Population and Community Ecology Overview
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Population
The individuals that belong to the same species and live in a given area at a particular time.
Community
All of the populations of organisms within a given area.
Population ecology
The study of factors that cause populations to increase or decrease.
Population size (N)
The total number of individuals within a defined area at a given time.
Population density
The number of individuals per unit area at a given time.
Population distribution
A description of how individuals are distributed with respect to one another.
Sex ratio
The ratio of males to females in a population.
Age structure
A description of how many individuals fit into particular age categories in a population.
Density-dependent factor
A factor that influences an individual's probability of survival and reproduction in a manner that depends on the size of the population.
Density-independent factor
A factor that has the same effect on an individual's probability of survival and the amount of reproduction at any population size.
Population growth models
Mathematical equations that can be used to predict population size at any moment in time.
Population growth rate
The number of offspring an individual can produce in a given time period, minus the deaths of the individual or its offspring during the same period.
Intrinsic growth rate (r)
The maximum potential for growth of a population under ideal conditions with unlimited resources.
Exponential growth model (Nt = N0ert)
A growth model that estimates a population's future size (Nt) after a period of time (t), based on the intrinsic growth rate (r) and the number of reproducing individuals currently in the population (N0).
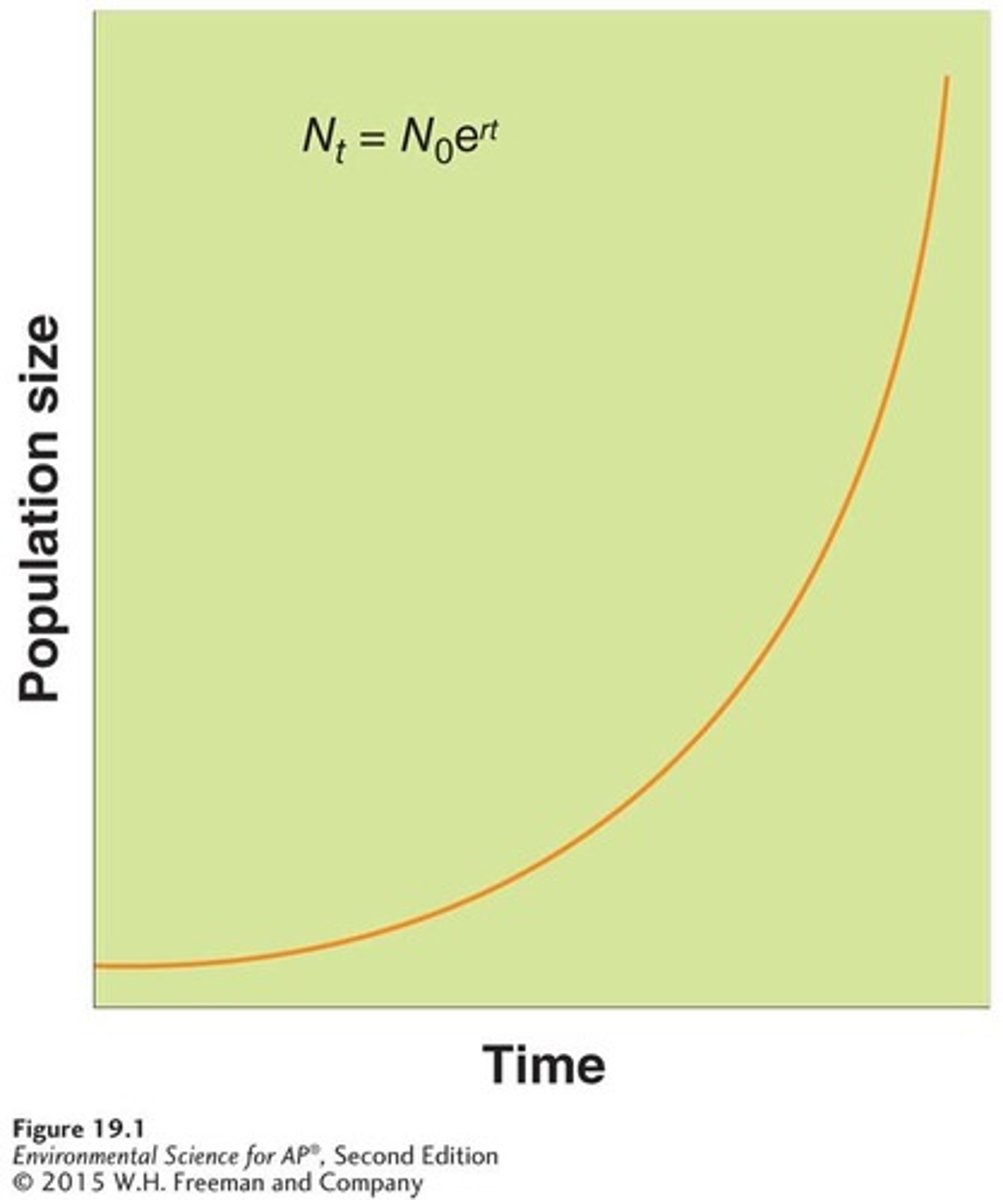
J-shaped curve
The curve of the exponential growth model when graphed.
Limiting resource
A resource that a population cannot live without and that occurs in quantities lower than the population would require to increase in size.
Carrying capacity (K)
The limit of how many individuals in a population the environment can sustain.
Logistic growth model
A growth model that describes a population whose growth is initially exponential, but slows as the population approaches the carrying capacity of the environment.
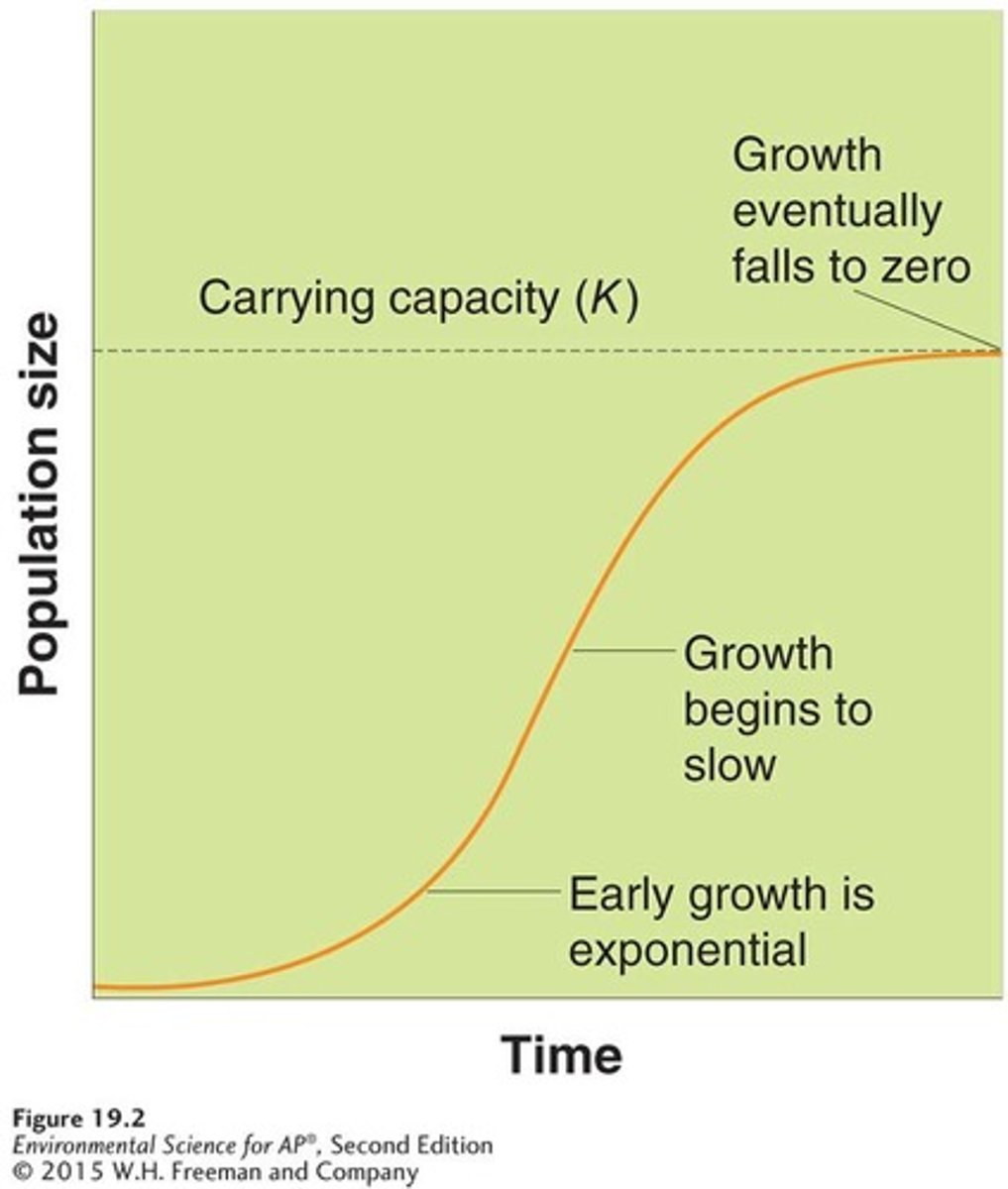
S-shaped curve
The shape of the logistic growth model when graphed.
Overshoot
When a population becomes larger than the environment's carrying capacity.
Die-off
A rapid decline in a population due to death.
K-selected species
A species with a low intrinsic growth rate that causes the population to increase slowly until it reaches carrying capacity.
r-selected species
A species that has a high intrinsic growth rate, which often leads to population overshoots and die-offs.
Survivorship curve
A graph that represents the distinct patterns of species survival as a function of age.
Type I survivorship curve
A pattern of survival over time in which there is high survival throughout most of the life span, but then individuals start to die in large numbers as they approach old age.
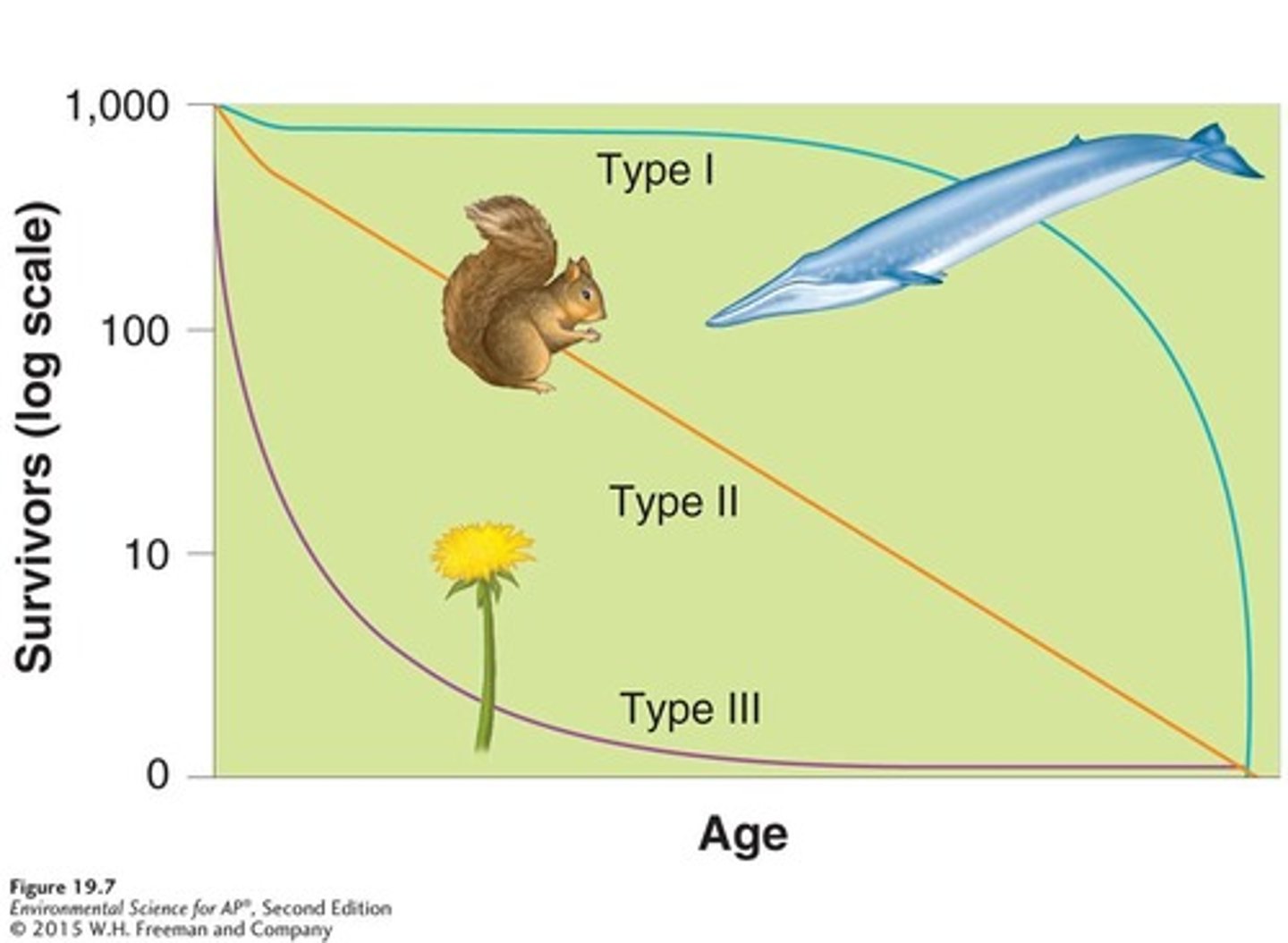
Type II survivorship curve
A pattern of survival over time in which there is a relatively constant decline in survivorship throughout most of the life span.
Type III survivorship curve
A pattern of survival over time in which there is low survivorship early in life with few individuals reaching adulthood.
Corridor
Strips of natural habitat that connect populations.
Metapopulation
A group of spatially distinct populations that are connected by occasional movements of individuals between them.
Inbreeding depression
When individuals with similar genotypes—typically relatives—breed with each other and produce offspring that have an impaired ability to survive and reproduce.
Community ecology
The study of interactions between species.
Symbiotic relationship
The relationship between two species that live in close association with each other.
Competition
The struggle of individuals to obtain a shared limiting resource.
Competitive exclusion principle
The principle stating that two species competing for the same limiting resource cannot coexist.
Paramecium
A genus of microorganisms that were used in experiments demonstrating competition for resources.
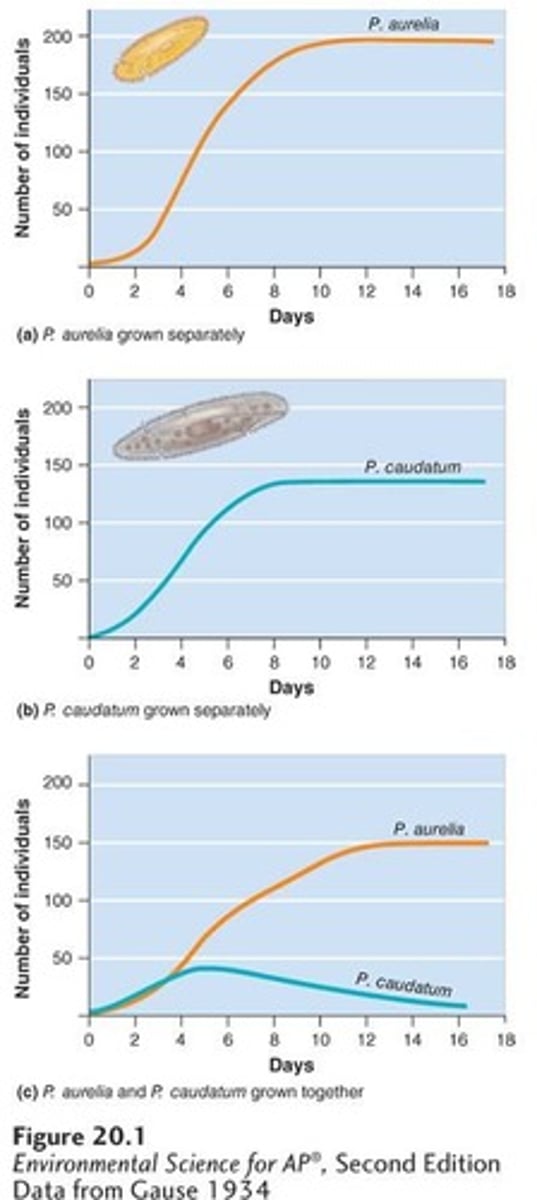
Competition
An interaction where two species compete for the same limiting resource, preventing coexistence.
Resource partitioning
When two species divide a resource based on differences in their behavior or morphology.
Predation
An interaction in which one animal typically kills and consumes another animal.
Parasitoid
A specialized type of predator that lays eggs inside other organisms, referred to as its host.
Parasitism
An interaction in which one organism lives on or in another organism.
Pathogen
A parasite that causes disease in its host.
Herbivory
An interaction in which an animal consumes a producer.
Mutualism
An interaction between two species that increases the chances of survival or reproduction for both species.
Commensalism
A relationship between species in which one species benefits and the other species is neither harmed nor helped.
Keystone species
A species that plays a far more important role in its community than its relative abundance might suggest.
Ecosystem engineer
A keystone species that creates or maintains habitat for other species.
Ecological succession
The predictable replacement of one group of species by another group of species over time.
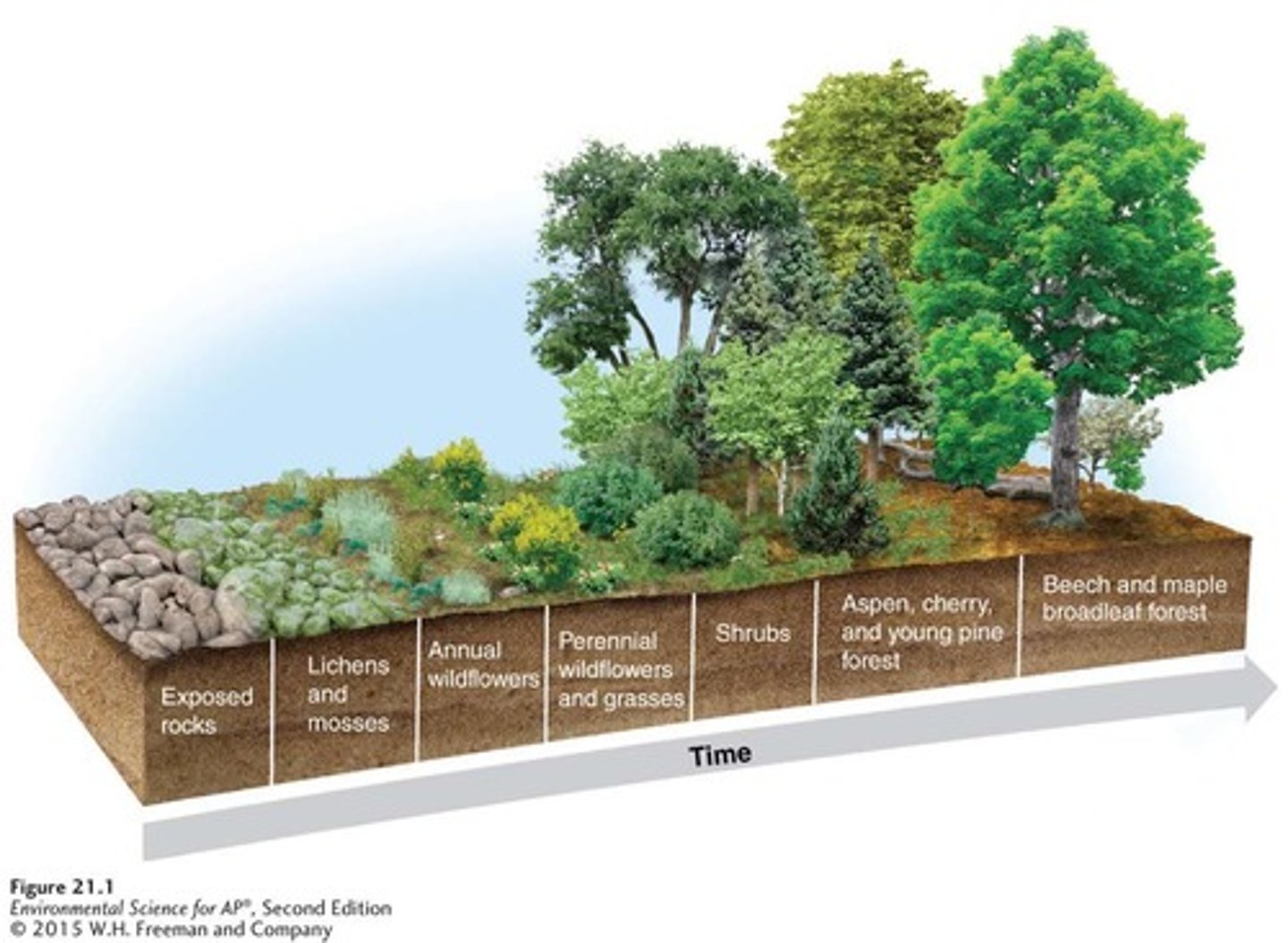
Primary succession
Ecological succession occurring on surfaces that are initially devoid of soil.
Secondary succession
The succession of plant life that occurs in areas that have been disturbed but have not lost their soil.
Species richness
The number of different species represented in a community.
Theory of island biogeography
A theory that demonstrates the dual importance of habitat size and distance in determining species richness.
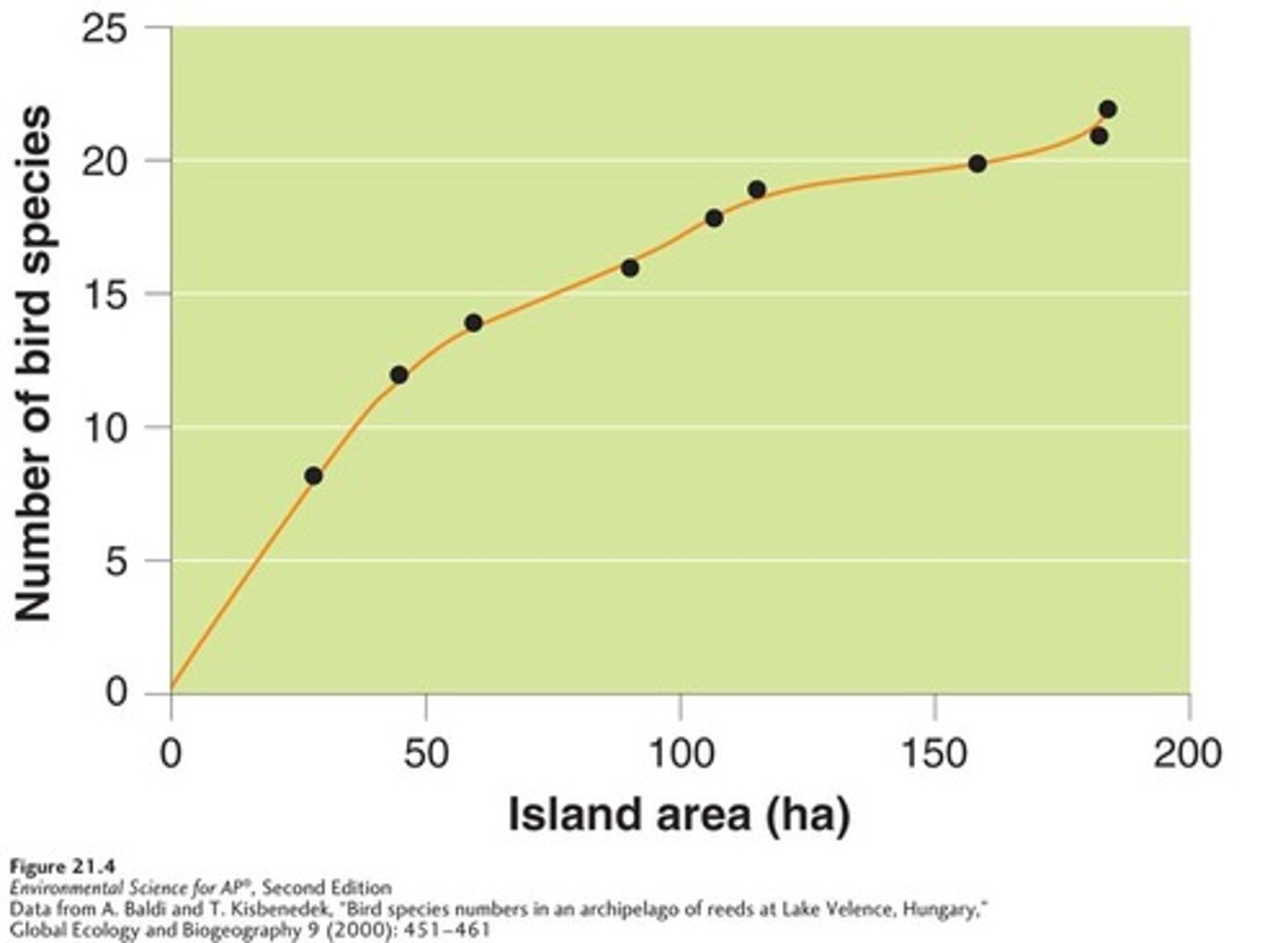
Habitat size
The physical space available for species to inhabit, influencing species richness.
Lichens
Early-arriving organisms that can colonize bare rock and help form soil.
Grasses
Early-arriving plants in secondary succession that set areas on a path of recovery.
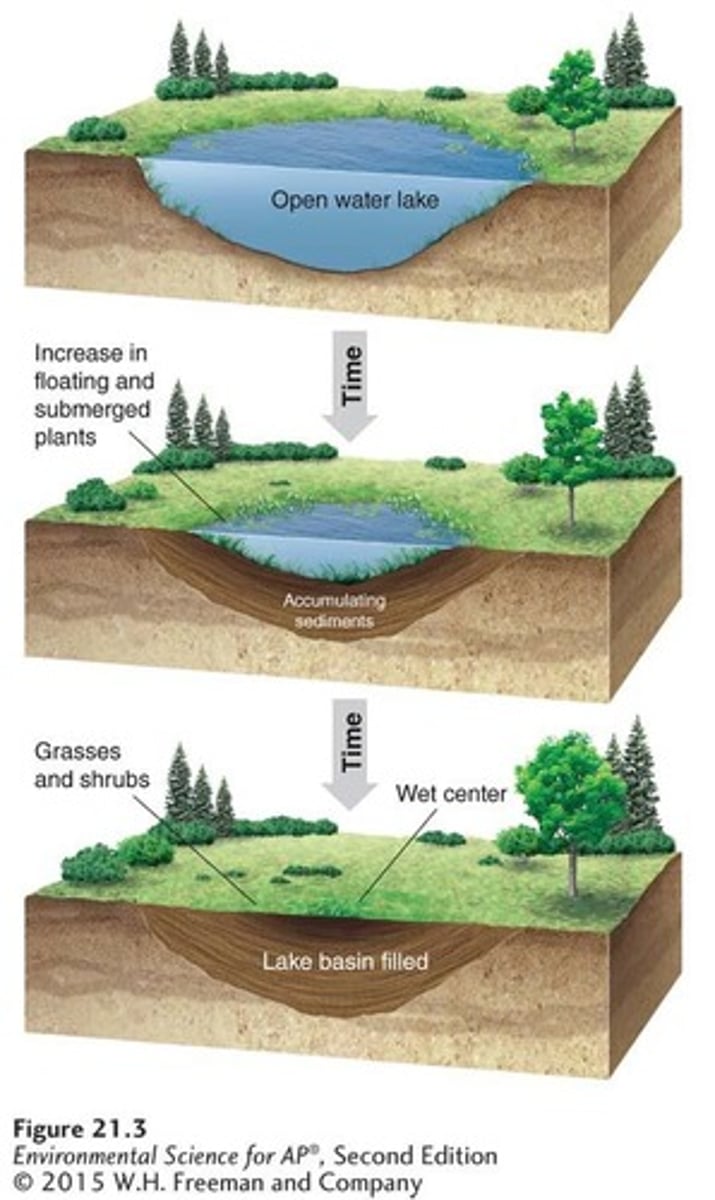
Sediments
Materials that fill lakes over time, contributing to the transition to terrestrial habitats.
Disturbance
An event that disrupts the structure of a community, initiating succession.
Aquatic succession
The process of ecological succession occurring in aquatic ecosystems.
New England forest
An example of a region where secondary succession begins with grasses and wildflowers.