Y1 IB History Semester Two Study Guide
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
Causes of the Civil War
Factors that led to the outbreak of the Civil War in the United States.
Mercantilism
An economic theory that trade generates wealth and is stimulated by the accumulation of profitable balances.
Middle Passage
The sea route taken by slave ships from West Africa to the Americas.
Bacon's Rebellion
A 1676 revolt in Virginia led by Nathaniel Bacon against the colonial government.
Stono Rebellion
A slave uprising that occurred in South Carolina in 1739.
Manifest Destiny
The 19th-century doctrine that the expansion of the US throughout the American continents was both justified and inevitable.
Compromise of 1850
A package of five bills passed in September 1850, aimed at defusing tensions between slave and free states.
Scott v. Sanford (1857)
A landmark Supreme Court case that ruled that African Americans could not be American citizens.
John Brown's Raid on Harpers Ferry
An attempt by abolitionist John Brown to start a slave revolt by seizing a United States arsenal at Harpers Ferry, Virginia.
Election of 1860
The election that led to the secession of Southern states and the start of the Civil War.
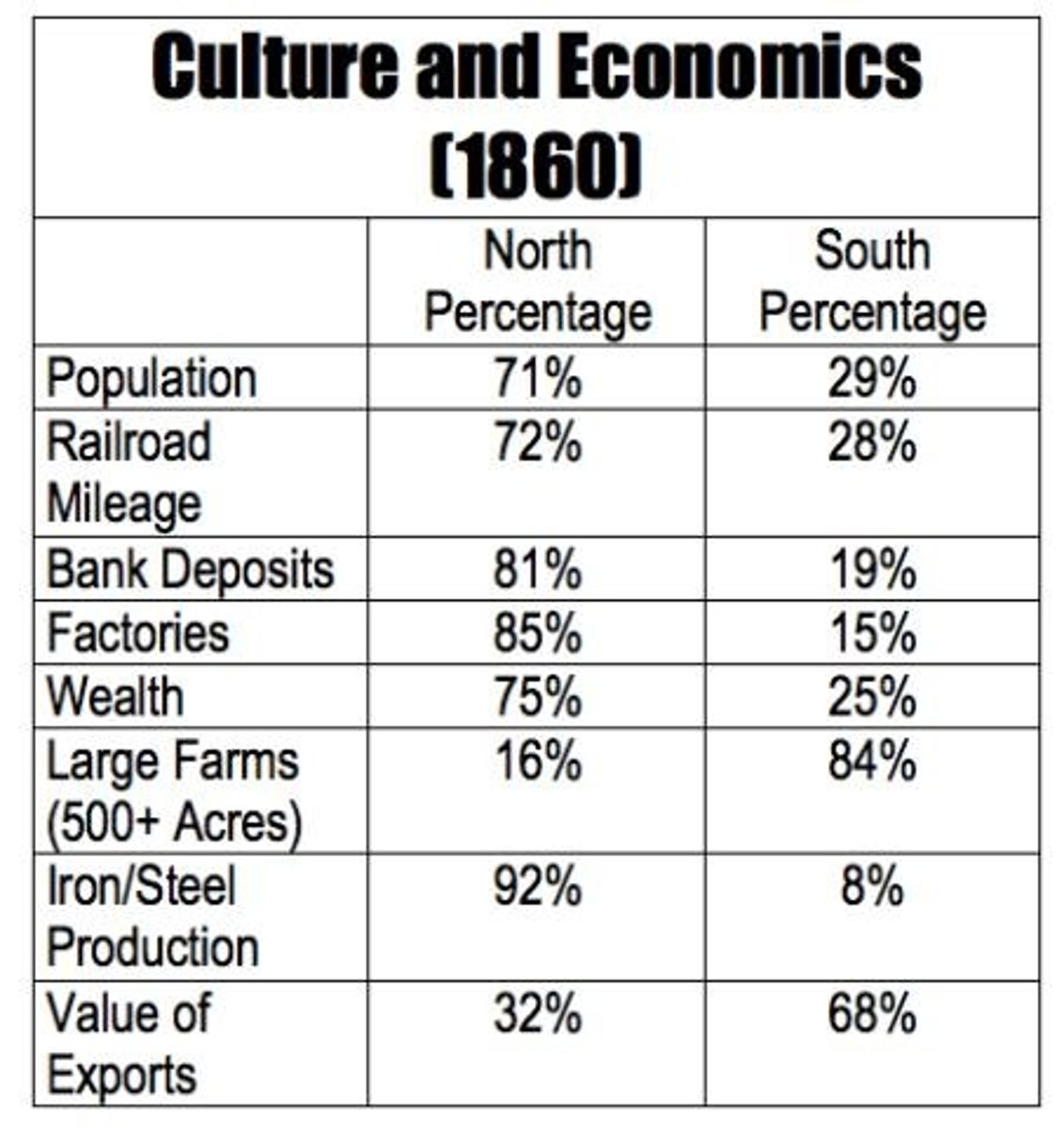
Freedmen's Bureau
A federal agency created in 1865 to aid freed slaves during the Reconstruction era.
Reconstruction Amendments
The 13th, 14th, and 15th amendments to the US Constitution aimed at establishing civil rights for former slaves.
Military Reconstruction Act (1867)
Legislation that divided the South into military districts and outlined how new governments would be created.
Ku Klux Klan
A secret society formed in the South after the Civil War that aimed to suppress the rights of African Americans.
Black Codes
Laws passed in Southern states after the Civil War to restrict the rights of freed slaves.
Lynchings
The extrajudicial killing of individuals, often associated with racial violence against African Americans.
Voting Interference
Actions taken to prevent specific groups from exercising their right to vote.
Treaty of Versailles
The peace agreement that ended World War I in 1919, which imposed heavy reparations on Germany.
Failure of Collective Security
The inability of nations to protect one another, leading to the breakdown of international cooperation.
League of Nations
An international organization proposed by Woodrow Wilson to provide collective security.
Great Depression
A worldwide economic crisis during the 1930s characterized by widespread unemployment, business failures, and bank closures.
Key factors contributing to the Great Depression
Speculation in the stock market, minimal banking regulations, and a reduction in purchasing power.
Fascism
A political system where the government is very powerful, people have few rights, and nationalism and military strength are emphasized.
Nazism
An extreme form of nationalism and racism that dominated Germany under Adolf Hitler from 1933 to 1945, characterized by antisemitism and the belief in the superiority of Germany.
Hitler's Rise to Power
The process through which Adolf Hitler consolidated power in Germany, including the unification of German people and the elimination of perceived 'others.'
Lebensraum
The concept of 'living space' in Eastern Europe into which the German population could expand.
Anschluss
The annexation of Austria in 1938 as part of Hitler's plan to unite all German-speaking areas.
Annexation of the Sudetenland
Hitler's desire to acquire this region of Czechoslovakia that had a significant German population.
Aryan Supremacy
Hitler's ideology advocating for a racially pure society, leading to the persecution and genocide of Jews and other 'inferior' groups.
Remilitarization of the Rhineland
Hitler's effort to rebuild Germany's military strength, which was restricted by the Treaty of Versailles.
Creation of alliances with Italy and Japan
The formation of the Rome-Berlin Axis with Italy and the Anti-Comintern Pact with Japan.
Rearmament
The process of rebuilding military capabilities in preparation for wars of conquest.
Invasion of Poland (1939)
The event marking the official outbreak of World War II when Germany attempted to regain its former port city of Danzig.
Tripartite Pact (1940)
An alliance between Germany, Italy, and Japan, creating the Axis Powers.
Appeasement
The policy of conceding to an aggressor to avoid conflict, which ultimately failed to prevent World War II.
Japanese militarism/nationalism
Fueled a desire to build a powerful empire in East Asia, mirroring Western powers' imperial ambitions and using the military to protect its empire from external threats.
Expansionist Aims
Starting in the early 1930s, Japan attempted to gain control of neighboring countries.
Bombing of Pearl Harbor
Japanese attack on the US naval base at Pearl Harbor, Hawaii on December 7, 1941 with the goal being the destruction of America's pacific fleet.
Blitz
German bombing campaign by the Luftwaffe against the British in 1940 and 1941 to destroy British industrial capacity and break British morale.
Casualties in the Blitz
Over 9 months, around 43,500 civilians were killed in the Blitz.
Blitzkrieg
'Lightning War' tactic used by Germany in the early years of the war that combined air attacks with the use of tanks to carry out a quick attack that would cause shock and chaos.
Phoney War
Eight-month period at the start of World War II after the UK and France had declared war on Germany; from September 1939 until May 1940, little actual warfare occurred.
Evacuation of Dunkirk
Took place in late May/early June 1940 in northern France.
Outcome of Dunkirk
Allied forces were trapped by the advancing German army, but the British Navy and civilian vessels were used to evacuate over 338,000 soldiers, boosting morale despite losing France.
Battle of Britain
A major aerial conflict between the Royal Air Force (RAF) and the German Luftwaffe from July 10 to October 31, 1940.
Goal of the Luftwaffe in the Battle of Britain
Gain air superiority over Britain to help with a future invasion.
RAF in the Battle of Britain
RAF was outnumbered but successfully defended their airspace, preventing a successful German invasion and securing Britain's survival.
Operation Barbarossa
Codename for surprise German invasion of the Soviet Union; while the Germans initially achieved some success, the invasion ultimately failed.
Battle of Stalingrad
Germany and the Soviet Union fought for control of Stalingrad from 1942 to 1943.
Casualties in the Battle of Stalingrad
One of the deadliest battles in history with millions of casualties.
Outcome of the Battle of Stalingrad
The Soviets surrounded and defeated the German army, forcing them to surrender.
Significance of the Battle of Stalingrad
Turning point in Europe; Germany started losing ground after this.
Battle of Midway
key naval battle between the US and Japan in the Pacific
Japanese aircraft carriers
four difficult to replace Japanese aircraft carriers sunk by the US near Midway Island
Island hopping
moving from island to island, conquering each along the way
Battle of El Alamein
Allied forces stopped German General Rommel's advances into North Africa, ending German hopes of controlling the Suez Canal
Operation Overlord/D Day
the Allied campaign to liberate Western Europe, specifically focusing on the Normandy landings
Largest amphibious assault
approximately 160,000 Allied troops landing on the beaches of Normandy via boat, land, and air
Battle of Berlin
the final major offensive of the European theater, fought between the Soviets and Germany, resulting in the fall of Berlin and the end of Hitler's rule
Manhattan Project
a top-secret US program that developed the world's first atomic weapons
Atomic bombs
used to devastate the cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki in order to force Japanese surrender
Holocaust
genocide in which Nazi Germany and its collaborators systematically murdered approximately 17 million people, including six million European Jews in death camps
Japanese Internment
forced relocation and internment of approximately 120,000 Japanese Americans due to fear of spies after Pearl Harbor
Role of Women in WWII
women took on traditionally 'male' jobs and could join the armed services and fight if they wanted to
Yalta Conference
February 4-11, 1945, where leaders discussed Europe's post-war reorganization and the establishment of the United Nations
Potsdam Conference
meeting of Allied leaders to discuss post-war order
Cold War
period of superpower tensions and rivalries following WWII
Salami Tactics
a strategy of gradual and incremental actions to achieve a larger goal
Iron Curtain
the division between the Soviet-controlled countries and the West
Truman Doctrine
US policy to support countries resisting communism
Marshall Plan
US program providing aid to Western Europe to rebuild economies after WWII
Containment
US strategy to prevent the spread of communism
Détente
the easing of strained relations, especially in a political situation
SALT I and II
strategic arms limitation talks between the US and the Soviet Union
Helsinki Agreement
a major diplomatic agreement signed by 35 nations in 1975 to improve relations between the Communist bloc and the West
Gorbachev's Policies
reforms including Glasnost and Perestroika aimed at revitalizing the Soviet Union
Nikita Khrushchev:
this Soviet leader, who served as premier from 1958 to 1964, largely pursued a
policy of peaceful coexistence with the West except when he instigated the Cuban Missile Crisis
Mikhail Gorbachev:
worked with Reagan to decrease political and military tension between the US
and USSR; he declared the Soviet Union was dissolved when he resigned, and he won the Nobel
Peace Prize for his “leading role in the peace process
John F Kennedy
his presidency was defined by the Bay of Pigs invasion, the Cuban Missile Crisis,
and the Limited Nuclear Test Ban Treaty