biostats - unit 1
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
console
stat output and successful code show up here
script (.rmd)
type codes here
viewer
graphs and help files show up here
environment
what I told R to plan to use today (objects, variables, models, etc. are stored here)
vector
set of numbers
creating a vector with 5 numbers: c(96, 95, 99, 97, 98, 96)
assign to a variable by: tempF ← c(96, 95, 99, 97, 98, 96)
goal of biostatistics
focuses on collecting, describing, and drawing conclusions from data to learn more about the world
uses estimation to infer an unknown of a population using sample data
data
cumulative measurements of individual biological entities
population
all individuals or observations in the world (group we are typing to gain info about)
sample
subset of measurements we collect and analyze to learn about the population (what we measure to draw inferences)
parameters
describe populations (true value)
fixed and constant
represented by mu
estimate/statistic
taken from samples
random, change with each sample
represented by capital Y with a bar on top
descriptive statistics
implies that statistics is an estimate of parameter
weighted mean
assigns different importance (weights) to each data points so it reflects relative importance in overall calculation
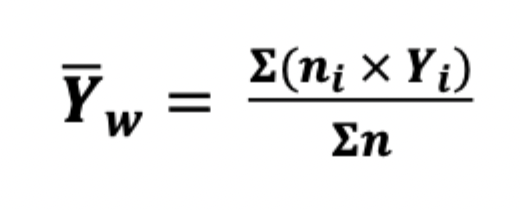
statistics of locatoin/central tendency
mean, median, mode
mean vs median
mean = mathematical center of gravity, median = average individual (middle measurement)
statistics of dispersion
range, IQR, variance, standard deviation, coefficient of variation
variance
expected squared difference between observations and the mean
estimate = s²
denominator is n-1 for degrees of freedom
parameter = lowercase sigma²
denominator is just N

standard deviation
measure of dispersion that weighs each item by distance from mean
estimate = s (sqrt of variance)
parameter = lowercase sigma (sqrt of variance)
coefficient of variation
standard deviation expressed as percent of mean
CV = sample standard deviation (s) / Y (sample mean) x 100
when to use variance
understand how much values in a dataset vary from each other
when to use standard deviation
understand how data points typically deviate from the mean
when to use coefficient of variation
used to compare variation between two datasets
inference
requires independent and random sampling
sampling bias
systematic difference between estimates and parameters
samples aren’t representative of population
sampling error
undirected deviation of estimates away from parameters
influenced by chance and differs among samples from the same population
decreases with increasing sampling size
sampling distribution
probability distribution of all possible sample means
random process
sample from a population provides an estimate of the parameter
sampling error
difference between parameter and estimate
key features of sampling distribution
normally distributed
mean of sampling distribution = true mean of population
spread depends on sample size used for estimate
as sampling size increases, parameter estimates become more precise and spread of sampling distribution decreases
standard error
standard deviation of an estimate’s sampling distribution

key features of standard error
decreases with increasing sample size
tells us how close sample mean is to true mean (population)
tells us how unusual a sample is
standard error vs standard deviation
SD describes how individuals in a sample differ from sample mean
SE describes how far sample mean is from true mean
95% CI
range of data around potential sample mean values in our sampling distribution for which we are 95% sure contains the true population parameter (2 * SE)
addition rule for probability
if two events are mutually exclusive, then P[A or B] = Pr[A] + Pr[B]
multiplication rule for probability
if two events are independent, then P[A and B] = Pr[A] x Pr[B]
Bayes Theorem
use for conditional probability
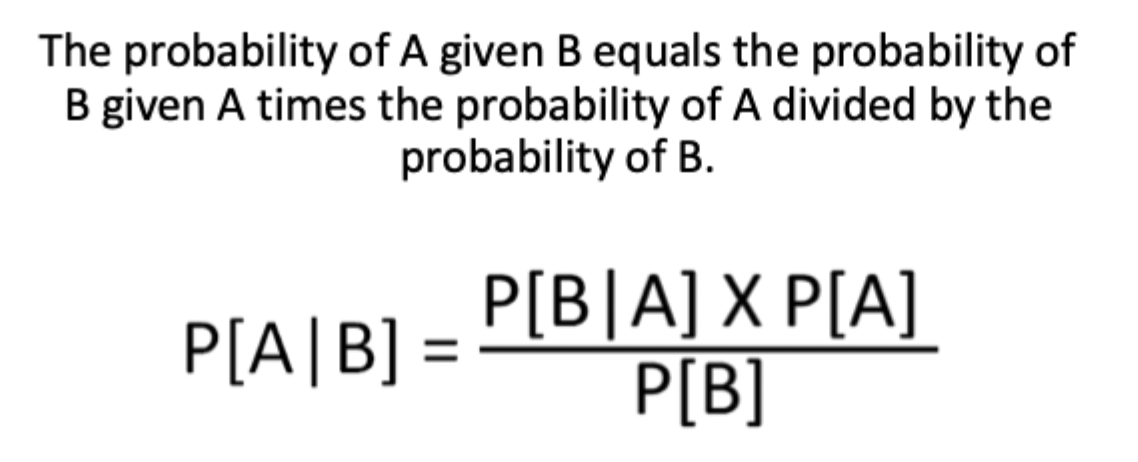
variable
any characteristic that varies from one biological entity to another
categorical variables
qualitative characteristics of individuals that do not have a numerical magnitude
nominal = unordered descriptions
ordinal = ordered descriptions (1-5 how are you feeling, etc.)
binary = 2 mutually exclusive outcomes (yes or no)
numerical variables
quantitative measurements of individuals that have a numerical magnitude
continuous = measured data, can have infinite values within possible range (decimals, fractions, etc.)
discrete = observations can only exist at limited values, often counts (whole numbers)
tidy data
standard way of mapping the meaning of a dataset to its structure
variable = column
observation = row
cell = single measurement
visualizing one variable categorical data
frequency table = counts of the number of occurrences of each category
bar graph = frequency distributions of categorical data
one variable numerical data
goal = measure center, spread, and shape of data
frequency table = counts the number of occurrences within set bins
histogram = displays the frequency distributions of numerical data
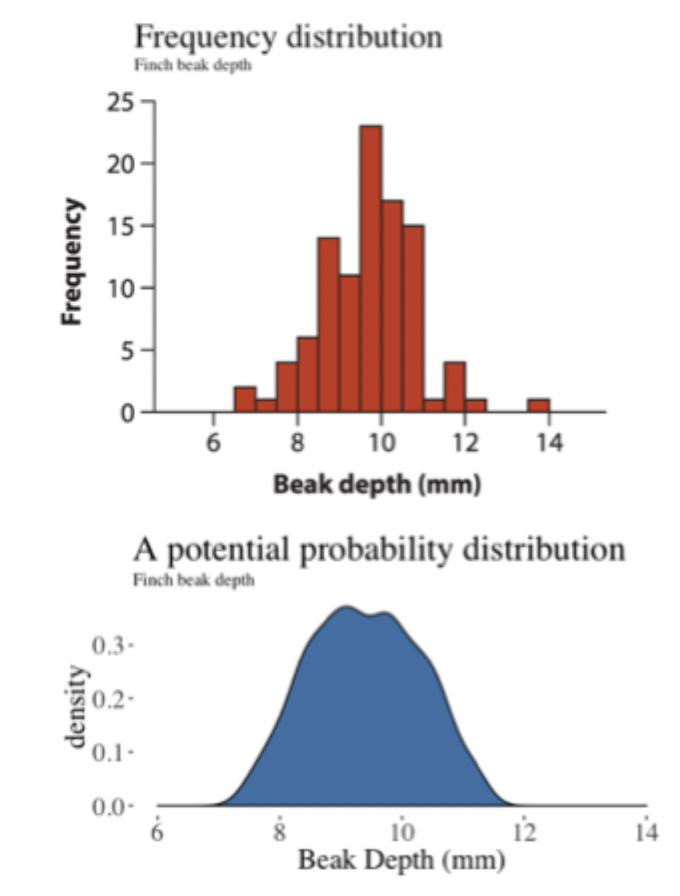
frequency distribution vs probability distribution
frequency distribution = describes the number of times a value occurs in a sample
probability distribution = describes the proportion of the population with a value
when is an estimate considered to be unbiased
when across infinite repeated samples, the average of the estimates equals the true parameter value