germany all chapters
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
when did hitler join the workers party and what changes were made?
1919, became leader in 1920, increased 1100 memberships, set up the SA soliders, renamed nazi party, 25 point programme.
when did the munich putch happen and some facts?
november 1923
· intention to overthrow weimar replublic
· hitler tried to convinve bavarian leaders with same view (Lossow and Khar)
· they betrayed nazis, so with ludendorff and supporters (2000) they marched into munich
outcomes of this failure / success (munich putch)
Nazis gained popularity, hitler could write mein kampf in prison, 14 dead nazis
when did the Nazi party become reorganized after the munich putch?
february 1925
new reorganizations in 1925?
· 4000 supporters attended munich beer hall meeting (where headquarters)
· SS bodyguards
· goebells = anti jewish propaganda
· Hitler youth
how many seats did Nazi get in 1924 and 1928?
32 and 12
when did the wall street crash happen and what did it do?
october 1929, raising 6 million people in unemployment
· coalitions fell in the reishtag
what did the Nazis provide after crash?
scapegoats, claimed it was due to jews and weimar and communists
short leaderships after crash in germany?
· BRUNING (SDP)= used article 48, became chancellor, raised taxes and cut unemployment benefits
· MULLER (centre)= resigned and taxes were raised.
crash effect on germans?

1930 elections results
Nazis = 107
Communism = 77
why was Hitler able to become chancellor?
· HIS APPEAL = strong leader, persuasive, good for businessmen and diff groups
· PROPAGANDA = nationalize industry, new tech, parades, 8 newspapers, posters
· ROLE OF SA = violence, 400,000 members, discipline in voting stations
results of 1932 elections
Nazi now biggest party, 203 seats
who removed bruning and chancellor and how? 1932
Von shleicher, army general, with coalition of army, land owners and industrialists and convinced Hindenburg the president
what happened in von schleichers rule?
underestimated hitler, appointed von papen as head of coalition, and wanted to take control
what happened in november after von papen appointed?
coalition was weak, people wanted hitler (business men and 190 seats) to be chancellor, and von papen resigned. hindenburg made von schleicher chancellor.
after…….
von schleisher’s plans to have a military dictatorship were leaked, so von papen (underestimating hitler) convinced hindenburg to make hitler chancellor.
when did hitler become chancellor?
january 30 of 1933
limitations of Hitlers chancellorcy?
· hindenburg kept presidential powers
· only 2 nazis in the cabinet of twelve
· only 1/3 of reishtag nazis
what were some opinions in all this start?
· people were happy that extremist parties were limited
·many blamed weimars for downfall and wated hitler to end it
· underestimation of hitler, but people feared him.
when did the reischag fire happen
27 february 1933
name of the ‘culprit’ of the fire
communist van der lubbe
in 1933, who was the new nazi chief of the police?
goering
consequences of fire?
· 4000 communists arrested
·decree for protection of people (search homes and arrest without trial)
march 1933 election results
nazis had 288 seats, but still not majority. hitler wanted a new law to get unlimited powers.
measures hitler established in 1933
huge propaganda, 50000 new SA members, anti hitler newspapers closed, funds from industrialists.
what was the enabling act?
hitler passed this act, banning communists and nationalist parties, and won support of centre party. gained majority with 444 seats. this was the end of democracy.
measures of nazi revolution 1933-1934
local governments, first each one had nazi majority, then abolished completely.
trade unions, arrested their leaders and created german’s worker front
other parties, all parties banned except the nazi party.
when did the night of the long knives happen?
30 june 1934, hitler wanted to reduce SA because they were embarassing and becoming too powerful (2 million members)
what happened on the night of tlk
hitler worked with Himmler, head of the SS
hitler saw Rohm as a rival, also homosexual.
90 exeecuted and 200 arrested
hitler wanted to rearm germany with 100000 soldiers, but SA was a problem.
when did hindenburg die and what did it mean?
1934 august, hitler combined forces and became the fuhrer.
what was the name of this new era?
the third reich.
an army oath was made to hitler, how many people agreed
plebescite vote on this showed 90% agreed.
when was the first ever concentration camp established?
1933.
what did hitlers totalitarian rule include at start
· control of = radio, tv, books, church, workers, police
· indoctrination and censorship
· police state = no opposition to government
· gestapo = secret nazi police.
TERROR!!!!
how many SS members were dismissed from 1933 to 1935
by himmler, 60000 dismissed for being gay, alcoholics etc.
what did the gestapo do?
reported suspicious behaiviour, no jokes about hitler, law of malicious gossip, and tortured people.
examples of censorship in nazi germany
· reich press chamber was nazi newspaper and others shut down
· reich radio only company in 1934
· banned communist jewish anti nazi authors
· reich chamber of commerce, aritists writers had to join.
hitler hated modern art like jazz so banned
examples of propaganda hitler spread (1933 onwards)
· aryan race supremacy
· against communism
· owners of shops had radios there
· parades and rallies
· german folk art
what was the nazi youth
children spent weekends and evenings there, discussed political hitler, racial purity and to get de influenced from parents ideas.
by 1939, how many people took part in nazi youth
8 million children
facts about the education system
· re written textbooks for nazi benefits
· geography taught lebensarum
· race studies implemented
in the 1920, how many women were part of reishctag
10% of reistchag was women
what was the law of encouragment of marriage
a loan given to married couples only if the woman gave up her job
what were women taught for?
· childcare and stay home
· abortion and contraception banned
· germans women enterprise for household skills
how did things change for women drastically?
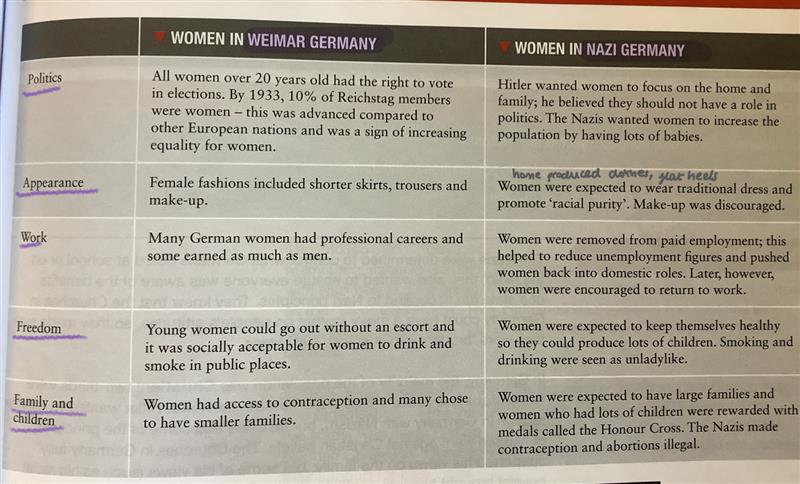
what was the percent of women working in 1939 compared to 1933
50% more because men had to fight in the army
statistic about the church in the 1930s
majority was christian 2/3 protestant and 1/3 roman catholic. hitler wanted nazism to be the religion
stats about catholic church.
1933 concordat - church wouldnt be in political affairs.
same family views
hitler broke agreement because he wanted to be supreme figure, and deinfluence children from catholic schools
propaganda against church (corrpuption) and banned symbols
1937 - all catholic youth and schools banned, and arrested neglective priests
stats about protestant church
many were nationalists
1933 = protestant church -} reich church with nazi ludwig muller bishop
18 pastors lost jobs for contradicting
1934 - confessional church by nienmaller and hoenffeler, 50000 members and rival
hundreds sent to concentration camps
by the end of 1930s and 1939, churches…
insignificant, only 5% of germans god believers
what was the name of the groups that were seen as inferior?
untermenchen - jews, gays, delinquents, tramps, people with chronic ilnesses
1933 - sterelization law stats
for people with ilnesses and tramps - 700000 people
from which year were gays, jews, tramps sent to concentration camps
1936
when was intermarriage banned?
1935
what happened to people with mental ilnesses
steralized, then killed (70,000 died)
what percent of germans were jewish
only 1%
when were jews banned from government working and boycotted and when were jews banned from public spaces
1933 and 1935
reich law of citizenship
only people with german blood, and for jews, no voting or passport
1938 jewish persecution…
possesions registered, identity cards, and jews only worked on jews
how many jews fled the country in 1939?
2/3 jews, but in 1941 banned, and 160000 unable to leave
kristallnact
german offical murdered by a jew, so hitler set chaos, with goebbels propaganda
kristallnact stats
90 and 30000 jews killed and arrested.
jewish homes, synagogues attacked
fined jews 1 billion retenmarks because property was from german landlords
in what years kindertransport, 10000 refugee children
1938-1940
strategies to reduce unemployment - autarky, self sufficiency

from 1932 to 1938, how did unemployment change
from 6 million to half a million
how many marks was germany in debt for (self sufficiency)
40 billion
what was invisible unemployment 1930s
women or jews not included in figures, temporary emplyment counted as full, wages raised and 10% more working hours.
when did germany invade poland and how many jews captured
1939, 3 million.
when were ghettos introduced and what were they
1941, walled off areas jews were forced to live in, with diseases, crammed, dirty, 4000 dead per month.
when were death squads and einstazgruppen introduced
1941, orders to put jewish to death, over 1.2 million in soviet union killed.
how many jews sent to concentration camps in 1941
250000
when was the final solution official?
1942, turned concentration camps into extermination.
what was the holocaust
mass extermination genocide of jews, tried to keep secret.
when did warsaw uprising happen and stats
1934, 56000 arrested and 7000 shot.
in 1944-1945, it was clear germany was losing, what did hitler decide?
importance killing jews = winning war
where and how many children were evacuated
1942, to major cities and bvaria, 2.5 million children.
rationing stats on homefront
food stamps given, winter 1939-40 incredibly bad, cut rations to 40g meat a day and ½ loaf a day.
3 million civilians moved into other cities for refuge and increased starvation
why did germany do bad in 1941 operation barbarossa
underestimated cold conditions, 2 million died and retreated a lot.
when was total war implemented
1934, everyone and everyhting fully commited
measures from total war

how many people from occupied countries and prisoners were working by 1944
7 million
changing role of women

how many civilians died in hamburg from bombing
42600 and 600000+ in germany home front
what was women’s psycological impact?
10000s died from suicide and attack, scared of soviets raping them and sad from dead husbands
allied bombing stats

who opposed the nazis and how
communists = underground movements and newspapers
kreisau circle = members of german lawyers and politicians
church = against sterelization and nazi education
there was a climate of fear
opposing nazi groups
swing youth
elderweiss pirates
white rose group
july bomb plot
swing youth
middle class germans who bought back banned music, like jazz and swing, then members to concentration camps
elderweiss pirates
bullied hitler youth members, objected to training gave shelter to prisoners, stole food, bombed ammunition trains. bathel stink executed
who was in charge of 4 year plan economic
goering
white rose group
hanna and sophie roll, campaigned for jews, leaflets released, warned that nazis would loose, then executed
july bomb plot
army leaders ludwig beck, stauffenberg and goelder. 1944, took a bomb to hitler meeting, but hitler survived. they were executed, and more than 14000 plotters shot and arrested plus family and friends
when did the kaiser abdicate + facts
1918 november, went into exile to holland, blamed for german defeat, mad people
when was german republic set up and name and facts
november 1918, weimar and ebert as chancellor, then armstice was signed and people were called november criminals.
facts about 1919 weimar republic
82% of electorate voted new democracy, held in national assembly, ebert SDP got 40%, guraranteed freedom and equality.called reischagrepublic was of 18 individual states.
how did the republic work?
parliamentary democracy, people elect representatives. head of state president and head of government chancellor
what was ebert like?
kept state running smoothly, reasured industry leaders that the gov would not take control and promised to reduce working hours
what small oppositions? weimar
many country senior figures did not support many wanted kaiser to return
germany remained unstable (riots)
what small problems did germany have in weimar era
politically and economically divided
lack of commitment for powerful forces to work together
proportional representation - seats awarded depending on votes