Module 9: Carboxylic Acids
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Carboxylic acids take their names from the alkane that contains the same number of carbons as the longest continuous chain that contains the _____. The
-e ending is replaced by -oic acid. Numbering begins at the carbon of the ____ gorup.
COOH, COOH
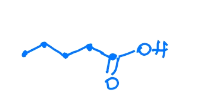
What is the name of this molecule?
pentanoic acid
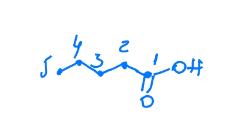
What is the name of this molecule?
3-methylpentanoic acid
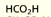
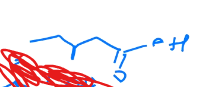
What are the systematic and common names for this molecule?
Systematic: methanoic acid
common: formic acid
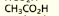
what are the systematic and common names of this molecule?
systematic: ethanoic acid
common name: acetic acid, also written as CH3COOH
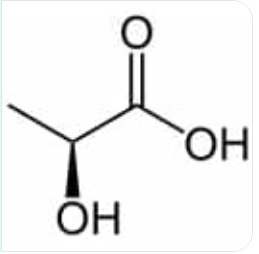
what are the systematic and common names of this molecule? also written as CH3C(OH)HCO2H
systematic: 2-Hydroxypropanoic acid
common: lactic acid
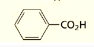
what are the systematic and common names of this molecule?
systematic: Benzenecarboxylic acid
common: Benzoic acid
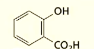
what are the systematic and common names of this molecule?
systematic: o-Hydroxybenzenecarboxylic acid
common: Salicylic acid
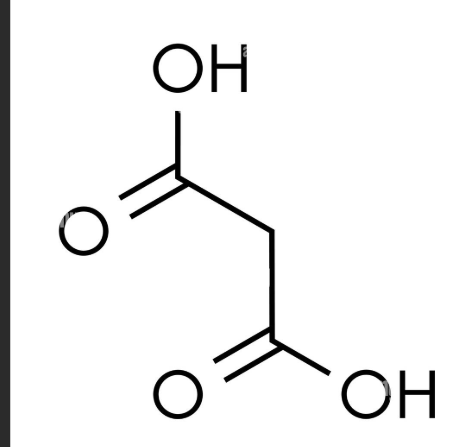
what are the systematic and common names of this molecule? also written as HO2CCH2CO2H
systematic: propanedioic acid
common: Malonic acid
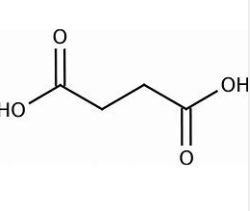
what are the systematic and common names of this molecule? also written as HO2CCH2CH2CO2H
systematic: butanedioic acid
common: succinic acid
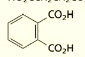
what are the systematic and common names of this molecule?
systematic: 1,2-Benzenedicarboxylic acid
common: Pthalic acid
The carbon of a carboxylic acid group has what kind of geometry? what is the hydridization of the carbon?
trigonal planar, Csp²
- Carboxylic acids have higher boiling and melting points than alcohols due to ____.
- more hydrogen bonding = ____ melting/boiling points.
- Carboxylic acids are more acidic than _____.
- higher electronegativity = more ____ effect = more ___
- more electron withdrawing groups are favored to increase ____
hydrogen bonding
higher
alcohols
inductive, acidity
acidity
Carboxylic acids are more acidic than alcohols due to stabilization by _____.
resonance structures
more stable conjugate base means the base is ____ and more ___ meaning its conjugate acid is ____.
weaker, stable, stronger
The shorter the carbon chain, the ____ the acidity.
higher
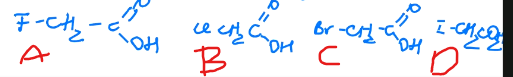
rank these in terms of decreasing acidity
A > B > C > D, the opposite is true for hydrocarbons

Rank these in order of decreasing acidity
HI > HBr > HCl > HF, comparing by size and polarizability
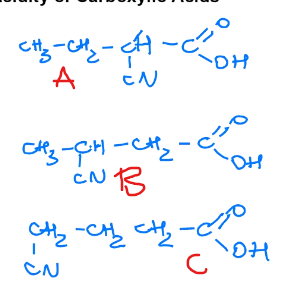
Rank these in terms of decreasing acidity
A > B > C
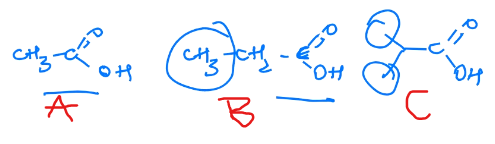
Rank these in terms of decreasing acidity
A > B > C, the closer the electronegative element is, the more acidic the molecule will be
The more alkyl groups present, the _____ acidic the molecule will.
less
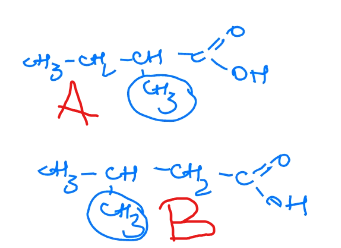
Rank these in terms of decreasing acidity.
B > A
To increase acidity of carboxylic acids, add more electron _____groups ____ to the CO2H.
withdrawing, closer
to decrease acidity, add more electron _____ groups ____ to the carboxylic group.
donating, closer
alkyl groups are electron ____ groups and make carboxylic acids ___ acidic.
donating, less

rank these in terms of decreasing acidity.
C > A > B