3 • Quantity of Heat
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What factors does the heat gained or lost by a body depend on?
Mass
Specific Heat Capacity
Temperature Change
Define Heat Capacity (C)
The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of a body by 1K
Define the SI Unit for Heat Capacity
JK-1
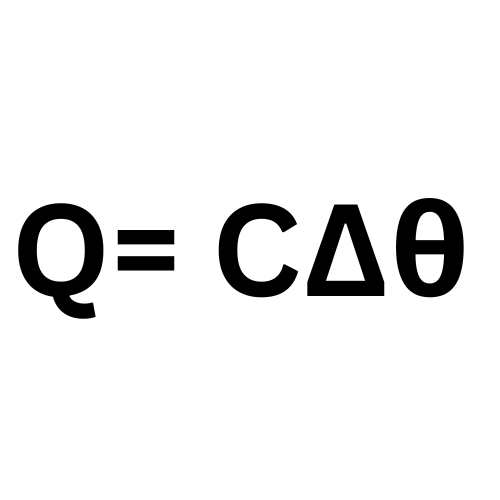
Label This Formula
Heat Capacity
Q - Heat Energy
C - Heat Capacity
Temperature Change
Define Specific Heat Capacity (c)
The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1kg of a substance by 1K
Define the SI Unit for Specific Heat Capacity
J Kg-1 K-1
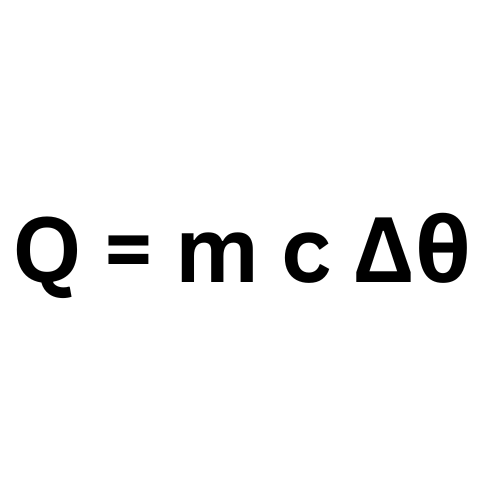
Label This Formula
Specific Heat Capacity
Q - Heat Energy
m - mass
c - specific heat capacity
Temperature change
Name a use of specific heat capacity
Storage Heaters
Demonstrate the process of Storage Heaters
High SHC
Cheap Night time electricity heats blocks
Releases heat during the day
Define Latent Heat (L)
The heat required to change the state of a body without a rise in temperature
Define the SI Unit of Latent Heat
Joule
J
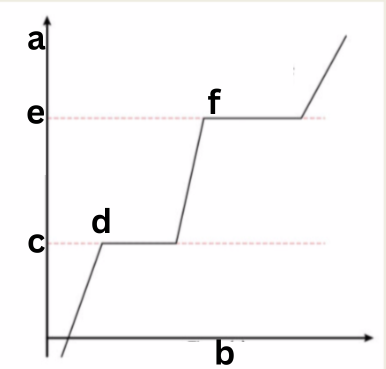
Label This Diagram
Latent Heat
a - Temperature (K)
b - Time (s)
c - melting point
d - latent heat of fusion
e - boiling point
f - latent heat of vaporisation
Define Specific Latent Heat (L)
The heat required to change the state of 1kg of a substance
Define the SI Unit for Specific Latent Heat
J kg-1
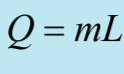
Label This Formula
Specific Latent Heat
Q - Heat Change
M - Mass
L - specific Latent Heat
Name the types of Specific Latent Heat
Specific Latent Heat of Fusion
Specific Latent Heat of Vaporisation
Define Specific Latent Heat of Fusion
The heat required to change kg of a solid to 1kg of a liquid at its melting point without a rise in temperature
Define Specific Latent Heat of Vaporisation
The heat required to change kg of a liquid to 1kg of vapour at its melting point without a rise in temperature
Name 2 examples of Latent Heat
Perspiration
Heat Pump
Demonstrate the process of Perspiration
Water evaporates from the surface of our skin
Removes latent heat and cools us down
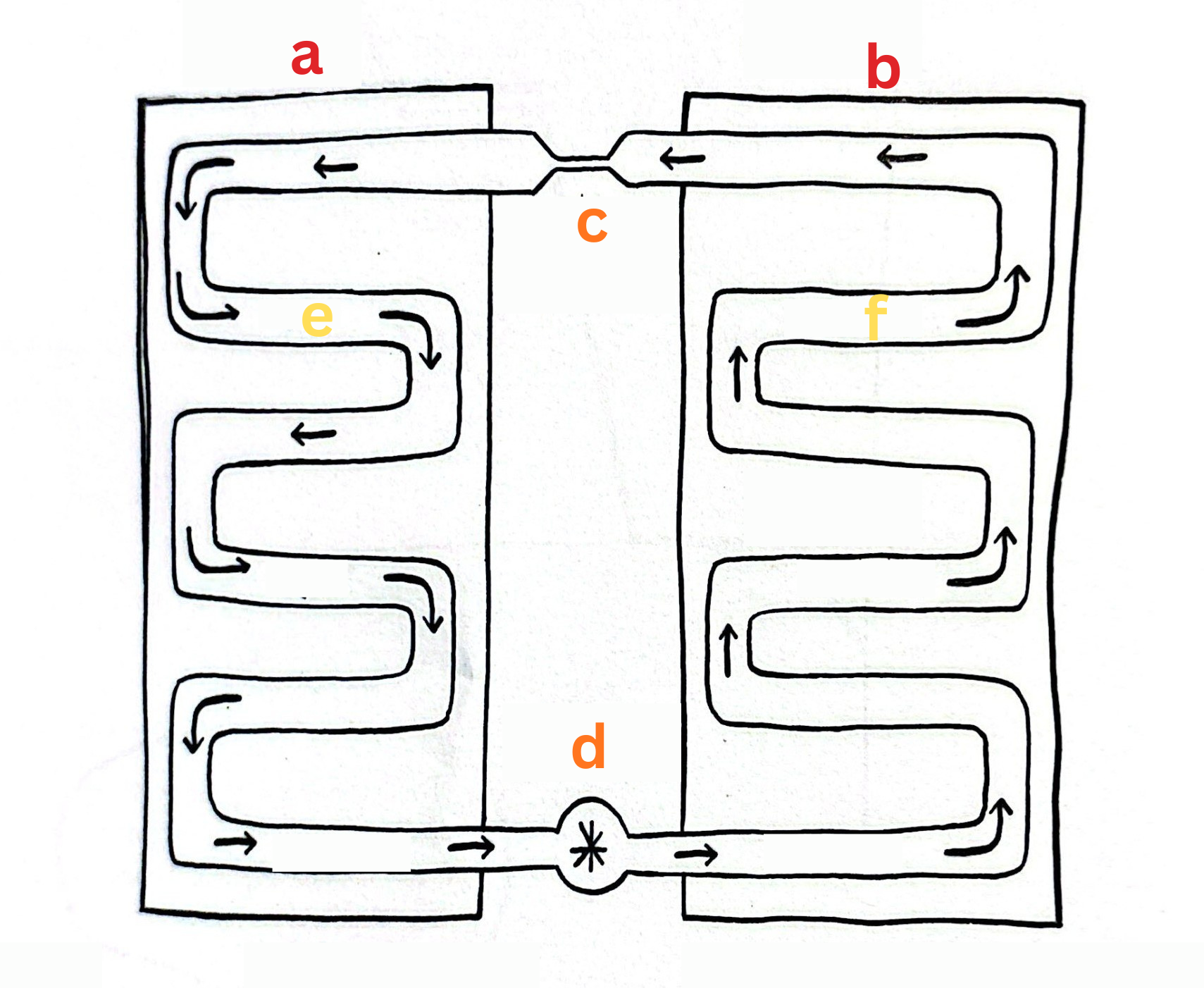
Label This Diagram
The Heat Pump
a - Cold
b - Hot
c - Expansion Valve
d - Compressor
e - Gas
f - Liquid
Demonstrate how a heat pump works
Heat taken in by liquid evaporating
Heat taken out by vapour condensing