Biology: A 4.1 (SL) Evolution
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Evolution
change in heritable characteristics
characteristics of population are changing over time
must be heritable not acquired (traits that are inherited by offspring from parents)
Theory of Evolution
Charles Darwin - by natural selection
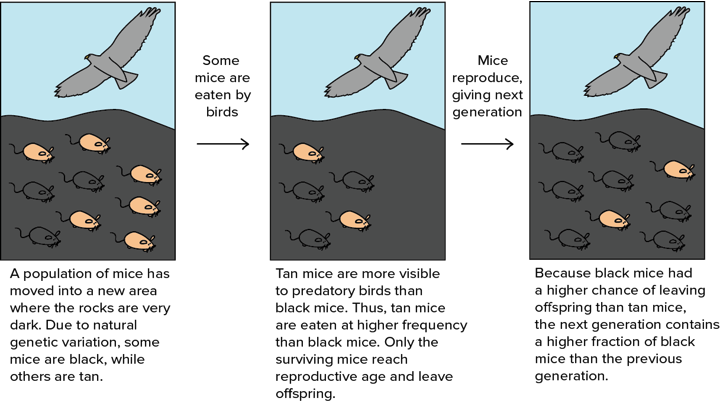
Selection Pressures (Darwin)
causes evolution & variation within a population
—> enables organisms that are better adapted to the environment to survive and pass on this advantage to future generations
Selection Pressures (Darwin) - EXAMPLE
Darwin vs. Lamarck Theories
Lamarck - Evolution by Transformation
(ancestral giraffes stretching their neck for food over time)
Darwin - Evolution by Descent w/ Modification (inheritance/selection pressures/adaptation)
Evidence for Evolution
molecular evidence from DNA, RNA, or amino acid alignment studies
comparative anatomy & morphology using homologous structures
evidence from fossil findings
evidence from selective breeding
Evidence for Evolution - Base DNA/RNA Sequences
evolution occurs
comparing base sequences of same gene in different species —> potential evolutionary relationships
Evidence for Evolution - Base DNA/RNA Sequences (EXAMPLE)
comparing gene sequences which control eye-development (Pax6) in different species
—> conclusion about evolutionary development of vision can be made
Pax Gene - responsible for eye development genes of different animal lineages (evolved from 500+ million years ago)
as descendant lineages evolved, basic eye-building gene was modified in different ways in different lineages —> rise to diversity in modern animals
Selective Breeding
form of deliberate selection in which humans actively choose which traits should be passed onto offspring
involves choosing parents w/ particular characteristics to breed and produce offspring —> w/ more desirable characteristics
continuous removal of progeny (descendants) - showing less-desired features generation-by- generation —> leads to genetic variation
Selective Breeding - EXAMPLE 1
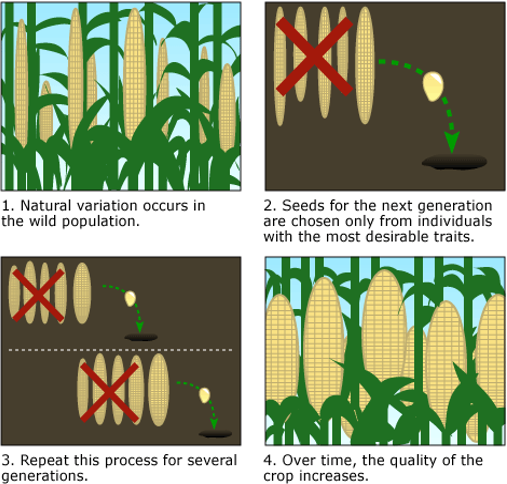
Selective Breeding - EXAMPLE 2
Tassels & seeds of a wild grass (Teosinte) became male tassels and female ears of modern corn —> selected for
stalk
seed size
nutrient
oil content
color
suppression of branching from the stalk resulted in a lower # of ears per plant —> allows each ear to grow larger
Selective Breeding - EXAMPLE 3
modern breeds of domesticated livestock —> differ from animal of origin
egg-laying hens increased MASSIVELY in size
dog breeds developed by artificial selection —> Grey Wolves (40,000 years ago)
most breeds related to wild species - can still interbreed
Homologous Structures - Divergent Evolution
similar anatomy but carry out different functions
developed from COMMON ANCESTOR —> DIVERGENT EVOLUTION
Convergent Evolution
analogous structures that have similar function but different origin
NO COMMON ANCESTOR

Homologous Structures - EXAMPLE
Limbs of Vertebrates - arms, forelegs, wings & fins are similar in anatomy (similar bone structure) —> indicator of having evolved from a common ancestor (divergent evolution)
may have different functions/purposes - similar design
due to different selection pressures (adaptive radiation)
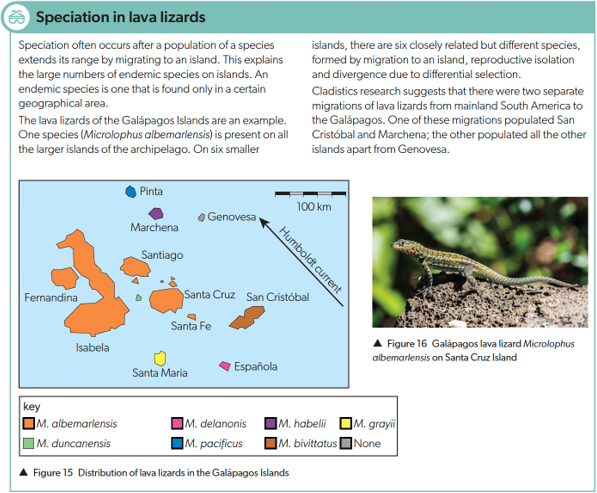
Adaptive Radiation
process of diversifying into a range of different species from a common ancestor
Lava Lizard - on main islands of Galapagos same species can be found
—> 6 smaller islands are closely related but different species found
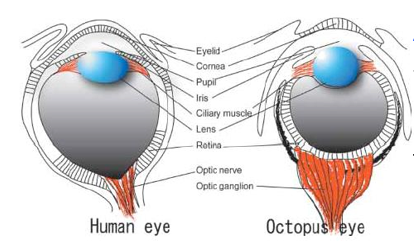
Analogous Structures
similar form & function
NOT developed from common ancestor
different evolutionary origins
—> octopus eye vs. human eye
—> lady bugs vs. birds
Morphology
form & structure of organisms
(less reliable for identifying evidence vs. base sequences)
Speciation 1
species become different after being separated from each other for an extended period of time
each species is adapting to slightly different conditions
Natural Selection - will allow for them to develop in 2 different ways until they become recognizably different
—> (Finches on Galapagos Islands)
DBQ
Roles of Reproductive Isolation in Speciation
Speciation - formation of a new species of by splitting an existing one
Reproductive Isolation -
Abrupt Speciation