Interpreting EKG
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Sinus Rhythm

a normal heart rhythm originating from the sinoatrial node, characterized by a rate of 60 to 100 beats per minute and a regular rhythm.
Sinus Tachycardia
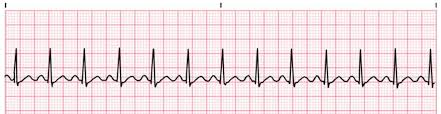
a condition where the heart rate exceeds 100 beats per minute while still maintaining a regular rhythm originating from the sinoatrial node.
Sinus Bradycardia
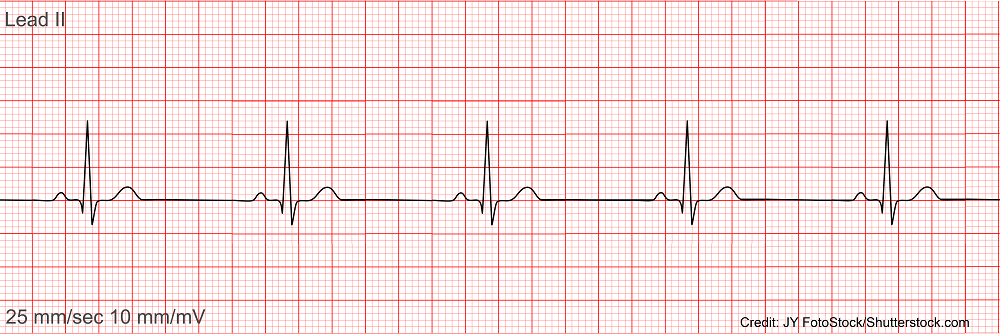
A slower than normal heart rate, typically defined as fewer than 60 beats per minute, originating from the sinus node.
Atrial Fibrillation
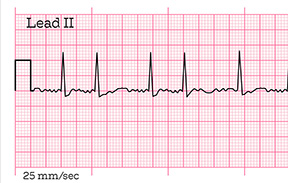
A common heart rhythm disorder characterized by irregular and often rapid heartbeat, leading to poor blood flow.
Atrial Flutter
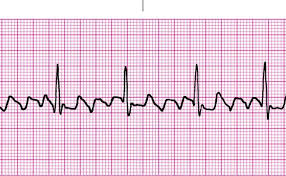
A type of abnormal heart rhythm characterized by rapid, organized contractions of the atria, often seen on an EKG as a distinct sawtooth pattern.
Ventricular fibrillation
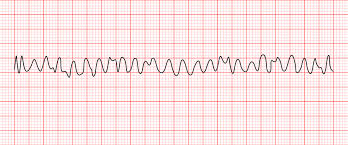
a life-threatening heart arrhythmia characterized by uncoordinated electrical activity in the ventricles, leading to ineffective pumping and requiring immediate medical intervention.
Ventricular tachycardia
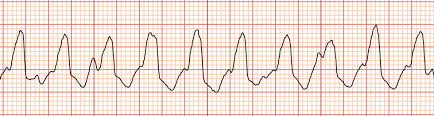
a fast heart rhythm originating from the ventricles, often resulting in reduced blood flow and potential collapse.
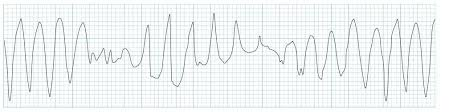
Torsades de Pointes
First Degree Heart Block
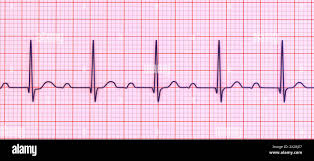
A type of atrioventricular block where there is a delay in the conduction through the AV node, leading to a prolonged PR interval on an EKG.
Second Degree Type 1 Heart Block
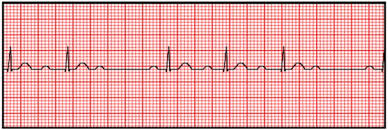
A condition characterized by progressively lengthening PR intervals leading to a dropped QRS complex. It is often benign and associated with increased vagal tone.
Third Degree Heart block
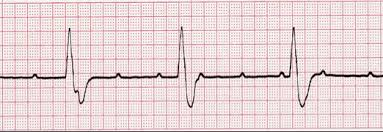
a complete block of electrical conduction between the atria and ventricles, resulting in dissociation of atrial and ventricular activities.
Asystole
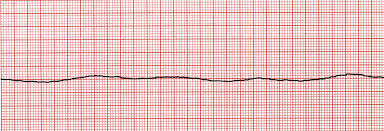
A state of no electrical activity in the heart, resulting in no heartbeat or blood flow. It is often referred to as flatline on an EKG.
Myocardial Infarction
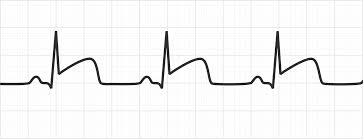
A condition caused by the blockage of blood flow to the heart muscle, often resulting in chest pain and damage to the heart tissue.
Idioventricular Rhythm
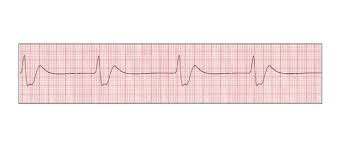
A cardiac rhythm that originates from the ventricles due to a failure of the higher pacemaker, characterized by wide QRS complexes and absence of P waves.