Fractional distillation of crude oil
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Crude oil
Fossil fuel from deep under ground
How was crude oil formed?
Crude oil is formed from the remains of dead plants and animals, particularly plankton.
These organic remains were covered by mud and sand, and buried in the earth.
Over millions of years, these organic remains were compressed under a lot of heat and pressure.
The heat and pressure chemically changed the organic remains into crude oil.
finite resources
limited resources
Non renewable fuels
coal, oil, natural gas, nuclear
Fractional distillation of crude oil
-crude oil is heated until most has turned into gas which is passed into a fractionating column
-fractionating column is heated from the bottom so it's cooler at the top
-hot gases rise to regions at cooler temps to condense into liquid
Hydrocarbons with the longest chains
Have highest boiling points , thick viscous liquids
Quickly condense into liquid and drain out early on
Poor fuels
Shorter chain hydrocarbons
Lower boiling points so stay as a gas longer
Most flammable-best fuels
Some stay as a gas the whole time
Petrochemical
Substances made from crude oil
Can be used as lubricants
Cracking
The breaking down of long-chained saturated hydrocarbons to form a mixture of shorter-chained alkanes and alkenes by heating them
Catalytic cracking
1. vaporise hydrocarbon
2. pass over hot powered aluminium oxide catalyst
Steam cracking
1. vaporise hydrocarbon
2. mix with steam
3. heat to a very high temperature
Cracking long chain hydrocarbons
Long chain—>shorter chain+alkene
(Decane—->heltane+propene)
covalent bonding
results from the sharing of electron pairs between two atoms
Limitations of dot and cross diagrams
Do not show the 3D shape of a molecule
Limitations of ball and stick model
Fails at indicating the movement of electrons
Simple molecules
Weak IMF which are broken down during melting not bonds
IMF increases with size of molecules
Don't conduct electricity as no charged particles
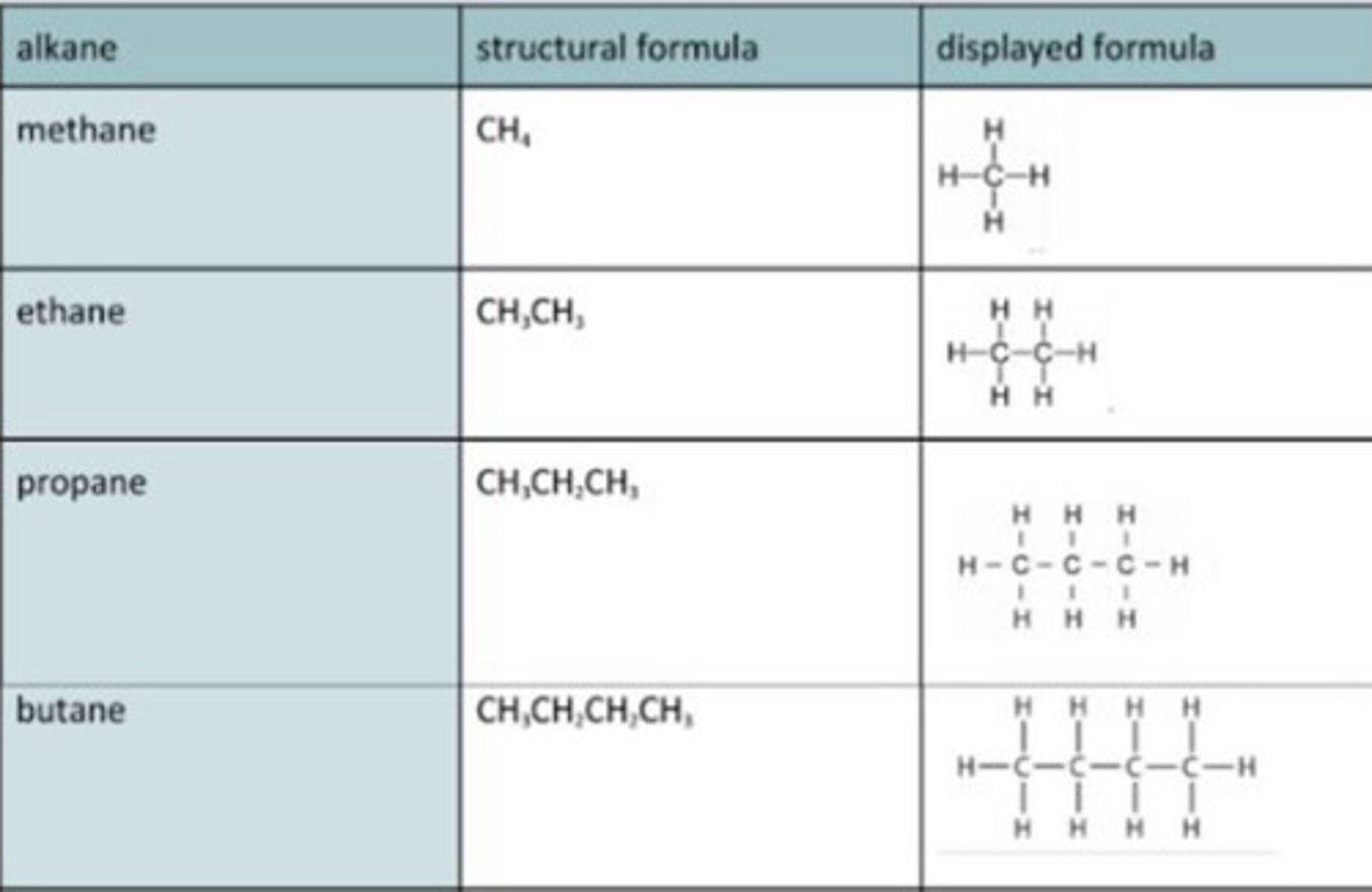
Alkanes
Hydrocarbons that contain only single bonds
Saturated
Viscous, volatile, flammable
Displayed formula for alkanes
alkane functional group
C-C
Alkane general formula
CnH2n+2
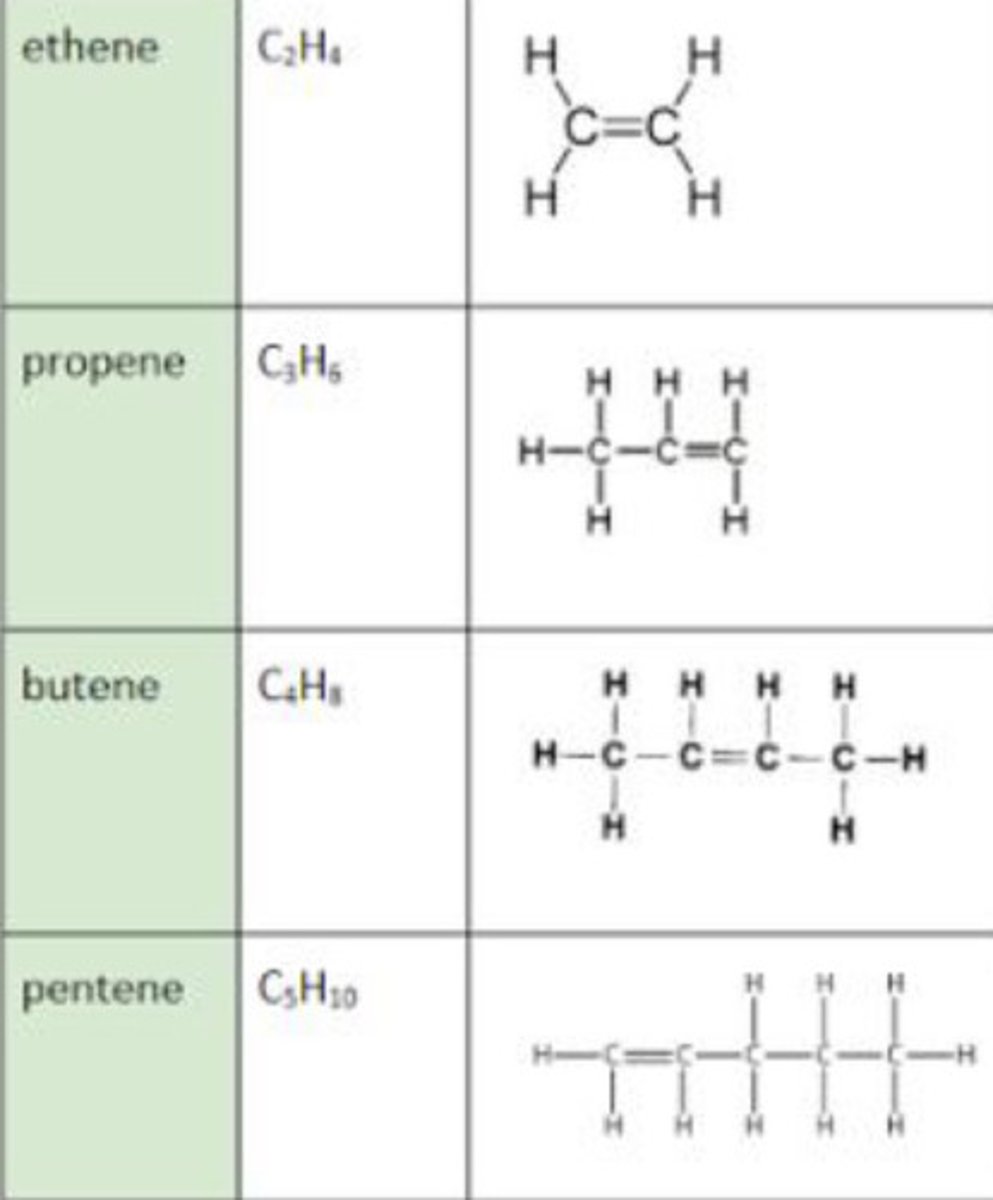
Alkenes
double bonds
Unsaturated
Displayed formula for alkenes
alkene functional group
C=C
Alkene general formula
CnH2n
Test for alkenes with bromine water
Colour change from orange to colourless
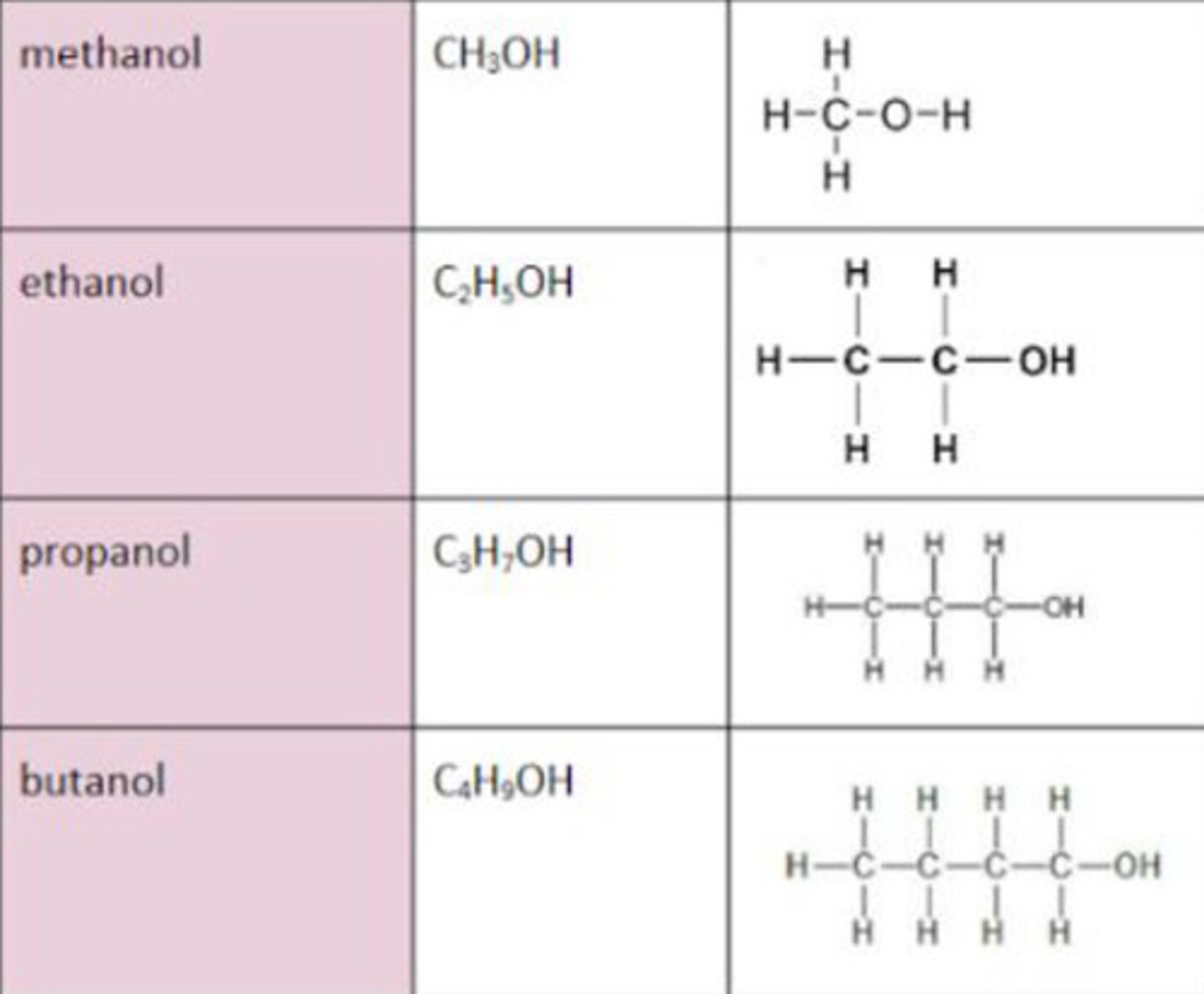
Alcohols functional group
OH-
Alcohol general formula
CnH2n+1OH
Displayed formula for alcohol
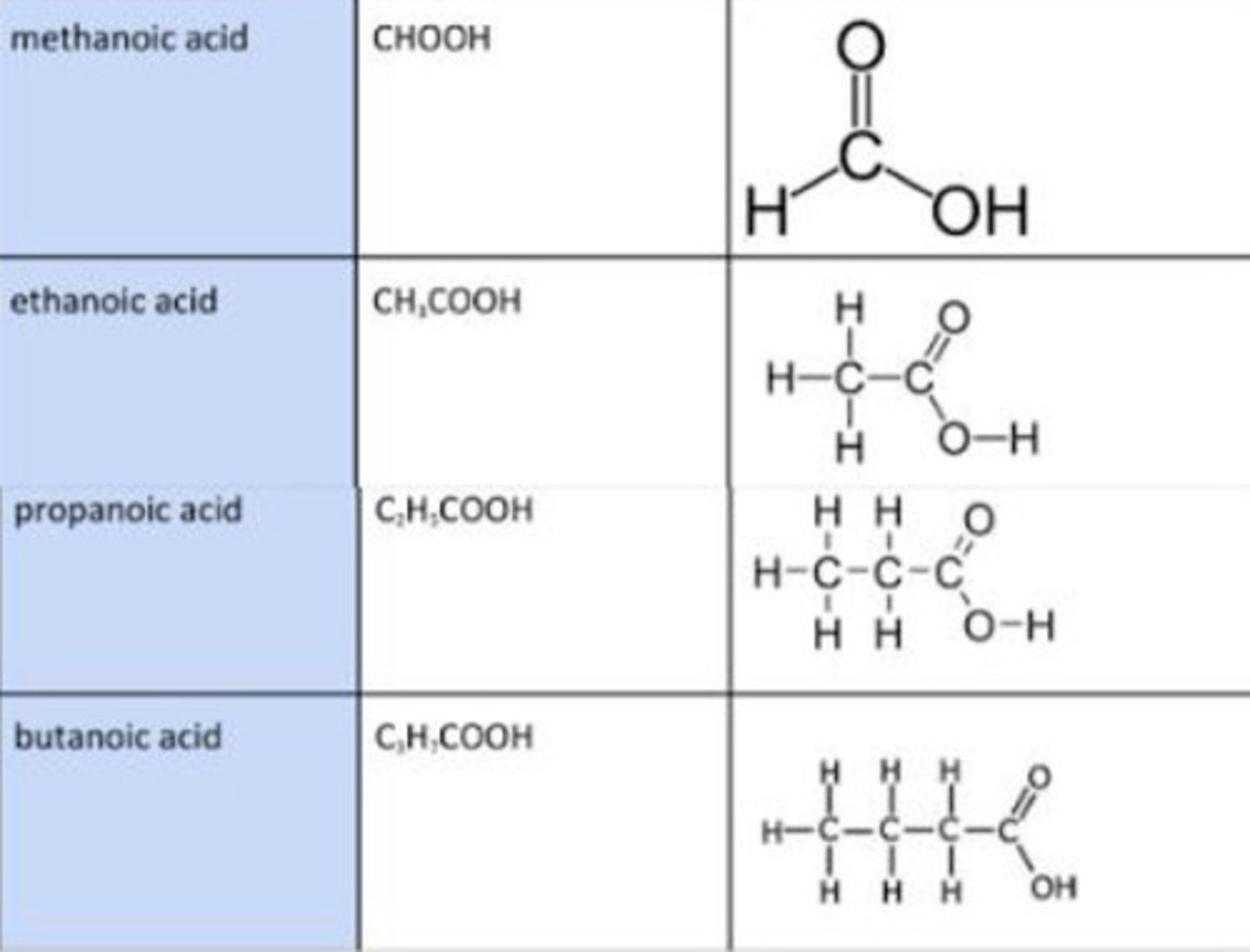
carboxylic acid functional group
COOH
Carboxylic acids general formula
CnH2n+1COOH
Displayed formula for Carboxylic Acid
functional group
group of atoms within a molecule that interacts in predictable ways with other molecules
Hydrocarbons
Compounds composed of only carbon and hydrogen
Homologous series
A family of molecules which share the same general for,ular and functional group