4.3 - Gas Exchange
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Gas Exchange
the process of obtaining oxygen from the environment and releasing carbon dioxide.
Process of Gas Exchange
1. Ventilation brings in oxygen-rich air and removes carbon dioxide-rich air, keeping a high oxygen and low carbon dioxide concentration gradient in the alveoli.
2. Oxygen dissolves in the moisture lining of the alveoli and diffuses into the blood, where it binds to haemoglobin in erythrocytes, forming oxyhaemoglobin.
3. Carbon dioxide in the blood diffuses into the alveoli and is breathed out.
4. Blood flow constantly brings in low-oxygenated and high-carbon dioxide blood, which maintains the concentration gradient between the blood and the alveoli.
In the alveoli are active surfactants, which help with breaking the water tensions to enable O2 to dissolve.
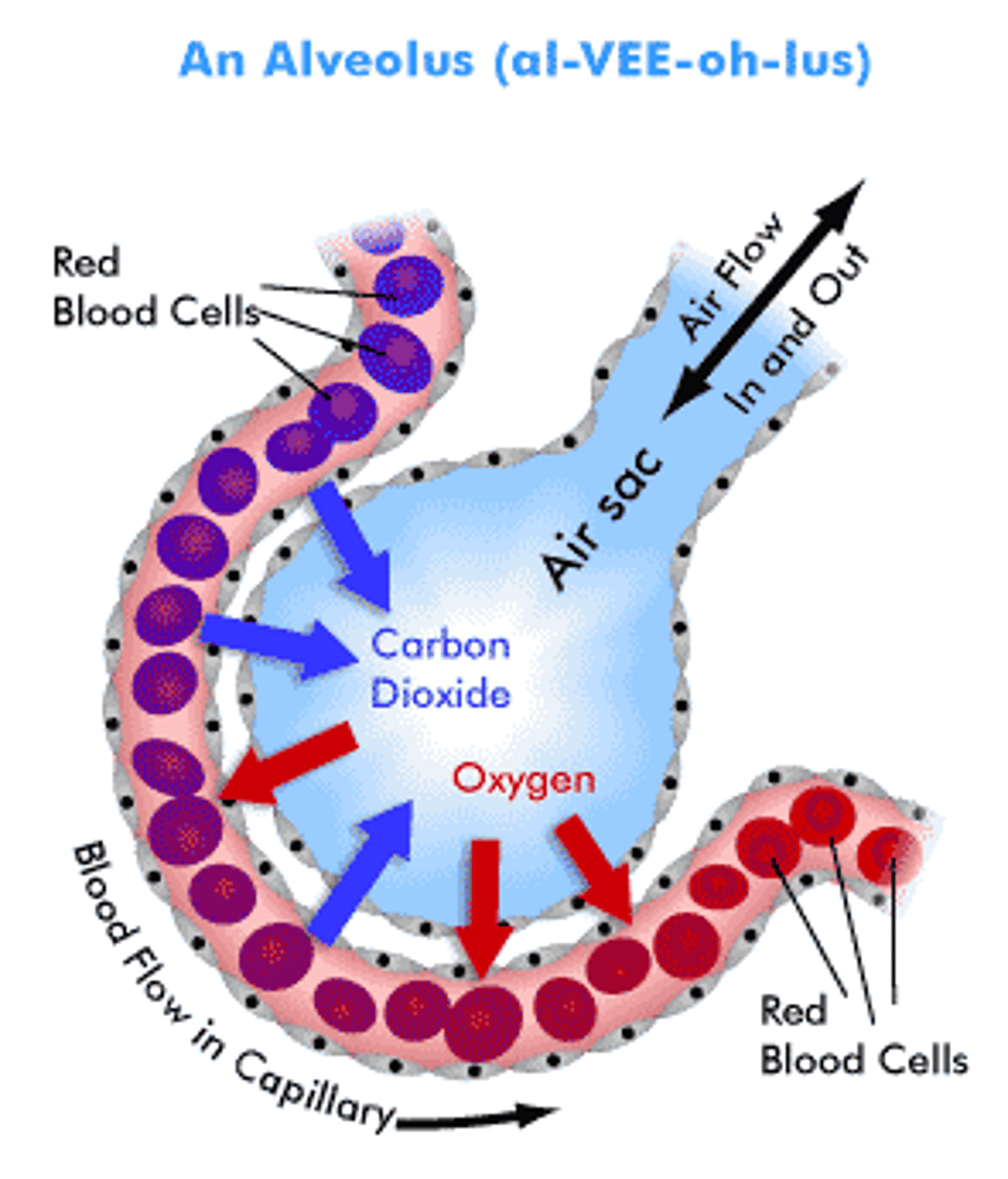
Structural Features for efficient Gas Exchange:
- Alveolus Wall
- 1 Cell thick -> Gas molecules have a short distance to diffuse.
- Exchange is faster/more efficient.
Structural Features for efficient Gas Exchange:
- Blood Supply
- A huge network of capillaries closely surrounds each alveolus.
- Allows for a continuous flow of blood to maintain the concentration gradient.
- Delivers blood high in CO2
- Removes blood high in O2
Structural Features for efficient Gas Exchange:
- Constant Ventiliation
- Air is constantly replaced to maintain concentration gradient.
- Delivers air high in O2
- Removes air high in CO2
Structural Features for efficient Gas Exchange:
- Deep inside the body
- Reduces the loss of essential fluid by evaporation.
- Gas must dissolve before they can diffuse into the body.
Structural Features for efficient Gas Exchange:
- Surface Area
- Huge internal SA of alveoli for gas exchange to occur
- More sites for exchange -> Exchange becomes faster.
External respiration
Occurs in the lungs between the alveoli and blood.
(Pulmonary Circuit)
Internal Respiration
Occurs between the blood and tissues
(Systemic Circuit)