TCA cycle
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
cellular respiration
process in when cells consume O2 and produce CO2
step 1: acetyl-CoA production generates some ______,______,_____.
- ATP
- NADH
- FADH2
step 2: acetyl-CoA oxidation generates more _____,_____,_____.
- NADH
- FADH2
- 1 GTP
step 3: oxidative phosphorylation generates what?
the vast majority of ATP during catabolism
glycolysis occurs where?
cytoplasm
citric acid cycle occurs where?
mitochondrial matrix
oxidative phosphorylation occurs where?
inner membrane of the mitochondria
succinate dehydrogense occurs where?
the inner membrane of the mitochondria
E1 enzyme (PDH complex)
pyruvate dehydrogenase
E2 enzyme (PDH complex)
dihydrolipoyl transacetylase
E3 enzyme (PDH complex)
dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase
what are the prosthetic groups in the PDH complex?
- TPP
- lipoyl-lysine
- FAD
what are the co-substrates in the PDH complex?
- NAD+
- CoA-SH
what is the function of coenzyme A?
accept and carry acetyl groups
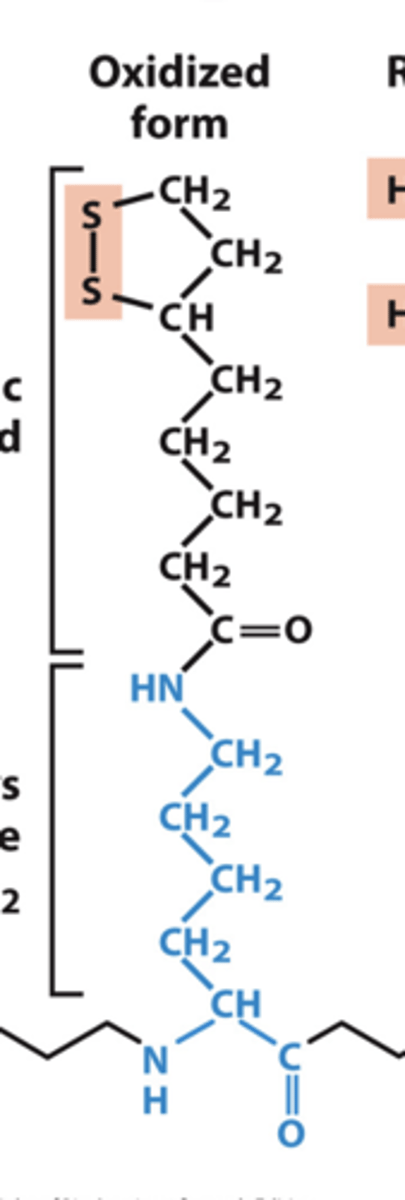
the __________ is covently linked to the enzyme via lysine residue.
lipoic acid
structure of lipoyllysine oxidized form
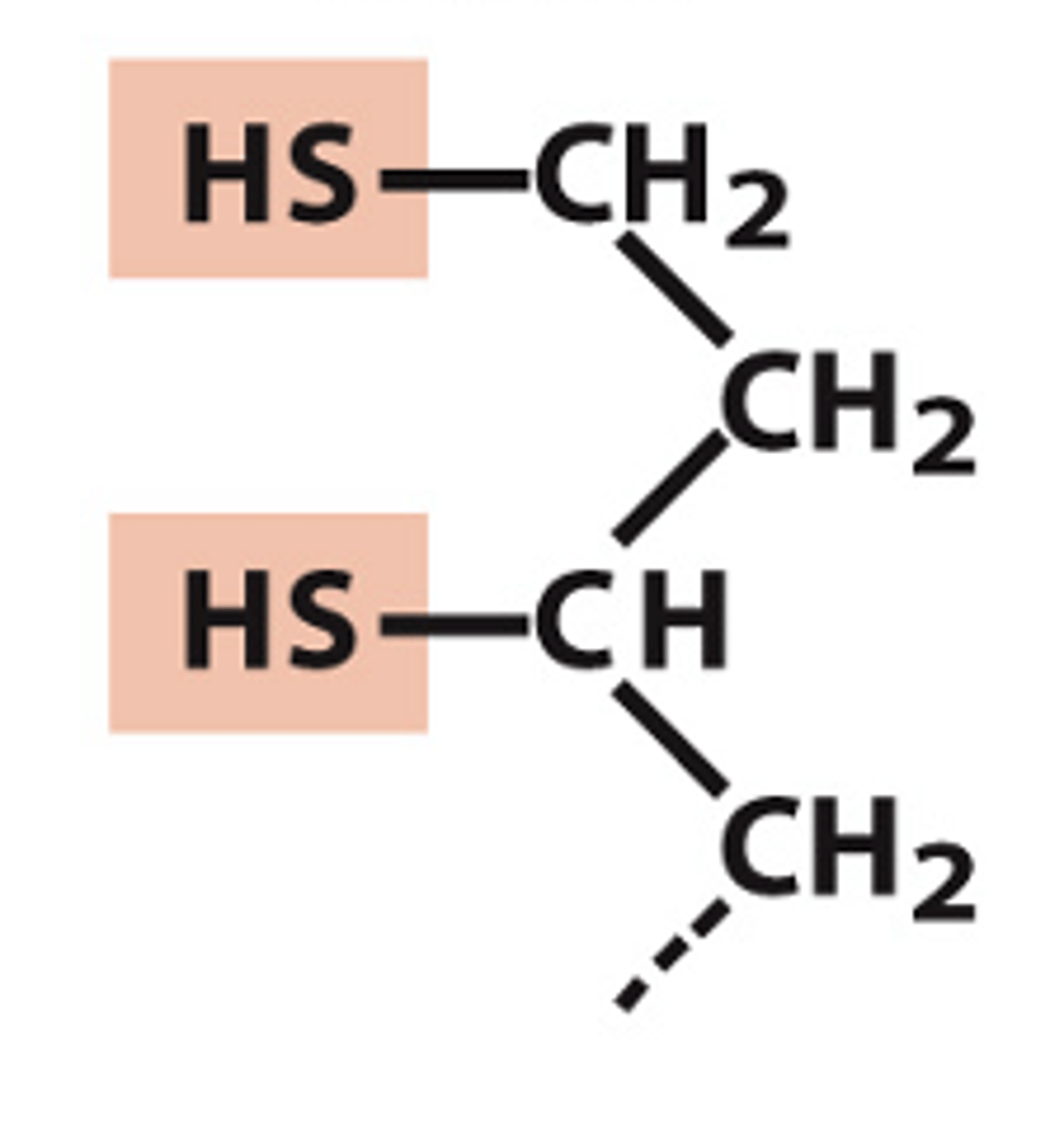
structure of lipoyllysine reduced form
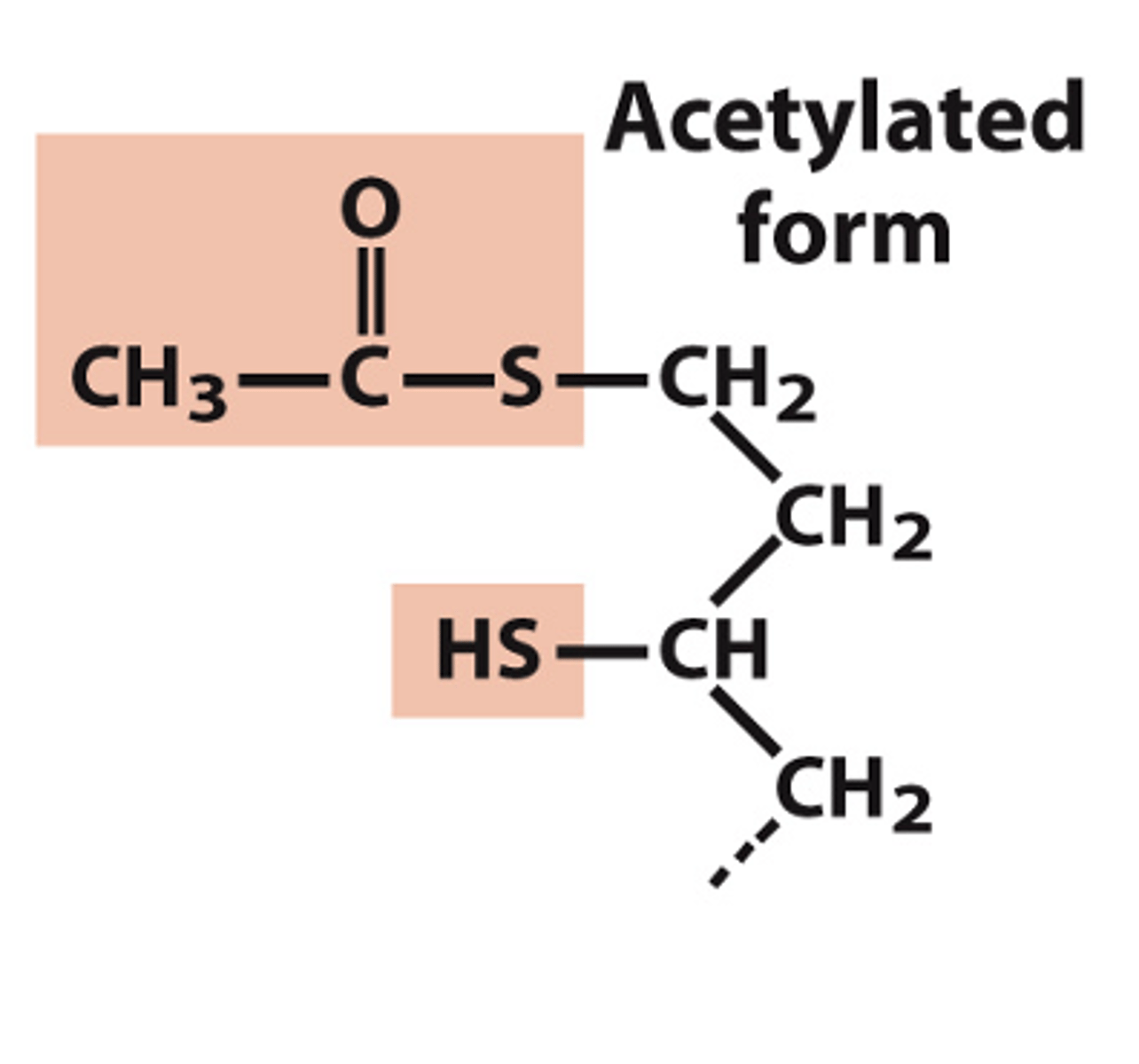
structure of lipoyllysine acetylated form
what are the two regulatory enzymes involved in PDH complex?
- pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase
- pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphatase
what are the advantages of PDH complex?
- short distance between catalytic sites allows channeling of substrate from one catalytic site to another
- channeling minimizes side reactions
- regulation of activity of one subunit affects the entire complex
E1 requires which cofactor?
thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP)
- thiamine diphosphate
E2 requires which cofactor?
- lipoic acid
- coenzyme A
E3 requires which cofactor?
- FAD
- NAD+
PDH kinase phosphorylates E1 and makes it __________.
inactive
PHD phosphatase dephosphorylates E1 and makes it ________.
active
_____ levels of pyruvate activate the PDH complex.
high
high levels of ATP, Acetyl CoA, and NADH ___________ the PDH complex.
inhibits
enzyme 1: step 1 (PDH complex)
decarboxylation of pyruvate to an aldehyde
enzyme 1: step 2 (PDH complex)
oxidation of aldehyde to a carboxylic acid
enzyme 1: electrons reduce _____________ and form a thioester. (PDH complex)
lipoamide
enzyme 2: step 3 (PDH complex)
formation of acetyl-CoA
enzyme 3: step 4 (PDH complex)
redoxidation of the lipoamide cofactor (product 1)
enzyme 3: step 5 (PDH complex)
regeneration of the oxidized FAD cofactor
- forming NADH (product 2)
step 1: citrate synthase (krebs cycle)
- c-c bond formation, via acid based catalysis
- condensation of acetyl-CoA and oxaloacetate
- highly thermodynamically favorable; irreversible
- H2O --> CoA-SH
induced fit in the citrate synthase
- conformational change occurs upon binding oxaloacetate
- prevents hydrolysis of thioester in acetyl-CoA
open conformation
free enzyme does not have a binding site for acetyl-CoA
closed conformation
- binding of OAA creates binding for acetyl-CoA
- reactive carbanion is protected
step 2: aconitase (kerbs cycle)
- isomerization by dehydration/rehydration
- elmination of H2O from citrate gives cis C=C bond (lyase)
- unfavorable; reversible
- addition of H2O to cis-aconitate is stereospecific
citrate, a tertiary alcohol, is a __________ substrate for oxidation.
poor
isocitrate, a secondary alcohol, is a __________ substrate for oxidation.
good
water removal from citrate and subsequent addition to cis-aconitate are catalyzed by the ____________________.
iron-sulfur center
aconitase is stereospecific
- only R-isocitrate is produced by aconitase.
step 3: isocitrate dehydrogenase (krebs cycle)
- oxidative decarboxylation release CO2
- enzyme isoforms are specific for NADP+ or NAD+
- highly favorable; irreversible; regulated by ATP
step 4: a-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase (krebs cycle)
- oxidative decarboxylation
- highly favorable; irreversible
- succinyl CoA is another high energy thioester bond like Acetyl CoA
- NADH --> NAD
step 5: succinyl-CoA synthetase (krebs cycle)
- substrate-level phosphorylation
- the energy of thioester bonds allows for incorporation in inorganic phosphate
- reaction produces GTP, which can be converted to ATP
- reversible
step 6: succinate dehydrogenase (krebs cycle)
- oxidation of an alkane to alkene
- FADH2 is produced
- enzyme is bound to mitochondrial inner membrane
- reversible
step 7: fumarase (krebs cycle)
- hydration of double bond
- stereospecific
- addition of water is alway trans and forms L-malate
- reversible
step 8: malate dehydrogenase (krebs cycle)
- reaction: oxidation of alcohol to a ketone
- regenerates OAA for citrate synthase
- highly thermodynamically unfavorable; reversible
what steps in the citric acid cycle produce NADH?
steps 3,4,8
in what step of the citric acid cycle is FADH2 formed?
steps 6
what step is GTP form in the citric acid cycle?
step 5
in the citric acid cycle which steps are irreversible?
steps 1,3,4
how manys ATPs are made in krebs cycle?
12 ATPS
- 1 NADH = 3 ATP (3 x 3 = 9)
- 1 FADH = 2 ATP (1 x 2 = 2)
- 1 GTP = 1 ATP (1 x 1 = 1)
what is the rate limiting step in krebs cycle?
step 3
overall products of the pathway are NADH and ATP.
- affect all regulated enzymes in the cycle
- inhibitors: NADH and ATP
- activators: NAD+ and AMP
_______ ________ _________ is allosterically inhibited when [ATP]/[ADP], [NADH]/[NAD+], and [acetyl-CoA]/[CoA] ratios are high, indicating an energy-sufficient metabolic state.
the PDH complex
entry of acetyl-CoA into the citric acid cycle is decreased when:
a. [ATP] is low
b. [GTP] is low
c. [AMP] is low
d. [ATP] is high
e. [NAD+] is high
d. [ATP] is high
Each molecule of acetyl-CoA oxidized by the citric acid results in the net production of _____ molecule(s) of _____.
a. one; citrate
b. one; FADH2
c. one; NADH
d. one; oxaloacetate
e. seven; ATP
b. one; FADH2
Which enzyme catalyzes a hydration reaction?
a. malate dehydrogenase
b. fumarase
c. citrate synthase
d. pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
e. succinyl-CoA synthetase
b. fumarase
Which combination of cofactors is involved in the conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA?
a. biotin, FAD, and TPP
b. biotin, NAD+, and FAD
c. NAD+, biotin, and TPP
d. pyridoxal phosphate, FAD, and lipoate
e. TPP, lipoate, and NAD+
e. TPP, lipoate, and NAD+
The reaction of the citric acid cycle that is MOST similar to the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex-catalyzed conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA is the conversion of:
a. citrate to isocitrate.
b. fumarate to malate.
c. malate to oxaloacetate.
d. succinyl-CoA to succinate.
e. α-ketoglutarate to succinyl-CoA.
e. α-ketoglutarate to succinyl-CoA.
Why is the citric acid cycle considered to be part of aerobic metabolism, even though oxygen is NOT a substrate in any reaction?
a. because it takes place in the mitochondrion
b. because it contains oxidation reactions
c. because it produces NADH and FADH2, which ultimately transfer their electrons to oxygen
d. because it produces carbon dioxide
c. because it produces NADH and FADH2, which ultimately transfer their electrons to oxygen
Which molecule(s) is an α-ketoacid?
a. oxaloacetate
b. citrate
c. α-ketoglutarate
d. oxaloacetate and α-ketoglutarate
e. citrate and α-ketoglutarate
d. oxaloacetate and α-ketoglutarate
What intermediate is formed upon isomerization of citrate to isocitrate?
a. semi-citrate
b. semi-isocitrate
c. trans-aconitate
d. cis-aconitase
e. cis-aconitate
e. cis-aconitate
Which cofactor is required for the conversion of succinate to fumarate in the citric acid cycle?
a. ATP
b. biotin
c. FAD
d. NAD+
e. NADP+
c. FAD
Choose the intermediate that is formed upon binding of pyruvate to PDH.
a. oxyethyl-TPP
b. carboxymethyl-TPP
c. carboxyethyl-TPP
d. hydroxymethyl-TPP
e. hydroxyethyl-TPP
e. hydroxyethyl-TPP
What are anaplerotic reactions of the citric acid cycle? Select all that apply.
a. pyruvate → oxaloacetate
b. glutamate → α-ketoglutarate
c. α-ketoglutarate → glutamate
d. malate → oxaloacetate
e. isocitrate → α-ketoglutarate
a. pyruvate → oxaloacetate
b. glutamate → α-ketoglutarate
What enzyme of the TCA cycle is similar to the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex?
a. α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
b. malate dehydrogenase
c. citrate synthase
d. isocitrate dehydrogenase
e. isocitrate lyase
a. α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
In addition to pyruvate dehydrogenase, what other enzyme in the citric acid cycle has a key thiamine pyrophosphate coenzyme?
a. isocitrate dehydrogenase
b. citrate synthase (in bacteria)
c. phosphatase
d. fumarase
e. α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
e. α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
In what step of the citric acid cycle is FADH2 formed?
a. conversion of malate to oxaloacetate
b. conversion of malate to fumarate
c. conversion of succinate to oxaloacetate
d. conversion of succinate to malate
e. conversion of succinate to fumarate
e. conversion of succinate to fumarate
What coenzyme does the E1 component of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex require for proper activity?
a. thiamine pyrophosphate
b. NADH
c. FAD
d. coenzyme A
e. NAD+
a. thiamine pyrophosphate
What is the CORRECT order of steps of conversion of pyruvate into acetyl CoA?
a. oxidation, transfer to lipoamide, decarboxylation
b. decarboxylation, transfer to CoA, transfer to lipoamide, oxidation *
c. decarboxylation, oxidation, transfer to CoA
d. oxidation, decarboxylation, transfer to CoA
e. oxidation, decarboxylation, transfer to CoA, recovery of lipoamide
c. decarboxylation, oxidation, transfer to CoA
What subunit of the pyruvate dehydrogenase regenerates the oxidized form of lipoamide?
a. pyruvate dehydrogenase component
b. E2
c. dihydrolipoyl transacetylase
d. E1
e. E3
e. E3
What enzyme catalyzes the first redox reaction of the TCA cycle?
a. pyruvate dehydrogenase
b. isocitrate lyase
c. α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
d. malate dehydrogenase
e. isocitrate dehydrogenase
e. isocitrate dehydrogenase
What condition is essential for conversion of pyruvate into acetyl coenzyme A rather than into lactic acid or ethanol?
a. aerobic conditions
b. high redox potential
c. acidic conditions
d. alkaline medium
e. anaerobic conditions
a. aerobic conditions
What subunit of the PDH decarboxylates pyruvate?
a. E5
b. E1
c. E4
d. E3
e. E2
b. E1