Chapter 10: Resource Markets with Applications to Labor
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
What are factor markets?
Factor markets are markets where resources (factors of production) are bought and sold.
These include:
Labor (e.g., workers)
Capital (e.g., machinery, tools)
Land (e.g., natural resources)
Entrepreneurship (e.g., business skills)
➡ In contrast to product markets (where consumers buy goods/services), factor markets are where firms are the demanders and households are the suppliers.
Derived Demand
Derived Demand : 📌 What is Derived Demand?
Derived demand means the demand for a resource or factor of production (like labor) comes from the demand for the final good or service it helps produce.
🔁 In Simple Terms:
A worker isn’t hired just for fun — they’re hired because the firm wants to make something.
So, the demand for labor depends on the demand for the product the labor creates.
The Marginal Revenue Product
MRP=Marginal Product (MP)×Price (P) of output (In perfect competition) (MOST QUESTIONS ASSUME PERFECT COMP)
MP = how much extra output one more worker produces
P = how much revenue the firm gets per unit sold
OR USE MP * MR
. MRP = Change in Total Revenue / Change in Input
Marginal Factor Cost
MFC is the additional cost of hiring one more unit of a factor of production (like labor or capital).
Firms will hire workers where MRP = MFC.
If MRP > MFC, hire more workers.
If MRP < MFC, stop hiring.
The least cost rule
The Least Cost Rule states that a firm should hire or use factors of production (like labor and capital) in such a way that the marginal product per dollar spent on each resource is equal.
Price of Marginal product labor/price of labor = marginal product capital/ price of capital
Where:
MP of Labor is the marginal product (extra output) produced by an additional unit of labor.
Price of Labor is the cost of hiring an additional unit of labor (usually the wage rate).
MP of Capital is the marginal product of an additional unit of capital (like machinery or equipment).
Price of Capital is the cost of using an additional unit of capital.
monopsony
A monopsony is a type of market structure where there is only one buyer of a particular factor of production (like labor or raw materials), but multiple sellers. In other words, the firm or entity that is the sole purchaser of a resource has significant control over the price and quantity of that resource.
MFC formula
change in total resource cost / change in resource quantity = wage
monospony vs monopoly
📊 Monopsony vs. Monopoly:
Monopoly: A monopoly refers to a market with a single seller and many buyers.
Monopsony: A monopsony refers to a market with a single buyer and many sellers.
profit maximizing rule for employing resources
MRP = MFC
Perfectly Competitive labor market
A perfectly competitive labor market is one where many employers are competing to hire labor, and many workers are competing for jobs. Neither firms nor workers have the power to influence the market wage — the wage is set purely by supply and demand.
HERE the firms are wage takers If firms or workers are wage takers, it means they accept the market wage and cannot influence it.
SUPPLY AND DEMAND OVERLAP = WAGE
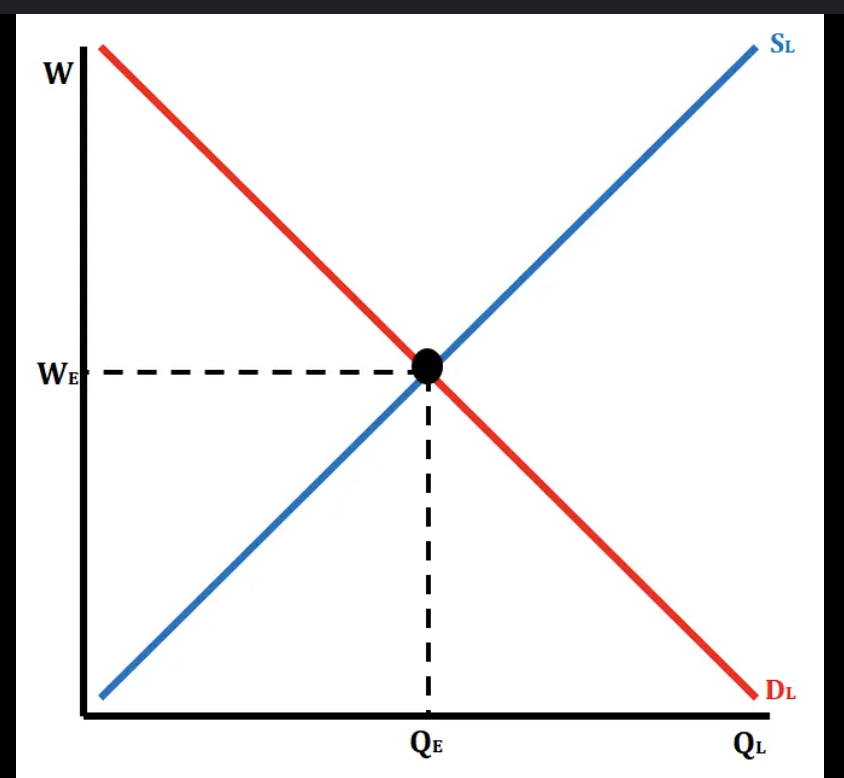
Minimum wage
a price floor set by government, the wage will increase and quantity hired in the labor market and firm will decrease
if MPL/PL > than MPk/Pk then
the firm will hire more labor and decrease use of capital.