Chem high yield
1/190
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
191 Terms
What is the ideal gas law?
PV = nRT
What are STP conditions?
1 atm, 273 K, 22.4 L/mol
What is the equation relating Gibbs free energy, enthalpy, and entropy?
ΔG=ΔH−TΔS
what does the ideal gas model assume:
no volume, no IMFS, random, elastic (no energy loss)
elastic collision in ideal gases means that
no kinetic energy is lost
When does a real gas behave MOST like an ideal gas?
at high temperatures and low pressures
when cooled which gas is more likely to remain in the gas phase?
the one with weaker intermolecular forces (lowest molar mass) except for hydrogen bonding- always higher
The weaker the IMF, the harder it is to condense →
Ex. London Dispersion (van der Waals) - between nonpolar molecules: CH₄, I₂, CO₂
the more likely it stays a gas
The stronger the IMF, the easier it condenses →
Ex. Ion–Dipole - attraction between ion and polar molecule (Na⁺ and H₂O)
the more likely it’s liquid/solid at low T
What atoms are needed for hydrogen bonding?
H bonded to F, O, or N
When both ΔH and ΔS are positive, when is the reaction spontaneous?
at high temperatures
When both ΔH and ΔS are negative, when is the reaction spontaneous?
at low temperatures
When ΔH < 0, ΔS > 0, what is the reaction spontaneous?
at all temperatures
when ΔH > 0, ΔS < 0, what is the reaction spontaneous?
it is never spontaenous
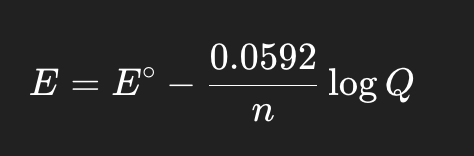
what does the Nernst equation calculate?
actual cell potential (E) under non-standard conditions.
At equilibrium, how are ΔG and Keq related?
ΔG = 0, lnKₑq = 0, Keq = 1

describe the properties of action potential
↑ Products → ↑ Q → ↓ E → less spontaneous
↑ Reactants → ↓ Q → ↑ E → more spontaneous
What is the relationship between E and spontaneity?
E > 0 → spontaneous (ΔG < 0)
E < 0 → non-spontaneous (ΔG > 0)
How many electrons are transferred in the reaction: Zn(s) + Cu²⁺(aq) → Zn²⁺(aq) + Cu(s)?
2 electrons (n = 2) (solids not included)
how do you calculate pH
pH=pKa+log [A−]/[HA]
If [A⁻] > [HA], is pH greater or less than pKa?
more A- (conjugate base) pH > pKa (more basic, since base > acid)
More acid →
more free H⁺ → lower pH
List the strong bases
NaOH, KOH, LiOH, Ca(OH)₂, Sr(OH)₂, Ba(OH)₂.
what are these examples of :
CH₃NH₂ (methylamine, other amines)
NH₃ (ammonia)
HCO₃⁻ (bicarbonate)
CH₃COO⁻, F⁻
weak bases
What is Kw at 25°C?
1.0×10-14 , increases with temperature
If [H⁺] = 1×10-3 M, what is the pH?
pH = 3
At the half-equivalence point of a titration of a weak acid with a strong base, what is true?
pH = pKa
How does blood maintain pH ~7.4?
Bicarbonate buffer system: H2CO3/HCO3−
Acid → ____ H⁺ →
loses; becomes base
Base → ____ H⁺ → becomes acid.
gains; becomes acid
In the pair CH₃COOH / CH₃COO⁻, which is the weak acid and which is the conjugate base?
CH₃COOH = weak acid (protonated, can donate H⁺).
CH₃COO⁻ = conjugate base (deprotonated, can accept H⁺).
In the pair NH₄⁺ / NH₃, which is the weak base and which is the conjugate acid?
NH₃ = weak base (deprotonated, can accept H⁺).
NH₄⁺ = conjugate acid (protonated, can donate H⁺).
How does a system at equilibrium respond to having equal gas moles on both sides
no shift change
Exothermic (ΔH < 0), → ↑T
shift left (heat is like a product)
Endothermic (ΔH > 0) → ↑T
shift right (heat is like a reactant)
Add strong base (_) →
OH⁻, consumes H⁺ → shift right.
Add strong acid (___)
H⁺, consumes conjugate base → shift left
What happens if the pressure of CO₂ above a liquid is increased?
More CO₂ dissolves → equilibrium shifts right toward dissolved CO₂
what happens to pH during hyperventilation?
pH increases (respiratory alkalosis due to ↓CO₂).
In respiratory alkalosis, how does the kidney compensate?
Excretes more bicarbonate (HCO₃⁻) to lower pH back toward normal.
In respiratory acidosis, how does the kidney compensate?
Retains more bicarbonate (HCO₃⁻) to raise pH back toward normal
In metabolic acidosis (e.g., ketoacidosis), how does the body compensate?
Hyperventilation → blows off CO₂ → raises pH.
In metabolic alkalosis (e.g., vomiting), how does the body compensate?
Hypoventilation → retains CO₂ → lowers pH
on the MCAT, which changes always drive pH shifts: CO₂ or HCO₃⁻?
↑CO₂ = ↓pH,
Respiratory = ____ Metabolic = ______
CO2, HCO3-
What does a negative ΔH mean?
the reaction is exothermic
At 25 °C, a reaction has Keq=1. What is ΔG°?
zero
If ΔG° < 0, what must be true about Keq?
Keq > 1, lnKₑq > 0 (products favored)
What is the relationship between Keq and ΔG°?
ΔG°=−RTlnKeq
Which electrode is the site of oxidation?
anode - negative
Which electrode is the site of reduction?
Cathode (redcat)- positive
How do you calculate cell potential from half-reactions?
Ecell =Ecathode −Eanode
What is true if Ecell > 0?
reaction is spontaneous
Electrons flow from
anode to cathode
In a galvanic cell, what is the sign of the anode and cathode?
Anode = negative, Cathode = positive
In an electrolytic cell, what is the sign of the anode and cathode?
Anode = positive, Cathode = negative
How do you recognize if a cell is galvanic or electrolytic?
Galvanic: spontaneous, Ecell > 0, generates current.
Electrolytic: nonspontaneous, Ecell < 0, requires power input.
lab errors and how they affect results (loss of product →
low yield
What is the equation for dilution?
M1V1 = M2V2
What does a triplet on ¹H NMR mean?
Proton has 2 equivalent neighbors (n+1 rule)
Which spectroscopy is best for conjugation or pi bonds?
UV-Vis spectroscopy
What is the effect of a catalyst on reaction rate?
Lowers activation energy (Ea) but does not change ΔG or Keq.
What is the equation for osmotic pressure?
Π=iMRT
i = van hofft factor (number of ions)
M = molarity of solute
R = ideal gas constant (.0821)
T = temp in K
How does solubility of a gas change with temperature?
Solubility decreases with increasing temperature.
a solution that minimizes changes in pH by neutralizing added acids or bases, pH changes slightly, but it resists large swings by consuming added H⁺ or OH⁻.
buffer
What is the order of carbocation stability (how well a positively charged carbon atom (a carbocation) can hold and distribute its positive charge) ?
3° > 2° > 1° > methyl (due to hyperconjugation)
More substituted carbocations are
more stable
What type of bonds hold together the primary structure?
covalent peptide bonds

Which level of protein structure is directly determined by the DNA sequence?
primary structure
If the question mentions “amino acid sequence” →_
primary structure
If the question mentions “hydrogen bonds in α-helix or β-sheet” → Secondary
secondary structure
what type of interaction stabilizes secondary structures?
Hydrogen bonds between carbonyl O and amide H
If it mentions “multiple polypeptide subunits” →
quaternary structure
if it mentions “R-group interactions or 3-D folding”
tertiary structure
hydrophobic ( nonpolar) molecules are located
inside
hydrophilic (polar) molecules are located
outside
If the question asks about covalent stabilization of tertiary structure →
Disulfide bonds
If it asks about interior folding due to water avoidance →
Hydrophobic interactions
For fine-tuned packing of non-polar side chains →
van der waals forces
_______ and _______ often stabilize both tertiary and quaternary structures.
salt bridges (ionic interactions), hydrogen bonds
rank the stability of each forces
Disulfide bonds (covalent) > Ionic interactions (salt bridges) > Hydrogen bonds > Hydrophobic interactions > Van der Waals forces
What best represents an ionic interaction (salt bridge) in a protein?
Attraction between Lys⁺ and Asp⁻ - form between acidic and basic side chains
Stronger acid →
larger Ka → smaller pKa → lower pH → weaker conjugate base
If asked which species donates protons most easily →
lowest pKa
If asked which conjugate base is strongest →
from the weakest acid (highest pKa)
for periodic trends what occurs?
across a period everything increases except atomic radius it decrease. down a group everything decreases except atomic radius increases
Highest electronegativity →
F > O > N > Cl
rank hybridzation
sp - 180 (most acidic), 2 regions. sp2 - 120, 3 regions. sp3 - 109.5 (least acidic), 4 regions
oxidation means
add oxygens/electrons, loose hydrogens
reduction means
loose oxygens, add hydrogens
Question mentions “oxygen as the final electron acceptor or hydrogenation of alkenes” →
reduction
rank from least to most oxidized
Alkane < Alcohol < Aldehyde/Ketone < Carboxylic acid < CO₂
Impurities →
lower melting point and broaden range.
Adding solute →
decreases vapor pressure + freezing point. increases boiling point and osmotic pressure
More dissociation
(higher van’t Hoff i → stronger effect
If asked which solute lowers freezing point most →
pick one with highest i × concentration
Acidic side chains (_____) are negatively charged ______ their pKa
asp, glu. above
Basic side chains (_____) are positively charged _____their pKa.
his, arg, lys. below
Isoelectric point (pI) occurs when net charge
0
what are common oxidizing agents
PCC, KMnO₄, CrO₃, H₂O₂