B4 Thermodynamics
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
typical thermodynamic system
consists of a fixed mass of gas separated from its surroundings by a rigid cylinder and moveable piston
heat
energy that flows by conduction, convection or radiation from one body to another due to temperature different between them
work
energy that is transferred from one system to another by a force moving its point of application in its own direction
internal energy
the total disordered energy of all the particles of the body
zeroth law of thermodynamics
when a hot body is placed in contact with a colder body, heat flows from the hot one to the cold one until bodies are in thermal equilibrium
first law of thermodynamics
the conversion of heat to work (and vice versa) in a thermodynamics system (energy conservation)
heat supplied (Q)
positive - heat flow into gas
negative - heat flow out of gas
internal energy (U)
positive - increase in internal energy of gas
negative - decrease in internal energy of gas
work done (W)
positive - work done by gas to surroundings (expand)
negative - work done by surroundings to gas (compress)
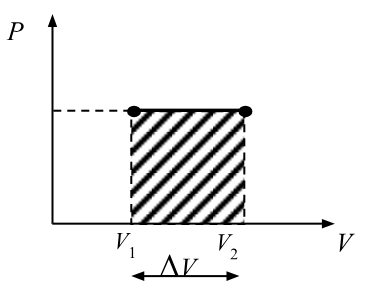
isobaric process
constant pressure
∆P=0
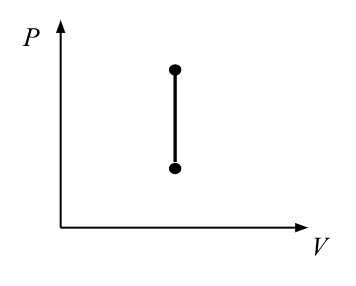
isochoric/isovolumetric process
constant volume
∆V=0, W=0
Q=∆U
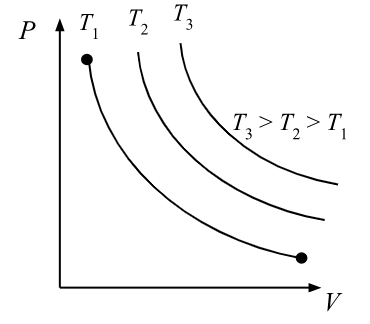
isothermal process
occurs slowly
follows Boyle’s law
∆T=0, ∆U=0
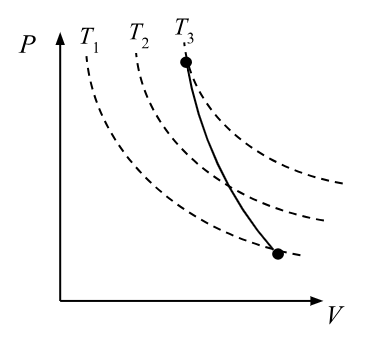
adiabatic process
occurs rapidly so no time for heat exchange and moves between isotherms
compression work on gas - increases internal energy and temperature
expansion work by gas - decreases internal energy and temperature
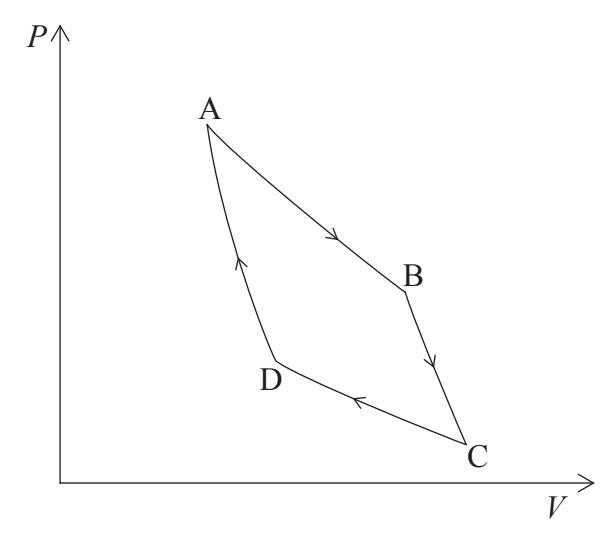
Carnot cycle
(A) isothermal expansion —> (B) adiabatic expansion —> (C) isothermal compression —> (D) isothermal compression
entropy
measure of disorder/randomness of a system
high entropy
greater number of possible speeds and positions for the particles to be in
lower probability of particles being in any particular state
an increase in volume increases the amount of positions particles can be in
second law of thermodynamics
when a heat engine converts heat into work, some energy is lost to the surroundings (i.e. never 100% efficiency)