NOVA- Anesthesia ECG Quiz 5
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Normal P waves
Origin in atria at or near the sinus node
Abnormal P wave
Atrial origin other than sinus node or retrograde activation from AV node
No P waves
Origin below atria, ectopic rhythm
Narrow QRS
Ventricular depolarization is following normal conduction path- efficient/ fast conduction
Wide QRS
Ventricular depolarization is initiated within ventricular myocardium- slow conduction
Sinus/ atrial origin
1:1 P:QRS
AV dissociation
Not 1:1 P:QRS
Types of nonsinus arrhythmias: ectopic rhythms
-junctional rhythm
-idioventricular rhythm
Ectopic rhythms
-nonsinus arrhythmias
-refers to originating outside of sinus node
-can be a single beat or a sustained beat
-caused by enhanced automaticity of a non-sinus node pacemaker site
-disorder or impulse formation
-digitalis toxicity, caffeine, alcohol, stimulants, and psychological stress
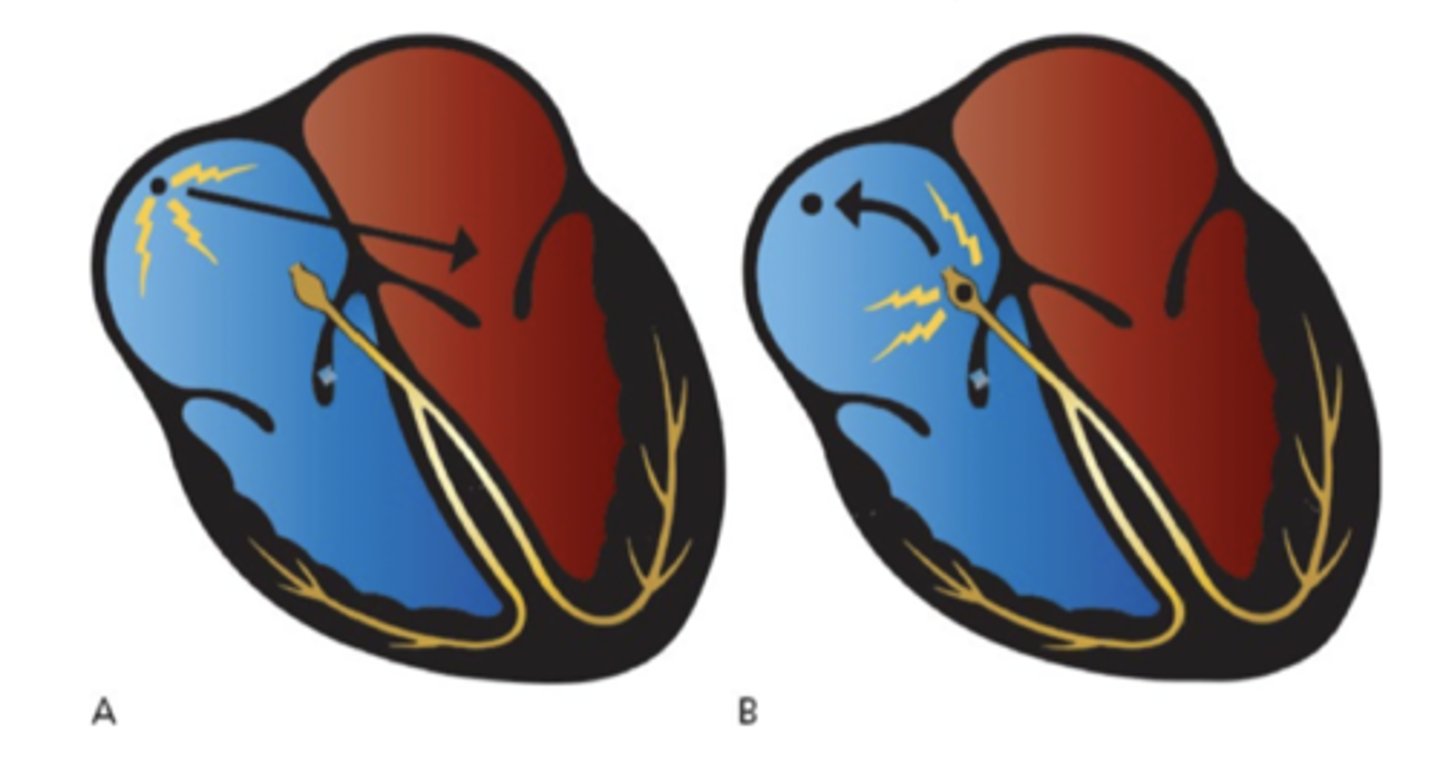
Junctional rhythm
-absence of P waves or possibly retrograde P waves
-narrow QRS
-40-60bpm (AV NODE ORIGIN)
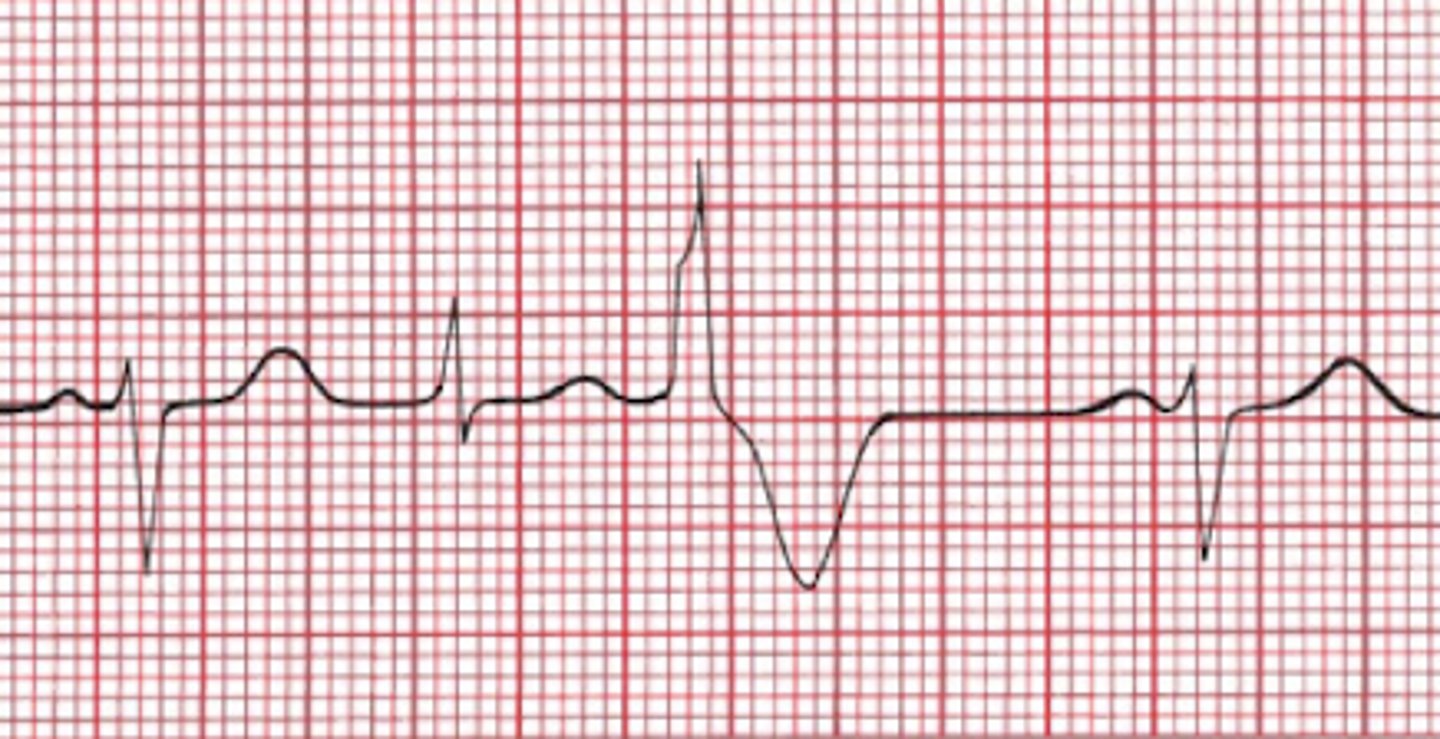
Accelerated Junctional Rhythm
-regular
-rate: 100-150bpm
-P Wave: NONE or INVERTED
-PR Interval: None or <0.12
-QRS: <0.12 sec
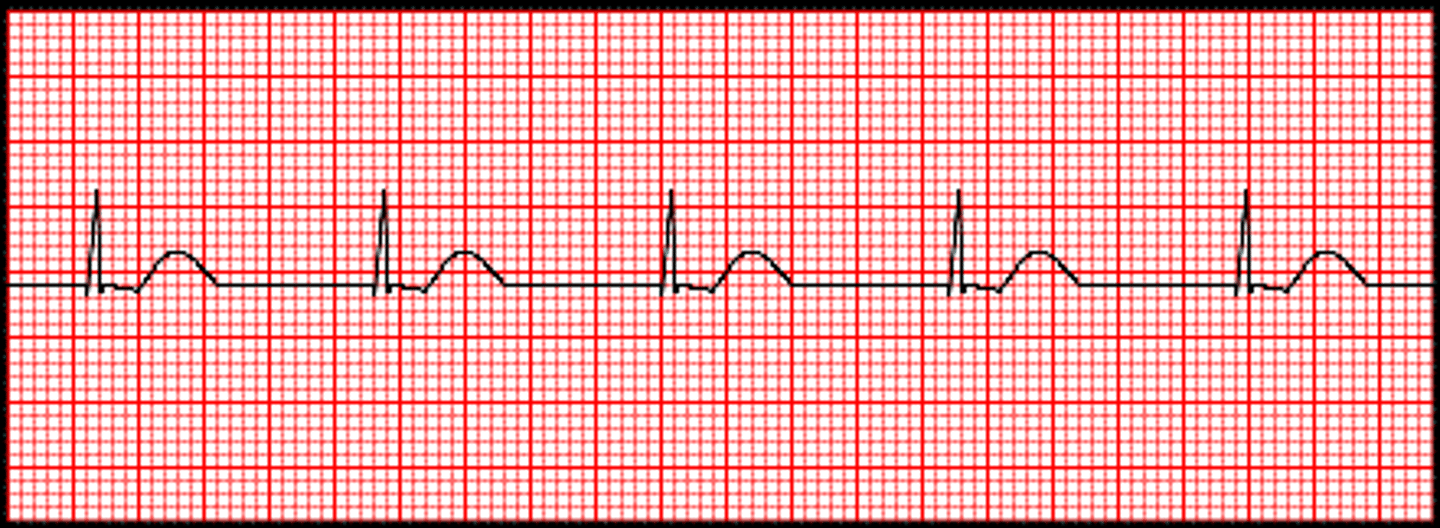
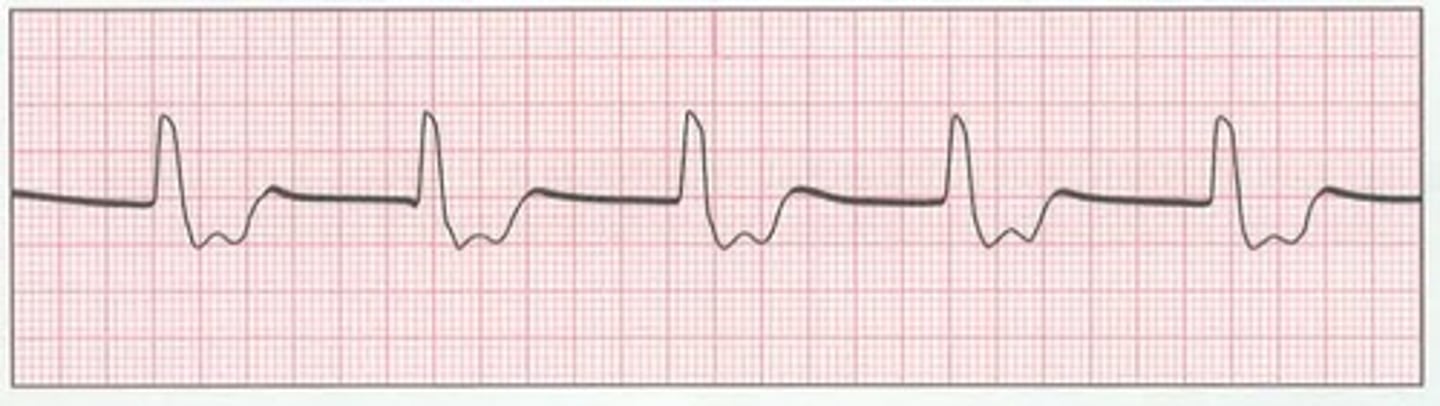
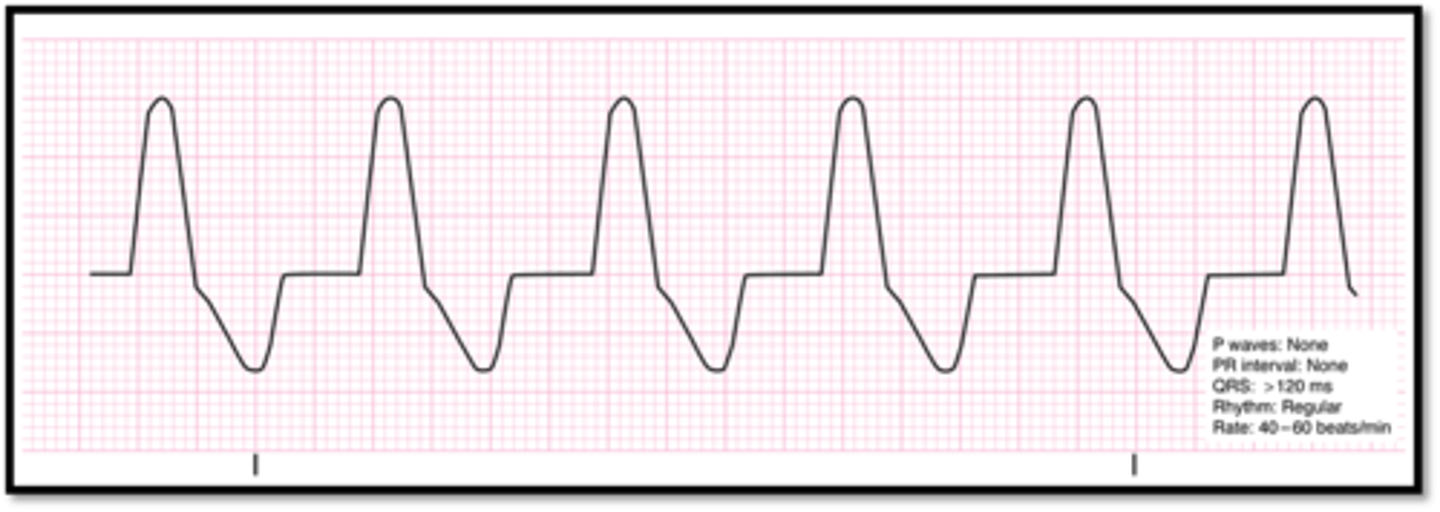
Idioventricular rhythm
-absence of P waves
-wide QRS
-rate <40bpm (ventricular origin)
-regular
Accelerated idioventricular rhythm
-p waves absent
-wide QRS
-P:QRS n/a
-regular
-rate: 75-100pm
-origin: ventricular foci, accelerated and over-driving other pacemakers
-seen during acute MI or during early hours of reperfusion (favorable sign that occluded coronary artery has been successfully reopened)
Reentrant rhythms
Abnormal rhythms due to the creation of a reentry loop
-most commonly caused by a combination of adjacent tissue heterogeneity and premature beat
-continues for as long as depolarization wavefront encounters excitable tissue
-disorder of impulse transmission
Types of nonsinus arrhythmias: reentrant rhythms
-premature atrial contraction (PAT)
-junctional premature beat (PJC)
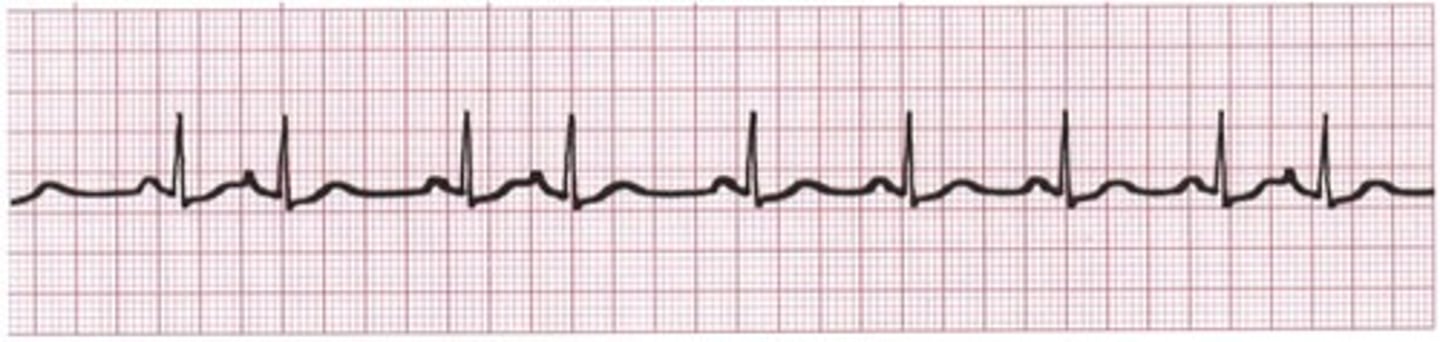
Premature atrial contraction (PAC)
-common benign phenomena
-can initiate sustained arrhythmias
-originates in the atrium, NOT SA NODE
-distinguished by contour of P wave and timing (happens earlier than next anticipated sinus wave)
-normal QRS
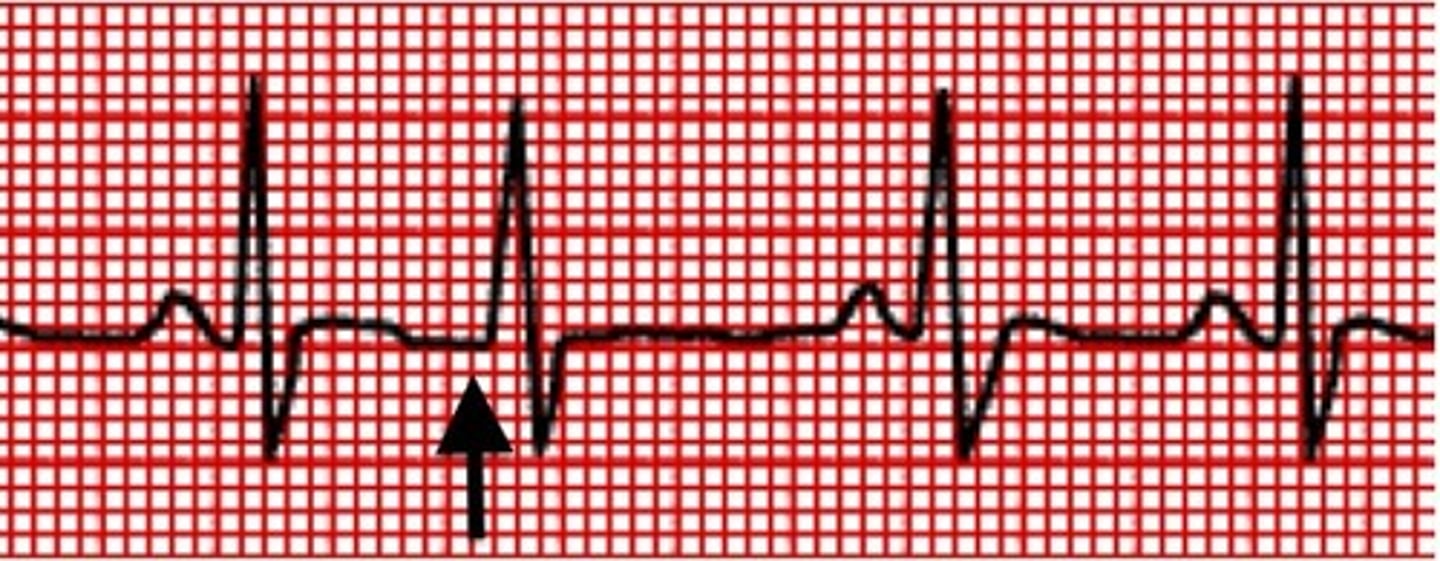
Junctional premature beat (PJC)
-common benign phenomena
-originates in the AV node
-absent or retrograde P wave
-normal QRS
-happens early
Types of sustained supraventricular arrhythmias
-AV nodal reentry tachycardia (AVNRT)
-atrial fibrilation
-atrial flutter
-multifocal atrial tachycardia (MAT)
-paroxysmal atrial tachycardia (PAT)
AV node reentry tachycardia (AVNRT)
-P waves buried within QRS
-pseudo R' seen in V1
-narrow QRS
-1:1 P:QRS
-Regular rhythm
-150-250bmp
-Origin: AV node reentry loop
-common arrhythmia, usually initiated by premature supraventricular beat, sudden onset/ termination
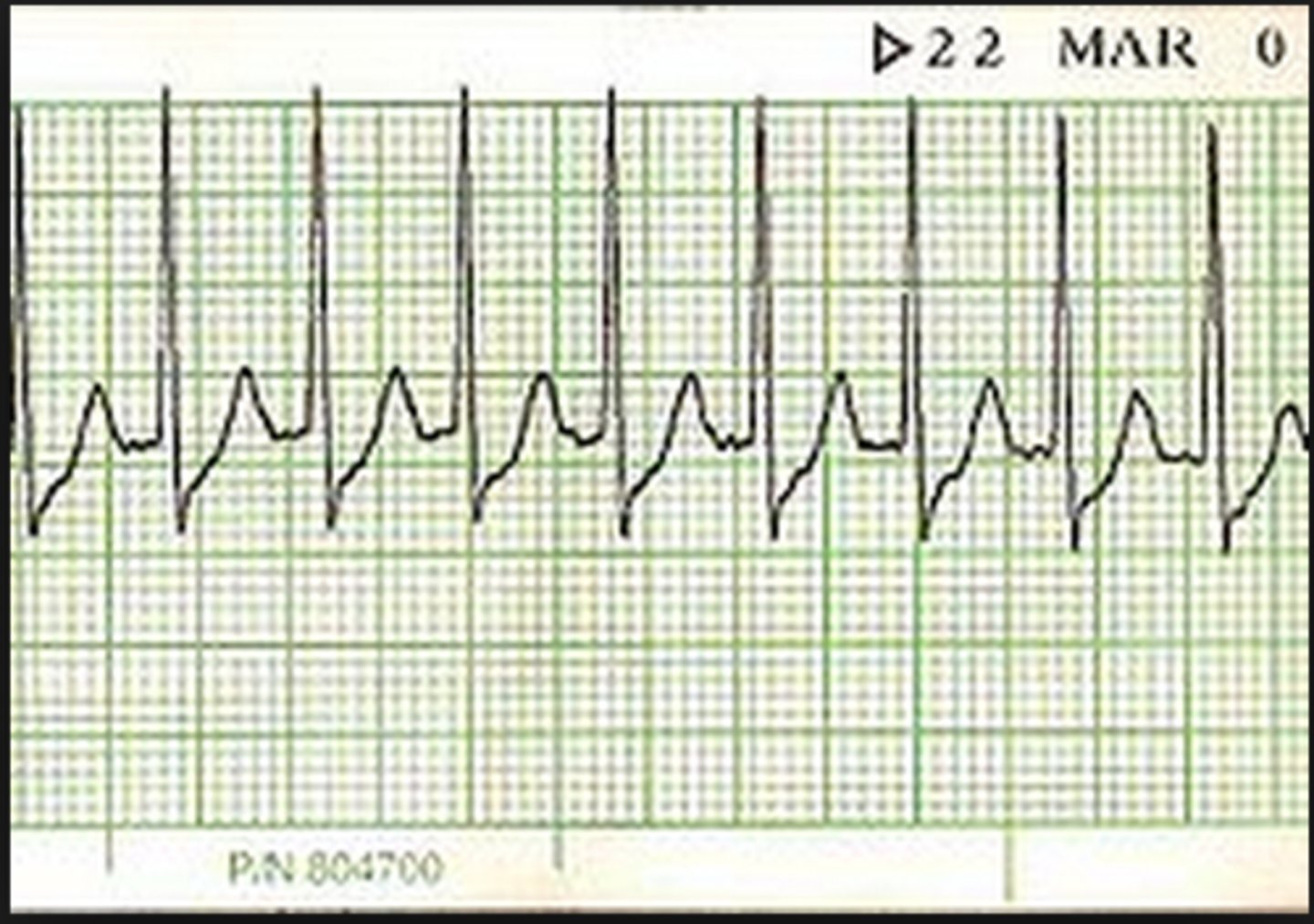
Treatment for AV node reentry tachycardia (AVNRT)
-vagal maneuvers (slows conduction through AV node)
-adenosine 6mg, second dose 12mg (blocks AV node)
-synchronized cardioversion 50-100J
Carotid massage
-common vagal maneuver
-check for carotid bruits or history for known carotid artery disease
-lay pt supine, extend neck and rotate head away
-palpate carotid artery at angle of jaw, apply pressure for 10-15s
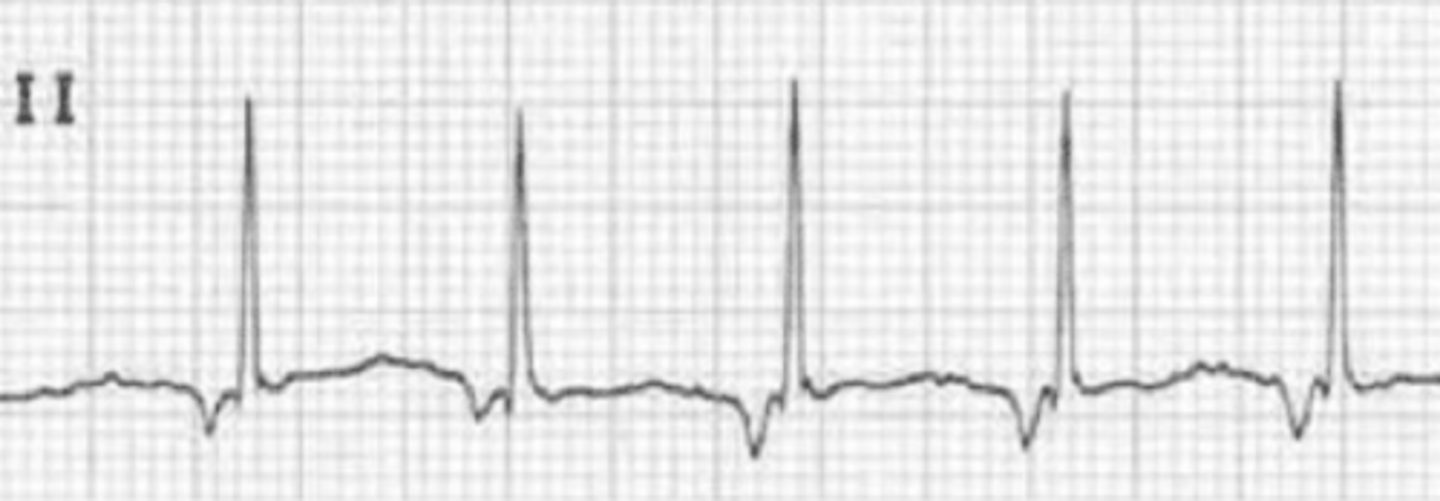
Atrial flutter
-P waves- characteristic "sawtooth" pattern or flutter waves (F waves) (most prominent in leads II and III
-Narrow QRS
-Multiple Ps: 1 QRS
-depends on degree of AV block
-regular rhythm
-250-350bpm for atrial rate, ventricular rate is 1/2, 1/3, or 1/4
-origin most commonly, single reentry circuit along annulus of tricuspid valve
-uncommon arrhythmia
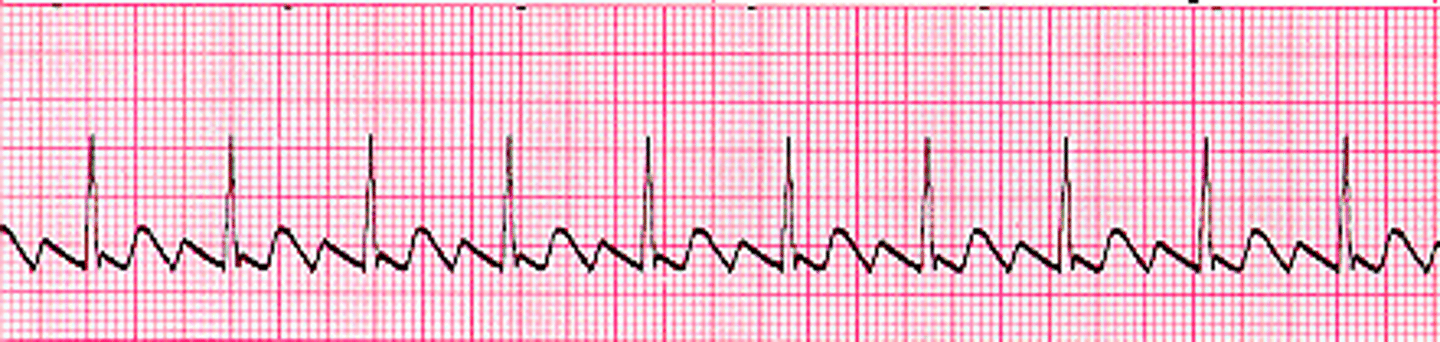
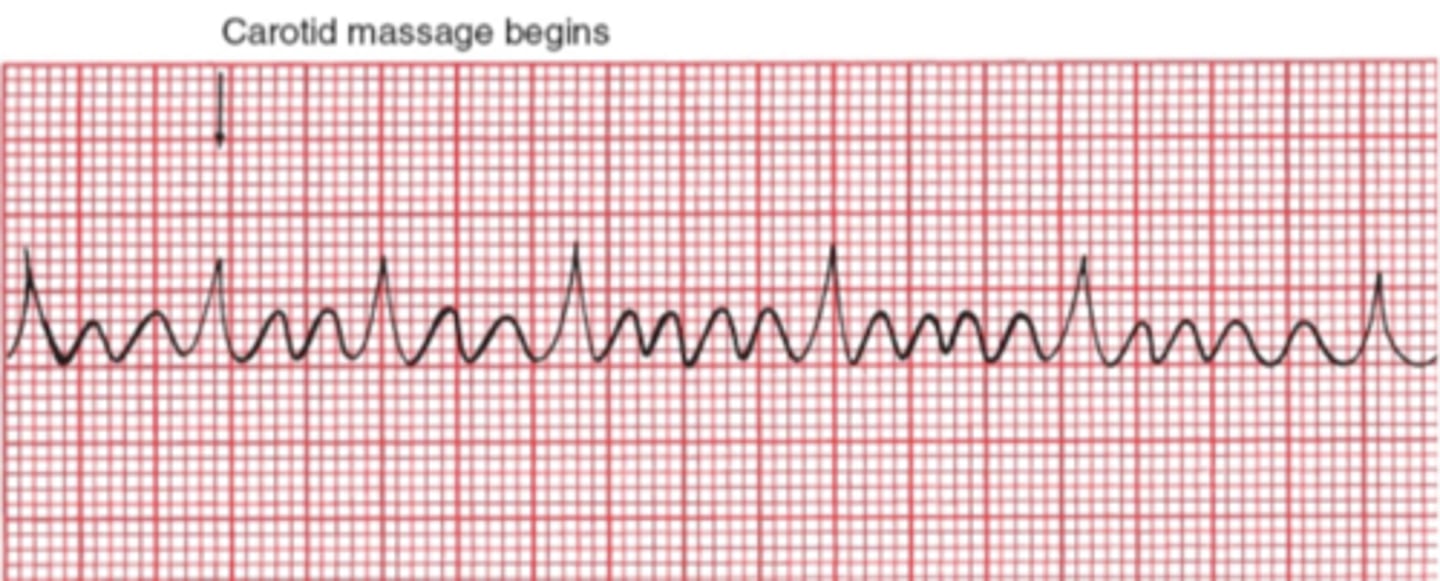
Atrial flutter AV block
-AV node cannot handle the extraordinary number of atrial impulses
-2:1 block most common
-carotid massage might increase the degree of the block (does not terminate rhythm)
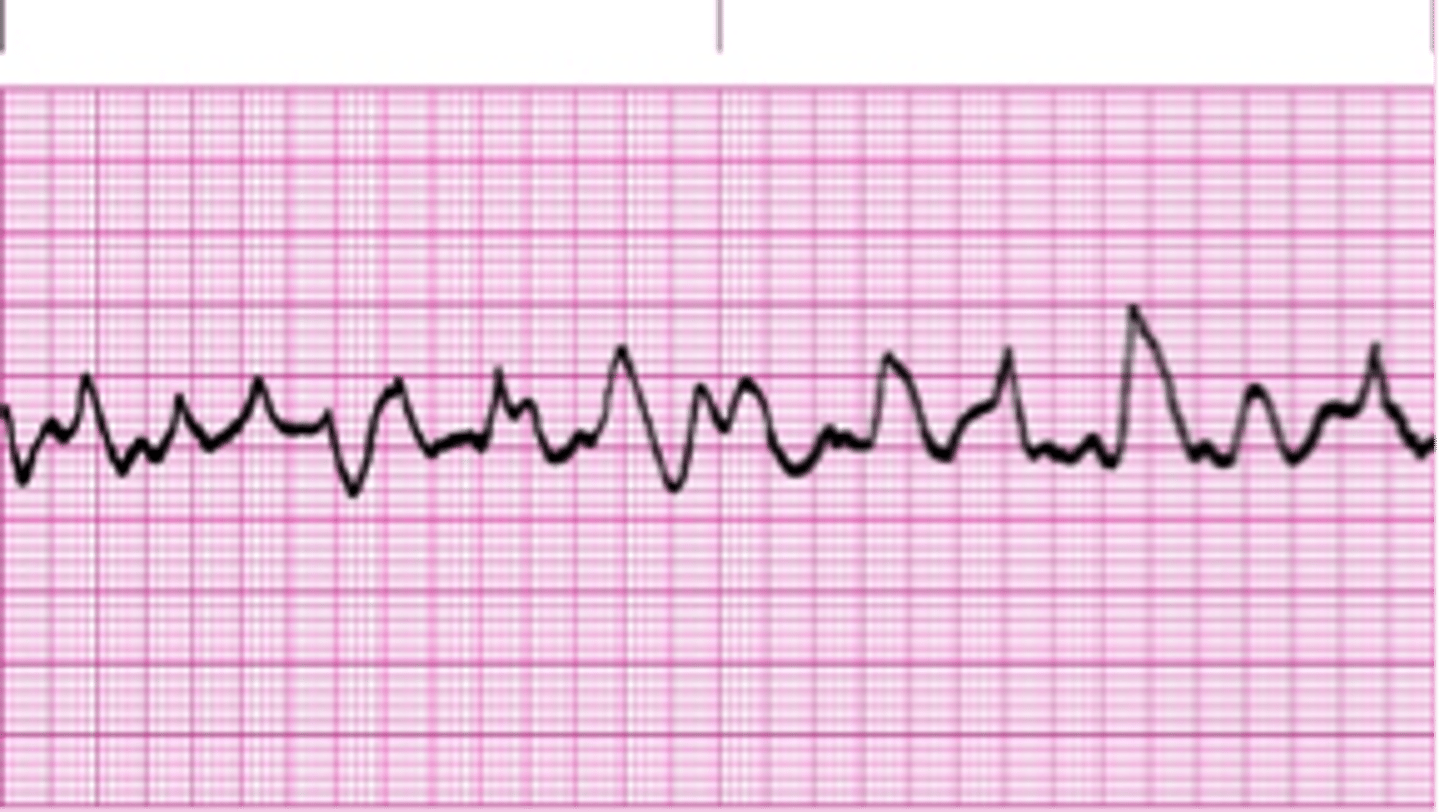
Atrial fibrillation
-P waves absent
-narrow QRS
-P:QRS unrelated/ variable
-irregularly irregular
-chaotic atrial activity 500 bpm (loss of atrial kick)
-origin: multiple tiny reentrant circuits in atria
-most common sustained arrhythmia
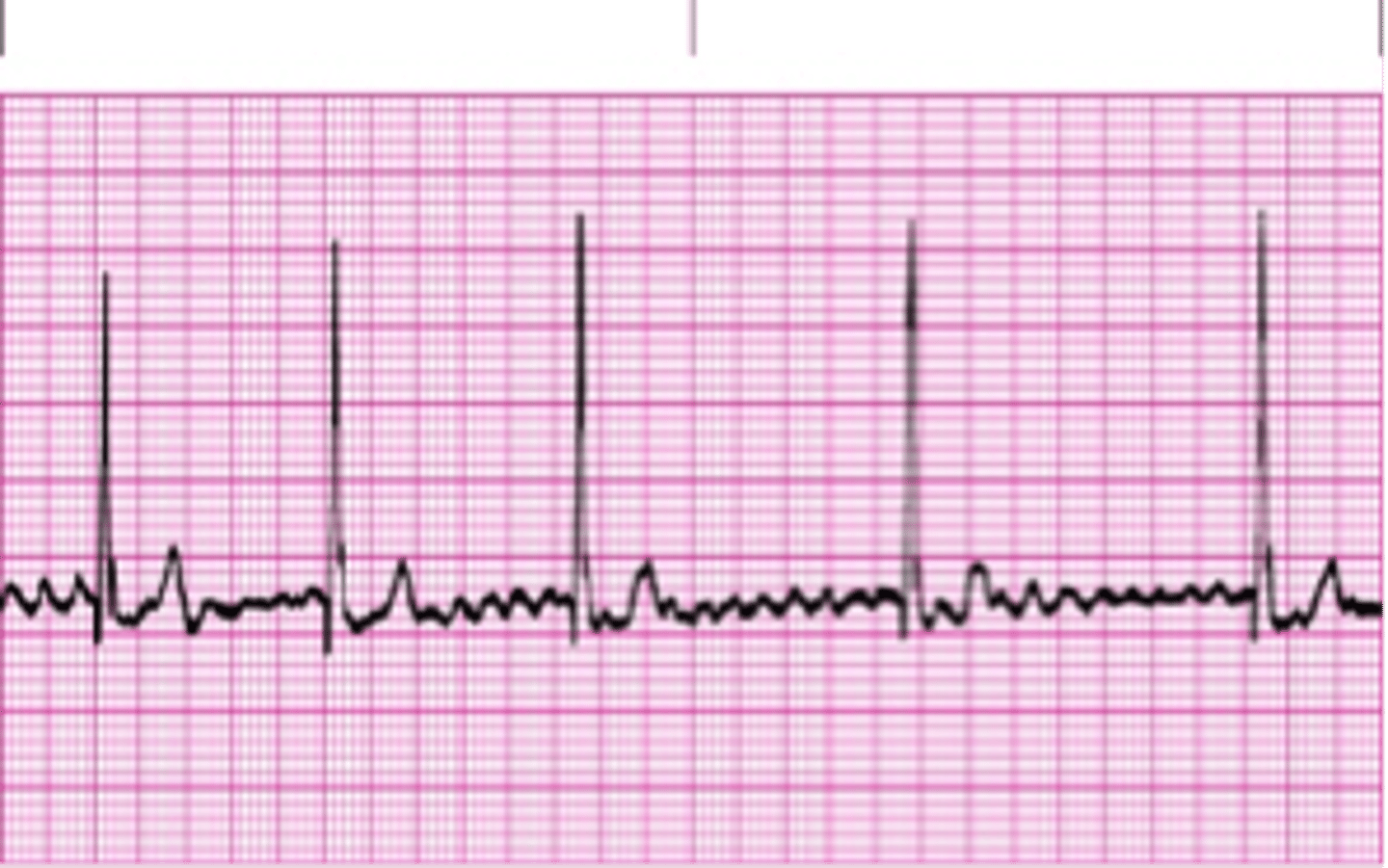
Atrial fibrillation
-risk factors: elderly, OSA, HTN, obesity, and alcoholism
-symptoms: angina, SOB, dizziness
-treatment:
-rate control: B blockers or Ca channel blockers in addition to an anticoagulant
-rhythm control: antiarrhythmic meds, catheter ablation, cardioversion
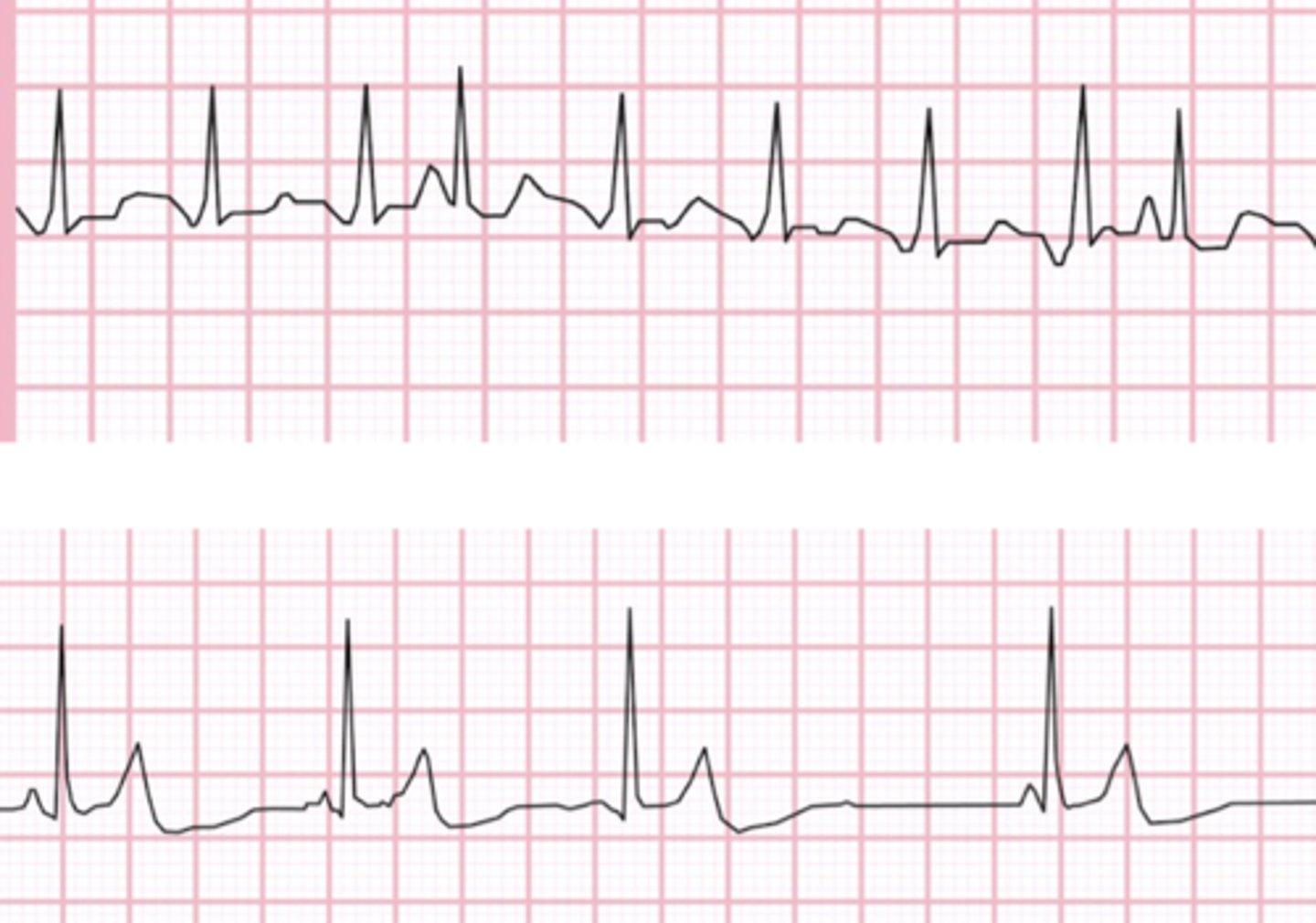
Multifocal atrial tachycardia (MAT)
-P waves present (varying morphology)
-need > 3 different P wave morphology to diagnose
-narrow QRS
-1:1 P:QRS
-varying irregular PR intervals
-rate: 100-200bpm
-<100bpm- wandering pacemaker
-origin: multiple sites in atria
-common in pts with severe lung disease
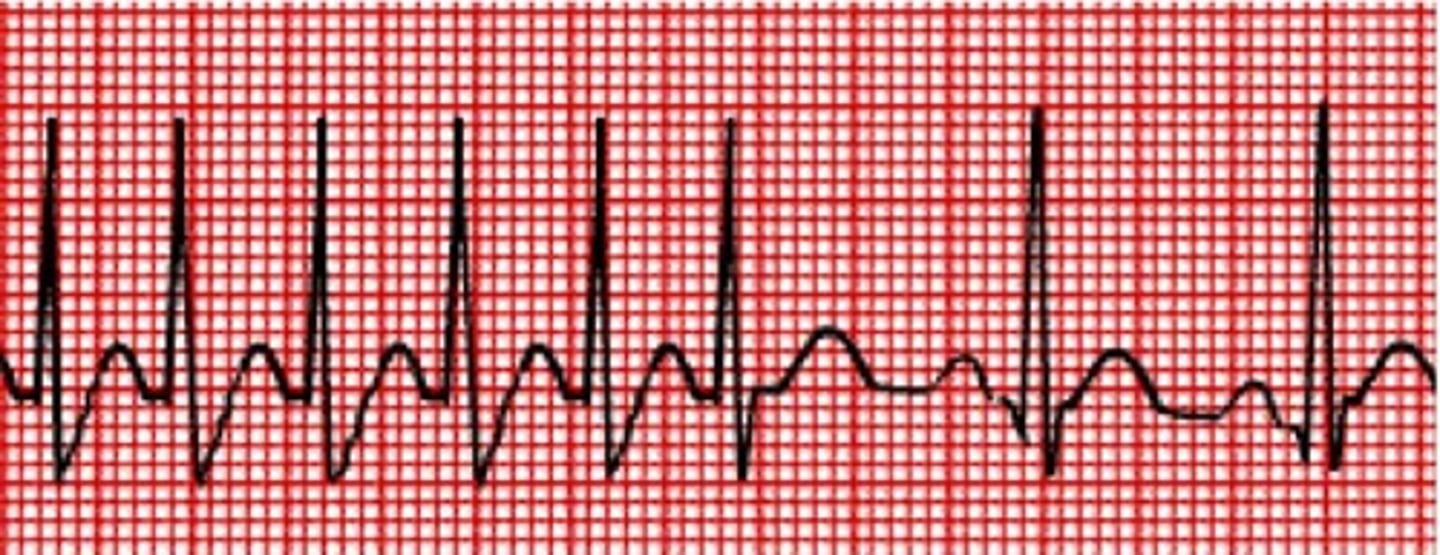
Paroxysmal atrial tachycardia (PAT)
-P waves normal
-narrow QRS
-1:1 P:QRS
-regular rhythm (warm up and cool down periods)
-rate: 100-200 bpm
-origin: enhanced automaticity of ectopic focus in atria
-caused by healthy hearts and digitalis toxicity
-CAROTID MASSAGE HAS NO EFFECT
Types of ventricular arrhythmias
-premature ventricular contractions (PVCs)
-ventricular tachycardia
-ventricular fibrillation
-accelerated idioventricular rhythm
-torsades de pointes
Premature ventricular contractions (PVCs)
-most common ventricular arrhythmia
-typically occur randomly
-origin: ventricular myocardium
-wide abnormal QRS (>0.12s)
-no P waves, sometimes retrograde
-usually followed by prolonged compensatory pause before next beat (>3 is considered VT)
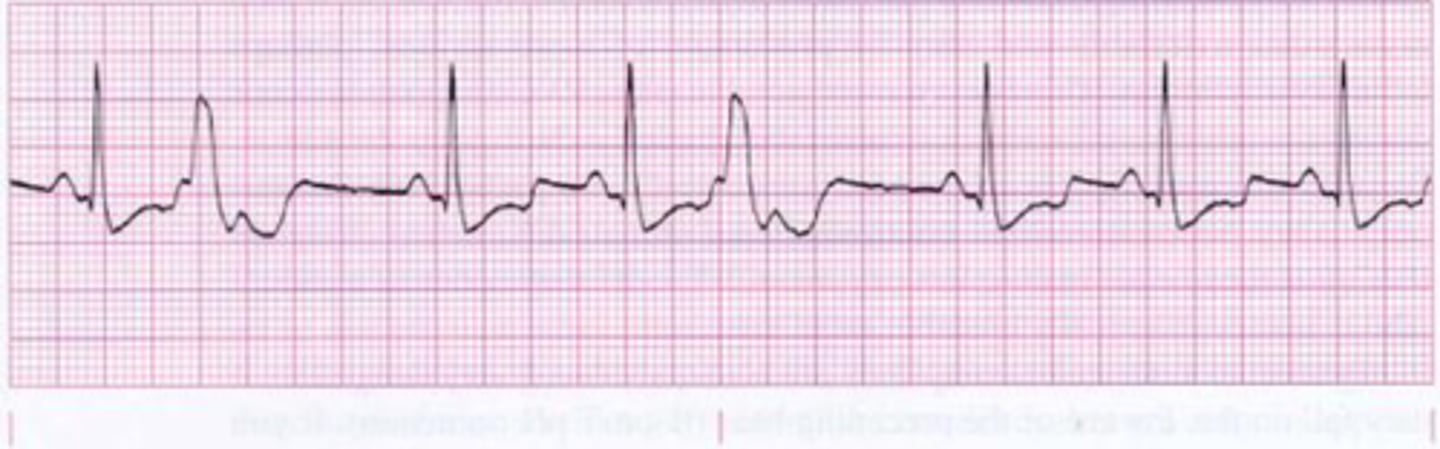
Bigeminy
Alternating normal and PVC
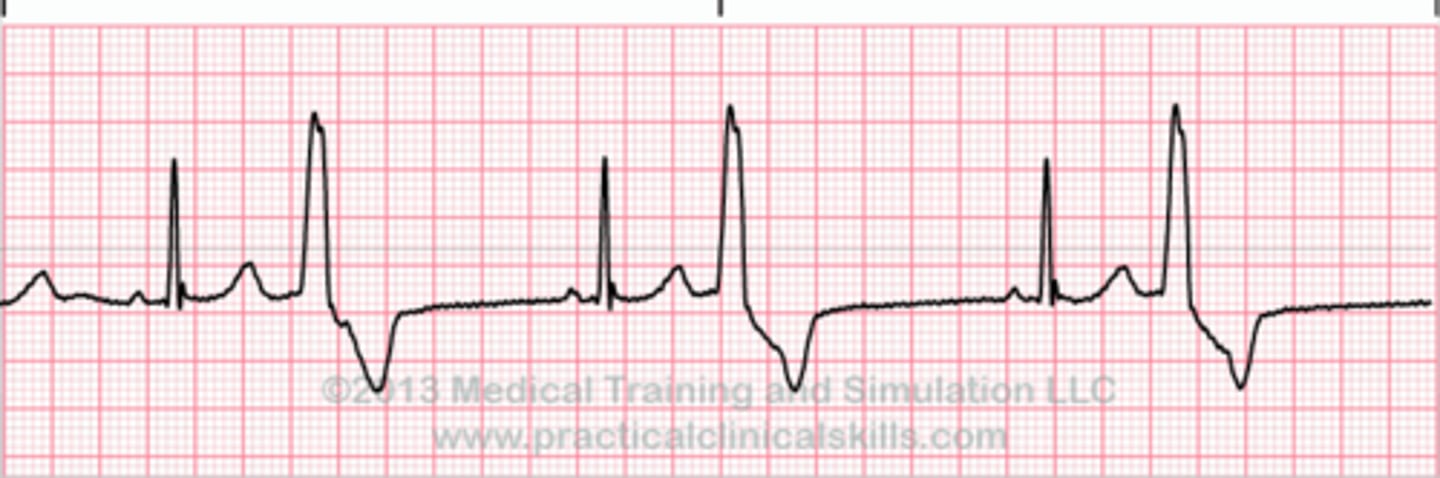
Trigeminy
PVC occurs every THIRD beat
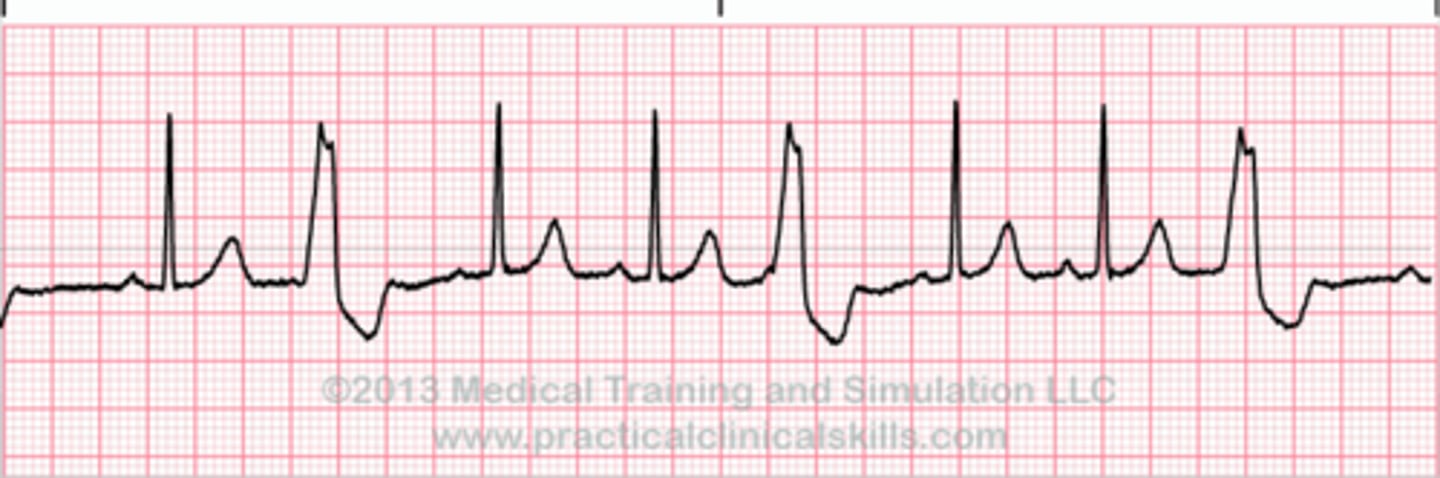
Rules of malignancy
-frequent PVCs
-runs of consecutive PVCs
-multiform PVCs
-R on T- PVCs falling on T wave, a vulnerable period in cardiac cycle, my percipitate VT
-PVCs during an acute MI
Ventricular tachycardia
-P wave absent
-wide QRS
-P:QRS n/a
-regular rhythm
-rate: 120-200bpm
-origin: ventricles
-scarred myocardium provides reentrant track (NO RESPONSE ON CAROTID MASSAGE)
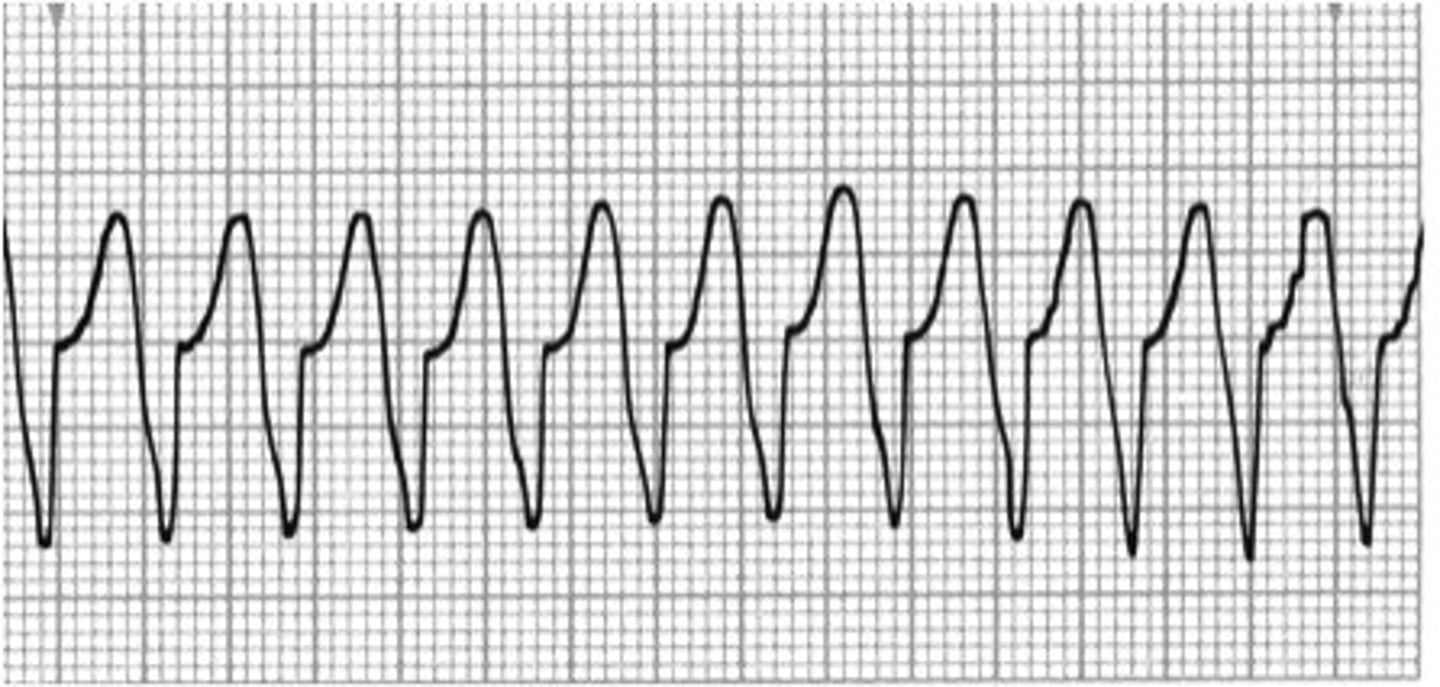
CO and coronary perfusion
Sustained VT severely compromises what two things?
Treatment for VT
Acute-
ACLS with pulse (amiodarone, lidocaine, and procainamide)
ACLS without pulse (defibrillation and CPR)
Chronic-
Antiarrhythmic drugs and catheter ablation
Ventricular fibrillation (VF)
-p waves absent
-QRS absent
-P:QRS n/a
-spasmodic (coarse) or gentle undulation (fine) of ECG tracing
-seen almost solely in dying hearts
-most frequently encountered arrhythmia in sudden death
-often preceded by VT
-need immediate CPR and defibrillation
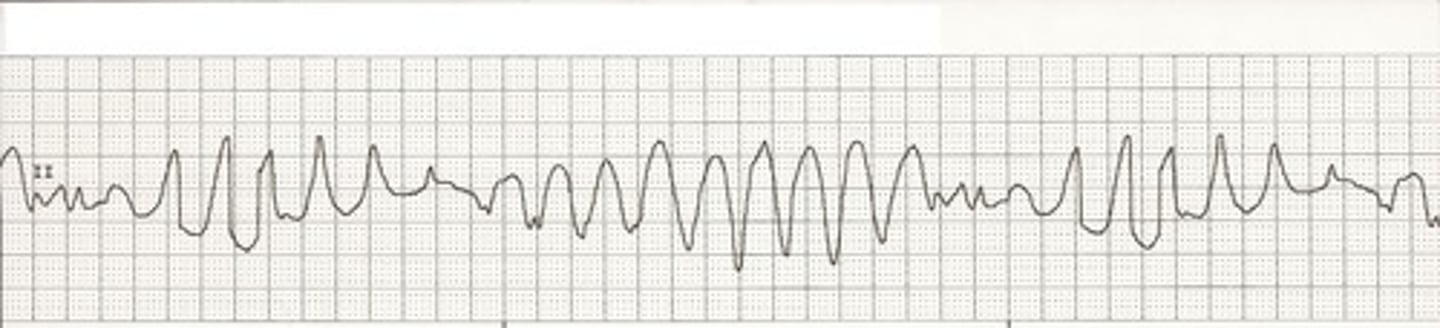
Torsade de Pointes
-twisting of the points
-outline looks like a party streamer
-P wave absent
-wide and polymorphic QRS
-associated with prolonged QT interval (QTc is associated with prolonged ventricular repolarization)
-caused by HypoCa2+, HypoMg2+, and HypoK+
-PVC falling during the QTI initiates this
-long QT syndrome
-treatment: magnesium
Supraventricular
Which arrhythmias are associated with a narrow QRS complex?
-may terminate with carotid massage
-cannon A and fusion beats are not seen
Ventricular
Which arrhythmias are associated with a wide QRS complex?
-no response to carotid massage
-may see cannon A waves and fusion beats
Bundle branch block and aberrant conduction
What two cases cause supraventricular origin arrhythmias to result in a wide QRS? These may terminate with carotid massage.
Cannon A waves
Seen in ventricular tachycardia
-occurs when atria contract against closed mitral/ tricuspid valves
Fusion beats
Seen in ventricular tachycardia
-atrial depolarization slips through AV node, results in QRS morphology that looks part supraventricular/ ventricular