APUSH Period 6 Review
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
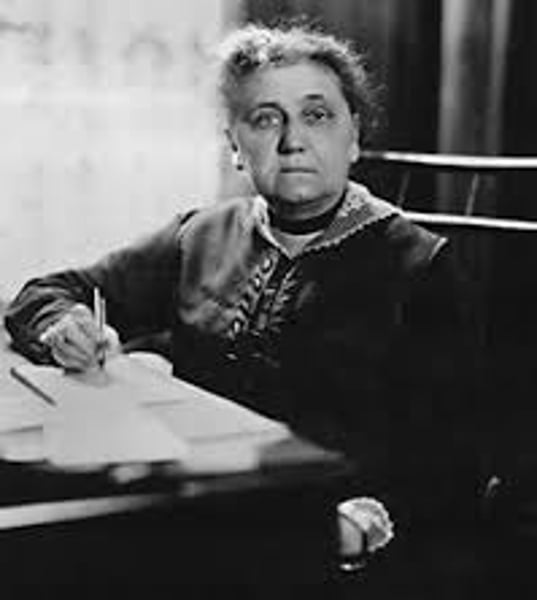
Jane Addams
Founder of Settlement House Movement (Hull House).

J.P. Morgan
An influential banker and businessman who bought and reorganized companies. His US Steel company would buy Carnegie steel and become the largest business in the world in 1901. He also loaned the US government $65 million in gold to support dollar and the gold standard.

John D. Rockefeller
Owner of Standard Oil Company. Used horizontal integration and ruthless tactics to eliminate other businesses. Built trusts and used money to influence government. Also a philanthropist who donated millions to science and education

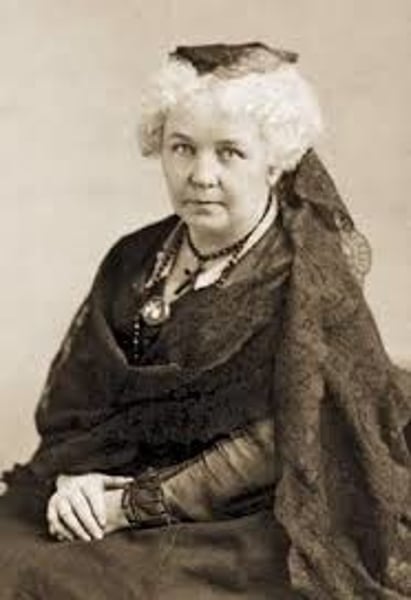
Elizabeth Cady Stanton
(1815-1902) A suffragette who, with Lucretia Mott, organized the first convention on women's rights, held in Seneca Falls, New York in 1848. Issued the Declaration of Sentiments which declared men and women to be equal and demanded the right to vote for women. Co-founded the National Women's Suffrage Association with Susan B. Anthony in 1869.

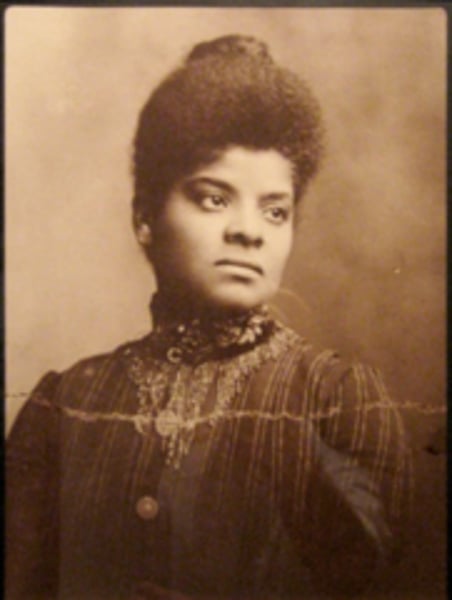
Ida B. Wells
African American journalist. published statistics about lynching, and led an anti-lynching campaign

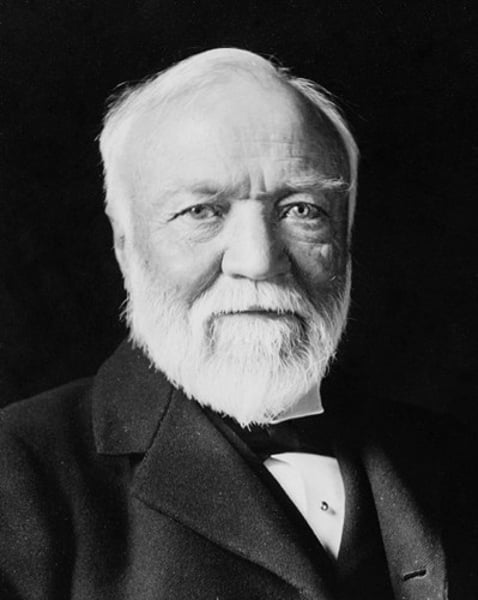
Andrew Carnegie
A Scottish-born American industrialist and philanthropist who founded the Carnegie Steel Company in 1892. By 1901, his company dominated the American steel industry.

Thomas Edison
American inventor best known for inventing the electric light bulb, acoustic recording on wax cylinders, and motion pictures.

Booker T. Washington
African American progressive who supported segregation and demanded that African American better themselves individually to achieve equality.

Williams Jennings Bryan
Three-time candidate for president for the Democratic Party, nominated because of support from the Populist Party. He never won, but was the most important Populist in American history.

holding companies
Companies that hold a majority of another company's stock in order to control the management of that company. Can be used to establish a monopoly.
laissez-faire
Idea that government should play as small a role as possible in economic affairs.
Dawes Act
1887 law which gave all Native American males 160 acres to farm and also set up schools to make Native American children more like other Americans
People's (Populist) Populists
A party made up of farmers and laborers that wanted direct election of senators and an 8hr working day
Social Darwinism
The idea that people and societies compete for survival with the fit becoming wealthy and successful while the weak struggle to survive
Gilded Age
1870s - 1890s; time period looked good on the outside, despite the corrupt politics & growing gap between the rich & poor. Coined by Mark Twain
Social Gospel
A movement in the late 1800s/early 1900s which emphasized charity and social responsibility as a means of salvation.
Chinese Exclusion Act
(1882) Denied any additional Chinese laborers to enter the country while allowing students and merchants to immigrate
National American Woman Suffrage Association (NAWSA)
Organization founded by Susan B. Anthony and Elizabeth Cady Stanton, fought for women's equality in courts and workplaces as well as the polls
Interstate Commerce Act
(1887) monitors the business operation of carriers transporting goods and people between states - created to regulate railroad prices
Plessy v Ferguson
a 1896 Supreme Court decision which legalized state ordered segregation so long as the facilities for blacks and whites were equal
settlement houses
a welfare agency for needy families, combated juvenile delinquency, and assisted recent immigrants in learning the English language and in becoming citizens
tenement
A building in which several families rent rooms or apartments, often with little sanitation or safety
Women's Christian Temperance Union
This organization was dedicated to the idea of the 18th Amendment - the Amendment that banned the manufacture, sale, or transportation of alcohol.
Jim Crow Laws
Laws that separated people of different races in public places in the south
Tuskegee Institute
Black educational institution founded by Booker T. Washington to provide training in agriculture and crafts
political machine
well organized political organization that controls election results by awarding jobs and other favors in exchange for votes
Coxey's Army (1894)
Unemployed individuals marched to Washington, broken up by police
robber baron
Refers to the industrialists or big business owners who gained huge profits by paying their employees extremely low wages and exploiting natural resources
captains of industry
A name given company owners such as Carnegie and Rockefeller by people who believed they steered the economy into prosperity
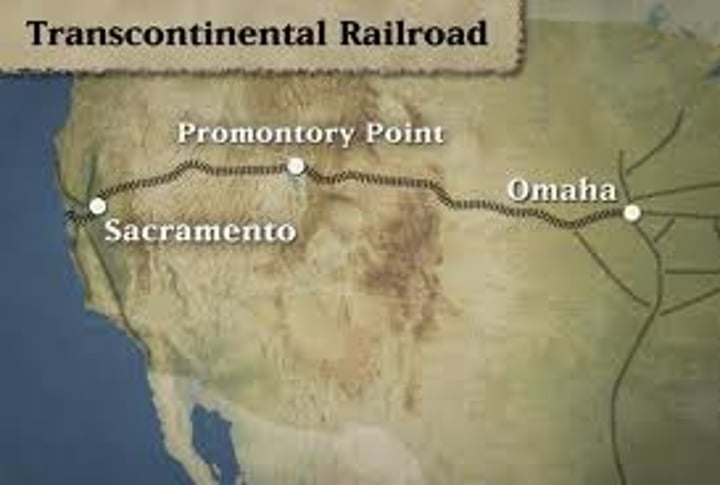
transcontinental railroad
Completed in 1869 at Promontory, Utah, it linked the eastern railroad system with California's railroad system, revolutionizing transportation in the west
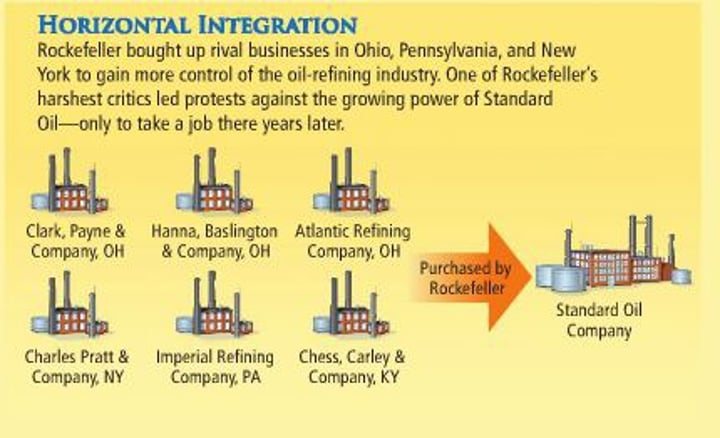
horizontal integration
Type of monopoly where a company buys out all of its competition. Ex. Rockefeller
vertical integration
When a business purchases and owns all businesses in its industry related with the process of its own products. Ex: McDonald's buys its own potato farms and cattle ranches, it's own butchers, it's own processors and packaging, and employs/manages all facets of those businesses within McDonald's corporation.

subsidies
Financial support from the government
Assimilation/Americanization
Adopting the traits of another culture. Often happens over time when one immigrates into a new country.
Sherman Anti-Trust Act
(1890) First federal action against monopolies, it was signed into law by Harrison and was extensively used by Theodore Roosevelt for trust-busting. However, it was initially misused against labor unions
new immigrants
Immigrants who came to the United States during and after the 1880s; most were from southern and eastern Europe.
old immigrants
immigrants who had come to the US before the 1880s from Britain, Germany, Ireland, and Scandenavia, or Northern Europe
Pendleton Civil Service Act (1883)
Reform measure that established the principle of federal employment on the basis of open, competitive exams and created the Civil Service Commission
Standard Oil Company
Owned by John D. Rockefeller. Controlled 90% of the oil refining in America. Will be forced to dissolve because of its stranglehold on the oil industry.
Credit Mobilier Scandal
1872 illegal manipulation of contracts by a construction and finance company associated with the building of the Union Pacific Railroad
Cornelius Vanderbilt
United States financier who accumulated great wealth from railroad and shipping businesses (1794-1877)
Alexander Graham Bell
Invented the telephone
Bessemer Process
A way to manufacture steel quickly and cheaply by blasting hot air through melted iron to quickly remove impurities.
Cyrus Field
American businessman who laid the first telegraph wire across the Atlantic. This cut down the time it took for a message to be sent from Europe to American and vice-versa.
Mail Order Catalogs
Marketing strategy developed in late 1800's and early 1900's. Brought consumer products to rural areas. Example: Sears and Roebuck, Montgomery Ward.
Boss Tweed and Tammany Hall
an American politician most notable for being the "boss" of Tammany Hall, the Democratic Party political machine that played a major role in the politics of 19th century New York City and State.
How the Other Half Lives by Jacob Riis
Exposé of the tenement slums
Purchase of Alaska, 1867
Called "Seward's Folly" and "Seward's Icebox", the purchase gave the U.S. Alaska's resources of fish, timber, oil and gold.
Panic of 1893
Serious economic depression. Began due to railroad companies over-extending themselves, causing bank failures. Was the worst economic collapse in the history of the country until that point, and, some say, as bad as the Great Depression of the 1930s.
Horatio Alger
Popular novelist during the Industrial Revolution who wrote "rags to riches" books praising the values of hard work
The "Gospel of Wealth" 1889
book written by Andrew Carnegie that described the responsibility of the rich to be philanthropists, meaning to use their wealth for the benefit of society by sponsoring the arts, science, libraries, etc. Nicer alternative to harsh philosophy of Social Darwinism, but it was still very elitist and gave power over society to rich.
Knights of Labor
Led by Terence V. Powderly; open-membership policy extending to unskilled, semiskilled, women, African-Americans, immigrants.
American Federation of Labor (AFL)
a national organization of labor unions founded in 1886 by Samuel Gompers
Haymarket Square Riot
A demonstration of striking laborers in Chicago in 1886 that turned violent, killing a dozen people and injuring over a hundred.
Railway Strike of 1877
striking workers responding to wage cuts, caused massive property destruction in several cities
Homestead Strike (1892)
It was one of the most violent strikes in U.S. history. It was against the Homestead Steel Works, which was part of the Carnegie Steel Company, in Pennsylvania in retaliation against wage cuts. The riot was ultimately put down by Pinkerton Police and the state militia, and the violence further damaged the image of unions.
Pullman Strike (1894)
Workers rebelled because the Pullman Palace Car Company cut wages by 1/3 and the American Federation of Labor refused to support the strikers. Military action was needed in order to keep mail delivery on track.
New South
After the Civil War, southerners promoted a new vision for a self-sufficient southern economy built on modern capitalist values, industrial growth, and improved transportation. Henry Grady played an important role.
Bonanza Farms
large farms that came to dominate agricultural life in much of the West in the late 1800s; instead of plots farmed by yeoman farmers, large amounts of machinery were used, and workers were hired laborers, often performing only specific tasks(similar to work in a factory).
Granger Laws
A set of laws designed to address railroad discrimination against small farmers, covering issues like freight rates and railroad rebates.
National Farmers Alliance
A group which worked to educate farmers about their rights with the railroads and banks.
Ocala Platform of 1890
National Farmers Alliance start a new political party, gov ownership of railroads, banks and telegraphs, ban on large land owning companies, graduated income tax, 8 hour work days, immigration restriction become known as Populist Party
Free Silver Movement
Free, unlimited coinage of free silver, which would cause inflation. Supported by farmers, Democrats, the Populist Party, Westerners, and Southerners
Ellis Island
An immigrant receiving station that opened in 1892, where immigrants were given a medical examination and only allowed in if they were healthy
Angel Island
The immigration station on the west coast where Asian immigrants gained admission to the U.S. at San Francisco Bay. Questioning and conditions at Angel Island were much harsher than Ellis Island.
Battle of Wounded Knee (1890)
US soldiers massacred 300 unarmed Native American in 1890. This ended the Indian Wars.
Great Sioux Reservation
located in the Dakota territory; federal governments moved southern Plains tribes and Indians were forced to give up their ancestral land in the exchange by Washington that they'd be left alone and given food, clothes, and supplies
Carlisle Indian School (1879)
Pennsylvania school for Indians funded by the government; children were separated from their tribe and were taught Engilsh and white values/customs. Motto of founder: "Kill the Indian and save the man."
Ghost Dance Movement (1890)
A movement of native Americans involving their spiritual beliefs and the hopes that the buffalo would come back, and the white man would leave.
McKinley Tariff of 1890
raised tariffs to the highest level they had ever been. Big business favored these tariffs because they protected U.S. businesses from foreign competition.
Greenback Labor Party (1878)
Political party devoted to improving the lives of laborers and raising inflation, reaching its high point in 1878 when it polled over a million votes and elected fourteen members of Congress.
Alice Paul
leader of the National Woman's party, campaigned for an Equal Rights Amendment to the Constitution
Margaret Sanger
American leader of the movement to legalize birth control during the early 1900's. Founded the first birth control clinic in the U.S. and the American Birth Control League, which later became Planned Parenthood.