Genomics, Transcriptomics, and Development
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
YASS
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Limitations of techniques used to study genes and proteins
These approaches typically have been restricted to studying a limited number of targets
Twin Studies
Quantifies phenotypic differences in monozygotic (genetically identical) and dizygotic (genetic similarity) twin pairs to calculate concordance and estimate heritability. Nature vs nurture?
Twin Studies Concordance for Autism MZ pairs (n==11)
36%
Twin Studies Concordance for Cognitive Disorder (including autism) MZ pairs (n==11)
82%
Heritability (h²)
a measure ranging in value from 0 to 1
H = 1
all variation is due to differences in genotype
H = 0
all variation due to differences in the environment
Twins study H²
Values range from .41 - .79 suggesting both environment and genotype can influence
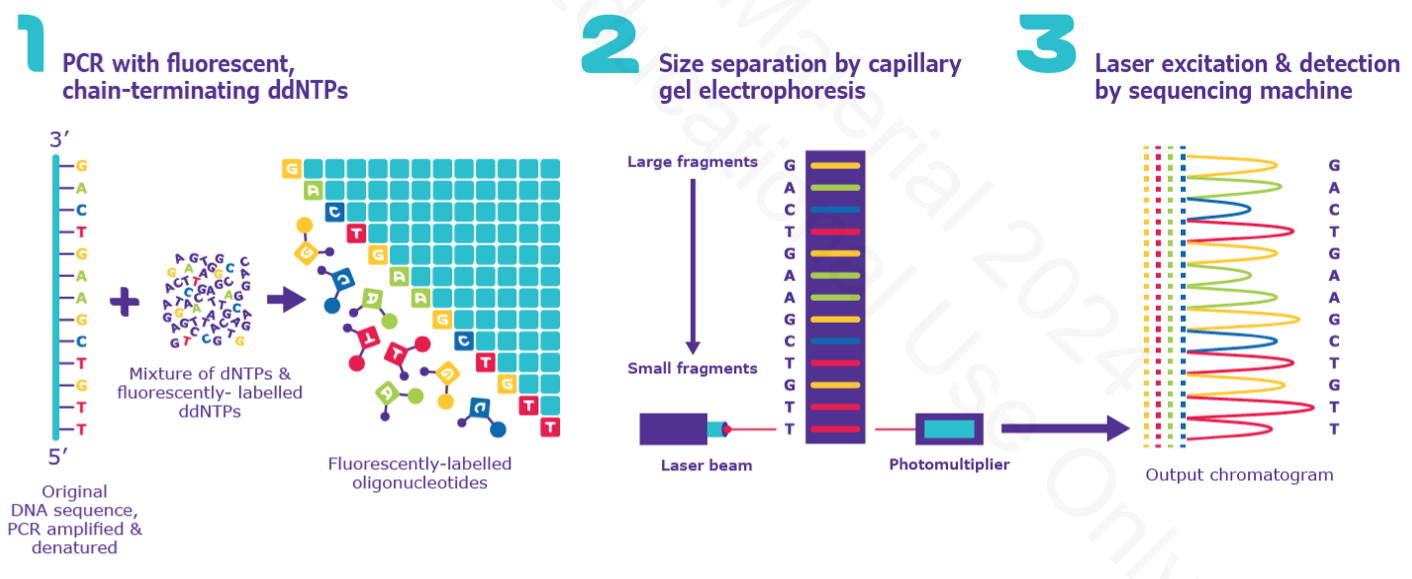
Sanger sequencing
chain-terminating dideoxynucleotide triphosphates (ddNTPs) that stop DNA polymerization during PCR to cleverly resolve sequence by measuring size
need regular dNTPs + fluorescently-conjugated ddNTPs and Taq polymerase
PCR initiates generation of fragments then fluorescent ddNTP is incorporated, amplification of the strand stops and is color coded.
size separation by gel electrophoresis; up to 1000 bp can be determined
Whole Genome Sequencing
the comprehensive sequencing of the entire genome
Human Genome Project
completed the first WGS of ~3 billion bp
What is transcriptomics and its evolved techniques?
studying expression of all genes
microarrays
next-generation sequencing
single-cell RNA-seq
spatial transcriptomics
Microarrays
attach small oligonucleotides to multiple genes of interest on a chip; by 2000s microarrays containing ~20,000 oligonucleotides complementary to all known protein-coding mRNAs were regularly used to study the transcriptome
Each dot = a collection of oligonucleotides complementary to a specific gene's mRNA
Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP)
a genomic variant at a single base position in the DNA; used to conduct Genome Wide Association Studies (GWAS) that detect associations between genetic loci and traits.
GWAS
90-95% of SNPs detected in GWAS are located in non-coding genomic regions that indirectly modulate gene expression ~40-50% of the time.
Next Generation Sequencing Technologies Approaches
DNAseq & RNAseq
Massively parallel sequencing allows for simultaneous processing of multiple DNA or RNA fragments.
RNAseq
Fragment RNA into smaller pieces.
Convert fragments to cDNA using reverse transcription and random priming.
Ligate adaptors to the cDNA.
Amplify the cDNA.
Sequence the prepared library.
NGS Example: Reversible Dye-Terminator (RDT)- based sequencing-by-synthesis (SBS)
fragments of sample DNA/RNA template of interest are anchored to chip;
RDT-ddNTPS fluorescently labeled are added during synthesis and picture is taken at end of each cycle
enzyme cleaves tag and turns RDT-ddNTP into dNTP to reverse termination and repeat (100-1000 bp each)
Bioinformatics and Resequencing
~100 GB .fastq file containing ~3 billion bases in the human genome
Resequencing: when reads are aligned back to known genome sequence to identify all genes/ variations, including: SNPS, insertions/deletions, structural variants, copy number variants)
Public Repositories and RPKM
provide RNAseq based information on gene expression
Reads Per Kilobase transcript per Million mapped reads
Single Cell RNAseq (scRNAseq)
By gently digesting/dissociating tissue, single cells/nuclei can be extracted and nucleic acids from individual cells/nuclei can be sequenced
Spatial Transcriptomics
Isolation of single cells in scRNA-seq destroys information on spatial localization and proximities to other cells.