Biotechnology and Genomics Overview ch. 11
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
What is biotechnology?
The use of natural biological systems to create a product or achieve some other end.
How has DNA knowledge impacted gene manipulation?
It has enabled scientists to modify genomes through genetic engineering to improve characteristics, create biotechnology products, or treat diseases.
What is a genetically modified organism (GMO)?
An organism with a modified genome, usually achieved through DNA technology.
What defines a transgenic organism?
A transgenic organism has had a gene from another species inserted into its genome.
What is cloning?
The production of identical copies of an organism, cell, or DNA through asexual means.
What is gene cloning?
The production of many identical copies of a single gene.
What are some uses of gene cloning?
To produce large quantities of a gene's protein product (like insulin), create GMOs, or perform gene therapy to treat diseases.
What is recombinant DNA (rDNA)?
DNA that contains sequences from two or more different sources.
What is a vector in recombinant DNA technology?
A piece of DNA that foreign DNA can be added to, commonly plasmids in bacteria.
What role do restriction enzymes play in recombinant DNA technology?
They cleave vector DNA at precise sequences, acting as molecular scissors.
What is the function of DNA ligase in recombinant DNA technology?
To seal the foreign DNA into the vector DNA after it has been cleaved by restriction enzymes.
What is DNA sequencing?
A procedure that determines the order of nucleotides in a segment of DNA.
How does DNA sequencing contribute to medicine?
It helps identify specific alleles and sequences, facilitating the development of disease treatments.
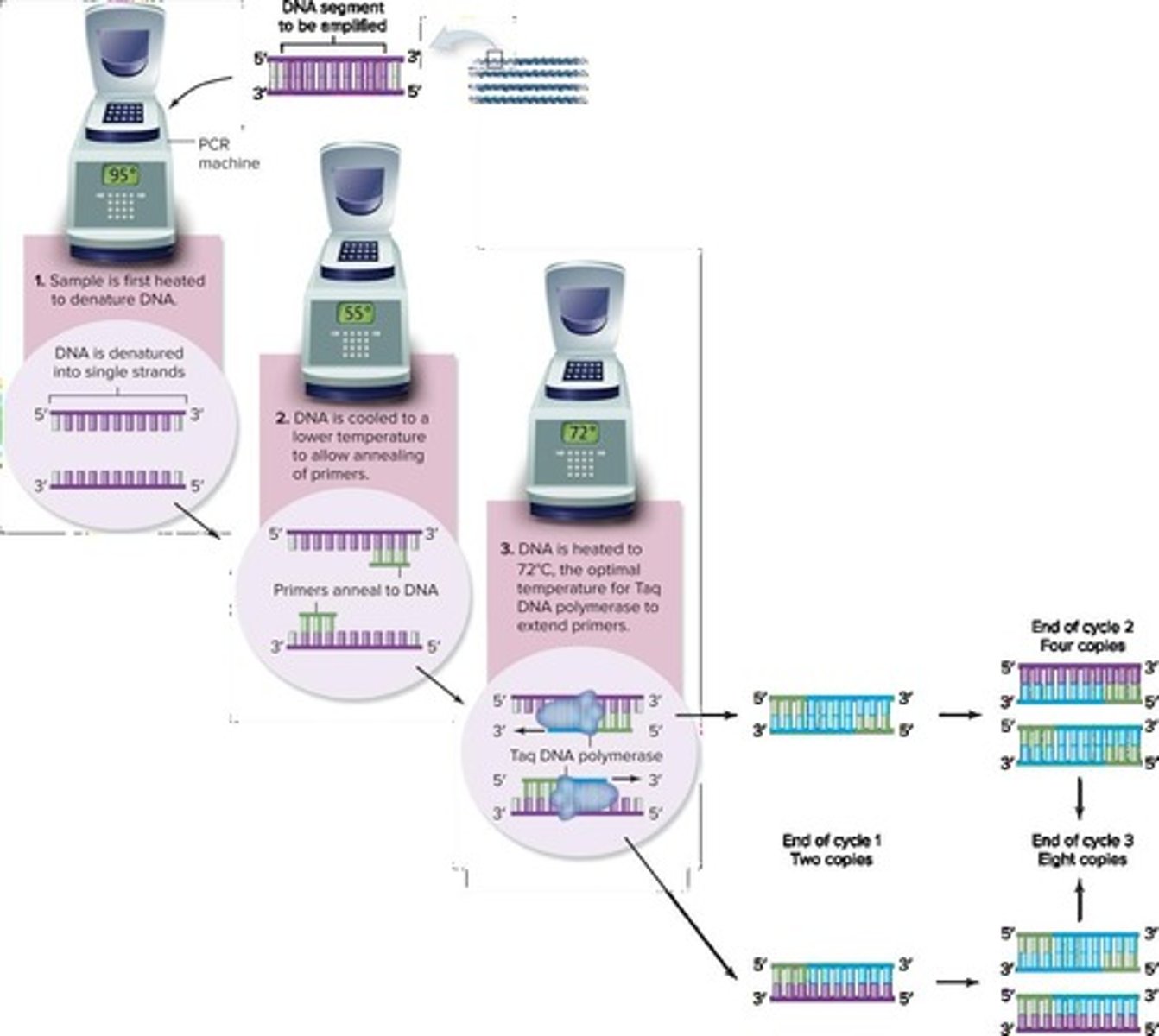
What is the polymerase chain reaction (PCR)?
A technique that creates billions of copies of a specific DNA segment in a test tube.
What is the typical length of the targeted DNA sequence in PCR?
Usually a few hundred bases in length.
What are the three basic steps of PCR?
Denaturation, annealing, and extension, which occur repeatedly for about 35 to 40 cycles.
What is the role of DNA polymerase in PCR?
It synthesizes new DNA strands by adding nucleotides to the targeted DNA sequence.
What is the significance of automated sequencers in DNA sequencing?
They use dyes attached to nucleotides to show the order of nucleotides.
What is the importance of DNA technology in treating genetic disorders?
It allows for the modification of genes to correct or replace defective ones.
What is the relationship between PCR and cloning?
PCR amplifies specific DNA sequences, which can then be cloned for further study or use.
How does DNA technology relate to forensic biology?
It provides methods for identifying individuals based on their unique DNA sequences.
What is the significance of the polymerase chain reaction in research?
It allows for the rapid amplification of DNA, making it easier to study and analyze.
What is denaturation in the context of DNA?
Denaturation is the process where DNA is heated at 95 degrees Celsius to become single-stranded.
What occurs during the annealing step of PCR?
During annealing, which occurs at 50 to 60 degrees Celsius, a primer binds to the end of each DNA strand.
At what temperature does the extension phase of PCR occur, and what happens during this phase?
The extension phase occurs at 72 degrees Celsius, where a unique DNA polymerase adds complementary bases to each of the single DNA strands, creating double-stranded DNA.
What was the previous method of DNA analysis before STR profiling?
The previous method involved treating the entire genome with restriction enzymes and separating fragments by gel electrophoresis, resulting in a distinctive pattern of bands known as a DNA fingerprint.
What are short tandem repeats (STRs) in DNA profiling?
STRs are short sequences of DNA bases that recur several times, and the number of repeats at a specific location varies among individuals.
How does PCR contribute to STR profiling?
PCR amplifies fragments in samples, which are of different lengths due to varying numbers of STR repeats, enhancing the distinctiveness of results for each person.
What is the role of fluorescent labeling in STR profiling?
Fluorescent labeling allows PCR products to be run through an automated DNA sequencer, where a laser detects and records the lengths of DNA fragments.
What are some applications of STR profiling?
STR profiling can be used to identify samples at crime scenes, detect genetic disorders, and identify relatives or victims.
What is genome editing?
Genome editing is a DNA technology that targets specific sequences in DNA for removal or replacement.
What is CRISPR and why is it significant?
CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) is the most widely used method for genome editing, allowing precise modifications to DNA.
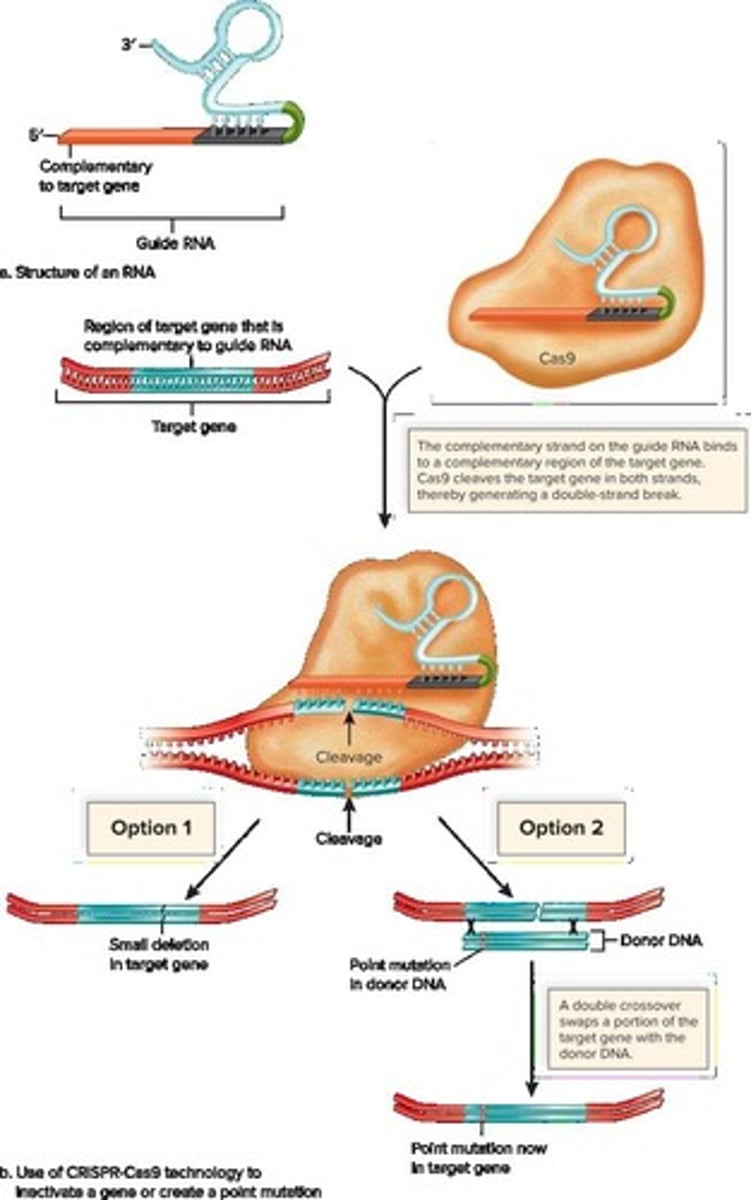
How does the CRISPR system function in prokaryotes?
In prokaryotes, CRISPR acts as an immune defense against invading viruses, using an endonuclease enzyme called Cas9 to break viral DNA.
What is the function of the Cas9 enzyme in CRISPR?
Cas9 identifies specific nucleotide sequences in genomic DNA, breaks both DNA strands, and can insert new nucleotides at specific locations.
What are some applications of CRISPR technology?
CRISPR applications include treatments for diseases like sickle-cell disease and cancer, and the development of rapid tests for viruses such as SARS-CoV-2.
What defines transgenic organisms?
Transgenic organisms are those that have had a foreign gene inserted into their genome.
What is the significance of using multiple STR loci in profiling?
Using more STR loci increases the confidence in obtaining distinctive results for each individual.
What happens to DNA fragments during gel electrophoresis?
During gel electrophoresis, smaller DNA fragments move faster than larger ones, creating a pattern of bands.
What is the purpose of using guide RNA in the CRISPR system?
Guide RNA base-pairs with the genomic DNA sequence to direct Cas9 to the specific location for editing.
How can scientists study a gene's role using CRISPR?
Scientists can study a gene's role in the cell after Cas9 inactivates the gene by breaking its DNA strands.
What is the relationship between the number of STRs at a locus and DNA fragment length?
The greater the number of STRs at a locus, the longer the resulting DNA fragment will be.
What advancements have been made in DNA analysis over time?
DNA analysis has evolved from using restriction enzymes and gel electrophoresis to employing STR profiling and PCR techniques.
What is the significance of fluorescently labeled PCR products?
Fluorescently labeled PCR products allow for automated sequencing and accurate detection of DNA fragment lengths.
What are transgenic organisms commonly referred to as?
Genetically modified organisms (GMOs)
What products do transgenic organisms produce?
Biotechnology products
How are transgenic bacteria produced?
By recombinant DNA technology, grown in bioreactors.
What biotechnology products are produced by transgenic bacteria?
Insulin, human growth hormone, tPA (tissue plasminogen activator), and hepatitis B vaccine.
What is one application of transgenic bacteria in agriculture?
Development of frost-resistant strawberries by altering bacteria that live on plants.
How have bacteria been engineered to protect corn plants?
Bacteria colonizing corn roots have been engineered to produce toxins that deter root-damaging insects.
What ability can transgenic bacteria be selected for?
The ability to degrade specific substances, such as oil or sulfur from coal.
How can foreign genes be introduced into plants?
By exposing immature plant embryos or protoplasts to an electric current in a liquid containing foreign DNA.
What is a pomato?
A genetically modified plant that produces potatoes below ground and tomatoes above ground.
What is an example of pest resistance in genetically modified crops?
Pest resistance in cotton, corn, and potato strains.
What is gene microinjection in animals?
A method to insert genes into the eggs of animals by hand or vortex mixing.
What is vortex mixing?
A technique where eggs are placed in an agitator with DNA and silicon-carbide needles to create tiny holes for DNA entry.
What is the purpose of inserting the gene for bovine growth hormone (BGH) into animals?
To produce larger fish, cows, pigs, rabbits, and sheep.
What is the AquAdvantage salmon?
A genetically modified salmon that grows three times faster than wild salmon and requires less food.
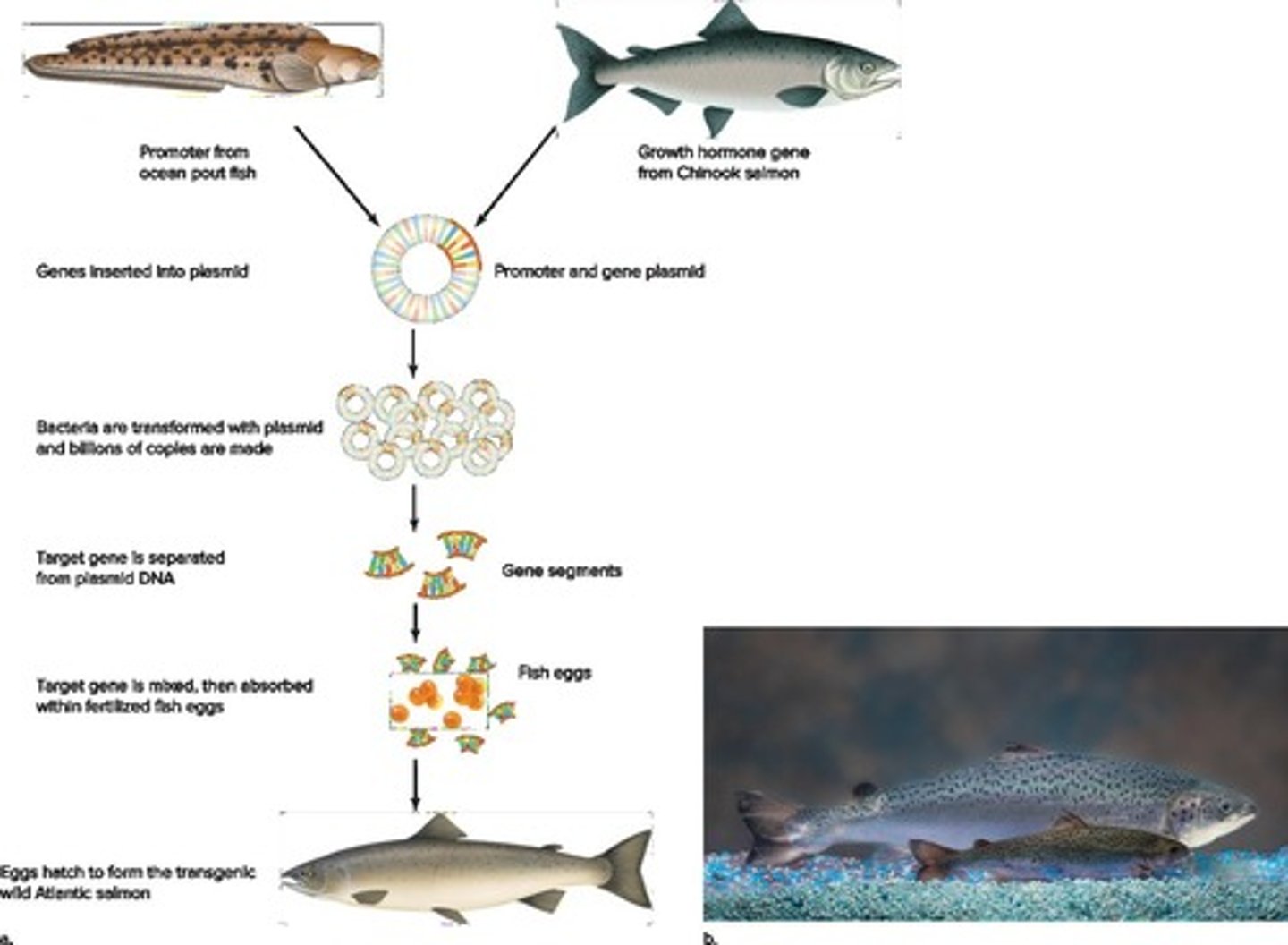
What genes are incorporated into the AquAdvantage salmon?
The growth hormone gene from Chinook salmon and a gene promoter from Ocean Pout.
What is gene pharming?
The use of transgenic farm animals to produce pharmaceuticals.
What types of proteins can transgenic animals produce?
Therapeutic and diagnostic proteins.
What happens when eggs are fertilized after microinjection of foreign genes?
Transgenic offspring are produced.
What is the role of the electric current in introducing foreign DNA into plant cells?
It forms self-sealing pores that allow the desired DNA to enter.
What is the significance of using bacterial plasmids in producing gene products?
Gene products are grown on bacterial plasmids, isolated, and then mixed with fertilized eggs.
What are the benefits of genetically modifying plants?
Enhanced pest resistance and the ability to produce human proteins.
What are therapeutic and diagnostic proteins in transgenic animals used for?
They are used for the treatment of cystic fibrosis, cancer, and blood diseases.
What is the significance of Dolly the sheep in cloning?
Dolly was the first cloned sheep, produced in 1997, marking a significant achievement in cloning technology.
What is the success rate of cloning transgenic animals?
The success rate is low, with only 1 or 2 viable embryos produced per 100 attempts.
Describe the cloning process of transgenic animals.
Donor eggs are microinjected with nuclei from a transgenic animal and then coaxed to develop in vitro before being implanted into host females.
What is gene therapy?
Gene therapy involves inserting genetic material into human cells to treat genetic disorders and illnesses like cardiovascular disease and cancer.
What methods are used for gene transfer in gene therapy?
Methods include using viruses modified to be safe, liposomes, or direct injection of the gene into specific body regions.
What is the ex vivo gene therapy method for treating SCID?
It involves removing bone marrow stem cells, infecting them with a virus carrying the normal ADA gene, and returning them to the patient.
How does ex vivo gene therapy treat familial hypercholesterolemia?
A portion of the liver is surgically excised, infected with a virus containing the normal gene for the cholesterol receptor, and then returned to the patient.
What gene is lacking in cystic fibrosis patients, and what is the treatment method?
Cystic fibrosis patients lack a gene coding for chloride transporter protein; treatment involves spraying the gene into the nose or delivering it via an adenovirus vector or liposomes.
How is in vivo gene therapy used in cancer treatment?
It is used to make healthy cells more tolerant of chemotherapy and to make tumor cells more sensitive to chemotherapy.
What is the role of the tumor suppressor gene p53 in cancer therapy?
The goal is to find a way to introduce the tumor suppressor gene p53 into cancer cells to enhance treatment efficacy.
What is the primary source of proteins harvested from transgenic animals?
Proteins are harvested from the milk of transgenic animals.
What are the potential applications of gene therapy?
Gene therapy can be applied to treat genetic disorders, cardiovascular diseases, and certain types of cancer.
What is the role of liposomes in gene therapy?
Liposomes are microscopic globules of lipids used to introduce normal genes into the body.
What challenges are associated with in vivo gene therapy for cystic fibrosis?
There has been limited success in effectively delivering the gene needed to cure cystic fibrosis.
What is the purpose of using genetically modified viruses in gene therapy?
They are used to safely introduce normal genes into the body.
What is the significance of the ADA enzyme in treating SCID?
The ADA enzyme is crucial for the maturation of T and B cells, and its absence leads to severe immunodeficiency.
What is the primary goal of gene therapy for patients with familial hypercholesterolemia?
To restore the function of the cholesterol receptor protein to lower blood cholesterol levels.
How does gene therapy aim to improve the quality of life for cancer patients?
By enhancing the tolerance of healthy cells to chemotherapy and targeting tumor cells more effectively.
What is the main challenge in cloning transgenic animals?
The cloning process is difficult and has a very low success rate.
What is the first step in the cloning process of transgenic animals?
Microinjecting donor eggs with nuclei from a transgenic animal.
What is the outcome for female clones of transgenic animals?
They produce the same product in their milk as the original transgenic animal.