Cognitive Neuro quiz 5: touch and movement
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
HAPTICS
perception of fine touch and pressure
primary somatosensory cortex
the main sensory receptive area for touch
Most sensitive to touch:
• Finger tips • Face • Bottoms of the feet
Least sensitive to touch:
Legs • Back • Arms
more receptors means
more sensitive
Larger receptive fields
decreased sensitivity
More cortical area =
increased sensitivity
smaller areas of the body
take up more area in the brain
Nocioception
perception of pain and temperature
free nerve endings
respond to pain and temperature
what neurons carry fine touch and pressure information
dorsal root ganglion neurons
somatasory pathways
process stimuli received from myelinated axons within the skin, muscles, and tendons
fine touch and pressure axons ascend in the
ipsilateral spinal cord forming the dorsal spinothalamic tract
somatosensory neuron
Neuron that carries information from the skin to the spinal cord
afferent neurons
neurons that take information from the senses to the brain
efferent neurons
neurons that take information from the brain to the rest of the body
fine touch and pressure signals enter spinal cord
at the same side the touch was, all the way into the brain
dorsal spinothalamic tract
Pathway that carries fine-touch and proprioception
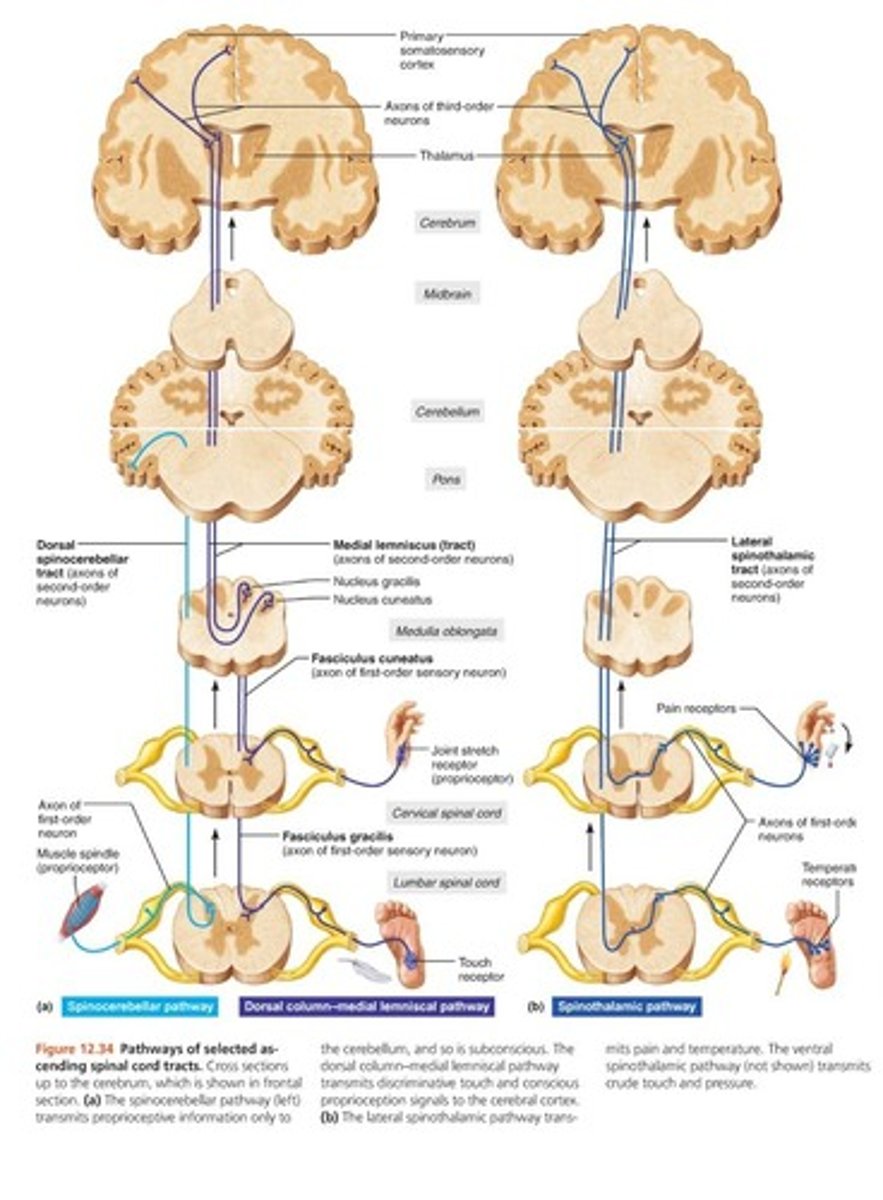
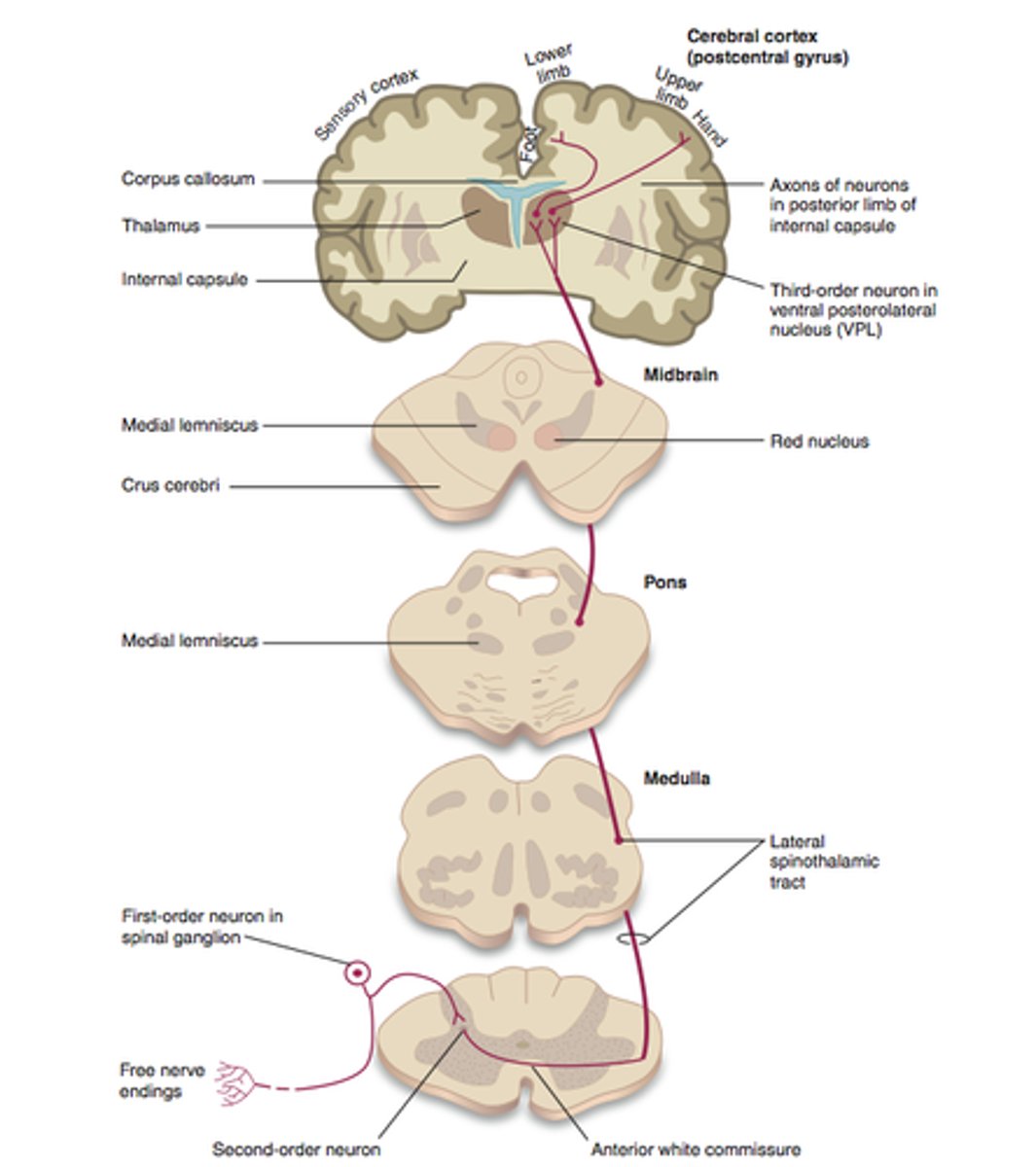
ventral spinothalamic tract
spinal cord to the thalamus that carries information about pain and temperature.
Unilateral damage to the spinal cord will result in the loss of ______ on the same side of the body and loss of ______ on the opposite side of the body below the site of the damage.
touch and proprioception; pain and temperature
Information from the ______ crosses to the other side of the brain in the brainstem, whereas the ______ crosses to the other side of the brain in the spinal cord.
dorsal spinothalamic tract; ventral spinothalamic tract
The ______ controls limbs and digits, whereas the ______ controls mainly trunk muscles.
lateral corticospinal tract; ventral corticospinal tract
Which part of the brain is responsible for planning and initiating movements?
frontal lobe
Axons that carry information about pain and temperature form the
ventral spinothalamic tract.
The haptic and proprioceptive axons form the:
dorsal spinothalamic tract.
Homunculus
representation of body parts in the cortex
secondary somatosensory cortex
recieves sensory info from the primary somatosensory cortex
The dorsal spinothalamic tract ascends on the ipsilateral side of the spine.
true
the ventral spinothalamic tract ascends
on the contralateral side (crosses over)
pain and temp
Pain and temperature receptors use the same pathways as touch.
false
Sensitive areas on the skin receive more area
in the somatosensory cortex
how do you drink coffee? 1-8
1. visual information is used to locate
2. frontal lobe motor area plans reach n command
3. spinal cord carries info 2 hand
4. motor neurons carry message to muscles
5. sensory receptors on fingers send message to sensory cortex saying cups been grasped
6. spinal cord carries sensory info 2 brain
7. basil ganglia judge grasp and cerebellum corrects movement errors
8. sensory cortex recieves message that cups been grasped
cervical division
breathing and heart rate;
head, neck, shoulder, hand/fingers, wrist and elbow movements
Thoracic division:
trunk stability, temperature regulation
lumbar nerves
: hip movement, knee extension, foot motion
Sacral nerves:
bowels, bladder, and sexual organs
Motor neurons in the spinal cord have their cell bodies in the dorsal root.
false: motor neurons in the spinal cord have cell bodies in the ventral
Cervical nerves aid in control of breathing and heart rate
true
Lumbar nerves control the muscles of the torso and temperature regulation of the trunk
false: thoracic not lumbar
Some reflexes are the result of communication between sensory and motor neurons in the spinal cord.
true
Cerebellum/ role
coordinating and learning skilled movements; and involved in balance
timing of movements
and maintains movement accuracy
folded more densely than cerebrum
How hard would each of these tasks be with an injured cerebellum
1) Running in a race or marathon.
2) Talking and listening to a friend.
3) Playing baseball in the park.
4) Swimming or diving in a pool.
5) Singing a song out loud.
1. very
2. low to moderate
3. very
4. very
5. low to moderate
basil ganglia/ role
voluntary movements of the limbs and body
Generates the force required for a movement
Initiates movement at the appropriate time and place
basil ganglia parts
• Globus pallidus • Substantia nigra • Subthalamic nucleus
Caudate nucleus, putamen, & nucleus accumbens (striatum)
when direct pathway is activated
the caudate/putamen inhibit the GPi which disinhibits the thalamus so it can excite the cortex
increases movement
when the indirect pathway is activated
caudate/ putamen inhibits the GPe which disinhibits the subthalamic nucleus so that it can excite the GPi which inhibits thalamus/ cortex
decreases movement
If the GPi was excited, would movement increase or decrease? Why?
movement would decrease
If the GPi was inhibited, would movement increase or decrease? Why?
increase movement
prefrontal cortex
plans movements
premotor cortex
organizes movement sequences
motor cortex
produces specific movements/ executes
damage to the premotor cortex
affects the ability to coordinate motor sequences
MIRROR NEURON
cell in the primate premotor cortex that fires when an individual observes a specific action taken by another individual
topographic organization
neural spatial representation of the body
CORTICOSPINAL TRACTS
nerve fibers connecting the cerebral cortex to the spinal cord
How will your cerebellum help you improve at darts?
it makes the necessary adjustments to keep movement accurate.
When the cortex sends information to the spine to carry out an intended movement (along corticospinal tracts), a copy is sent to the cerebellum through the inferior olive.
Sensory receptors in the body and muscles records movement and sends information back to the cerebellum through the spinocerebellar tract.
Now the cerebellum has information about what you intended to do and what actually happened. It calculates the error and then informs the cortex on how to correct the movement.
Describe how the nervous system produces the movement sequence required to catch a baseball.
visual system tracks the ball, sending information to the motor and somatosensory cortices allowing them to position the body in response to the balls trajectory
The prefrontal cortex selects the goal, (catching) and relays it to the premotor cortex where the appropriate motor sequences are chosen to achieve the goal. The premotor cortex communicates this to the primary motor cortex which directs muscles
info from cortical areas will be sent to the basal ganglia, which determines force and initiation of the movements. As the motor sequences unfold, there will be moments when movement needs to increase/decrease via activation of the direct pathway of the basal ganglia.
motor commands travel via spinal cord to innervate the muscles of the body which will execute the plans. Motor commands for the trunk will be passed along the ventral corticospinal tract and the commands for the limbs will be passed along the lateral corticospinal tract.
Another component of this will be feedback from the haptic and proprioception pathways, indicating the success or failure of the motor sequence so that corrections can be made.
In the direct pathway of the basal ganglia, the caudate/putamen inhibit the______________________ , which disinhibits the ______________________ , allowing it to excite the cortex. This will ______________________ movement.
GPi; thalamus; increase;
In the indirect pathway of the basal ganglia, the caudate/putamen inhibit the(D)______________________ , which disinhibits the (E)______________________,allowing it to excite the GPi. This will (F)______________________ movement.
(D) GPe; (E) subthalamic nucleus; (F) decrease