Arthropods and Echinoderms
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Defining characteristics of Arthropods
Jointed appendages and an exoskeleton
Chitin
Structural sugar, it is what the exoskeleton is made of
Simple eyes
used for light sensing
Compound eyes
used for image formation
Decapods
Specific group of crustaceans who possess 10 legs
Crab abdomen variation among sexes
U-shaped females, V-shaped males
Barnacle feeding
They are sessile filter feeders, using their cirri to grab food.
Uniramia
insects, centipedes, millipedes
Chelicerata
Horseshoe crabs, spiders, scorpions, mites etc.
Trilobita
trilobites (extinct), early arthropods
Crustacea
a large class of arthropods, including crabs and lobsters
Pereopod
walking legs
Antennae
A feeler that senses touch, taste or smell. On the head.
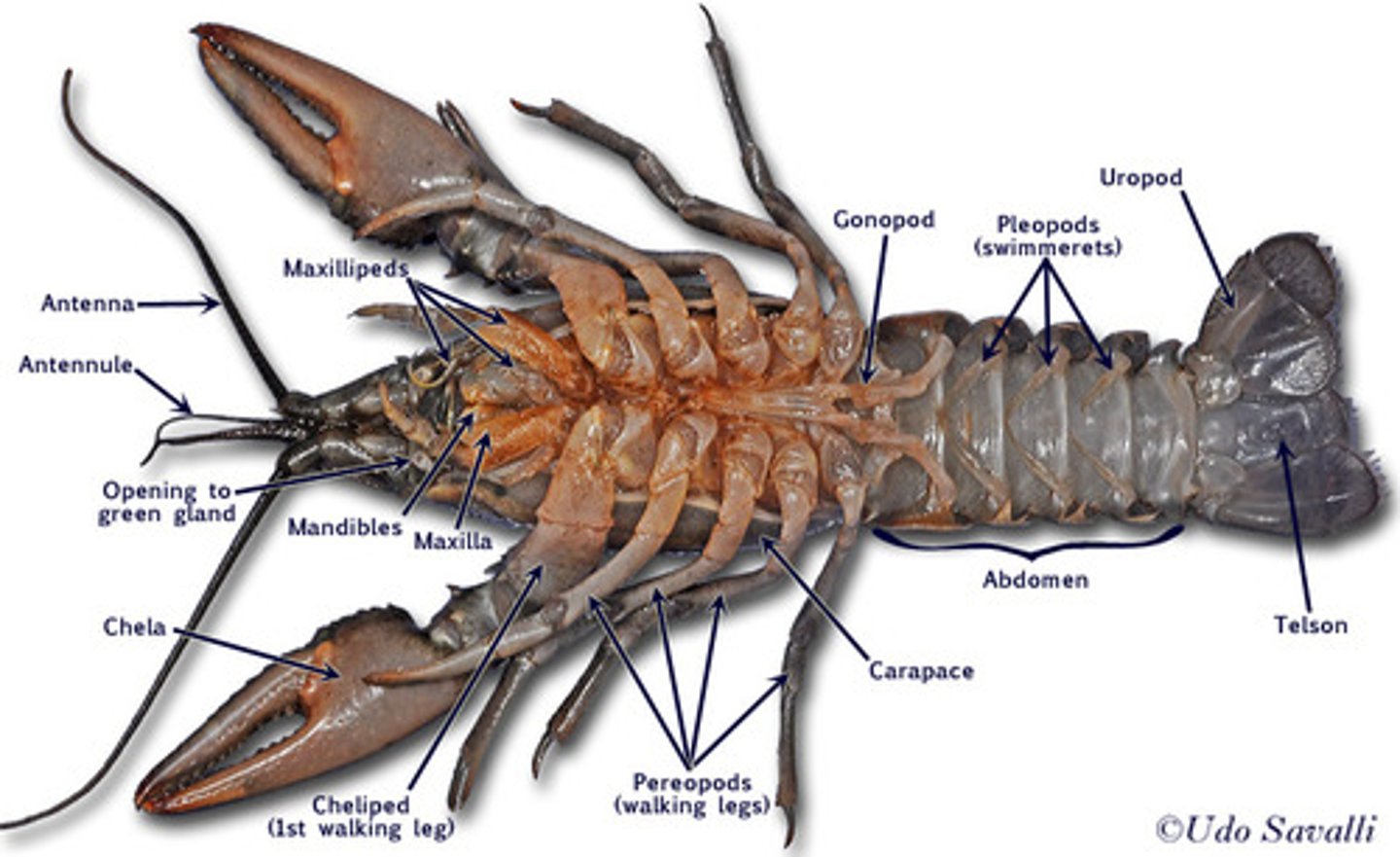
Mandible
Chewing structure in arthropods
Uropod
The tail appendage in crustaceans
Pleopod
swimming limb of a crustacean
Maxilliped
Specialized appendage used to hold food
Maxilla
Appendage that passes food into the mandible
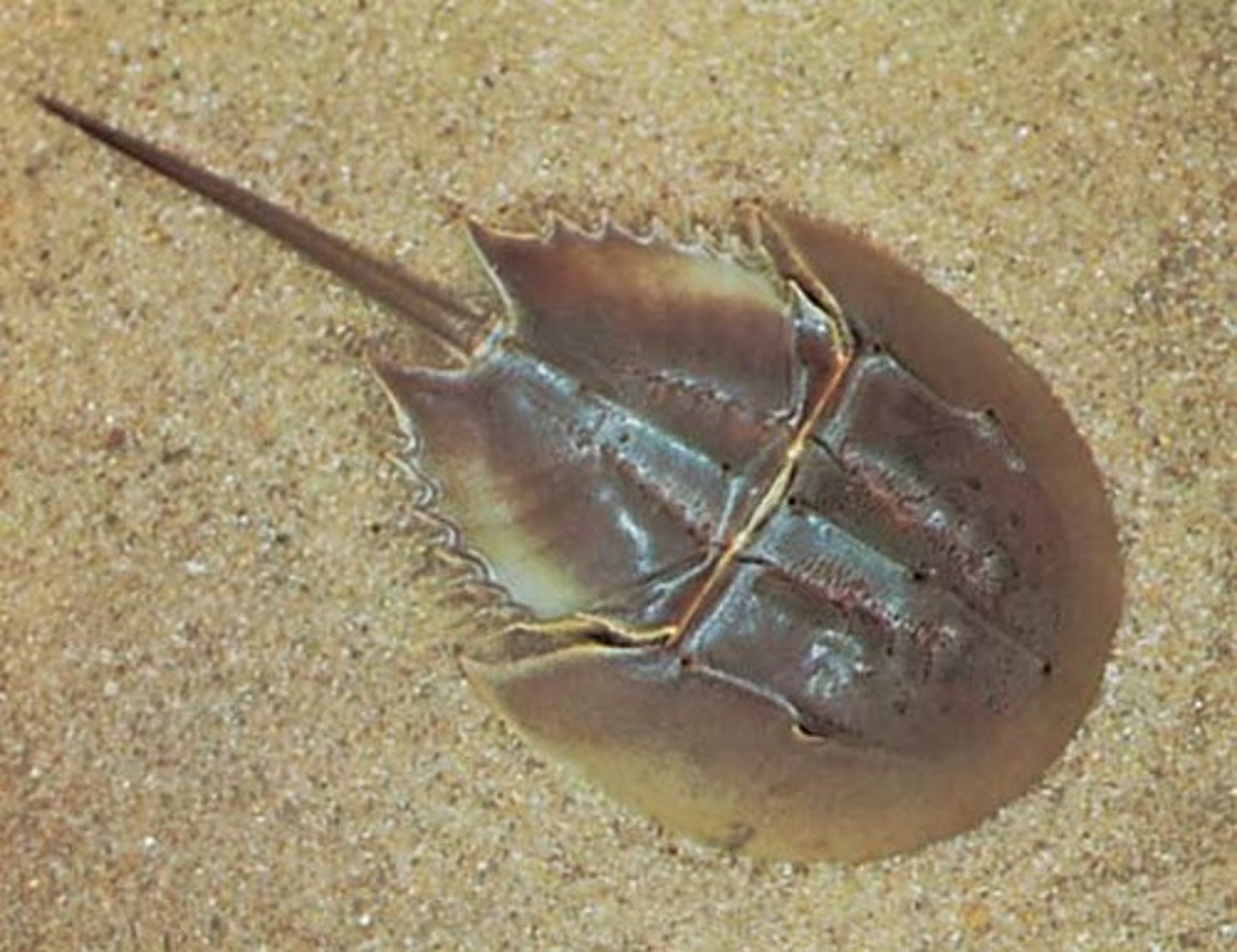
Horseshoe Crab
A bottom-dwelling marine chelicerate. Not a true crab.

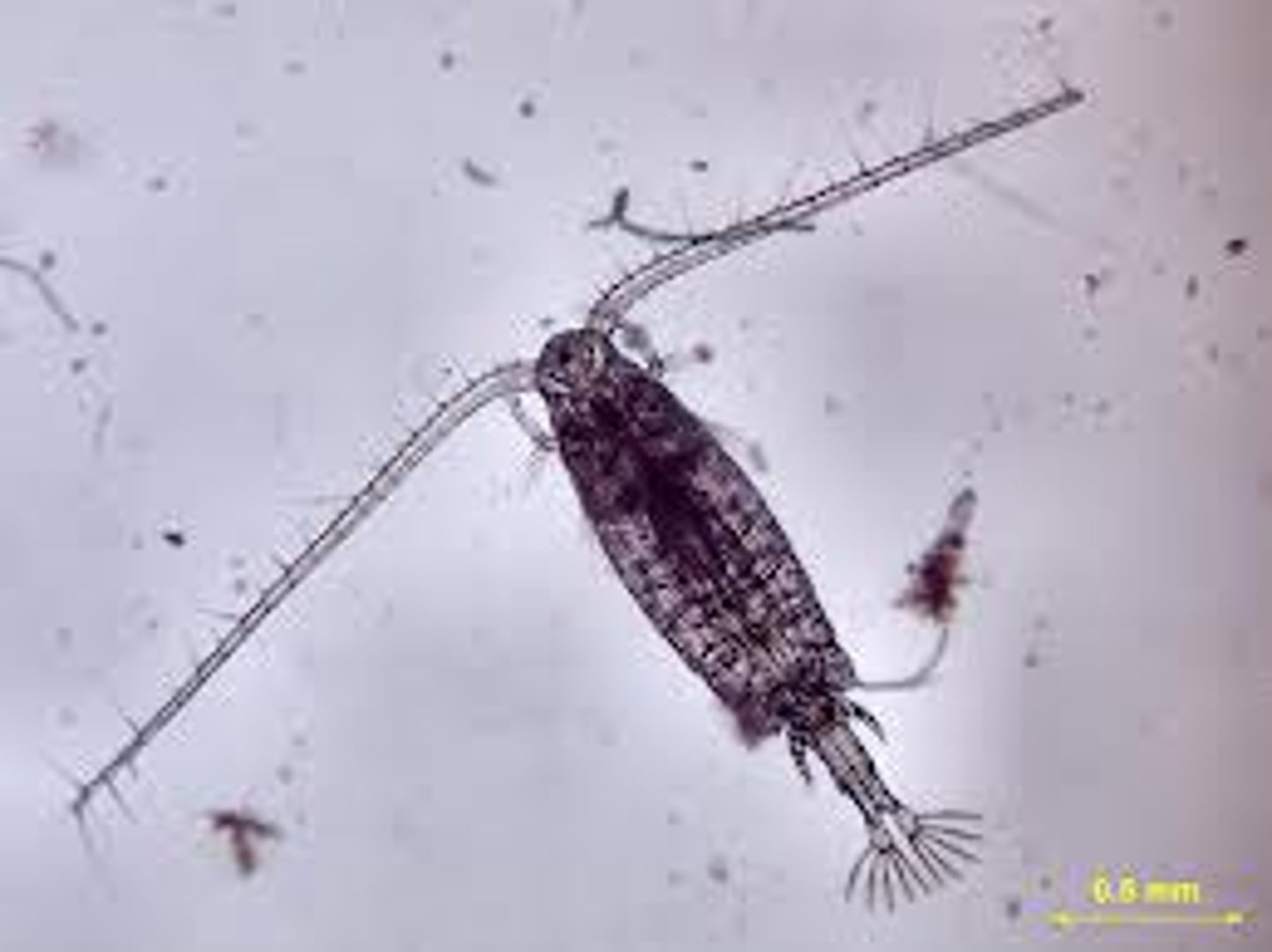
Copepod
A small planktonic arthropod, uses large antennae to swim. A key member of the food chain.

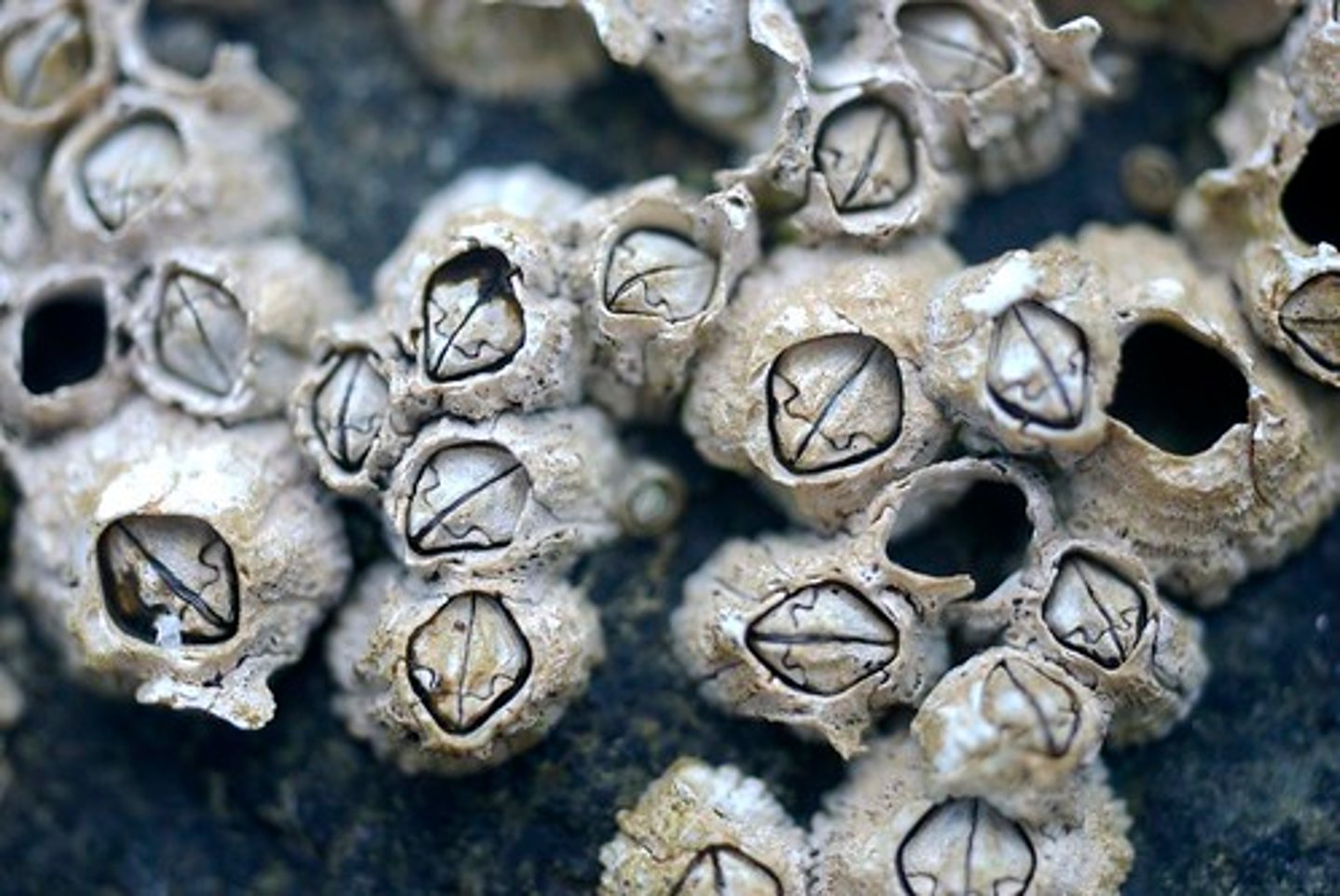
Barnacle
a marine crustacean which attaches itself permanently to a variety of surfaces

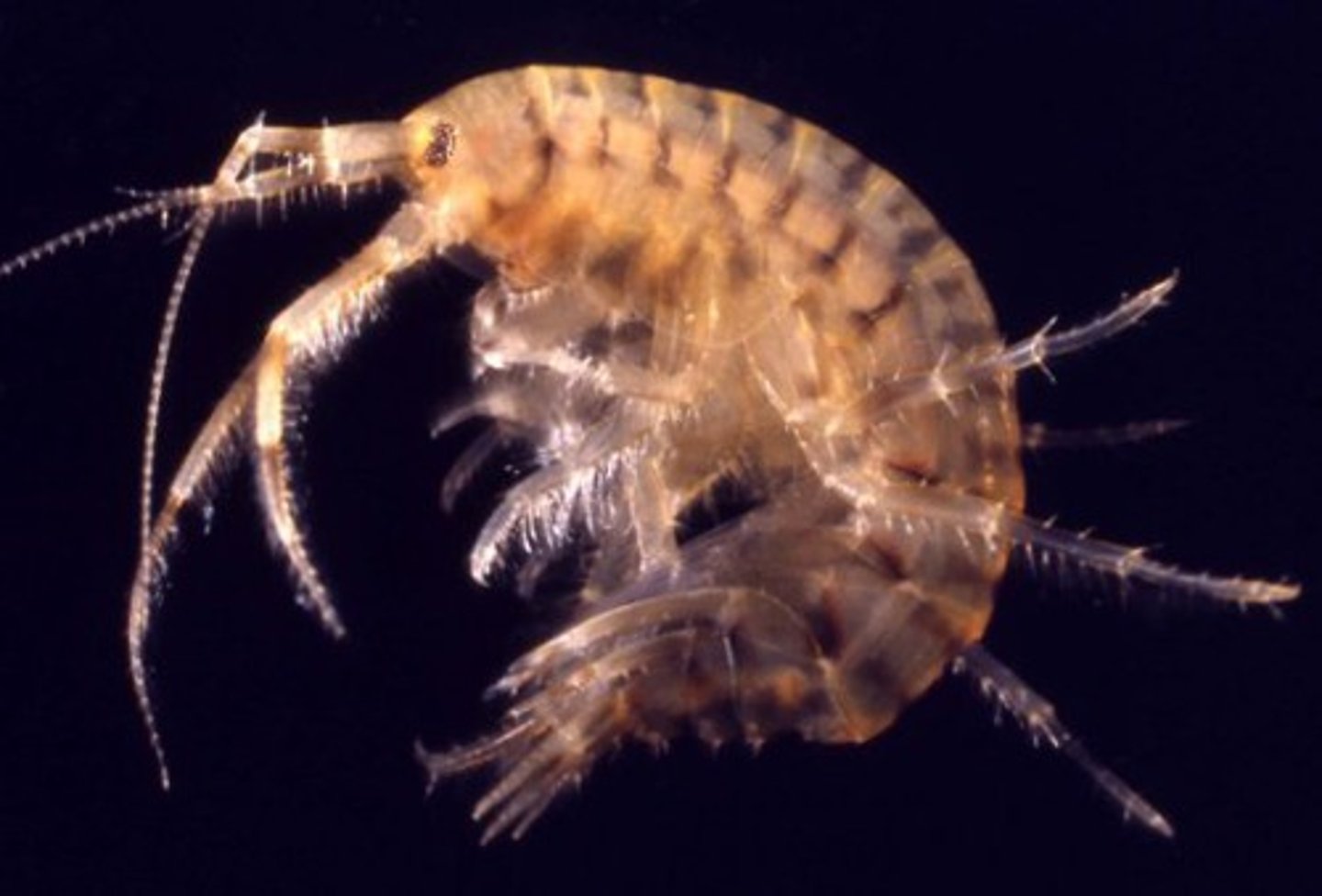
Amphipod
small crusraceans with a curved body that is flattened sideways

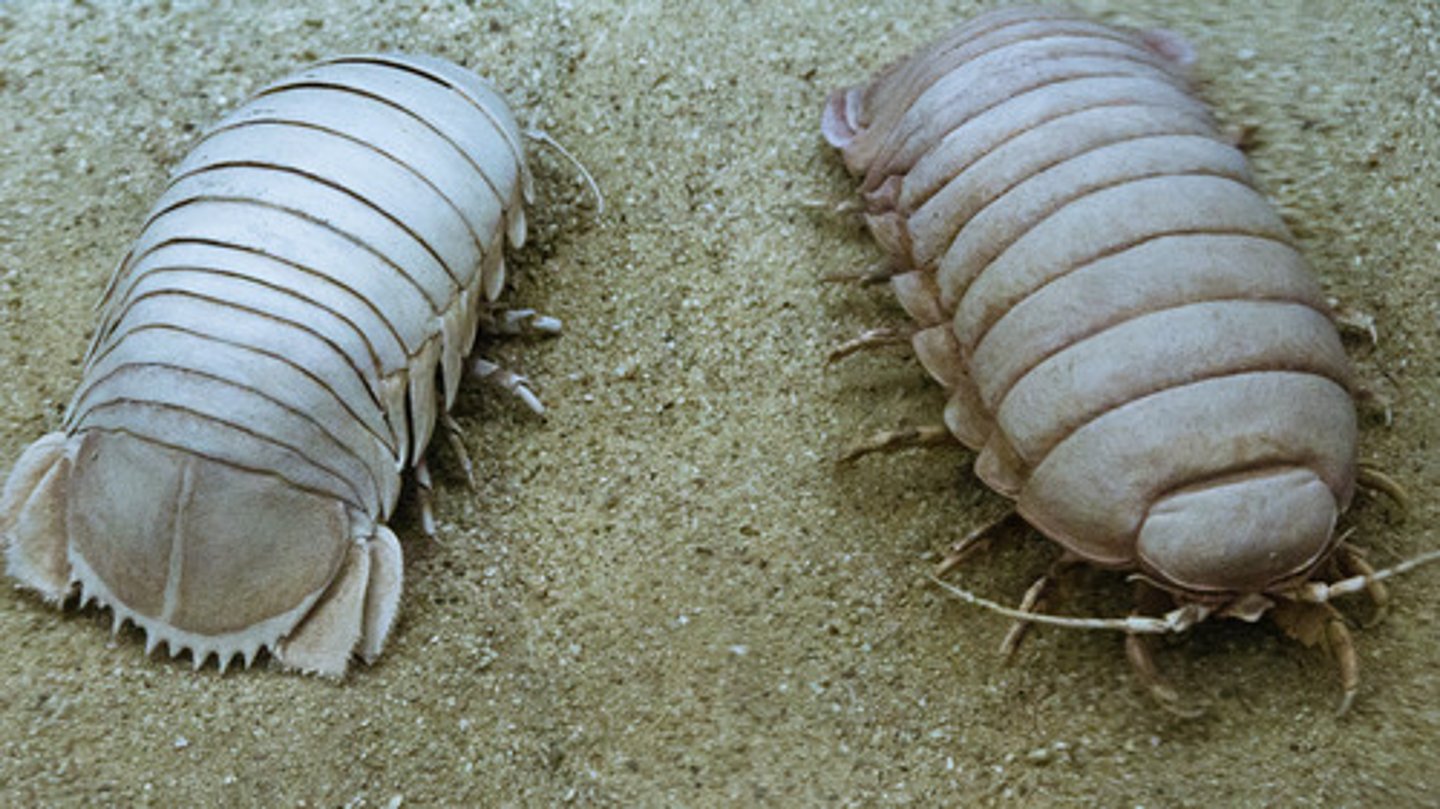
Isopod
a laterally flattened crustacean with 14 legs, common scavenger

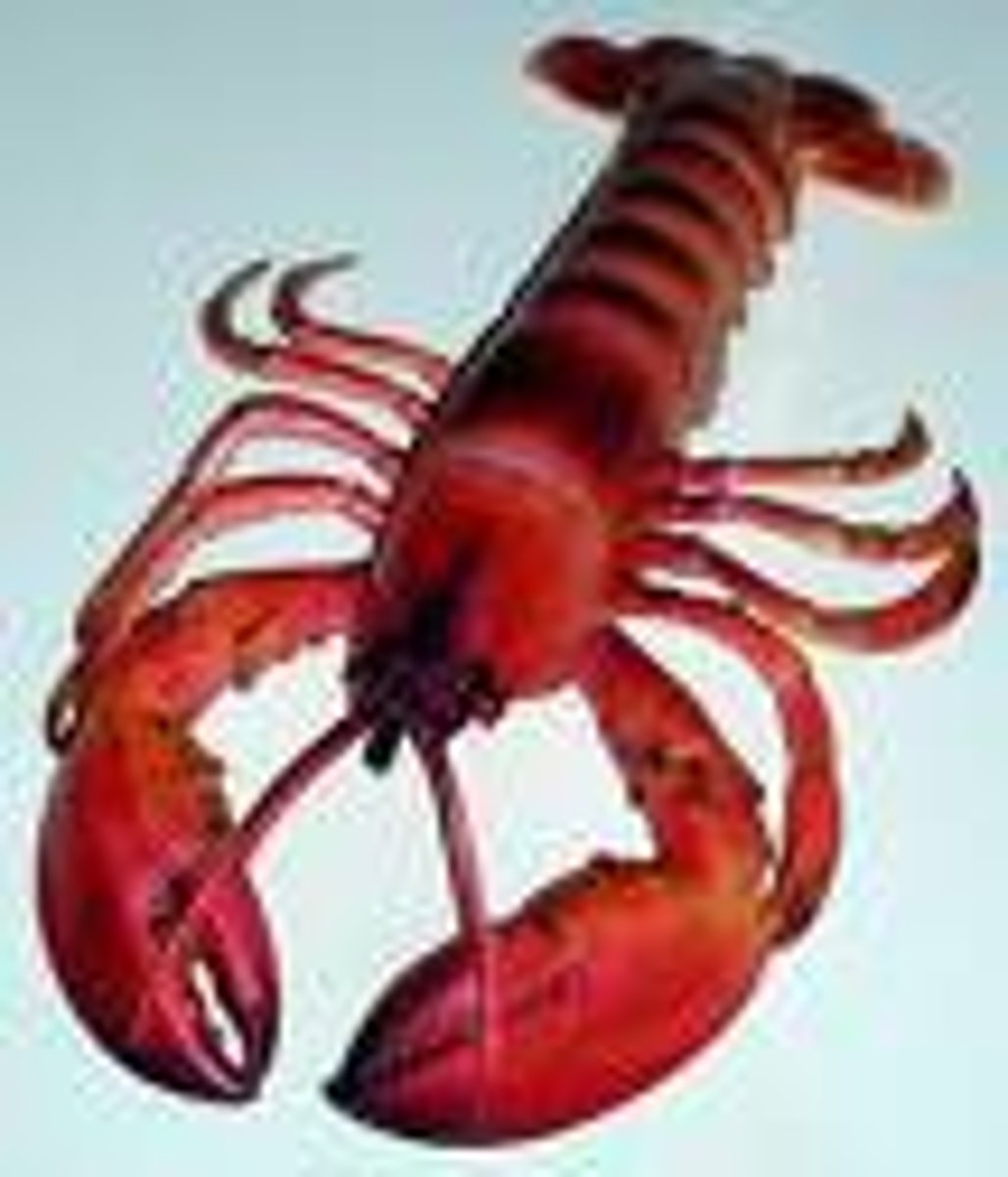
Lobster
A decapod, usually with large claws. Commonly used for food.

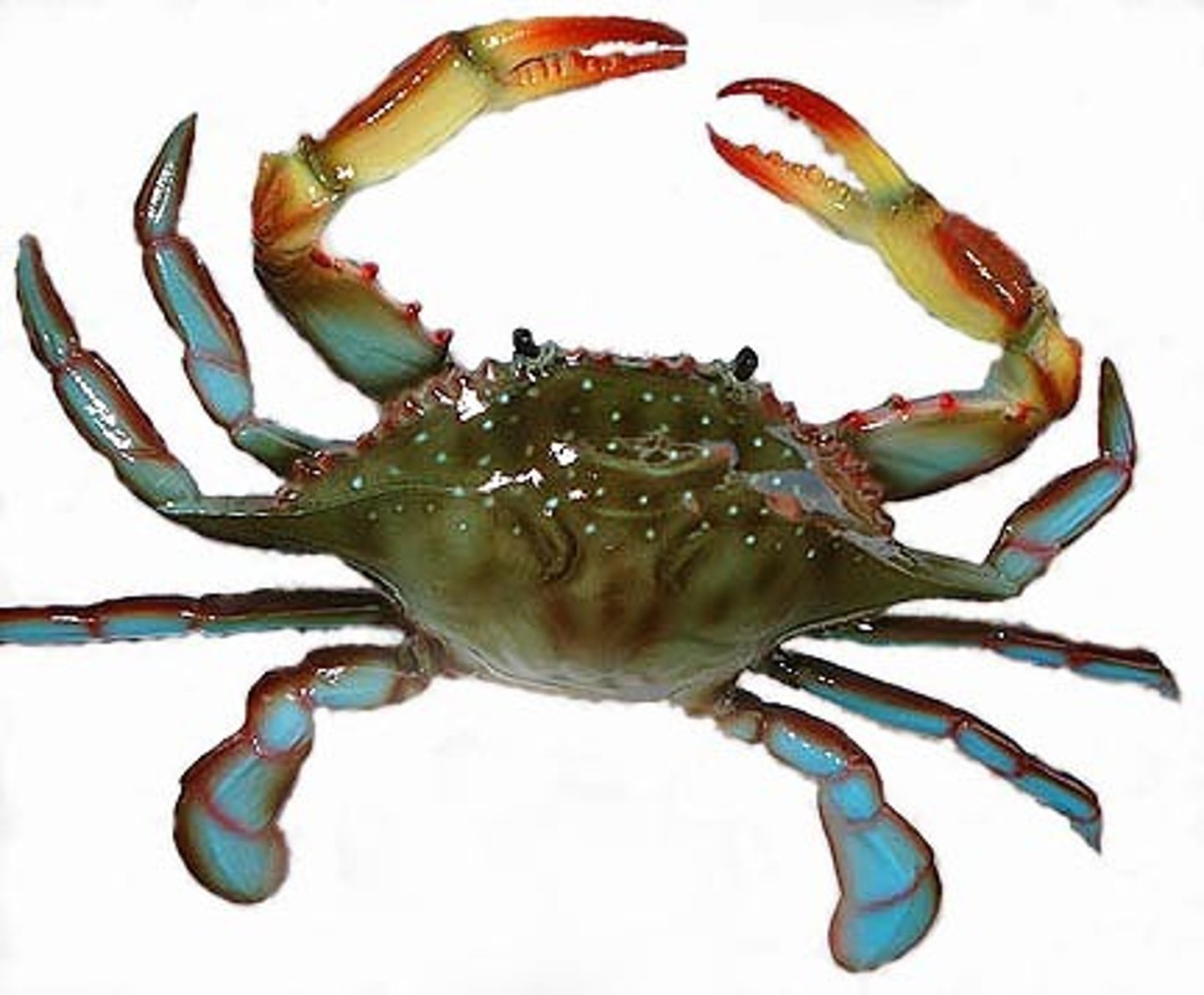
Brachyuran (true) crabs
True crabs; reduced abdomen; one pair of pincers; Football shaped

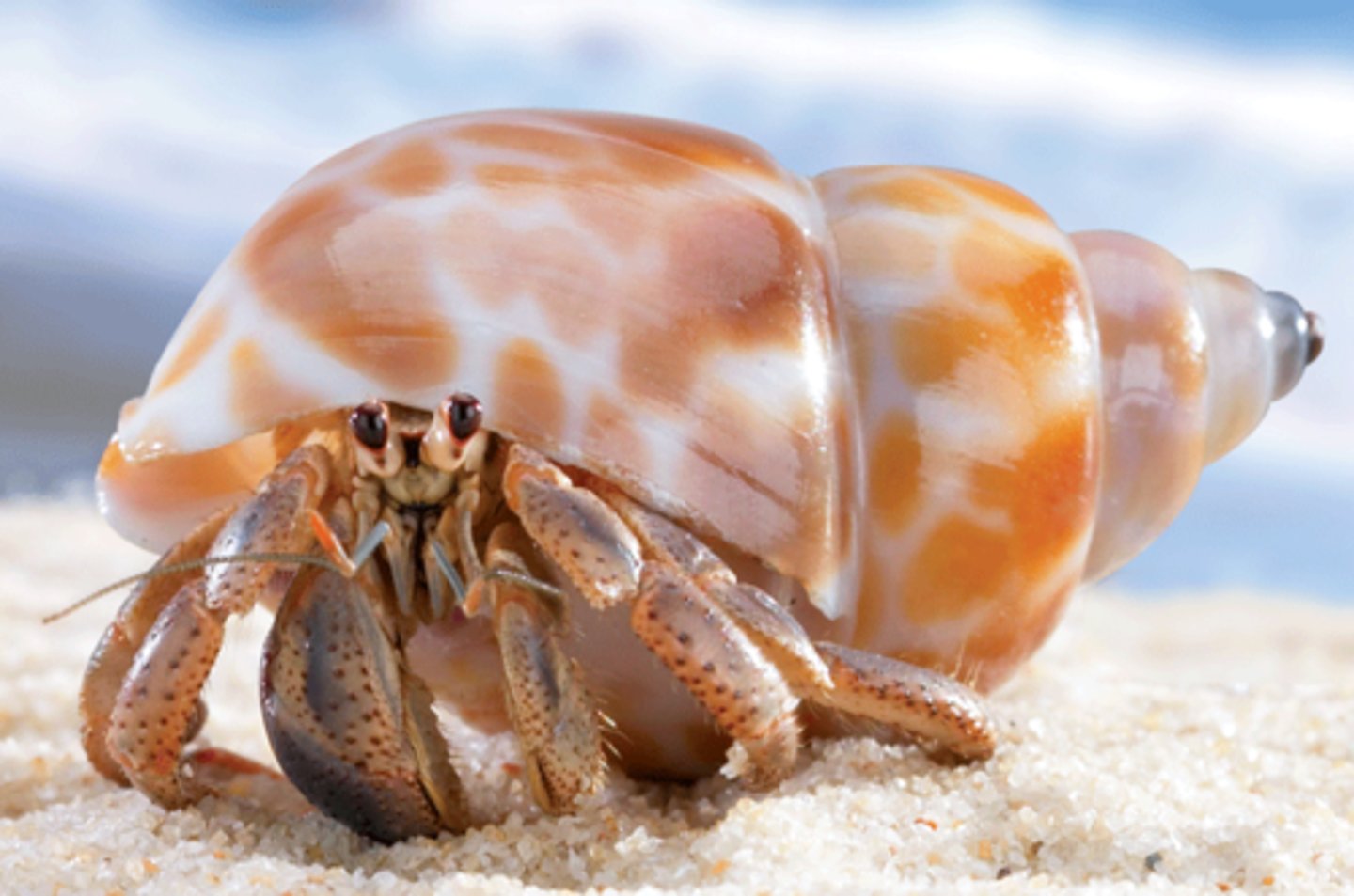
Hermit (anomuran) crabs
Not true crabs, hide their soft abdomens in abandoned gastropod shells

Molting
Process in which an arthropod sheds its exoskeleton and manufactures a larger one.
Disadvantages of exoskeletons
Weight; Also requires molting which leaves the animal vulnerable.
Pentaradial Symmetry
circular body plan that can be divided into 5 equal parts. Adult echinoderms have this.
Deuterostome development
Advanced development found in echinoderms and chordates. Can repair embroyos.
Water Vascular System
system of fluid-filled tubes used by echinoderms in locomotion, feeding, and respiration
Order of the water vascular system
madreporite, stone canal, ring canal, radial canal, ampullae, tube feet (podia)
Sea star feeding
uses two stomachs. one pushed out of body to capture prey, one for digestion.
Pedicellaria
pincerlike appendages on echinoderms used for protection and cleaning
Asteroidea
True sea stars. Organs extend into arms, move with tube feet.
Ophiuroidea
brittle stars. No organs in arms, move with snakelike motions.
Echinoidea
sea urchins and sand dollars. Have spines.
Crinoidea
sea lilies and feather stars
Holothuroidea
sea cucumbers