Earth Materials Exam Two
1/141
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
142 Terms
Name three chemical analysis of minerals methods
wet chemistry, scanning electron microscope energy dispersive analysis, electron microprobe wave-length dispersive analysis
How is Wet Chemistry analysis completed?
mineral is grinded and physically separated, sample is dissolved in acid
what are the main parts of scanning electron microscope
electron gun, focusing lenses, sample chamber, detectors
what are the detectors in scanning electron microscope
secondary electrons, backscattered electrons, cathodoluminescence, electron backscattered detector, energy dispersive x-ray detector
what are the four ways an electron beam interacts with a sample
backscatter electrons, secondary electrons, x-rays, light (cathodoluminescence)
what happens with backscatter electrons
electrons bounce back, sensitive to density with denser samples being brighter
what happens with secondary electrons
interactions with valence electrons, sensitive to topography, generates 3D images
what happens with x-rays
electrons remove electrons from inner orbitals, electrons from higher orbitals fall in and x-ray is generated, wavelength and energy is quantized based on the energy levels of orbitals
what happens with cathodoluminescence
light is given off when bombarded with electrons
brightness depends on density with backscatter electron image. denser minerals are ___ and less dense are ___
bright, dark
elements with 1 peak are what kind of radiation
Ka
elements with 2 peaks are
Ka and KB
intensity of peak is proportional to what
amount present
Who created the Rowland Circle Geometry
Henry Augustus Rowland
with Rowland Circle, you can change the position of the crystal and detector to obtain a different ___
incident angle; to get a different element of interest
secondary electrons gives images of surface ___
topography
backscattered electrons gives images of
mean atomic number
calcium x-ray map
diffracting crystal is used to detect Ca Ka x-rays
cathodoluminescence image
a few elements emit visible light when bombarded with electrons. bright bands are a specific color and probably reflect relatively high dysprosium concentration
use WDS X-ray mapping to
collect elemental “maps” showing the distribution of an element within a crystal
if a “random” nucleus has a radius larger than r*, the nucleus will (grow/not grow)
grow
if a “random” nucleus has a radius smaller than r*, the nucleus will (grow/not grow)
not grow
what is overstepping
deltaG being slightly off of equilibrium; off of temperature=pressure
why is nucleation favored by large degrees of overstepping?
rate of nucleation depends on the amount of overstepping (affinity)
what are 3 ways to achieve overstepping
changing temperature and/or pressure, cooling below freezing curve, supersaturation of a vapor or liquid
What are the 4 main ways minerals can form?
solid-solid reactions, crystallization from a liquid, deposition from a vapor (no intermediate liquid), precipitation from a fluid such as H2O or CO2
what does polymorph mean
minerals in different forms with the same composition but different structures
what is polymorphic transformation/solid-solid reaction
when one polymorph transforms into another
what controls the conditions which a particular polymorph is stable?
temperature and pressure
name 3 polymorphs of SiO2
quartz (trigonal), tridymite (triclinic), cristobalite (tetragonal)
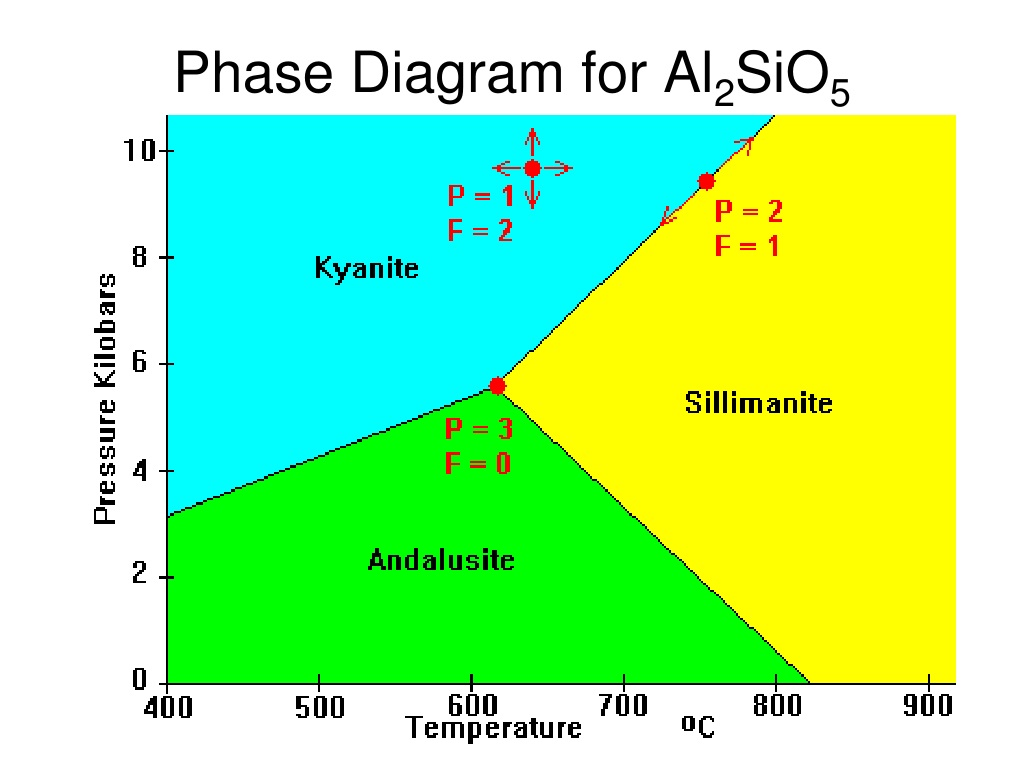
name 3 polymorphs of Al2SiO3
kyanite, sillimanite, andalusite
draw the Al2SiO3 phase diagram
what are the 3 energy states
unstable, stable, and metastable
what is Gibbs Free Energy
measure of chemical energy, all chemical systems tend naturally toward states of minimum free energy
At higher temperature, the phase with larger entropy (S) will have (higher/lower) G
lower
at higher pressure, the phase with the lower volume will have the (higher/lower) G
lower
smallest volume means (highest/lowest) pressure
highest
largest volume means (highest/lowest) pressure
lowest
largest entropy means (highest/lowest) temperature
highest
smallest entropy means (highest/lowest) temperature
lowest
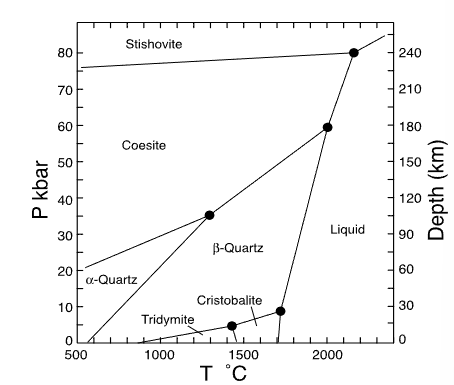
which mineral has the smallest volume?
stishovite
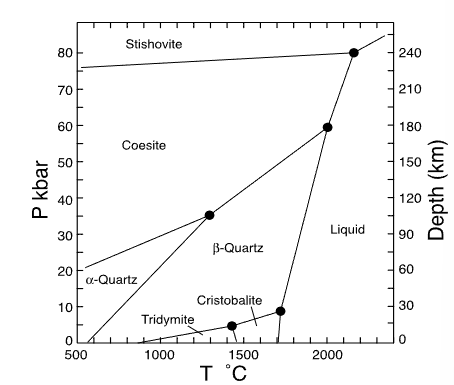
which mineral has the largest volume?
tridymite
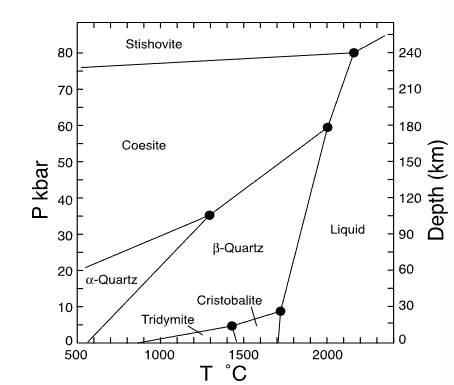
which mineral has the smallest entropy?
alpha quartz
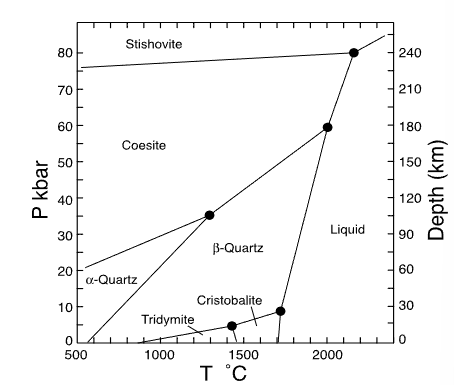
which mineral has the largest entropy?
liquid
what are the 2 polymorphs of CaCO3
aragonite and calcite
what are the 3 types of polymorphic transformations? with examples
reconstructive transformation (quartz to coesite, kyanite to sillimanite), displasive transformation (alpha quartz to beta quartz), order-disorder (sanidine to orthoclase to microcline)
give the mineral names of an example of solid-solid reaction involving more than one phase
albite, jadeite + quartz
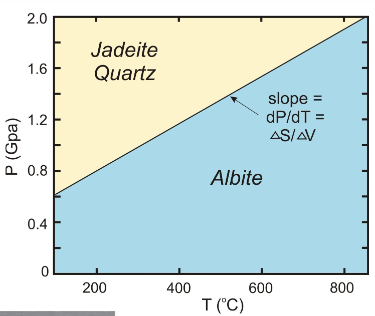
which indicates higher pressure?
jadeite + quartz
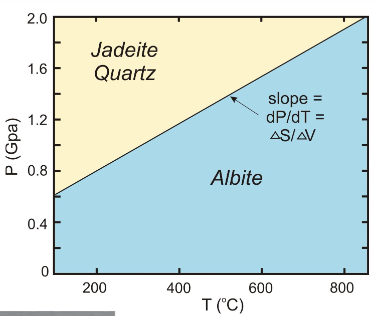
which has a smaller volume?
jadeite + quartz b/c the pressure is higher
what is nucelation
formation of new minerals
why do displasive and order-disorder transformation NOT require nucleation?
bonds stretch or shrink but do not break in displasive transformation (beta-quartz to alpha-quartz)
atosm order on different crystallographic sites in order-disorder (sanidine to orthoclase to microcline)
what are the five types of bonding found in minerals
ionic, covalent, hydrogen, metallic, van der waals
which is larger, O(2-) or Si(4+)
O(2-)
what are the 6 common coordination polyhedral found in minerals?
2 fold (linear), 3 fold (planar), 4 fold (tetrahedral), 6 fold (octahedral), 8 fold (cubic), 12 fold (dodecahedral)
what does Pauling’s first rule say about ionic radii of anions and cations?
Rc/Ra controls type of coordination for an anion-cation pair
who discovered X-rays
Wilhelm Rontegen
what is reflection
bouncing of waves
what is refraction
change in direction of waves
what is diffraction
waves spread out
when diffraction grating was too coarse to diffract x-rays, what was suggested
crystal lattice with smaller spacings
why are x-rays used in determining crystal structures
wave lengths are 0.01-10nm, similar to the atomic distances between layers in crystalline solids
what is the order in the electromagnetic spectrum
radio, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, x-rays, gamma rays
what happens in x-ray generation
incident electron ejects “inner shell” electron, an electron from higher-energy shell drops “down” to fill the vacated position
how are x-rays made
bombarding a material with electrons
what is the relationship between wavelength and energy of electromagnetic radiation
E = hv or E = hc/λ. E and λ are inversely proportional
what are the two ways waves interact and how
destructive waves cancel each other out and constructive waves add to each other
what is Bragg’s law and what is it used for
nλ = 2dsin
Bragg’s law gives the relationship between wavelength, d spacing of a set of planes in a crystal lattice, and the angle of incidence
it specifies the conditions where x-ray diffraction will occur
do x-rays have longer or shorter wavelength than visible light
shorter
do x-rays have longer or shorter wavelengths than ultraviolet light
shorter
what do peaks represent in power diffraction patterns
each peak corresponds to a specific d spacing of planes in a crystal lattice
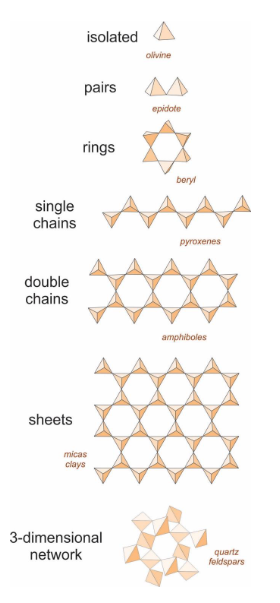
what are the 7 arrangements of SiO4 tetrahedra in silicate minerals and how are they linked together
isolated, pairs, rings, single chains, double chains, sheets, network
what happens in ionic bonding
one element gives up an electron and another element gains it
what happens in covalent bonding
electrons are shared
what happens in metallic bonding
valence electrons are given up and ionized and delocalized
what is the main characteristic of van der waal bonds and hydrogen bonds
they are very weak because of uneven charge distribution in the atoms
what are Pauling’s Rules
1) radius ratio principle
2) electrostatic valency principle
3) edge and face sharing are unstable
4) cations of high valence and low C.N. tend not to share anions with other cations
5) principle of parsimony
what is the Rowland Circle used for
to focus x-rays emitted from a sample for a single x-ray wavelength for chemical analysis
change the position of the crystal and detector to obtain a different theta angle
when a mineral is bombarded with electrons, what radiation does it give off
secondary electrons, back scattered electrons, and x-rays
why is scanning electron microscope (SEM) or electron microprobe (EMP) more useful than wet chemistry
wet chemistry requires a mineral separate, which might not be pure
wet chemistry makes a bulk analysis but the mineral might be zoned
wet chemistry is destructive (uses up all the material)
SEM and EMP are spot-sensitive, non-destructive, and can be used to determine zoning
what 2 related characteristics of x-rays are used to determine the composition of a mineral
wavelength and energy
what is a mole
unit of measurement for amount of substance, refers to the number of particles, amount of substance containing the same number of molecules
which has more “units of quantity” a mole of SiO2 or Al2O3
same moles because both equal 6.022×10^(23)
which has more “units of quantity” mole of SiO2 or mole of Si2O4
Si2O4 has more because it is double
what are the 3 major divisions of Earth structure
core, crust, mantle
what are the most abundant rock types in the crust
95% igneous and metamorphic rock
what is the average composition of the continental crust
oxygen, silicon, aluminum
what is the average composition of continental crust
granodiorite
what is the most abundant mineral in the crust
plagioclase, alkali feldspar, quartz
what is the most and second most abundant element in the crust
oxygen, then silicon
what are the three most abundant elements in the mantle
oxygen, silicon, magnesium
which are typically larger, anions or cations
anions
what is a coordination number
number of atoms bonded to a central atom
what are the feldspar polymorphs from disorder to order
sanidine, orthoclase, microcline
name the polymorphs of SiO2
alpha-quartz (low quartz)
beta-quartz (high quartz)
Tridymite
Cristobalite
Coesite
Stishovite
what are some examples of nucleation
rain forming in a cloud
ice forming on a pond
bubbles in your soda
differentiate homogenous vs heterogenous nucleation
homogenous is spontaneous in a clean environment, and is energetically more difficult
heterogenous is on top of an existing phase, and is energetically easier
what is meant by “overstepping”
measure of how far we are from equilibrium (T, P, or composition)
what is nucleation
formation of a new mineral (phase)
why is nucleation favored by large degrees of overstepping
rate of nucleation depends on amount of overstepping
the larger deltaG, the smaller critical radius, and nucleation rate will increase
what are 3 ways to achieve overstepping
changing temperature and/or pressure
cooling below freezing curve
supersaturation of a vapor or a liquid