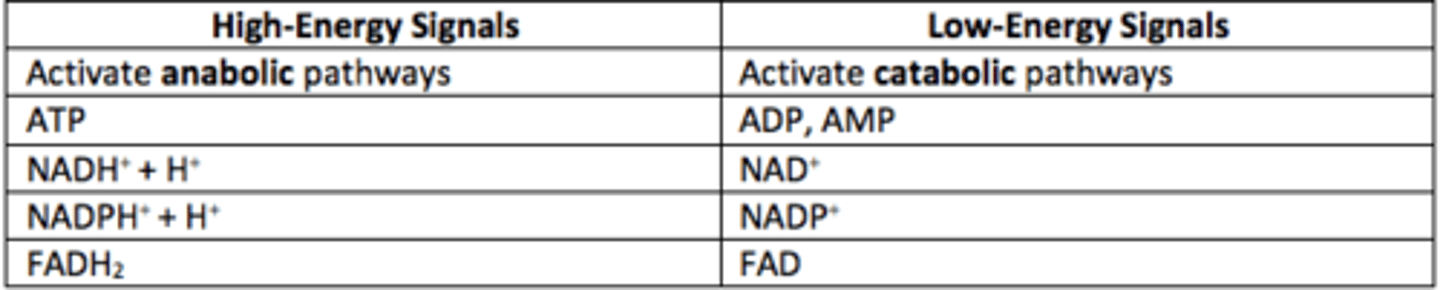
High-energy signals activate what types of pathways?
Anabolic
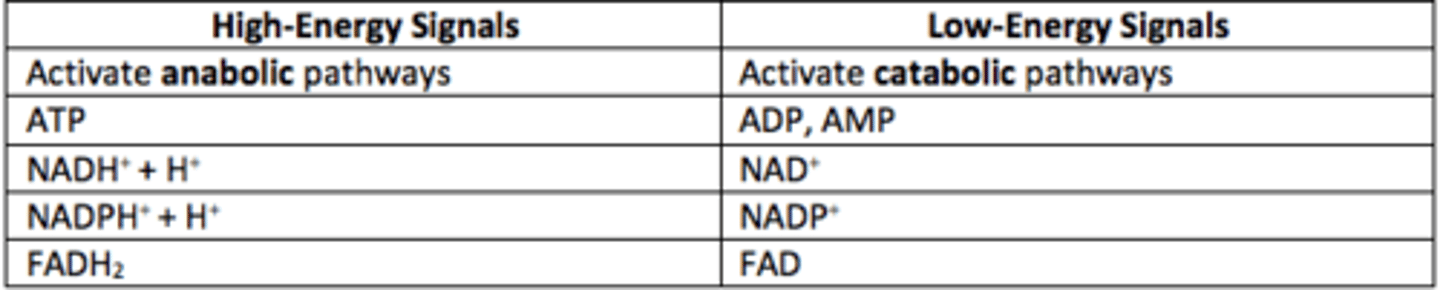
What are low-energy signals?
ADP, AMP, NAD+, NADP+, FAD
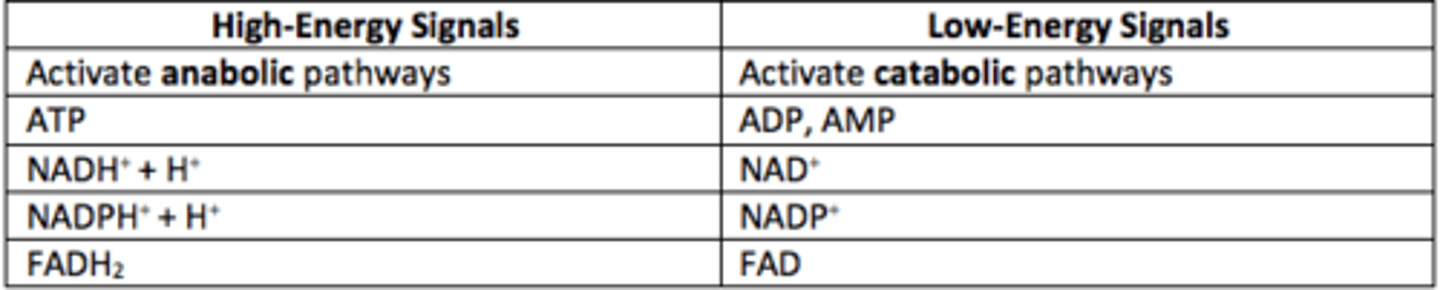
Low-energy signals activate what types of pathways?
Catabolic
What reaction occurs in exercising muscle to produce ATP for muscle to use?
Creatine phosphate is broken down into creatine using creatine kinase enzyme.
This reaction produces ATP for exercising muscle to use.
What reaction occurs in muscles (at rest)?
Creatine is converted to creatine phosphate at rest in muscle.
ATP accumulates and is used to carry this out at rest.
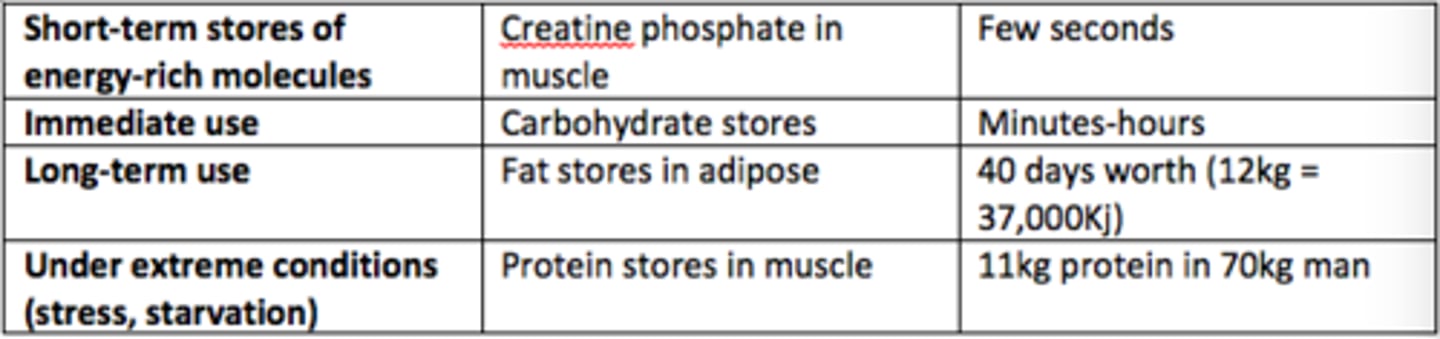
Short-term stores of energy-rich molecules example
Creatine phosphate in muscle (few seconds worth)
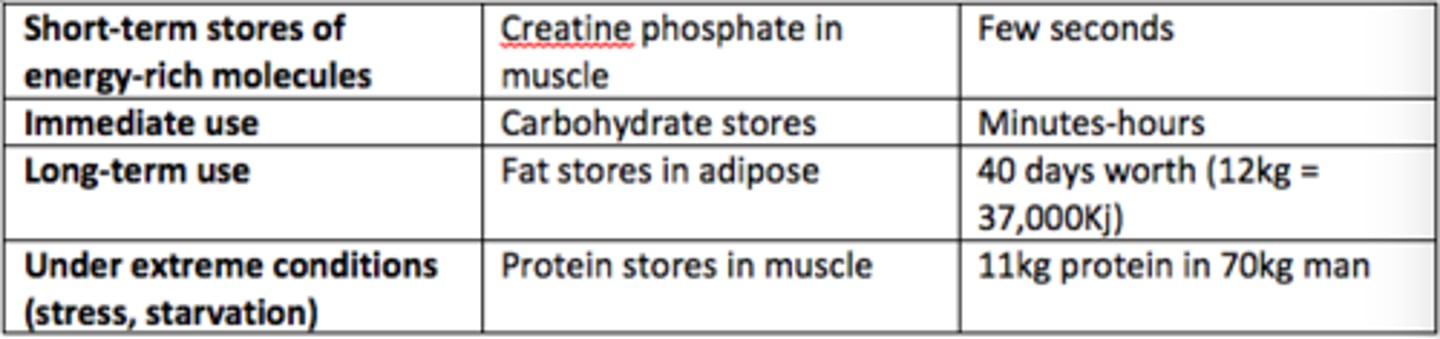
There are roughly how many days worth of fat stores in our adipose tissue (70kg man)?
40 days worth of energy (12kg, 37,000kJ)
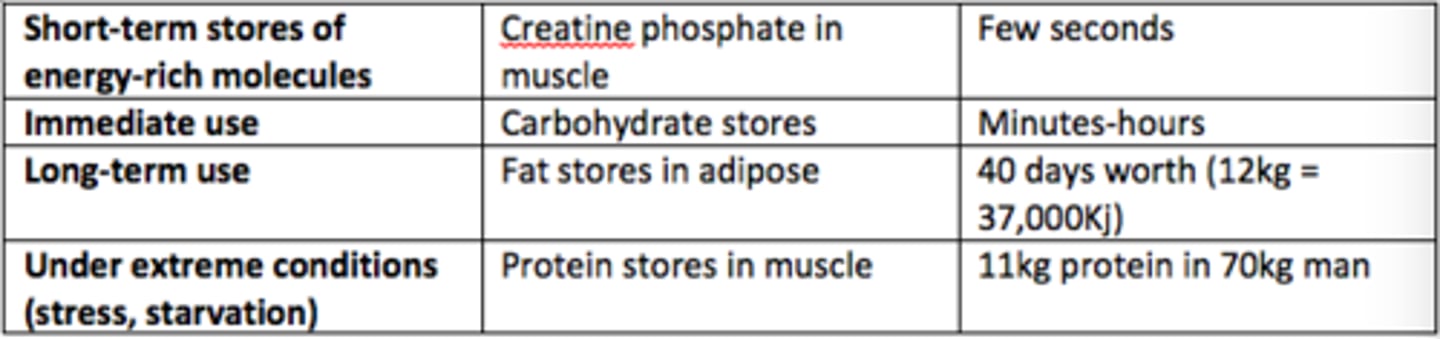
In what scenarios are protein stores in muscle used to provide energy?
Under extreme conditions (stress, starvation)