AP world unit 4-5 Maritime empires 1450-1750
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Main takeaways, key points, colonization, exploration, and more
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Main takeaways/introduction
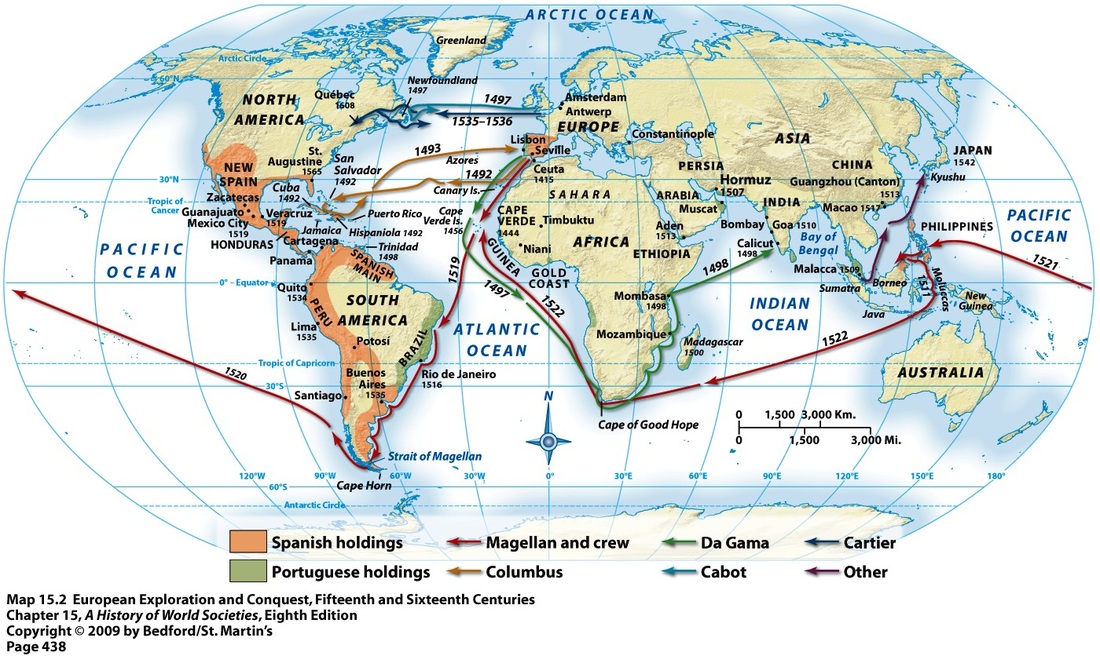
Maritime exploration reshaped global connections, especially with the European powers expanding overseas empires
new trade routes (Atlantic and Pacific) connected distant parts of the world leading to the columbian exchange , which had massive ecological demographic and economic consequences
European colonization sparked shifts in power and the exploitation of labor systems (atlantic slave trade and rebellions such as haitian revolutions)
gunpowder empires and maritime empires rose, blending military power with centralized political control
Technological innovations + Tech transfers
caravel - early portuguese ship
astrolabe
flaut
compass
lateen sail
monsoon winds
carrack
new knowledge from Islamic and Asian worlds helped European sailors
Portugal
A European maritime power during the Age of Exploration, known for its early dominance in global trade routes and exploration, particularly along the coast of Africa and into Asia.
trading post empire in Africa , India, Southeast Asia and Brazil
Prince Henry the Navigator
Vasco da Gama (Indian ocean routes)
expansion: initiated the Age of exploration by creating a series of trading posts around West Africa, India, Brazil, and SE Asia
economy: dominated by trade in spices, gold, and sugar, and Brazilian sugar plantations
religion: Catholic with missionaries accompanying explorers to convert indigenous populations
impact : European overseas expansion, influenced language and culture

Spain
encomienda system:
wealth from silver
Christopher Columbus
magellan (circumnavigation)
expansion: following Columbus voyages establishing vast territories across the americas, caribbean, mexico, and south america
religion : catholicism was enforced through missions and the establishments of religious institutions. The spanish inquisition looked to maintain religious orthodoxy
government :centralized bureaucracy

Dutch
powerful spice trade
empire that established a significant presence in the East Indies during the 17th century, known for its dominance in the spice trade and innovation in maritime trade techniques
economy: trade, commerce, strong presence in spice and trade
religion: protestant with religious tolerance in its colonies
governance: joint-stock companies with a decentralized governance structure, such as the Dutch East India Company.

Britain
established a vast colonial empire, dominated trade in North America and the Caribbean, and played a significant role in the transatlantic slave trade.
settler colonies in North America and Caribbean
growing naval power
expanded its influence through colonization, establishing powerful trade routes and participating in the exploitation of resources and people.
religion: protestantism promoted
missionary activities aimed at converting indigenous peoples
government: centralized monarchy with a focus on mercantilism, promoting trade and accumulation of wealth through colonies and regulation of commerce.
engaged in mercantilism

France
fur trade
settlements in Canada and Louisiana
economy: relied on sugar plantations in the Caribbean
governance: centralized monarchy
french colonization led to cultural exchanges
strong emphasis on the fur trade, especially with Native American tribes, leading to a thriving economy in New France.
settlements developed along the St. Lawrence River, fostering trade and cultural exchanges with indigenous peoples.
economy also benefited from sugar and tobacco cultivation in the Caribbean colonies.
centralized monarchy strengthened French control over colonial affairs.
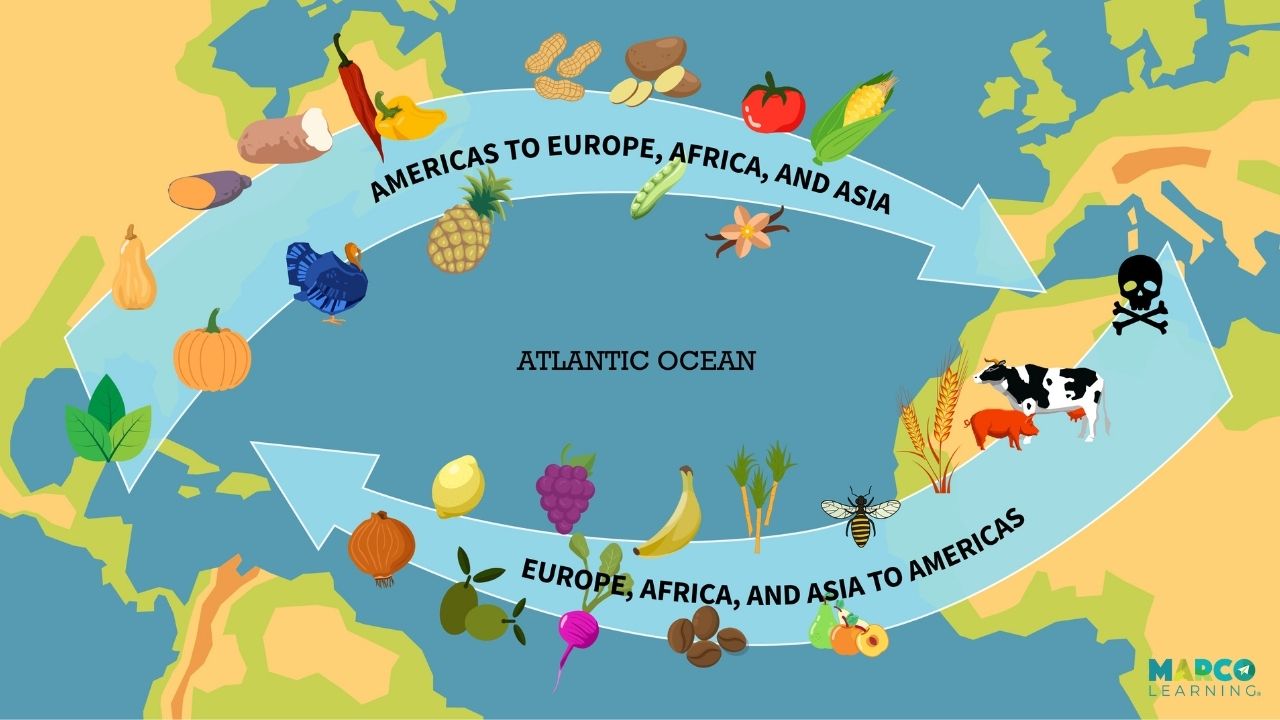
Columbian exchange
smallpox
new crops: sugarcane, potatoes, maize, tomatoes
live stock
old world to new world : horses, sugarcane, diseases (smallpox)
new world to old world: potatoes , maize, tomatoes
mass depopulation of indigenous people
global population growth in Europe and Asia
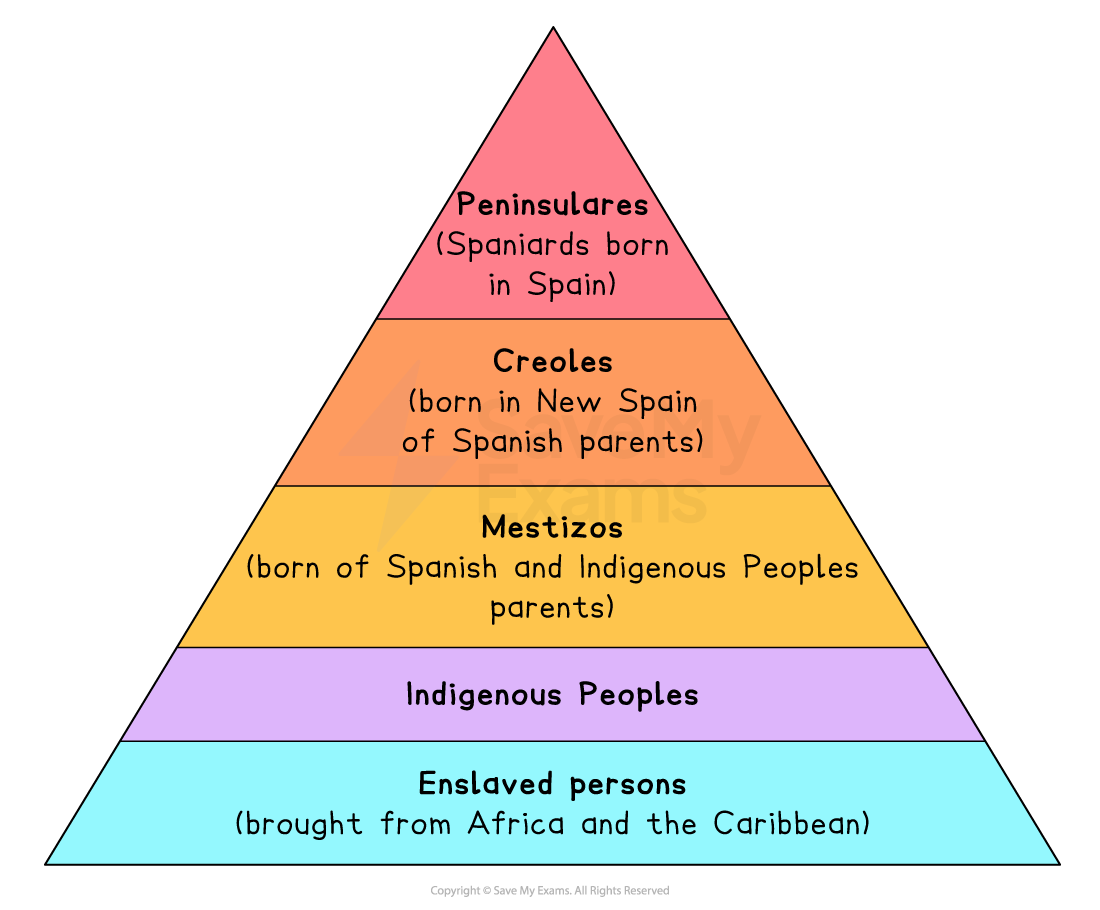
Labor systems
encomienda system -demanding of labor from indigenous populations in exchange for protection and other beliefs
mit'a system
chattel slavery - expansion of the atlantic slave trade
indentured servitude
coerced labor
various methods of forced labor used in colonies, including the exploitation of indigenous peoples and imported enslaved Africans.

resistance and conflict
indigenous revolts(pueblo revolt)
maroon societies - free blacks (runaway slaves lead by queen nanny leading to the signing of a treaty)
Tokugawa Japan resisting intrusion of western powers
the fronde - peasants leading spontaneous rebellions

cultural & religious spread
christianity spread via missionaries (often forcibly)
blending of indigenous and European traditions (syncretism)
the exchange of beliefs and practices among diverse cultures through trade and colonization.

economic systems:
Joint-Stock companies (Dutch East India Company, British East India Company)
mercantilism: colonies existing for the benefit of the mother country
Economic systems in which trade, wealth accumulation, and resource exploitation were centered around the needs of the colonizing nation, often through joint-stock companies like the Dutch and British East India Companies and driven by mercantilist policies.

Key Themes
Major historical patterns that emerged during maritime empires, including resistance and conflict, cultural and religious spread, and economic systems.
Global maritime expansion : the establishment of trade networks, colonization, and intercultural exchanges driven by European powers.
colonialism & imperialism: European powers established colonies, especially in Americas and Asia
economic transformations: The rise of mercantilism , joint-stock companies, and transatlantic commerce
environmental & demographic changes : The columbian exchange and population shifts due to migration, slavery, and the introduction of new crops.

Continuity and change
Change from units 1-3 ap world: The persistence of existing practices alongside transformative developments across cultures and societies in response to maritime imperialism.
continuity:the enduring aspects of societies, such as established trade practices and cultural exchanges, despite the disruptions caused by maritime empires.