Global economic history lecture 10 (Global crises)
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What are signs of a recession?
Signs of a recession may include decreased consumer spending due to reduced confidence, rising unemployment rates as businesses cut jobs, falling stock markets reflecting investor pessimism, declining GDP indicating economic contraction, and increased bankruptcies among companies. Additional indicators can include reduced industrial production and slowing retail sales.
What are the three types of crisis?
Financial crisis: Characterised by credits, sudden destruction in financial intermediation balance sheet problems and economic instability (unemployment)
Debt crisis: Countries unable to repay loans (European debt crisis 2009-2012)
Inflation crisis: hyper inflation or high inflation erode purchasing power and economies (Germany after WW1)
How did Schumpeter view crisis in capitalism?
Crisis are embedded in capitalism driven by innovation and necessary for removing production methods and economic organisation
What are kondratievs long cycles?
Periods of economic growth ending in systemic crisis, leading to new growth models. Ex. The 1970s inflation crisis transitioned to neoliberalism
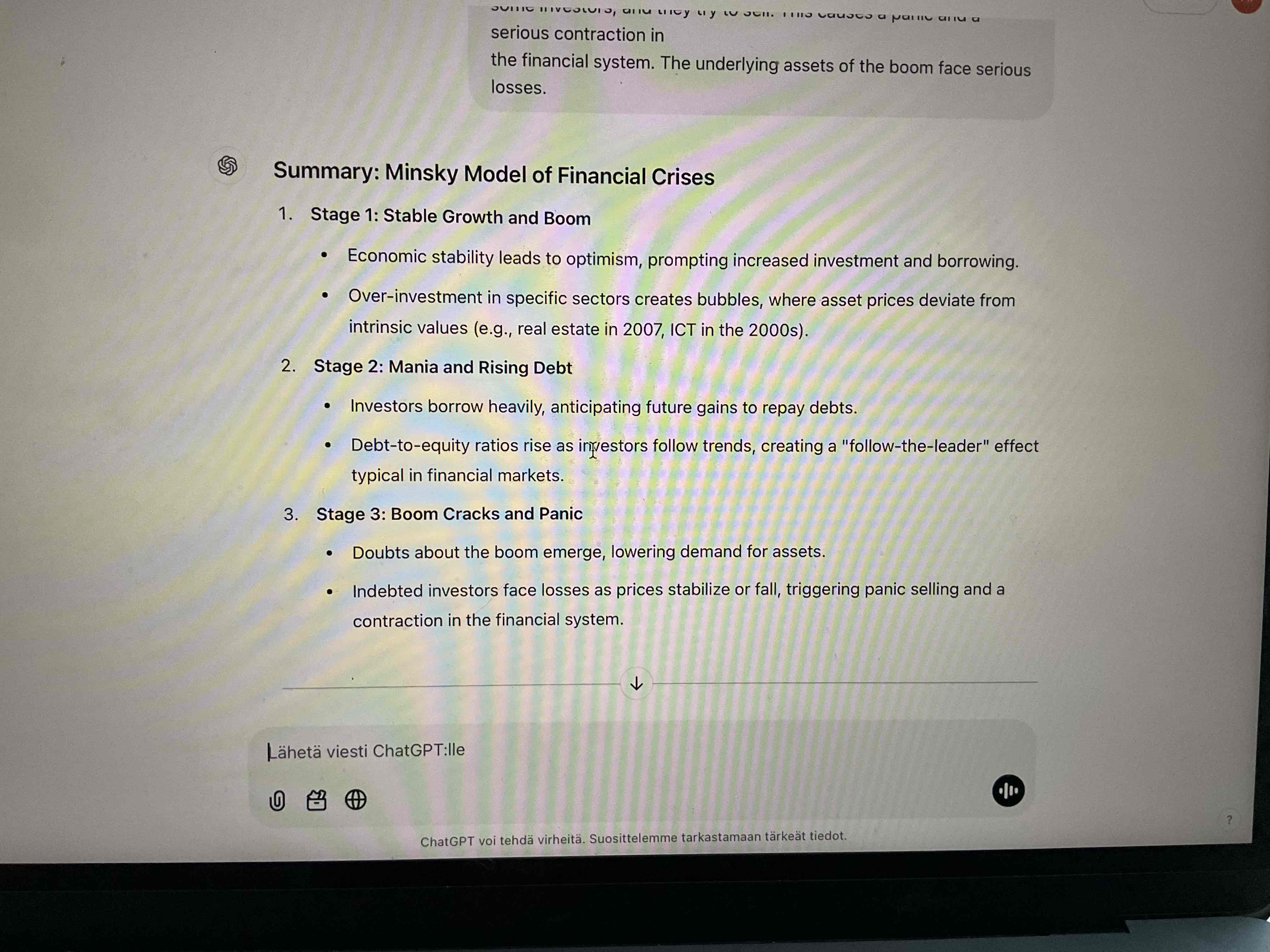
What is the Minsky model?
The Minsky model explains how financial instability arises in capitalist economies through cycles of boom and bust, emphasizing the role of debt and investor psychology. According to Minsky, economic stability can lead to increased risk-taking behavior among investors, resulting in over-leverage during boom periods. This is characterized by three stages: 'Hedge finance' where cash flows cover debt obligations, 'Speculative finance' where cash flows cover interest but not principal, and 'Ponzi finance' where cash flows do not cover either. Eventually, the accumulation of debt and speculative behavior leads to a financial crisis, illustrating the inherent instability in capitalist economies.
What is Adam Smith's invisible hand?
The invisible hand is a metaphor used by Adam Smith to describe the self-regulating nature of the marketplace, where individual self-interest leads to economic benefits for society as a whole.
Why did Keynes criticise classical economics?
Keynes argued that individual rational actions during crisis reduce demand, worsening economic downturns instead of restoring equilibrium
What is the keysian solutions for economic crisis?
Governments should adopt anti-cyclical policies, increasing spending during downturns and reducing spending during upturns to stabilise demand.
What is the multiplier effect in Keynesian economics?
Government spending generates additional incomes and spending, causing national income to rise more than initial investment
What do monetarists like Milton Friedman argue is the primary cost of inflation?
Inflation is caused by Lewis monetary policies and excessive money supply, not demand side factors
What is the “crowding out” effect?
When government spending increases, it reduces resources (borrowing capacity) available to private actors, undermining economic growth
What were the six causes of the great depression?
Stock market collapse in 1929
Industrial overproduction
Demand shock
Tight monitor policy (Adherence to the gold standard for countries like Britain to maintain high interest rates, Which limited money supply)
Balanced budget (Government’s got public spending and raised taxes in response to declining revenue)
Protectionism: Countries including the US implemented high tariffs to protect domestic industries
What were the three consequences for the great depression?
Economic downturn (unemployment and reduced industrial output)
Social instability: Economic hardships led to widespread discontent and the rise of fascist parties leveraging social unrest
Collapse of international trade: Declining trades and the imposition of tarriffs Intensified economic isolation and overproduction
Tell me 3 solutions and lessons from the Great depression
Abandonment of the gold standards (allowed more flexible monetary policies)
Keynesian economics: anti-cyclical intervention
Avoiding protectionism: no more excessive tarriffs
What was the New Deal?
The New Deal was a series of programs and policies implemented by President Franklin D. Roosevelt in the 1930s to address the Great Depression, focusing on relief for the unemployed, recovery of the economy, and reforms to prevent future economic disasters.
What was the Glass-Steagall Act?
The Glass-Steagall Act, enacted in 1933, was a law that separated commercial banking from investment banking in the United States to reduce the risks of financial speculation, and it established the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) to protect bank deposits.
What was the Tennessee Valley Authority? And how was it related to the New Deal program?
The Tennessee Valley Authority (TVA) was a New Deal program established in 1933 as part of President Franklin D. Roosevelt's efforts to combat the Great Depression. The TVA aimed to modernize the Tennessee Valley, a region significantly impacted by the economic downturn, through a variety of initiatives. It focused on providing navigation, flood control, electricity generation, and economic development. The TVA constructed numerous dams which provided hydroelectric power to rural areas, improving living standards and attracting industries. Additionally, it created jobs during a time of severe unemployment, thereby alleviating poverty and stimulating the economy in the region. The TVA was a pioneering model of regional planning and played a significant role in reshaping the American South through infrastructure development and economic revitalization.
What were the four key causes of the Global financial crisis in 2007-2008?
Housing market bubble (low interest rates, subprime lending, speculation)
Deregulation of banks: (repeal of the glass-stegall act 1999)
Securitization of loans: (mortgage backed securities, collateral debt obligations, credit default swaps)
Systemic risk
What were the three key developments leading to the crisis in 2004 to 2008?
Interest rate hikes and rising defaults
Underwater borrowers (Falling home prices meant many homeowners owed more on their loans than their homes were worth)
Subprime crisis
How did the US housing crisis become a global crisis?
The US housing crisis turned into a global crisis due to interconnected financial markets; subprime mortgage defaults led to the devaluation of mortgage-backed securities, affecting banks worldwide. The resulting credit freeze and economic downturns in the US propagated through international markets, leading to a global recession.
What was the Troubled Asset Relief Program (TARP) of 2008?
The Troubled Asset Relief Program (TARP) was a financial bailout program enacted by the US government in response to the financial crisis of 2007-2008, aimed at stabilizing the economy by purchasing distressed assets and providing capital injections to banks.
What was the European sovereign debt crisis?
The European sovereign debt crisis was a multi-year financial crisis that occurred in the Eurozone, beginning in late 2009, wherein several European countries faced difficulties in repaying or refinancing their government debt, leading to fears of default and significant financial instability, especially in countries like Greece, Ireland, and Portugal.
What was the Occupy Wall Street movement?
The Occupy Wall Street movement began in 2011 as a protest against economic inequality, corporate greed, and the influence of money in politics, symbolized by the slogan 'We are the 99%.' It started in New York City and gained global attention, inspiring similar movements worldwide.