Exam 3
1/312
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
313 Terms
H+K+-ATPase pump
enzyme known as the proton pumo
exchange is stimulated by secondary messengers (Ca++ and cAMP) from GPCR activation_
basal, stimulated
inhibitors of the proton pump will block both ____ scretion
PPI backbone
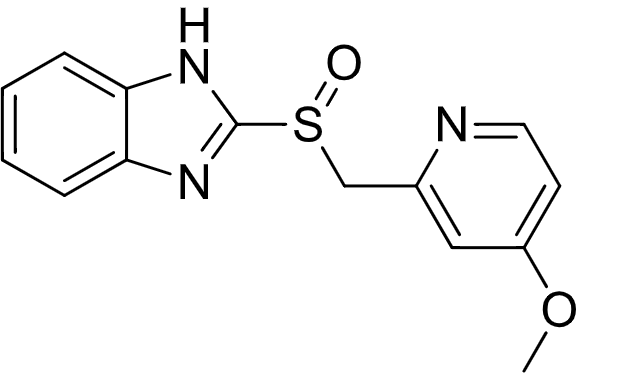
conjugate base
PPIs are formulated with their ____
PPI MOA
prodrugs that are trnasformed within the acid compartment of the parietal cell, into an inhibitor that reacts with an essential thiol group on the enzyme
at neutral pH they are inactive, chemically stable, lipid soluble, weak bases
they reach the parietal cells from the blood, then diffuse into the secretory canaliculi where they become protonated, and thus trapped
PPI covalent attachement
at least 2 molecules of the sulfenamide react with thiol gorups in the active site of H+/K+ atpase
one is Cys-813,
full inhibition occurs when 2 molecules of inhibitor react with one molecule of enzyme ****
permanent inhibiton
administration of omeprazole results in ___ of enzyme activity in vivo
PPI formulation
formulated as enteric coated microcapsules or granules designed to withstand gastric acid and ensure release in the intestine.
absorbed from the systemic circulation
how do PPIs enter the parietal cells of the stomach?
A
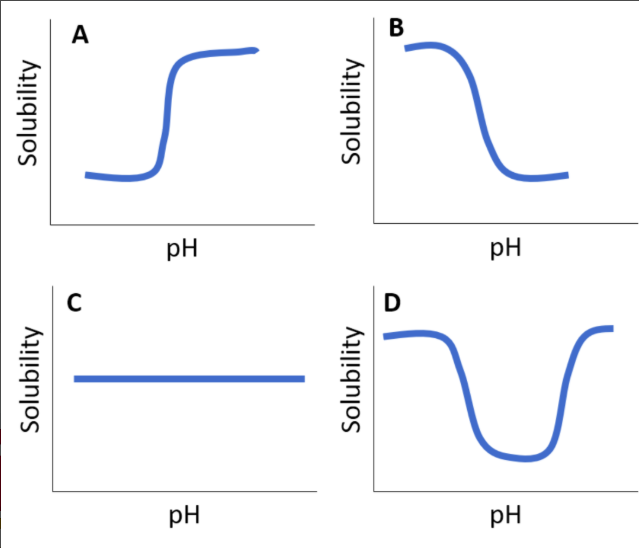
which best depicts solubility of an enteric coating as a function of pH?
intestines
which location are PPIs most likely absorbed?
acidic pH
what drives activation of a PPI?
PPIs are bioactivated in parietal cells because of a low pH
PPIs are bioactivated into an electrophile, which can be toxic (like acetaminophen), why then are PPIs safe?
2
how many molecules are depicted in the following structure?
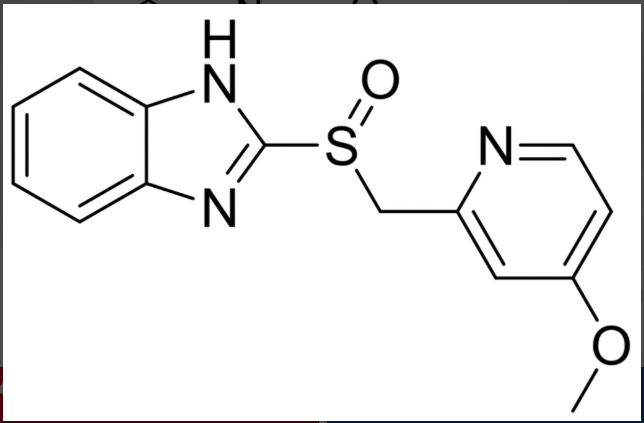
A
which location is acidic?
True
T/F PPIs block both stimulated and basal gastric acid secretion
eicosanoids
structurally simple but highly biologically diverse, endogenous substances
all structurally similar 20-carbon molecules
derived from oxidation of lipids
all are unstable ****
prostaglandins, thromboxanes, prostacyclins, leukotrienes
local
eicosanoids are ___ hormones
local hormone
unstable, very potent, synthesized specifically near the action site, quick response, rapid degradation
ex: eicosanoids
uniquitous
eicosanoids are ___ in the body
mediators of inflammation
eicosanoids are the most important _____
how do eicosanoids work
as chemical messengers through ecosanoid receptors
a particular PG may have different effects in different tissues, depending on which receptors are expressed
prostaglandins (latanoprost)
block w oxidation
limited success- instability and off target effects, best for local adminisratoin
agonists- goals are to increase stability and increase selectivity
add a phenol group - block w oxidaiton
reduce a double bond
prodrug (increase lipophilicity)
indication- glaucoma
prostaglandins (carboprost)
block dehydrogenase
agonists- goals are to increase stability and increase selectivity
add a methyl in place of the hydrogen. this will block oxidation at carbon 15 by dehydrogenase
uses: abortion, treat postpartum hemorrhage
prostaglandins as drugs
block w oxidation
block dehydrogenase
target PG receptors
all are agonists= goal is to increase stability and increase selectivity
leukotrienes
mediators of inflammation
potent hypotensives
potent bronchoconstirctors
act via specific GCPRs
cysteine leukotriene receptors→ CysLT1, CysLT2
zafirlukast, montelukast, zileuton
important target for asthma
agonists or antagonsts
therapeutics based on eicosanoid signaling can act as ___
local delivery
typically ___ is required for eicosanoids due to cell specific expression of receptors
GCPRs activated by eicosanoids are tissue specific
how do eicosanoids achieve different effects in different tissues?
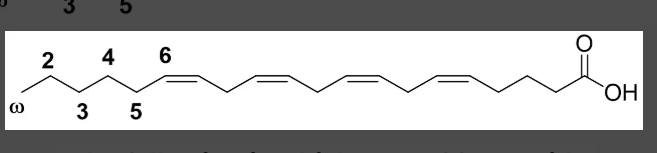
omega 6
the following is which type of fatty acid?
hydrolysis
membrane phospholipids are cleaved by phospholipases by which metabolic process?
completely block oxidation
how would the following modification influence oxidation on carbon 15?
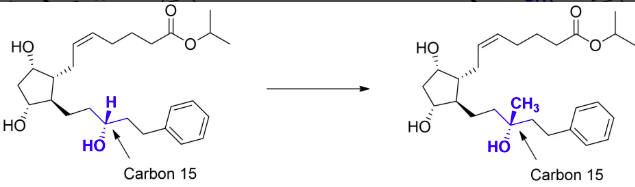
increase
would the following increase, decrease, or have no effect on stability?

no effect
would the following increase, decrease, or have no effect on stability?
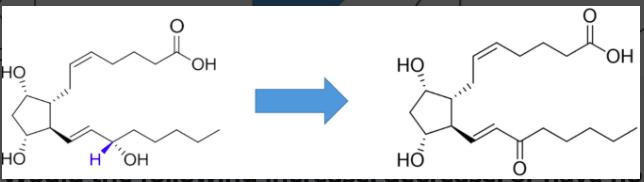
increase
would the following increase, decrease, or have no effect on stability?

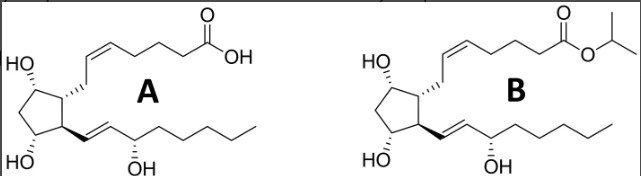
B
which would have a higher corneal permeability?
analgesic
acting to relieve pain
antipyretic
prevent or reduce fever
anti-inflammatory
a substance or treatment that reduces inflammation or swelling
tNSAIDs
traditional, inhibit both COX-1 and COX-2
NSAIDS
new, selectively inhibits COX-2
cyclooxygenase
prostaglandin G/H synthase enzymes are also known as this
COX-1 inhibiton
unwanted side effects in the gastrointestinal tract
COX-2 inhibtion
antipyretic, analgesic, and anti-inflammatory actions
arginine 120
is important for binding in the NSAID MOA
functional groups
NSAIDs are classified based on __
NSAID classifications
salicylic acids (aspirin)
para-aminophenols (acetaminophen)
acetic acids (indomethacin)
propanioc acids (ibuprofen)
enolic acids (piroxicam)
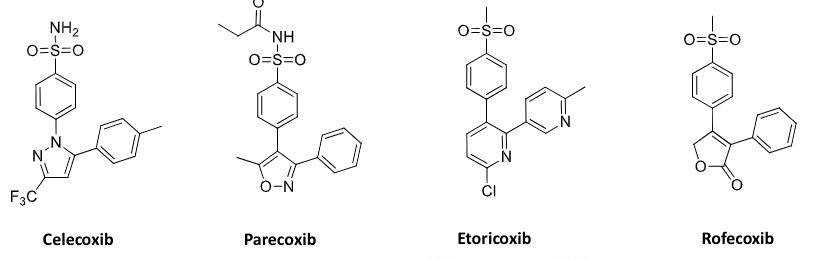
diarylheterocyclics (celecoxib) → cox-2 selective
salicylic acid (aspirin)
NSAID
irreversible COX inhibition → covalently modified COX
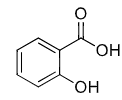
esterase, CYP3A4, UGT, NACt
how are salicylic acid derivatives metobolized?
diflusional
salicylic acid derivative not metabolized by phase 1 systems
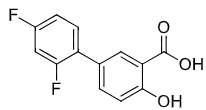
para-aminophenol (acetaminophen)
not as NSAID***
not a good COX2 inhibitor therefore has very weak anti-inflammatory effects
extremely toxic at higher doses due to quinone
acetic acid derivatives
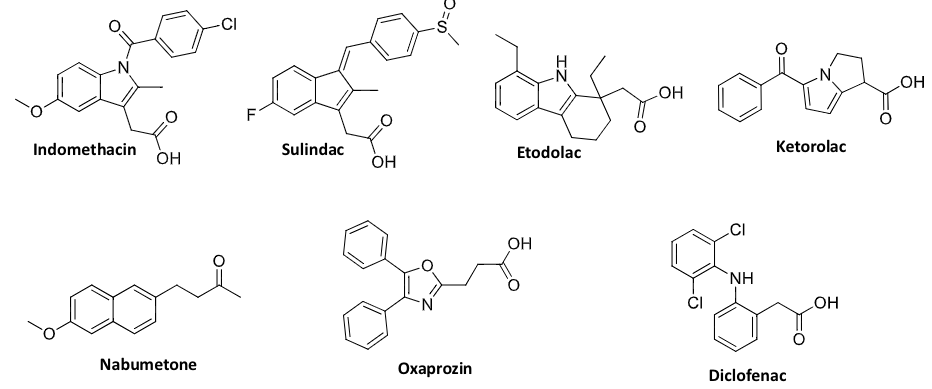
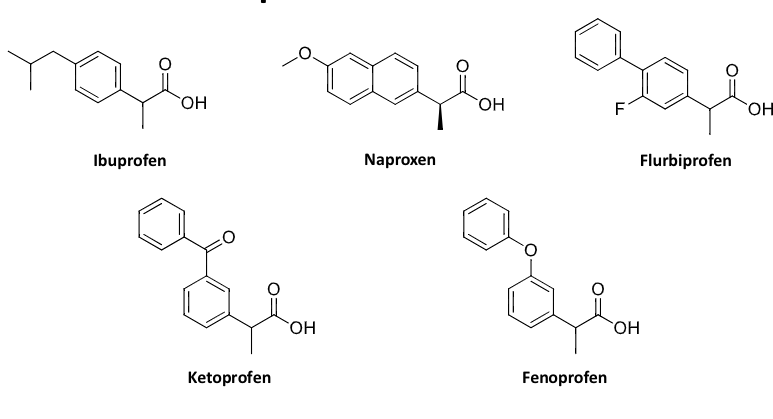
propanoic acid derivatives
enolic acid derivatives
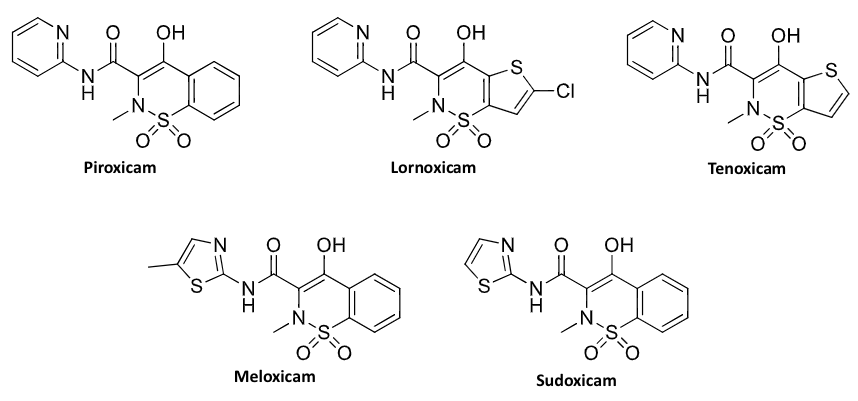
COX 2 selective inhibitors
COX selectively
no real advantage for it
selectivity increases toxicity for other liabilities
D
which NSAID is a prodrug?
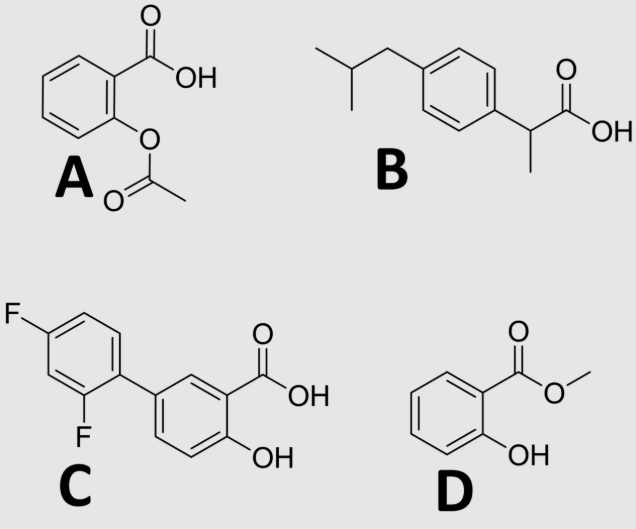
C
which NSAID is not likely metabolized by phase 1 systems?
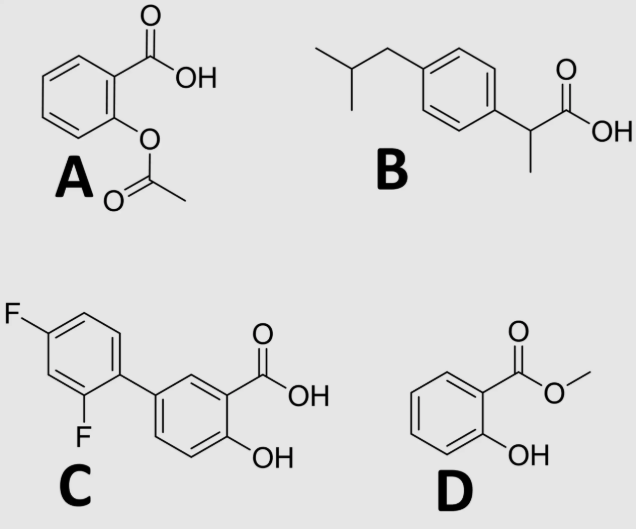
D
which NSAID is most suitable for topical administration?
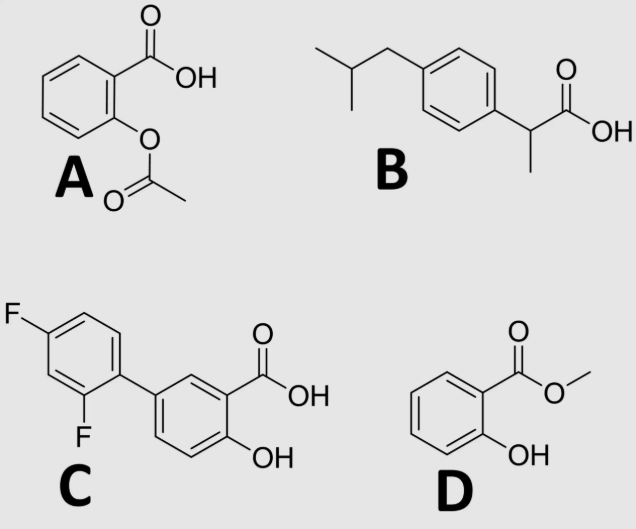
A
which NSAID covalently binds to COX?
carboxylic acid (usually)
which functional group is essential for NSAID activity?
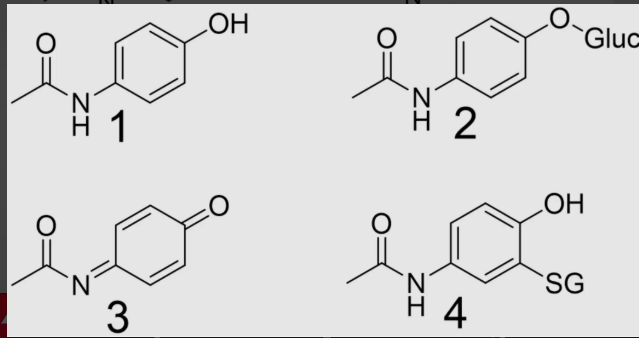
3
which metabolite of acetaminophen is toxic?
cyclooxygenase
which enzyme do NSAIDs inhibit?
false
T/F NSAIDs that are bioactivated outside of the GI tract do not cause GI toxicities
carboxylic acid
Nabumetone is an NSAID that requires bioactivation. which functional gorup is nabumetone missing to be an NSAID?
false
T/F the anti-inflammatory effect of NSAIDs is through COX-1 inhibiton
C
what is the most likely phase 1 metabolite of diclofenac?
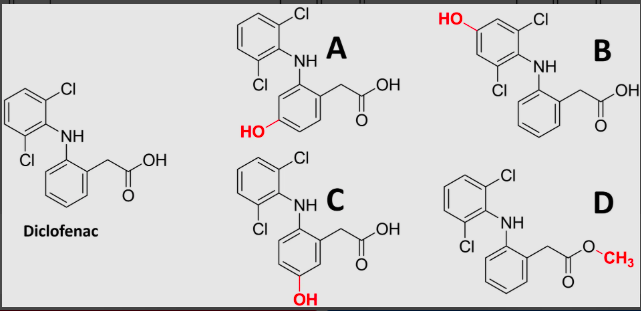
3
which is most likely to have the highest topical absorption? (numbered left to right 1-3)
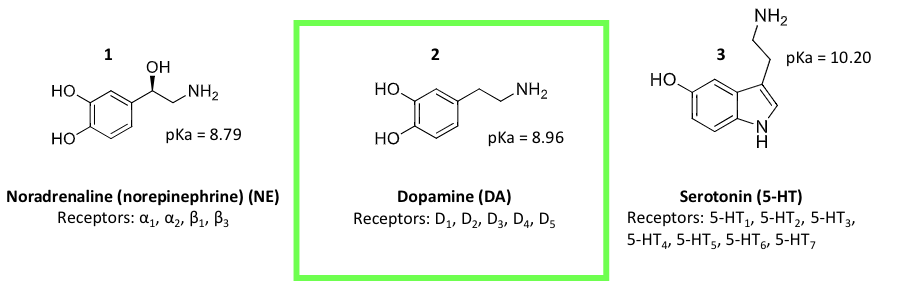
dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia
exact cause is unkown
current hypothesis- the accepted hypothesis is that it is caused by an increase in dopaminergic neurotransmission
schizophrenia is a disease that is treated with medicine derived from a working hypothesis
secondary amine
functional group that common neurotransmitters share
schizophrenia
disease that is attributed to abnormal dopamine signaling in the CNS
increased signaling through the D2 receptor
antipsychotic classification
phenothiazine class
benzamide class
benzazepines
benzisoxazole and benzisothiazole
all work by modulating dopamine signaling
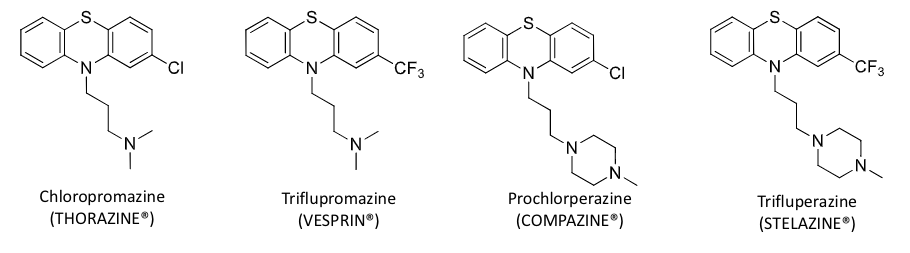
phenothiazine antipsychotics
based on phenothiazine core
slightly bent and not planar
chlorpromazine, promethazine, diethazine, ehtopropazine
can be short or long acting, depending on structure
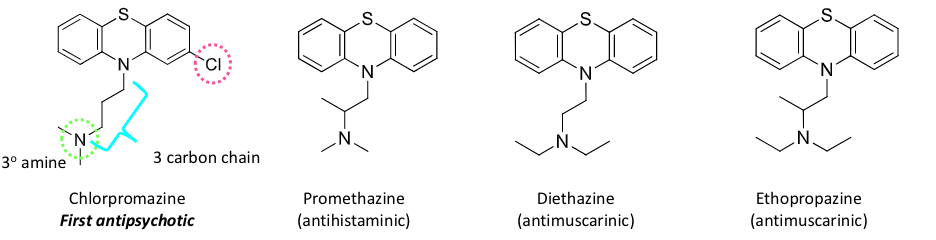
short acting phenothiazine
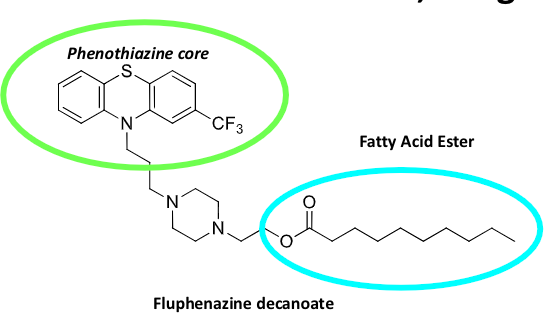
long acting phenothiazine
benzamide antipsychotics
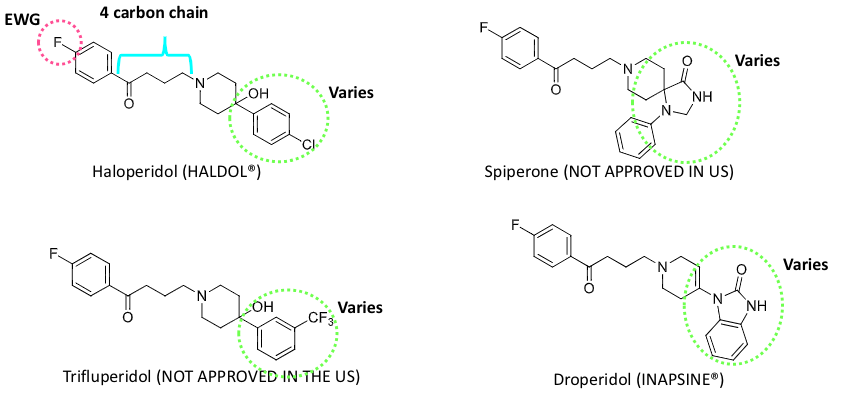
haloperidol
long acting benzamide
duration is 4-6 weeks for compliance
prodrug→ fatty acid ester cleaved by hydrolysis
can become toxic through bioactivation → HPP+ is neurotoxic to dopaminergic and serotonergic neurons
caused tardive dyskinesia, which is repetitive, involuntary movements
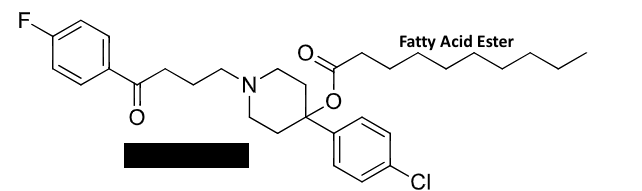
chronic haloperidol toxicity
bioactivation creates HPP+ → neurotoxic to dopaminergic and serotonergic neurons
severity of toxicity is associated with an increase in HPP+ to haloperidol
causes tardive dyskinesia, which is repetitive, involuntary body movements
patients frequently exhibit extrapyramidal symtoms (EPS)
benzazepine antipsychotics
synthesized based on imipramine (TCA)
less EPS toxicity
substitution of the amine target specificity → 3 amine and not secondary
efficacy of this class challenges the dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia
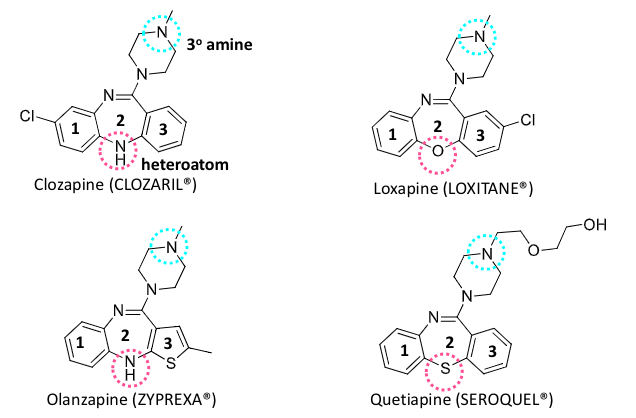
clozapine
benzazepine class antipsychotics
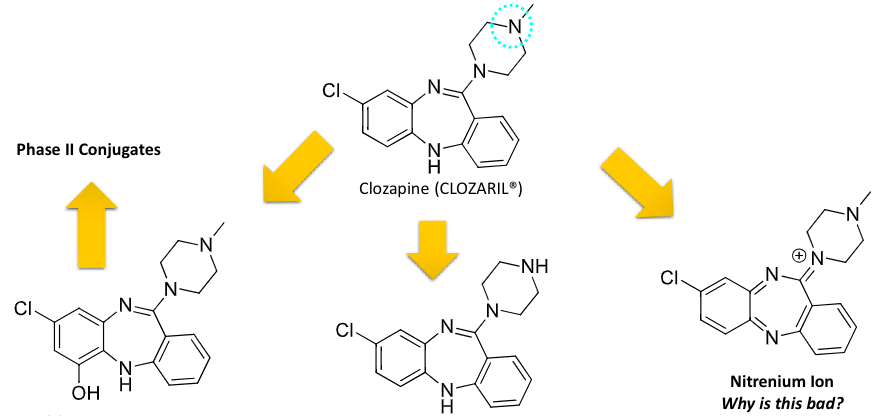
bioactivation created toxic metabolite
catalyzed by peroxidases in neutrophils
reactive metabolite responsible for covalent binding in neutrophils
agranulocytosis occurs in 1-2% of patients from neutrophil toxicity
benzisoxazole and benzisothiazole antipsychotic
generate compounds with D2 and 5-HT2A activity
phenothaizine + benzazepine ?
aripiprazole
paliperidone palmitate
aripiprazole
benzisoxazole and benzisothiazole antipsychotic
high affinty antagonists for D2 and 5HT2A
reduce extrapyramidal receptors
5HT2C agonist help reduce weight gain
typical antipsychotics
first generation
based on blocking D2 receptor signaling
phenothiazine class
benzamide class
atypical antipsychotics
2nd genration
based on blocking D2/5HT2A receptor signaling
benzazepine class
benzisozazole and benzisothioazole class
sedatives
reduce anxiety and exert a calming effect
anxiolytics
anything that inhibits anxiety
hypnotics
produces drowsiness and facilitates the onset and maintenance of a state of sleep (not necessarily healthy sleep)
GABA receptor complex
barbituates
benzodiazepines
z drugs
GABA system
drug binding leads to increased GABA binding to GABAA receptors
drug binding inhibits firing of the neuron
gamma amino butyric acid (GABA)
a major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the CNS
benzodiazepines
bind the alpha and gamma subunits
increase GABA binding
causes greater influx of chlorine into the neuron
decrease the rate of firing of the neuron
CNS depression, helps lower anxiety
barbituates
cyclic diacylureas
substituted derivates of barbituric acid- generally, only the 5,5-disubstituted barbituric acid derivatives are active ***
depending on the dose, can produce→ sedation, hypnosis, anesthesia
the long acting are often used as anticonvulsants ***
in order to possess hypnotic activity, must enter the CNS
issues with barbituates
decrease REM sleep and dream time → not “natural sleep”
tolerance develops
5 mono-substituted barbituric acids
inactive
too acidic to cross the blood brain barrier
ionized in blood, no CNS penetrance, no activity
5,5 disubstituted barbituric acids
active
imide NH pKa= 7.1-8.1
have CNS distribution
ex: phenobarbital
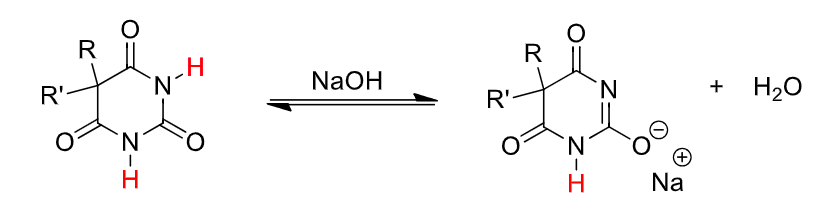
barbituate SAR (5 carbon)
both C-5 H atoms must be substituted
as the number of C5 substituent atoms increases, lipid solubility increases (increases potency, volume of distribution, shortens duration of action)
halogens on alkyl groups at C5 increase lipid solubily
polar functional groups at C5 decrease potency (decreased lipid solubility)
barbiturate SAR (2 carbon)
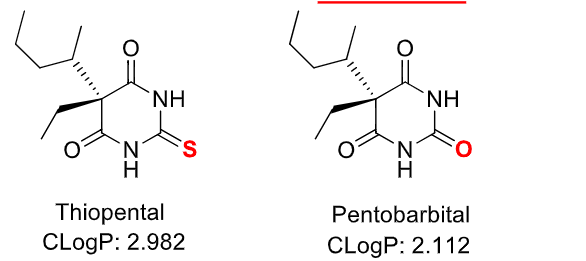
replacement of O with S gives increased lipid solubility, faster onset, and shorter duration
maximal brain levels of thiobarbiturates are rapidly achieves, this, they have been used as IV anesthetics
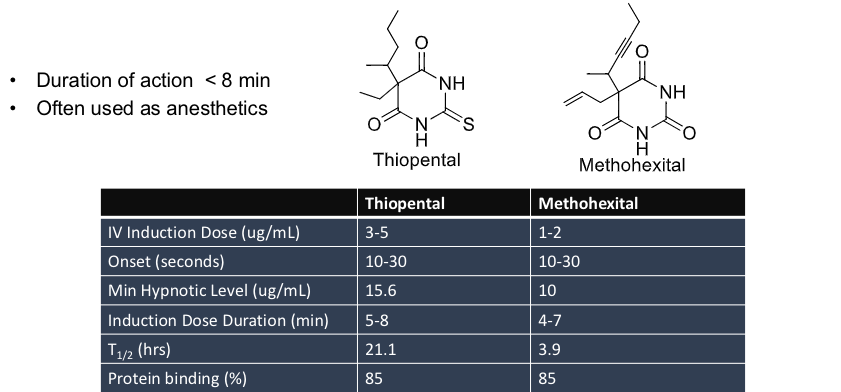
why is barbiturate duration so short?
large volume of distribution
rapid absorption and distribution into the CNS followed by rapid redistribution to other sites
ultra short acting barbiturates
thiopental
methohexital
thiopental
barbiturates used in lethal injection
autopsies of executed inmates showed the level of thiopental in their bloodstream was insufficient to cause unconsiousness